1 GenBank
1.1 NCBI——美国国家生物技术信息中心(美国国立生物技术信息中心)
NCBI(美国国立生物技术信息中心)是在NIH的国立医学图书馆(NLM)的一个分支。它的使命包括四项任务:1. 建立关于分子生物学,生物化学,和遗传学知识的存储和分析的自动系统 ;2.实行关于用于分析生物学重要分子和复合物的结构和功能的基于计算机的信息处理的,先进方法的研究;3. 加速生物技术研究者和医药治疗人员对数据库和软件的使用;4. 全世界范围内的生物技术信息收集的合作努力。NCBI数据库由Nucleotide(核苷酸序列数据库)、 Genome(基因组数据库)、Structure(结构数据库或称分子模型数据库)、Taxonomy(生物学门类数据库)、 PopSet几个子库组成。
美国国立生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information),是由美国国立卫生研究院(NIH)于1988年创办。创办NCBI的初衷是为了给分子生物学家提供一个信息储存和处理的系统。除了建有GenBank核酸序列数据库(该数据库的数据资源来自全球几大DNA数据库,其中包括日本DNA数据库DDBJ、欧洲分子生物学实验室数据库EMBL以及其它几个知名科研机构)之外,NCBI还可以提供众多功能强大的数据检索与分析工具。目前,NCBI提供的资源有Entrez、Entrez Programming Utilities、My NCBI、PubMed、PubMed Central、Entrez Gene、NCBI Taxonomy Browser、BLAST、BLAST Link (BLink)、Electronic PCR等共计36种功能,而且都可以在NCBI的主页www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov上找到相应链接,其中多半是由BLAST功能发展而来的。
1.2 GenBank DNA数据库
GenBank是美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information ,NCBI)建立的DNA序列数据库,从公共资源中获取序列数据,主要是科研人员直接提供或来源于大规模基因组测序计划( Benson等, 1998)。为保证数据尽可能的完全,GenBank与EMBL(欧洲EMBL-DNA数据库)、DDBJ(日本DNA数据库:DNA Data Bank of Japan)建立了相互交换数据的合作关系。
GenBank文件就是NCBI支持的主要生信格式。读懂 GenBank 后 EMBL 就很简单了。
GenBank格式是最早和最古老的生物信息学数据格式之一,最初的发明是为了弥补人类可读的表达方式和可被计算机有效处理的表达方式之间的差距,为人类阅读而优化的,不适合大规模的数据处理。该格式有一个所谓的固定宽度格式,前十个字符组成一列,作为一个标识符,其余的行是与该标识符相对应的信息。
1.3 GenBank文件实例
LOCUS SCU49845 5028 bp DNA PLN 21-JUN-1999
DEFINITION Saccharomyces cerevisiae TCP1-beta gene, partial cds, and Axl2p
(AXL2) and Rev7p (REV7) genes, complete cds.
ACCESSION U49845
VERSION U49845.1 GI:1293613
KEYWORDS .
SOURCE Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast)
ORGANISM Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Eukaryota; Fungi; Ascomycota; Saccharomycotina; Saccharomycetes;
Saccharomycetales; Saccharomycetaceae; Saccharomyces.
REFERENCE 1 (bases 1 to 5028)
AUTHORS Torpey,L.E., Gibbs,P.E., Nelson,J. and Lawrence,C.W.
TITLE Cloning and sequence of REV7, a gene whose function is required for
DNA damage-induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
JOURNAL Yeast 10 (11), 1503-1509 (1994)
PUBMED 7871890
REFERENCE 2 (bases 1 to 5028)
AUTHORS Roemer,T., Madden,K., Chang,J. and Snyder,M.
TITLE Selection of axial growth sites in yeast requires Axl2p, a novel
plasma membrane glycoprotein
JOURNAL Genes Dev. 10 (7), 777-793 (1996)
PUBMED 8846915
REFERENCE 3 (bases 1 to 5028)
AUTHORS Roemer,T.
TITLE Direct Submission
JOURNAL Submitted (22-FEB-1996) Terry Roemer, Biology, Yale University, New
Haven, CT, USA
FEATURES Location/Qualifiers
source 1..5028
/organism="Saccharomyces cerevisiae"
/db_xref="taxon:4932"
/chromosome="IX"
/map="9"
CDS <1..206
/codon_start=3
/product="TCP1-beta"
/protein_id="AAA98665.1"
/db_xref="GI:1293614"
/translation="SSIYNGISTSGLDLNNGTIADMRQLGIVESYKLKRAVVSSASEA
AEVLLRVDNIIRARPRTANRQHM"
gene 687..3158
/gene="AXL2"
CDS 687..3158
/gene="AXL2"
/note="plasma membrane glycoprotein"
/codon_start=1
/function="required for axial budding pattern of S.
cerevisiae"
/product="Axl2p"
/protein_id="AAA98666.1"
/db_xref="GI:1293615"
/translation="MTQLQISLLLTATISLLHLVVATPYEAYPIGKQYPPVARVNESF
TFQISNDTYKSSVDKTAQITYNCFDLPSWLSFDSSSRTFSGEPSSDLLSDANTTLYFN
VILEGTDSADSTSLNNTYQFVVTNRPSISLSSDFNLLALLKNYGYTNGKNALKLDPNE
VFNVTFDRSMFTNEESIVSYYGRSQLYNAPLPNWLFFDSGELKFTGTAPVINSAIAPE
TSYSFVIIATDIEGFSAVEVEFELVIGAHQLTTSIQNSLIINVTDTGNVSYDLPLNYV
YLDDDPISSDKLGSINLLDAPDWVALDNATISGSVPDELLGKNSNPANFSVSIYDTYG
DVIYFNFEVVSTTDLFAISSLPNINATRGEWFSYYFLPSQFTDYVNTNVSLEFTNSSQ
DHDWVKFQSSNLTLAGEVPKNFDKLSLGLKANQGSQSQELYFNIIGMDSKITHSNHSA
NATSTRSSHHSTSTSSYTSSTYTAKISSTSAAATSSAPAALPAANKTSSHNKKAVAIA
CGVAIPLGVILVALICFLIFWRRRRENPDDENLPHAISGPDLNNPANKPNQENATPLN
NPFDDDASSYDDTSIARRLAALNTLKLDNHSATESDISSVDEKRDSLSGMNTYNDQFQ
SQSKEELLAKPPVQPPESPFFDPQNRSSSVYMDSEPAVNKSWRYTGNLSPVSDIVRDS
YGSQKTVDTEKLFDLEAPEKEKRTSRDVTMSSLDPWNSNISPSPVRKSVTPSPYNVTK
HRNRHLQNIQDSQSGKNGITPTTMSTSSSDDFVPVKDGENFCWVHSMEPDRRPSKKRL
VDFSNKSNVNVGQVKDIHGRIPEML"
gene complement(3300..4037)
/gene="REV7"
CDS complement(3300..4037)
/gene="REV7"
/codon_start=1
/product="Rev7p"
/protein_id="AAA98667.1"
/db_xref="GI:1293616"
/translation="MNRWVEKWLRVYLKCYINLILFYRNVYPPQSFDYTTYQSFNLPQ
FVPINRHPALIDYIEELILDVLSKLTHVYRFSICIINKKNDLCIEKYVLDFSELQHVD
KDDQIITETEVFDEFRSSLNSLIMHLEKLPKVNDDTITFEAVINAIELELGHKLDRNR
RVDSLEEKAEIERDSNWVKCQEDENLPDNNGFQPPKIKLTSLVGSDVGPLIIHQFSEK
LISGDDKILNGVYSQYEEGESIFGSLF"
ORIGIN
1 gatcctccat atacaacggt atctccacct caggtttaga tctcaacaac ggaaccattg
61 ccgacatgag acagttaggt atcgtcgaga gttacaagct aaaacgagca gtagtcagct
121 ctgcatctga agccgctgaa gttctactaa gggtggataa catcatccgt gcaagaccaa
181 gaaccgccaa tagacaacat atgtaacata tttaggatat acctcgaaaa taataaaccg
241 ccacactgtc attattataa ttagaaacag aacgcaaaaa ttatccacta tataattcaa
301 agacgcgaaa aaaaaagaac aacgcgtcat agaacttttg gcaattcgcg tcacaaataa
361 attttggcaa cttatgtttc ctcttcgagc agtactcgag ccctgtctca agaatgtaat
421 aatacccatc gtaggtatgg ttaaagatag catctccaca acctcaaagc tccttgccga
481 gagtcgccct cctttgtcga gtaattttca cttttcatat gagaacttat tttcttattc
541 tttactctca catcctgtag tgattgacac tgcaacagcc accatcacta gaagaacaga
601 acaattactt aatagaaaaa ttatatcttc ctcgaaacga tttcctgctt ccaacatcta
661 cgtatatcaa gaagcattca cttaccatga cacagcttca gatttcatta ttgctgacag
721 ctactatatc actactccat ctagtagtgg ccacgcccta tgaggcatat cctatcggaa
781 aacaataccc cccagtggca agagtcaatg aatcgtttac atttcaaatt tccaatgata
841 cctataaatc gtctgtagac aagacagctc aaataacata caattgcttc gacttaccga
901 gctggctttc gtttgactct agttctagaa cgttctcagg tgaaccttct tctgacttac
961 tatctgatgc gaacaccacg ttgtatttca atgtaatact cgagggtacg gactctgccg
1021 acagcacgtc tttgaacaat acataccaat ttgttgttac aaaccgtcca tccatctcgc
1081 tatcgtcaga tttcaatcta ttggcgttgt taaaaaacta tggttatact aacggcaaaa
1141 acgctctgaa actagatcct aatgaagtct tcaacgtgac ttttgaccgt tcaatgttca
1201 ctaacgaaga atccattgtg tcgtattacg gacgttctca gttgtataat gcgccgttac
1261 ccaattggct gttcttcgat tctggcgagt tgaagtttac tgggacggca ccggtgataa
1321 actcggcgat tgctccagaa acaagctaca gttttgtcat catcgctaca gacattgaag
1381 gattttctgc cgttgaggta gaattcgaat tagtcatcgg ggctcaccag ttaactacct
1441 ctattcaaaa tagtttgata atcaacgtta ctgacacagg taacgtttca tatgacttac
1501 ctctaaacta tgtttatctc gatgacgatc ctatttcttc tgataaattg ggttctataa
1561 acttattgga tgctccagac tgggtggcat tagataatgc taccatttcc gggtctgtcc
1621 cagatgaatt actcggtaag aactccaatc ctgccaattt ttctgtgtcc atttatgata
1681 cttatggtga tgtgatttat ttcaacttcg aagttgtctc cacaacggat ttgtttgcca
1741 ttagttctct tcccaatatt aacgctacaa ggggtgaatg gttctcctac tattttttgc
1801 cttctcagtt tacagactac gtgaatacaa acgtttcatt agagtttact aattcaagcc
1861 aagaccatga ctgggtgaaa ttccaatcat ctaatttaac attagctgga gaagtgccca
1921 agaatttcga caagctttca ttaggtttga aagcgaacca aggttcacaa tctcaagagc
1981 tatattttaa catcattggc atggattcaa agataactca ctcaaaccac agtgcgaatg
2041 caacgtccac aagaagttct caccactcca cctcaacaag ttcttacaca tcttctactt
2101 acactgcaaa aatttcttct acctccgctg ctgctacttc ttctgctcca gcagcgctgc
2161 cagcagccaa taaaacttca tctcacaata aaaaagcagt agcaattgcg tgcggtgttg
2221 ctatcccatt aggcgttatc ctagtagctc tcatttgctt cctaatattc tggagacgca
2281 gaagggaaaa tccagacgat gaaaacttac cgcatgctat tagtggacct gatttgaata
2341 atcctgcaaa taaaccaaat caagaaaacg ctacaccttt gaacaacccc tttgatgatg
2401 atgcttcctc gtacgatgat acttcaatag caagaagatt ggctgctttg aacactttga
2461 aattggataa ccactctgcc actgaatctg atatttccag cgtggatgaa aagagagatt
2521 ctctatcagg tatgaataca tacaatgatc agttccaatc ccaaagtaaa gaagaattat
2581 tagcaaaacc cccagtacag cctccagaga gcccgttctt tgacccacag aataggtctt
2641 cttctgtgta tatggatagt gaaccagcag taaataaatc ctggcgatat actggcaacc
2701 tgtcaccagt ctctgatatt gtcagagaca gttacggatc acaaaaaact gttgatacag
2761 aaaaactttt cgatttagaa gcaccagaga aggaaaaacg tacgtcaagg gatgtcacta
2821 tgtcttcact ggacccttgg aacagcaata ttagcccttc tcccgtaaga aaatcagtaa
2881 caccatcacc atataacgta acgaagcatc gtaaccgcca cttacaaaat attcaagact
2941 ctcaaagcgg taaaaacgga atcactccca caacaatgtc aacttcatct tctgacgatt
3001 ttgttccggt taaagatggt gaaaattttt gctgggtcca tagcatggaa ccagacagaa
3061 gaccaagtaa gaaaaggtta gtagattttt caaataagag taatgtcaat gttggtcaag
3121 ttaaggacat tcacggacgc atcccagaaa tgctgtgatt atacgcaacg atattttgct
3181 taattttatt ttcctgtttt attttttatt agtggtttac agatacccta tattttattt
3241 agtttttata cttagagaca tttaatttta attccattct tcaaatttca tttttgcact
3301 taaaacaaag atccaaaaat gctctcgccc tcttcatatt gagaatacac tccattcaaa
3361 attttgtcgt caccgctgat taatttttca ctaaactgat gaataatcaa aggccccacg
3421 tcagaaccga ctaaagaagt gagttttatt ttaggaggtt gaaaaccatt attgtctggt
3481 aaattttcat cttcttgaca tttaacccag tttgaatccc tttcaatttc tgctttttcc
3541 tccaaactat cgaccctcct gtttctgtcc aacttatgtc ctagttccaa ttcgatcgca
3601 ttaataactg cttcaaatgt tattgtgtca tcgttgactt taggtaattt ctccaaatgc
3661 ataatcaaac tatttaagga agatcggaat tcgtcgaaca cttcagtttc cgtaatgatc
3721 tgatcgtctt tatccacatg ttgtaattca ctaaaatcta aaacgtattt ttcaatgcat
3781 aaatcgttct ttttattaat aatgcagatg gaaaatctgt aaacgtgcgt taatttagaa
3841 agaacatcca gtataagttc ttctatatag tcaattaaag caggatgcct attaatggga
3901 acgaactgcg gcaagttgaa tgactggtaa gtagtgtagt cgaatgactg aggtgggtat
3961 acatttctat aaaataaaat caaattaatg tagcatttta agtataccct cagccacttc
4021 tctacccatc tattcataaa gctgacgcaa cgattactat tttttttttc ttcttggatc
4081 tcagtcgtcg caaaaacgta taccttcttt ttccgacctt ttttttagct ttctggaaaa
4141 gtttatatta gttaaacagg gtctagtctt agtgtgaaag ctagtggttt cgattgactg
4201 atattaagaa agtggaaatt aaattagtag tgtagacgta tatgcatatg tatttctcgc
4261 ctgtttatgt ttctacgtac ttttgattta tagcaagggg aaaagaaata catactattt
4321 tttggtaaag gtgaaagcat aatgtaaaag ctagaataaa atggacgaaa taaagagagg
4381 cttagttcat cttttttcca aaaagcaccc aatgataata actaaaatga aaaggatttg
4441 ccatctgtca gcaacatcag ttgtgtgagc aataataaaa tcatcacctc cgttgccttt
4501 agcgcgtttg tcgtttgtat cttccgtaat tttagtctta tcaatgggaa tcataaattt
4561 tccaatgaat tagcaatttc gtccaattct ttttgagctt cttcatattt gctttggaat
4621 tcttcgcact tcttttccca ttcatctctt tcttcttcca aagcaacgat ccttctaccc
4681 atttgctcag agttcaaatc ggcctctttc agtttatcca ttgcttcctt cagtttggct
4741 tcactgtctt ctagctgttg ttctagatcc tggtttttct tggtgtagtt ctcattatta
4801 gatctcaagt tattggagtc ttcagccaat tgctttgtat cagacaattg actctctaac
4861 ttctccactt cactgtcgag ttgctcgttt ttagcggaca aagatttaat ctcgttttct
4921 ttttcagtgt tagattgctc taattctttg agctgttctc tcagctcctc atatttttct
4981 tgccatgact cagattctaa ttttaagcta ttcaatttct ctttgatc
//
2 GenBank 格式详解
2.1 LOCUS 基座
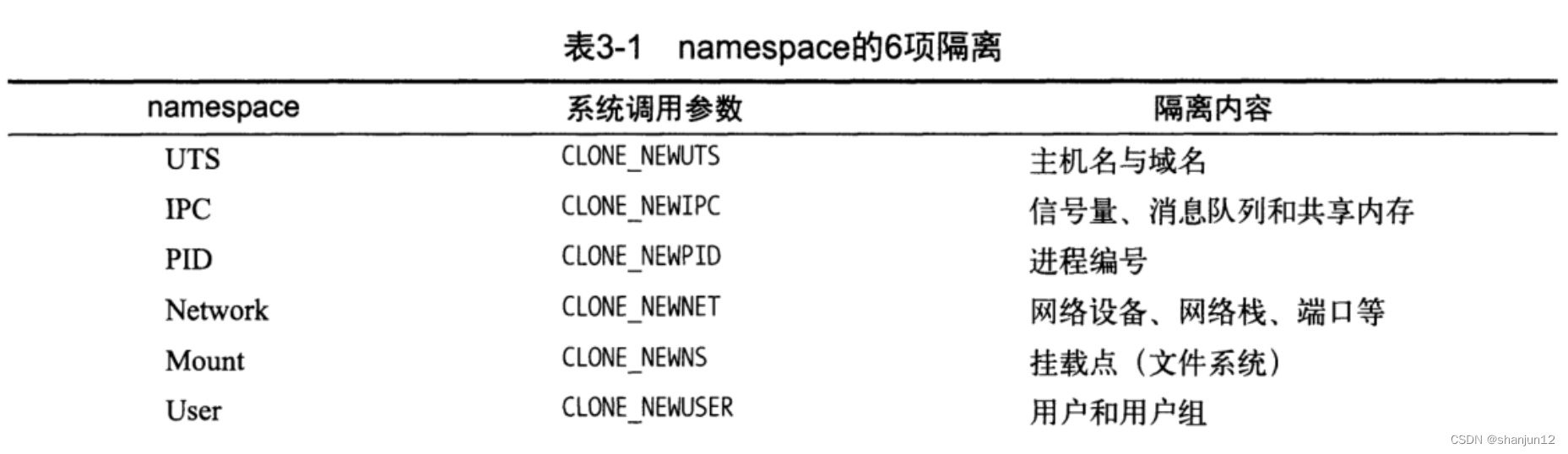
The LOCUS field contains a number of different data elements, including locus name, sequence length, molecule type, GenBank division, and modification date. Each element is described below.
LOCUS字段包含许多不同的数据元素,包括基因座名称、序列长度、分子类型、GenBank划分和修饰日期。每个元素的描述如下。
2.1.1 Locus Name 基座名
The locus name in this example is SCU49845.
本例中的基因座名称为SCU49845。
The locus name was originally designed to help group entries with similar sequences: the first three characters usually designated the organism; the fourth and fifth characters were used to show other group designations, such as gene product; for segmented entries, the last character was one of a series of sequential integers. (See GenBank release notes section 3.4.4 for more info.)
Locus Name最初是为了帮助将具有相似序列的条目分组:前三个字符通常指定生物体;第四个和第五个字符用于显示其他组名称,如基因产物;对于分段条目,最后一个字符是一系列连续整数中的一个。(有关更多信息,请参阅GenBank发行说明第3.4.4节。)
However, the 10 characters in the locus name are no longer sufficient to represent the amount of information originally intended to be contained in the locus name. The only rule now applied in assigning a locus name is that it must be unique. For example, for GenBank records that have 6-character accessions (e.g., U12345), the locus name is usually the first letter of the genus and species names, followed by the accession number. For 8-character character accessions (e.g., AF123456), the locus name is just the accession number.
然而,基因座名称中的10个字符不再足以表示基因座名称最初打算包含的信息量。现在在指定轨迹名称时应用的唯一规则是它必须是唯一的。例如,对于具有6个字符的材料的GenBank记录(例如,U12345),基因座名称通常是属和种名称的第一个字母,后面是登录号。对于8个字符的材料(例如AF123456),基因座名称只是材料编号。
The RefSeq database of reference sequences assigns formal locus names to each record, based on gene symbol. RefSeq is separate from the GenBank database, but contains cross-references to corresponding GenBank records.
参考序列的RefSeq数据库根据基因符号为每个记录分配正式的基因座名称。RefSeq独立于GenBank数据库,但包含对相应GenBank记录的交叉引用。
Entrez Search Field: Accession Number [ACCN] Search Tip : It is better to search for the actual accession number rather than the locus name, because the accessions are stable and locus names can change.
Entrez搜索字段:登录号[ACCN]搜索提示:最好搜索实际的登录号,而不是基因座名称,因为材料是稳定的,基因座名称可以改变。
2.1.2 Sequence Length 序列长度
Number of nucleotide base pairs (or amino acid residues) in the sequence record. In this example, the sequence length is 5028 bp.
序列记录中核苷酸碱基对(或氨基酸残基)的数量。在本例中,序列长度为5028 bp。
Entrez Search Field : Sequence Length [SLEN] Search Tips : (1) To retrieve records within a range of lengths, use the colon as the range operator, e.g., 2500:2600[SLEN]. (2) To retrieve all sequences shorter than a certain number, use 2 as the lower bound, e.g., 2:100[SLEN]. (3) To retrieve all sequences longer than a certain number, use a series of 9's as the upper bound, e.g., 325000:99999999[SLEN].
Entrez搜索字段:序列长度[SLEN]搜索提示:(1)要检索长度范围内的记录,请使用冒号作为范围运算符,例如2500:2600[SLEN]。(2) 要检索所有短于某个数字的序列,请使用2作为下限,例如2:100[SLEN]。(3) 要检索长于某个数字的所有序列,请使用一系列9作为上限,例如325000:999999999[SLEN]。
2.1.3 Molecule Type 分子类型
The type of molecule that was sequenced. In this example, the molecule type is DNA.
被测序的分子类型。在这个例子中,分子类型是DNA。
Each GenBank record must contain contiguous sequence data from a single molecule type. The various molecule types can include genomic DNA, genomic RNA, precursor RNA, mRNA (cDNA), ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, small nuclear RNA, and small cytoplasmic RNA.
每个GenBank记录必须包含来自单个分子类型的连续序列数据。各种分子类型可以包括基因组DNA、基因组RNA、前体RNA、mRNA(cDNA)、核糖体RNA、转移RNA、小核RNA和小细胞质RNA。
Entrez Search Field : Properties [PROP] Search Tip : Search term should be in the format: biomol_genomic, biomol_mRNA, etc. For more examples, view the Properties field in the Index mode.
Entrez搜索字段:属性[PROP]搜索提示:搜索术语的格式应为:biomol_genomic、biomol_mRNA等。有关更多示例,请在索引模式下查看属性字段。
2.1.4 GenBank Division 分支
The GenBank division to which a record belongs is indicated with a three letter abbreviation. In this example, GenBank division is PLN.
记录所属的GenBank部门用三个字母的缩写表示。
The GenBank database is divided into 18 divisions:
GenBank数据库分为18个部分:
PRI - primate sequences 灵长类动物序列
ROD - rodent sequences 啮齿动物序列
MAM - other mammalian sequences 其他哺乳动物序列
VRT - other vertebrate sequences 其他脊椎动物序列
INV - invertebrate sequences 无脊椎动物序列
PLN - plant, fungal, and algal sequences 植物、真菌和藻类序列
BCT - bacterial sequences 细菌序列
VRL - viral sequences 病毒序列
PHG - bacteriophage sequences 噬菌体序列
SYN - synthetic sequences 合成序列
UNA - unannotated sequences 未注释序列
EST - EST sequences (expressed sequence tags) EST序列(表达序列标签)
PAT - patent sequences 专利序列
STS - STS sequences (sequence tagged sites) STS序列(序列标记位点)
GSS - GSS sequences (genome survey sequences) GSS序列(基因组调查序列)
HTG - HTG sequences (high-throughput genomic sequences) HTG序列(高通量基因组序列)
HTC - unfinished high-throughput cDNA sequencing 未完成的高通量cDNA测序
ENV - environmental sampling sequences 环境采样序列
Some of the divisions contain sequences from specific groups of organisms, whereas others (EST, GSS, HTG, etc.) contain data generated by specific sequencing technologies from many different organisms. The organismal divisions are historical and do not reflect the current NCBI Taxonomy. Instead, they merely serve as a convenient way to divide GenBank into smaller pieces for those who want to FTP the database. Because of this, and because sequences from a particular organism can exist in technology-based divisions such as EST, HTG, etc., the NCBI Taxonomy Browser should be used for retrieving all sequences from a particular organism.
其中一些部分包含来自特定生物体群的序列,而另一些部分(EST、GSS、HTG等)包含由许多不同生物体的特定测序技术产生的数据。组织分类是历史性的,并不反映当前的NCBI分类。相反,它们只是为那些想通过FTP传输数据库的人提供了一种方便的方式,将GenBank分成更小的部分。正因为如此,而且来自特定生物体的序列可以存在于基于技术的部门中,如EST、HTG等,NCBI分类浏览器应该用于检索来自特定生物体中的所有序列。
Entrez Search Field : Properties [PROP] Search Tip : Search term should be in the format: gbdiv_pri, gbdiv_est, etc. For more examples, view the Properties field in the Index mode. For example, to eliminate all sequences from a particular division, such as all ESTs, you can use a Boolean query formatted such as: human[ORGN] NOT gbdiv_est[PROP] For the reasons noted above, do not use GenBank divisions to retrieve all sequences from a specific organism. Instead, use the NCBI Taxonomy Browser.
Entrez搜索字段:Properties[PROP]搜索提示:搜索项的格式应为:gbdiv_pri、gbdiv_est等。有关更多示例,请在索引模式下查看Properties字段。例如,要从特定的分区(如所有est)中删除所有序列,可以使用布尔查询格式,例如:human[ORGN]NOT gbdiv_est[PROP]。由于上述原因,不要使用GenBank分区从特定生物体中检索所有序列。相反,请使用NCBI分类浏览器。
2.1.5 Modification Date 修改日期
The date in the LOCUS field is the date of last modification. The sample record shown here was last modified on 21-JUN-1999.
LOCUS字段中的日期是最后一次修改的日期。此处显示的样本记录最后一次修改是在1999年6月21日。
Entrez Search Field : Modification Date [MDAT] Search Tips : (1) Enter search term in the format: yyyy/mm/dd, e.g., 1999/07/25. (2) To retrieve records modified between two dates, use the colon as a range operator, e.g., 1999/07/25:1999/07/31[MDAT]. (3) You can use the Publication Date [PDAT] field of Entrez to limit search results by the date on which records were added to the Entrez system. Publication date can be in the form of a range, just like the Modification Date.
Entrez搜索字段:修改日期[MDAT]搜索提示:(1)以yyyy/mm/dd的格式输入搜索项,例如1999/07/25。(2) 要检索在两个日期之间修改的记录,请使用冒号作为范围运算符,例如1999/07/25:1999/07/31[MDAT]。(3) 您可以使用Entrez的Publication Date[PDAT]字段,根据记录添加到Entrez系统的日期来限制搜索结果。发布日期可以是范围的形式,就像修改日期一样。
2.2 DEFINITION
Brief description of sequence; includes information such as source organism, gene name/protein name, or some description of the sequence's function (if the sequence is non-coding). If the sequence has a coding region (CDS), description may be followed by a completeness qualifier, such as "complete cds".
序列的简要描述;包括来源生物、基因名称/蛋白质名称或序列功能的某些描述(如果序列是非编码的)等信息。如果序列有一个编码区(CDS),那么描述后面可能会有一个完整性限定符,比如“完整的CDS”。
Entrez Search Field: Title Word [TITL] Search Tip : Although nucleotide definition lines follow a structured format, GenBank does not use a controlled vocabulary, and authors determine the content of their records. Therefore, if a search for a specific term does not retrieve the desired records, try other terms that authors might have used, such as synonyms, full spellings, or abbreviations. The "related records" (or "neighbors") function of Entrez also allows you to broaden your search by retrieving records with similar sequences, regardless of the descriptive terms used by the submitters.
Entrez搜索字段:标题词[TITL]搜索提示:尽管核苷酸定义行遵循结构化格式,但GenBank不使用受控词汇表,作者决定其记录的内容。因此,如果对特定术语的搜索无法检索到所需的记录,请尝试作者可能使用过的其他术语,如同义词、完整拼写或缩写。Entrez的“相关记录”(或“邻居”)功能还允许您通过检索具有相似序列的记录来扩大搜索范围,而不考虑提交者使用的描述性术语。
2.3 ACCESSION
The unique identifier for a sequence record. An accession number applies to the complete record and is usually a combination of a letter(s) and numbers, such as a single letter followed by five digits (e.g., U12345) or two letters followed by six digits (e.g., AF123456). Some accessions might be longer, depending on the type of sequence record.
序列记录的唯一标识符。登录号适用于完整的记录,通常是字母和数字的组合,例如一个字母后面跟着五位数字(例如U12345)或两个字母后面跟六位数字(如AF123456)。有些材料可能更长,这取决于序列记录的类型。
Accession numbers do not change, even if information in the record is changed at the author's request. Sometimes, however, an original accession number might become secondary to a newer accession number, if the authors make a new submission that combines previous sequences, or if for some reason a new submission supercedes an earlier record.
即使记录中的信息应作者的要求而更改,登录号也不会更改。然而,有时,如果作者提交了一份合并了以前序列的新提交文件,或者由于某种原因,新提交的文件取代了以前的记录,那么原始的登录号可能会成为新登录号的次要登录号。
Records from the RefSeq database of reference sequences have a their own accession number format that begins with two letters followed by an underscore bar and six or more digits; for example:
参考序列RefSeq数据库中的记录有自己的登录号格式,以两个字母开头,后面跟着下划线和六个或更多数字;例如:
NT_123456 constructed genomic contigs 构建的基因组重叠群
NM_123456 mRNAs 信使核糖核酸
NP_123456 proteins 蛋白
NC_123456 chromosomes 染色体
Note: Most records have both a series of accession numbers (Version for nucleotide sequences and protein_id for amino acid sequences) and sequence identifiers (GI for nucleotide sequences and GI for amino acid sequences). See the online documentation for Sequence IDs for details.
注:大多数记录都有一系列的登录号(核苷酸序列的版本和氨基酸序列的protein_id)和序列标识符(核苷酸序列为GI,氨基酸序列为GI)。有关详细信息,请参阅序列ID的在线文档。
Entrez Search Field: Accession [ACCN] Search Tip : The letters in the accession number can be written in upper- or lowercase. RefSeq accessions must contain an underscore bar between the letters and the numbers, e.g., NM_002111.
Entrez搜索字段:登录[ACCN]搜索提示:登录号中的字母可以用大写或小写书写。RefSeq附件必须在字母和数字之间包含下划线条,例如NM_002111。
2.4 VERSION 版本信息
A nucleotide sequence identification number that represents a single, specific sequence in the GenBank database. This identification number uses the accession.version format implemented by GenBank/ENA/DDBJ in February 1999.
一种核苷酸序列识别号,表示GenBank数据库中的单个特定序列。该识别号使用了GenBank/ENA/DDBJ于1999年2月实施的addition.版本格式。
If there is any change to the sequence data (even a single base), the version number will be increased, e.g., U12345.1 ? U12345.2, but the accession portion will remain stable.
如果序列数据有任何变化(即使是单个碱基),版本号也会增加,例如U12345.1?U12345.2,但加入部分将保持稳定。
The accession.version system of sequence identifiers runs parallel to the GI number system--when any change is made to a sequence, it receives a new GI number AND its version number is incremented by one.
To find out about the revision history of a sequence, see GenBank Sequence Revision History.
Entrez Search Field: use the default setting of "All Fields"
序列标识符的addition.version系统与GI编号系统并行运行——当对序列进行任何更改时,它将接收一个新的GI编号,并且其版本号将增加一。
要了解序列的修订历史,请参阅GenBank序列修订历史。
Entrez搜索字段:使用“所有字段”的默认设置
GI 识别号
"GenInfo Identifier" sequence identification number, in this case, for the nucleotide sequence. If a sequence changes in any way, a new GI number will be assigned.
A separate GI number is also assigned to each protein translation within a nucleotide sequence record, and a new GI is assigned if the protein translation changes in any way (see below).
GI sequence identifiers run parallel to the new accession.version system of sequence identifiers.
Read more about GenBank Sequence Revision History and Sequence IDs.
Entrez Search Field: use the default setting of "All Fields"
在这种情况下,核苷酸序列的“GenInfo Identifier”序列识别号。如果序列以任何方式发生变化,将分配一个新的GI编号。
核苷酸序列记录中的每个蛋白质翻译也会分配一个单独的GI编号,如果蛋白质翻译以任何方式发生变化,则分配一个新的GI(见下文)。
GI序列标识符与序列标识符的新加入版本系统并行运行。
阅读有关GenBank序列修订历史和序列ID的更多信息。
Entrez搜索字段:使用“所有字段”的默认设置。
2.5 KEYWORDS 关键字
Word or phrase describing the sequence. If no keywords are included in the entry, the field contains only a period.
The Keywords field is present in sequence records primarily for historical reasons, and is not based on a controlled vocabulary. Keywords are generally present in older records. They are not included in newer records unless the record contains a special type of sequence such as EST, STS, GSS, HTG, etc.
Entrez Search Field: Keyword [KYWD] Search Tip : Because keywords are not present in many records, it is best not to search that field. Instead, search All Fields [ALL], the Text Word [WORD] field, or the Title Word [TITL] field, for progressively narrower retrieval.
描述序列的单词或短语。如果条目中不包含关键字,则该字段仅包含一个句点。
Keywords字段出现在序列记录中主要是由于历史原因,而不是基于受控词汇表。关键字通常出现在较旧的记录中。除非记录包含特殊类型的序列,如EST、STS、GSS、HTG等,否则它们不会包含在较新的记录中。
Entrez搜索字段:关键字[KYWD]搜索提示:因为关键字在许多记录中都不存在,所以最好不要搜索该字段。相反,搜索所有字段[All]、文本单词[Word]字段或标题单词[TITL]字段,以逐步缩小检索范围。
2.6 SOURCE 来源
Free-format information including an abbreviated form of the organism name, sometimes followed by a molecule type.
Entrez Search Field: Organism [ORGN] Search Tip : For some organisms that have well-established common names, such as baker's yeast, mouse, and human, a search for the common name will yield the same results as a search for the scientific name, e.g., a search for "baker's yeast" in the organism field retrieves the same number of documents as "Saccharomyces cerevisiae". This is true because the Organism field is connected to the NCBI Taxonomy Database, which contains cross-references between common names, scientific names, and synonyms for organisms represented in the Sequence databases.
自由格式信息,包括生物体名称的缩写形式,有时后面跟着分子类型。
Entrez搜索领域:Organism[ORGN]搜索提示:对于一些具有公认通用名称的生物体,如面包酵母、小鼠和人类,搜索通用名称会产生与搜索科学名称相同的结果,例如,在生物体领域搜索“面包酵母”会检索到与“酿酒酵母”相同数量的文档。这是真的,因为Organism字段连接到NCBI分类数据库,该数据库包含序列数据库中表示的生物的常见名称、科学名称和同义词之间的交叉引用。
Organism 有机体
The formal scientific name for the source organism (genus and species, where appropriate) and its lineage, based on the phylogenetic classification scheme used in the NCBI Taxonomy Database . If the complete lineage of an organism is very long, an abbreviated lineage will be shown in the GenBank record and the complete lineage will be available in the Taxonomy Database. (See also the /db_xref=taxon:nnnn Feature qualifer, below.)
Entrez Search Field: Organism [ORGN] Search Tip : You can search the Organism field by any node in the taxonomic hierarchy, e.g., you can search for the term "Saccharomyces cerevisiae", "Saccharomycetales", "Ascomycota", etc. to retrieve all the sequences from organisms in a particular taxon.
源生物(属和种,如适用)及其谱系的正式学名,基于NCBI分类学数据库中使用的系统发育分类方案。如果一个生物体的完整谱系很长,GenBank记录中将显示一个缩写谱系,分类学数据库中将提供完整谱系。(另请参见下面的/db_xref=分类单元:nnnn特征限定符。)
Entrez搜索字段:Organism[ORGN]搜索提示:您可以按分类层次中的任何节点搜索Organism字段,例如,您可以搜索术语“酿酒酵母”、“酿酒菌”、“子囊菌门”等,以检索特定分类单元中生物体的所有序列。
2.7 REFERENCE 参考
Publications by the authors of the sequence that discuss the data reported in the record. References are automatically sorted within the record based on date of publication, showing the oldest references first.
Some sequences have not been reported in papers and show a status of "unpublished" or "in press". When an accession number and/or sequence data has appeared in print, sequence authors should send the complete citation of the article to update@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov and the GenBank staff will revise the record.
Various classes of publication can be present in the References field, including journal article, book chapter, book, thesis/monograph, proceedings chapter, proceedings from a meeting, and patent.
The last citation in the REFERENCE field usually contains information about the submitter of the sequence, rather than a literature citation. It is therefore called the "submitter block" and shows the words "Direct Submission" instead of an article title. Additional information is provided below, under the header Direct Submission. Some older records do not contain a submitter block.
Entrez Search Field: The various subfields under References are searchable in the Entrez search fields noted below.
序列作者讨论记录中报告的数据的出版物。引用将根据发布日期在记录中自动排序,首先显示最旧的引用。
一些序列没有在论文中报道,显示为“未发表”或“正在出版”。当登录号和/或序列数据出现在印刷品中时,序列作者应将文章的完整引文发送至update@ncbi.nlm.nih.govGenBank的工作人员将修改记录。
参考文献领域可以提供各种类型的出版物,包括期刊文章、书籍章节、书籍、论文/专著、会议记录章节、会议记录和专利。
REFERENCE字段中的最后一个引用通常包含序列提交者的信息,而不是文献引用。因此,它被称为“提交者块”,并显示“直接提交”而不是文章标题。下文在“直接提交”标题下提供了其他信息。一些较旧的记录不包含提交程序块。
Entrez搜索字段:参考文献下的各个子字段可在下面提到的Entrez搜索域中搜索。
2.7.1 AUTHORS 作者
List of authors in the order in which they appear in the cited article.
Entrez Search Field: Author [AUTH] Search Tip : Enter author names in the form: Lastname AB (without periods after the initials). Initials can be omitted. Truncation can also be used to retrieve all names that begin with a character string, e.g., Richards* or Boguski M*.
按作者在引用文章中出现的顺序列出的作者列表。
Entrez搜索字段:作者[AUTH]搜索提示:以姓氏AB的形式输入作者姓名(首字母后无句点)。首字母缩写可以省略。截断也可以用于检索所有以字符串开头的名称,例如Richards*或Boguski M*。
2.7.2 TITLE 标题
Title of the published work or tentative title of an unpublished work.
Sometimes the words "Direct Submission" instead of an article title. This is usually true for the last citation in the REFERENCE field because it tends to contain information about the submitter of the sequence, rather than a literature citation. The last citation is therefore called the "submitter block". Additional information is provided below, under the header Direct Submission. Some older records do not contain a submitter block.
Entrez Search Field: Text Word [WORD] Note: For sequence records, the Title Word [TITL] field of Entrez searches the Definition Line, not the titles of references listed in the record. Therefore, use the Text Word field to search the titles of references (and other text-containing fields). Search Tip : If a search for a specific term does not retrieve the desired records, try other terms that authors might have used, such synonyms, full spellings, or abbreviations. The 'related records' (or 'neighbors') function of Entrez also allows you to broaden your search by retrieving records with similar sequences, regardless of the descriptive terms used by the submitters.
已发表作品的标题或未发表作品的暂定标题。
有时用“直接提交”代替文章标题。这通常适用于REFERENCE字段中的最后一个引用,因为它往往包含序列提交者的信息,而不是文献引用。因此,最后一个引用被称为“提交者块”。下文在“直接提交”标题下提供了其他信息。一些较旧的记录不包含提交程序块。
Entrez搜索字段:文本词[Word]注意:对于序列记录,Entrez的标题词[TITL]字段搜索定义行,而不是记录中列出的引用的标题。因此,请使用“文本单词”字段来搜索引用的标题(以及其他包含文本的字段)。搜索提示:如果搜索某个特定术语没有检索到所需的记录,请尝试作者可能使用过的其他术语,如同义词、完整拼写或缩写。Entrez的“相关记录”(或“邻居”)功能还允许您通过检索具有相似序列的记录来扩大搜索范围,而不考虑提交者使用的描述性术语。
2.7.3 JOURNAL 期刊
MEDLINE abbreviation of the journal name. (Full spellings can be obtained from the Entrez Journals Database.)
Entrez Search Field: Journal Name [JOUR] Search Tip : Journal names can be entered as either the full spelling or the MEDLINE abbreviation. You can search the Journal Name field in the Index mode to see the index for that field, and to select one or more journal names for inclusion in your search.
MEDLINE期刊名称的缩写。(完整的拼写可以从Entrez期刊数据库中获得。)
Entrez搜索字段:期刊名称[JOUR]搜索提示:期刊名称可以输入全名或MEDLINE缩写。您可以在“索引”模式下搜索“日记账名称”字段,以查看该字段的索引,并选择一个或多个日记账名称以包含在搜索中。
2.7.4 PUBMED 出版物
PubMed Identifier (PMID).
References that include PubMed IDs contain links from the sequence record to the corresponding PubMed record. Conversely, PubMed records that contain accession number(s) in the SI (secondary source identifier) field contain links back to the sequence record(s).
Entrez Search Field: It is not possible to search the Nucleotide or Protein sequence databases by PubMed ID. However, you can search the PubMed (literature) database of Entrez for the PubMed ID, and then link to the associated sequence records.
PubMed标识符(PMID)。
包括PubMed ID的引用包含从序列记录到相应PubMed记录的链接。相反,在SI(二级源标识符)字段中包含登录号的PubMed记录包含返回序列记录的链接。
Entrez搜索字段:无法通过PubMed ID搜索核苷酸或蛋白质序列数据库。但是,您可以在Entrez的PubMed(文献)数据库中搜索PubMed的ID,然后链接到相关的序列记录。
Direct Submission 直接提交
Contact information of the submitter, such as institute/department and postal address. This is always the last citation in the References field. Some older records do not contain the "Direct Submission" reference. However, it is required in all new records.
The Authors subfield contains the submitter name(s), Title contains the words "Direct Submission", and Journal contains the address.
The date in the Journal subfield is the date on which the author prepared the submission. In many cases, it is also the date on which the sequence was received by the GenBank staff, but it is not the date of first public release.
Entrez Search Field: Use the Author Field [AUTH] if searching for the author name. Use All Fields [ALL] if searching for an element of the author's address (e.g., Yale University). Note, however, that retrieved records might contain the institution name in a field such as Comment, rather than in the Direct Submission reference, so you might get some false hits. Search Tip : It is sometimes helpful to search for both the full spelling and an abbreviation, e.g., "Washington University" OR "WashU", because the spelling used by authors might vary.
提交人的联系信息,如机构/部门和邮寄地址。这总是参考文献字段中的最后一个引用。一些较旧的记录不包含“直接提交”引用。然而,在所有新记录中都需要它。
“作者”子字段包含提交者姓名,“标题”包含“直接提交”,“期刊”包含地址。
Journal子字段中的日期是作者准备提交的日期。在许多情况下,这也是GenBank工作人员收到序列的日期,但这不是首次公开发布的日期。
Entrez搜索字段:如果搜索作者名称,请使用作者字段[AUTH]。如果搜索作者地址的元素(例如,耶鲁大学),请使用All Fields[All]。然而,请注意,检索到的记录可能在Comment等字段中包含机构名称,而不是在Direct Submission引用中,因此您可能会得到一些错误的点击。搜索提示:有时搜索完整拼写和缩写是有帮助的,例如“Washington University”或“WashU”,因为作者使用的拼写可能会有所不同。
2.8 FEATURES 属性数据
Information about genes and gene products, as well as regions of biological significance reported in the sequence. These can include regions of the sequence that code for proteins and RNA molecules, as well as a number of other features.
A complete list of features is available in the following places:
Appendix III: Feature keys reference of the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank Feature Table provides definitions, optional qualifiers, and comments for each feature. An alphabetical list is also available. Appendix IV: Summary of qualifiers for feature keys provides definitions for the Feature qualifiers.
The location of each feature is provided as well, and can be a single base, a contiguous span of bases, a joining of sequence spans, and other representations. If a feature is located on the complementary strand, the word "complement" will appear before the base span. If the " < " symbol precedes a base span, the sequence is partial on the 5' end (e.g., CDS <1..206). If the ">" symbol follows a base span, the sequence is partial on the 3' end (e.g., CDS 435..915>).
The sample record shown here only includes a small number of features (source, CDS, and gene, all of which are described below). The Other Features section, below, provides links to some GenBank records that show a variety of additional features.
Entrez Search Field: Feature Key [FKEY] Search Tip : To scroll through the list of available features, view the Feature Key field in Index mode. You can then select one or more features from the index to include in your query. For example, you can limit your search to records that contain both primer_bind and promoter features.
关于基因和基因产物的信息,以及序列中报告的具有生物学意义的区域。这些可以包括编码蛋白质和RNA分子的序列区域,以及许多其他特征。
以下位置提供了完整的功能列表:
附录III:DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank功能表的功能键参考提供了每个功能的定义、可选限定符和注释。还提供了按字母顺序排列的列表。附录四:功能键限定符摘要提供了功能限定符的定义。
还提供了每个特征的位置,并且可以是单个碱基、碱基的连续跨度、序列跨度的连接以及其他表示。如果一个特征位于互补链上,则“互补”一词将出现在基跨之前。如果“<”符号在基跨之前,则序列在5'端是部分的(例如,CDS<1..206)。如果“>”符号在基跨之后,则序列是3'端的部分(例如,CDS 435..915>)。
这里显示的样本记录只包括少量特征(来源、CDS和基因,所有这些都在下面描述)。下面的“其他功能”部分提供了一些GenBank记录的链接,这些记录显示了各种附加功能。
Entrez搜索字段:功能键[FKEY]搜索提示:要滚动浏览可用功能的列表,请在索引模式下查看功能键字段。然后,您可以从索引中选择一个或多个要包含在查询中的功能。例如,您可以将搜索限制为同时包含prime_bind和promoter功能的记录。
2.8.1 source 来源
Mandatory feature in each record that summarizes the length of the sequence, scientific name of the source organism, and Taxon ID number. Can also include other information such as map location, strain, clone, tissue type, etc., if provided by submitter.
Entrez Search Field: All Fields [ALL] can be used to search for some elements in the source field, such as strain, clone, tissue type.
Use the Sequence Length [SLEN] field to search by length and the Organism [ORGN] field to search by organism name.
Because map location is written as free text and can be represented in a number of ways (e.g., chromosome number, cytogenetic location, marker name, physical map location), it is not directly searchable in the Entrez Nucleotide or Protein databases. However, there are a number of resources that allow you to browse and/or search the maps of various genomes.
每个记录中的强制性特征,总结序列长度、来源生物的学名和紫杉醇ID号。如果提交者提供,还可以包括其他信息,如地图位置、菌株、克隆、组织类型等。
Entrez搜索字段:所有字段[All]可用于搜索源字段中的一些元素,如菌株、克隆、组织类型。
使用序列长度[SLEN]字段按长度搜索,使用生物体[ORGN]字段以生物体名称搜索。
由于地图位置被写成自由文本,并且可以以多种方式表示(例如,染色体编号、细胞遗传学位置、标记名称、物理地图位置),因此无法在Entrez核苷酸或蛋白质数据库中直接搜索。然而,有许多资源可以让你浏览和/或搜索各种基因组的地图。
2.8.2 Taxon 分类
A stable unique identification number for the taxon of the source oganism. A taxonomy ID number is assigned to each taxon (species, genus, family, etc.) in the NCBI Taxonomy Database. See also the Organism field, above.
Entrez Search Field: The Taxonomy ID number is not searchable in the Organism search field of Entrez but is searchable in the Taxonomy Browser.
Note: The /db_xref qualifier is one of many that can be applied to various features. A complete list is available in Appendix IV: Summary of qualifiers for feature keys of the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank Feature Table, and in section 3.4.12.3 of the GenBank release notes. Appendix III: Feature keys reference shows which qualifiers can be used with specific features (see alphabetical list).
Taxonomy分类单元的一个稳定的唯一识别号。NCBI分类数据库中的每个分类单元(物种、属、科等)都有一个分类ID号。另请参见上文的生物体领域。
Entrez搜索字段:分类ID号在Entrez的Organism搜索字段中不可搜索,但可在分类浏览器中搜索。
注意:/db_xref限定符是可以应用于各种功能的众多限定符之一。完整列表见附录IV:DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank功能表的功能键限定符摘要,以及GenBank发行说明的第3.4.12.3节。附录三:功能键参考显示了哪些限定符可以与特定功能一起使用(见按字母顺序排列的列表)。
2.8.3 CDS 编码序列
2.8.3.1 位置信息
Coding sequence; region of nucleotides that corresponds with the sequence of amino acids in a protein (location includes start and stop codons). The CDS feature includes an amino acid translation. Authors can specify the nature of the CDS by using the qualifier "/evidence=experimental" or "/evidence=not_experimental".
Submitters are also encouraged to annotate the mRNA feature, which includes the 5' untranslated region (5'UTR), coding sequences (CDS, exon), and 3' untranslated region (3'UTR).
Entrez Search Field: Feature Key [FKEY] Search Tip : You can use this field to limit your search to records that contain a particular feature, such as CDS. To scroll through the list of available features, view the Feature Key field in Index mode. A complete list of features is also available from the resources noted above.
编码顺序;与蛋白质中氨基酸序列相对应的核苷酸区域(位置包括起始密码子和终止密码子)。CDS特征包括氨基酸翻译。作者可以通过使用限定词“/recurity=experimental”或“/recurce=not_experimental”来指定CDS的性质。
还鼓励提交者注释信使核糖核酸特征,包括5'非翻译区(5'UTR)、编码序列(CDS、外显子)和3'非翻译区域(3'UTR)。
Entrez搜索字段:功能键[FKEY]搜索提示:您可以使用此字段将搜索限制为包含特定功能的记录,如CDS。要滚动浏览可用功能的列表,请在索引模式下查看功能键字段。上面提到的资源中也提供了一个完整的功能列表。
<1..206
Base span of the biological feature indicated to the left, in this case, a CDS feature. (The CDS feature is described above, and its base span includes the start and stop codons.) Features can be complete, partial on the 5' end, partial on the 3' end, and/or on the complementary strand. Examples:
A complete feature is simply written as n..m. Example: 687..3158 The feature extends from base 687 through base 3158 in the sequence shown
The < symbol indicates partial on the 5' end. Example: <1..206. The feature extends from base 1 through base 206 in the sequence shown, and is partial on the 5' end
The > symbol indicates partial on the 3' end. Example: 4821..>5028. The feature extends from base 4821 through base 5028 and is partial on the 3' end.
<1..206 向左指示的生物特征的基本跨度,在这种情况下,是CDS特征。(CDS特征如上所述,其碱基跨度包括起始密码子和终止密码子。)特征可以是完整的,部分在5'端,部分在3'端,和/或在互补链上。示例:
一个完整的特征简单地写为n.m.示例:687..3158该特征按所示顺序从底部687延伸到底部3158
<符号表示5'端的部分。示例:<1..206。该特征按所示顺序从基底1延伸到基底206,并且在5'端是部分的
>符号表示3'端的部分。示例:4821.>5028。该特征从基部4821延伸穿过基部5028,并且在3'端是部分的。
complement(range) indicates that the feature is on the complementary strand. Example: complement(3300..4037). The feature extends from base 3300 through base 4037 but is actually on the complementary strand. It is therefore read in the opposite direction on the reverse complement sequence. (For an example, see the third CDS feature in the sample record shown on this page. In this case, the amino acid translation is generated by taking the reverse complement of bases 3300 to 4037 and reading that reverse complement sequence in its 5' to 3' direction.)
互补(范围)表示特征在互补链上。示例:互补(3300..4037)。该特征从基部3300延伸到基部4037,但实际上在互补链上。因此,它在反补码序列上以相反的方向读取。(例如,请参阅本页所示样本记录中的第三个CDS特征。在这种情况下,氨基酸翻译是通过获取3300至4037碱基的反向互补序列并沿其5'至3'方向读取该反向互补序列来产生的。)
2.8.3.2 protein_id
A protein sequence identification number, similar to the Version number of a nucleotide sequence. Protein IDs consist of three letters followed by five digits, a dot, and a version number. If there is any change to the sequence data (even a single amino acid), the version number will be increased, but the accession portion will remain stable (e.g., AAA98665.1 will change to AAA98665.2).
The accession.version format of protein sequence identification numbers was implemented by GenBank/ENA/DDBJ in February 1999 and runs parallel to the GI number system. More details about sequence identification numbers and the difference between GI number and version are provided in Sequence Identifiers: A Historical Note.
Entrez Search Field: use the default setting of "All Fields"
一种蛋白质序列识别号,类似于核苷酸序列的版本号。蛋白质ID由三个字母、五位数字、一个点和一个版本号组成。如果序列数据(即使是单个氨基酸)发生任何变化,版本号将增加,但登录部分将保持稳定(例如,AAA98665.1将变为AAA98665.2)。
1999年2月,GenBank/ENA/DDBJ实施了蛋白质序列识别号的材料版本格式,并与GI编号系统并行。序列标识符:历史注释中提供了有关序列标识号以及GI号和版本之间差异的更多详细信息。
Entrez搜索字段:使用“所有字段”的默认设置
2.8.3.3 GI
"GenInfo Identifier" sequence identification number, in this case, for the protein translation.
The GI system of sequence identifiers runs parallel to the accession.version system, which was implemented by GenBank, EMBL, and DDBJ in February 1999. Therefore, if the protein sequence changes in any way, it will receive a new GI number, and the suffix of the protein_id will be incremented by one..
More details about sequence identification numbers and the difference between GI number and version are provided in Sequence IDs.
Entrez Search Field: use the default setting of "All Fields"
“GenInfo Identifier”序列识别号,在这种情况下,用于蛋白质翻译。
序列标识符的GI系统与1999年2月由GenBank、EMBL和DDBJ实现的addition.version系统并行运行。因此,如果蛋白质序列以任何方式发生变化,它将接收一个新的GI编号,并且protein_id的后缀将增加一。。
序列ID中提供了有关序列标识号以及GI号和版本之间差异的更多详细信息。
Entrez搜索字段:使用“所有字段”的默认设置
2.8.3.4 translation
The amino acid translation corresponding to the nucleotide coding sequence (CDS). In many cases, the translations are conceptual. Note that authors can indicate whether the CDS is based on experimental or non-experimental evidence.
Entrez Search Field: It is not possible to search the translation subfield using Entrez. If you want use a string of amino acids as a query to retrieve similar protein sequences, use BLAST instead.
与核苷酸编码序列(CDS)相对应的氨基酸翻译。在许多情况下,翻译都是概念性的。请注意,作者可以指出CDS是基于实验证据还是非实验证据。
Entrez搜索字段:无法使用Entrez搜索翻译子字段。如果您想使用一系列氨基酸作为查询来检索类似的蛋白质序列,请使用BLAST。
2.8.3.5 gene 基因
A region of biological interest identified as a gene and for which a name has been assigned. The base span for the gene feature is dependent on the furthest 5' and 3' features. Additional examples of records that show the relationship between gene features and other features such as mRNA and CDS are AF165912 and AF090832.
Entrez Search Field: Feature Key [FKEY] Search Tip : You can use this field to limit your search to records that contain a particular feature, such as a gene. To scroll through the list of available features, view the Feature Key field in Index mode. A complete list of features is also available from the resources noted above.
一种生物感兴趣的区域,被确定为一个基因,并为其指定了一个名称。基因特征的碱基跨度取决于最远的5'和3'特征。显示基因特征与其他特征(如mRNA和CDS)之间关系的记录的其他例子是AF165912和AF090832。
Entrez搜索字段:功能键[FKEY]搜索提示:您可以使用此字段将搜索限制为包含特定功能(如基因)的记录。要滚动浏览可用功能的列表,请在索引模式下查看功能键字段。上面提到的资源中也提供了一个完整的功能列表。
2.8.3.6 complement
Indicates that the feature is located on the complementary strand.
表示特征位于互补链上。
2.8.3.7 Other Features
Examples of other records that show a variety of biological features; a graphic format is also available for each sequence record and visually represents the annotated features:
显示各种生物特征的其他记录的例子;图形格式也可用于每个序列记录,并且在视觉上表示注释的特征:
AF165912 (gene, promoter, TATA signal, mRNA, 5'UTR, CDS, 3'UTR)
AF090832 (protein bind, gene, 5'UTR, mRNA, CDS, 3'UTR)
L00727 (alternatively spliced mRNAs)
A complete list of features is available from the resources noted above.
2.9 ORIGIN
The ORIGIN may be left blank, may appear as "Unreported," or may give a local pointer to the sequence start, usually involving an experimentally determined restriction cleavage site or the genetic locus (if available). This information is present only in older records.
The sequence data begin on the line immediately below ORIGIN. To view or download the sequence data in FASTA format, append ?format=fasta to the record's URL; for example, /nucleotide/U49845?format=fasta&report=text.
ORIGIN可以留空,可以显示为“未报告”,或者可以给出序列起始的局部指针,通常涉及实验确定的限制性切割位点或遗传基因座(如果可用)。此信息仅存在于较旧的记录中。
序列数据从ORIGIN正下方的行开始。要查看或下载FASTA格式的序列数据,请附加?format=fasta到记录的URL;例如核苷酸/U49845?format=fasta&report=text。
源代码稍后奉上。
POWER BY 《多可科研文档管理系统》。
![Linux操作系统CentOS7安装Nginx[详细版]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f6c59cfb56724dd5a56d3df7f355e614.png#pic_center?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBATmFpamlhX092Tw==,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)