SpringBoot
- 一、简介
- 概述
- Spring Boot特性
- SpringBoot四大核心
- 二、SpringBoot项目分析
- 1、创建第一个案例
- 结构目录和pom文件
- 2、Springboot集成mvc
- Springboot核心配置文件application.properties
- Springboot核心配置文件application.yml或者application.yaml
- application.yml
- application.yaml
- 两种配置文件同时存在
- 设置Maven私服仓库
- 三、多环境开发核心配置文件
- 多环境配置文件切换(properties)
- 多环境配置文件切换(yaml/yml)
- 获取自定义配置(单个值)
- 获取自定义配置(映射成对象)
- 四、SprigBoot集成Mybatis
- 步骤
- mybatis逆向工程1
- 案例——springboot集成Mybatis
- Mapper映射文件存放位置(不在pom文件中指定资源目录)
- springboot集成mybatis总结
- 五、 SpringBoot支持事物
- 前言
- 添加事务
一、简介
概述
Spring Boot是spring家族中的一个全新的框架,它用来简化Spring应用程序的创建和开发过程,也可以说Spring Boot可以简化我们SSM框架进行开发的过程
Spring Boot特性
- 能够快速创建基于Spring的应用程序
- 能够直接使用java main方法启动内嵌的Tomcat服务器运行SpringBoot程序,不需要部署war包文件
- 提供约定的starter POM来简化Maven配置,让Maven的配置更加简单
- 自动化配置,根据项目的Maven依赖配置,SpringBoot自动配置Spring、SpringMVC等
- 提供了程序的健康检查功能
- 基本可以完全不使用XML配置文件,采用注解配置
SpringBoot四大核心
- 自动配置
- 起步依赖
- Actuator(检测程序运行状态)
- 命令行界面
二、SpringBoot项目分析
1、创建第一个案例
1、我这里使用的是阿里云的镜像
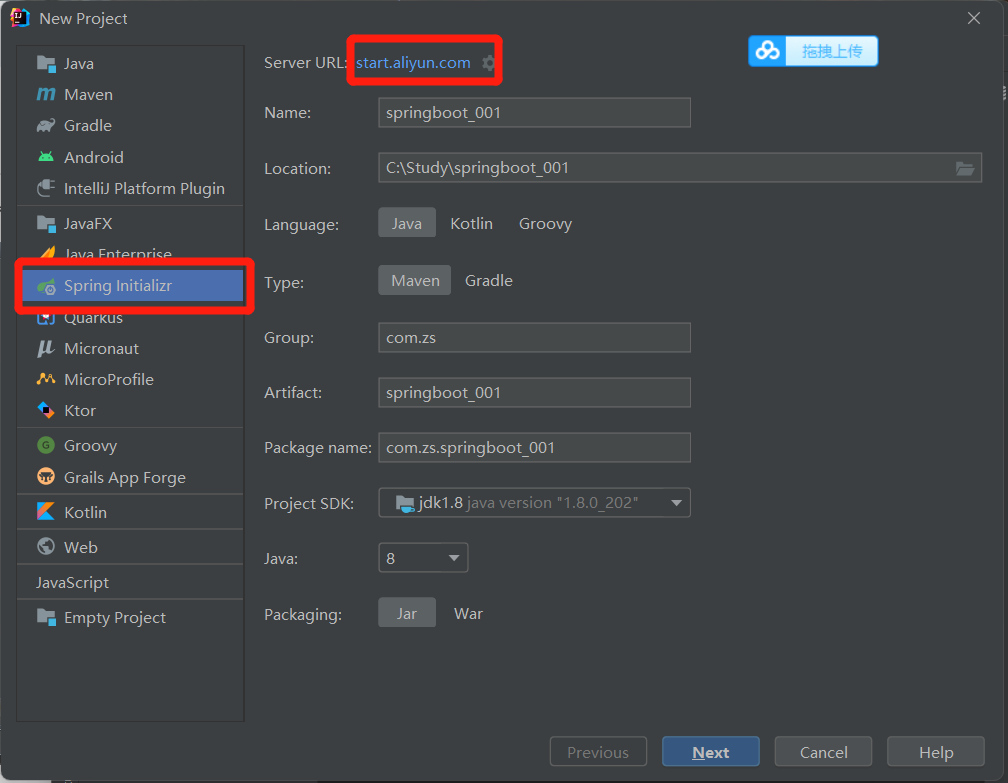
2、勾选需要的起步依赖

结构目录和pom文件
大体目录:
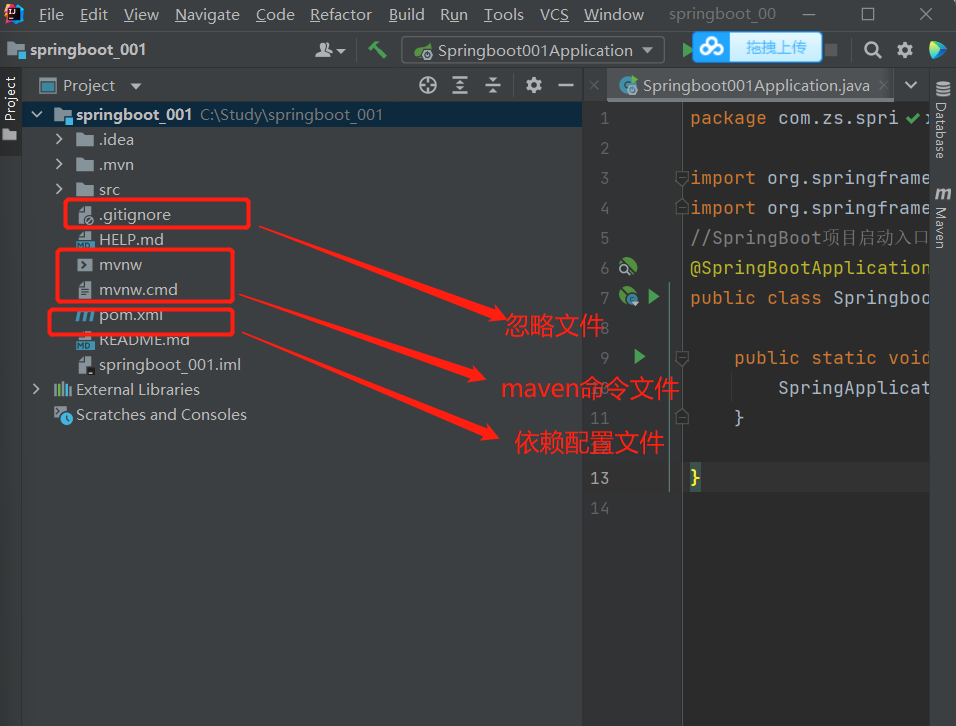
resource下的目录结构
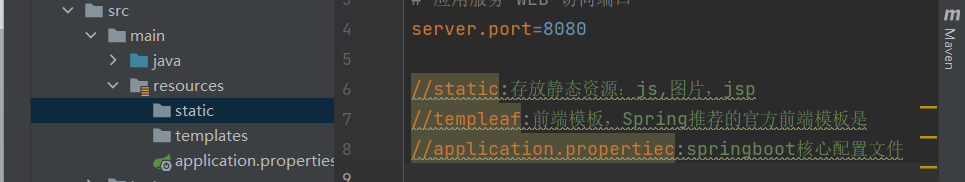
pom中的部分依赖
<!--Springboot框架的web项目起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Springboot框架的测试起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--Springboot框架的打包起步依赖-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.3.7.RELEASE</version>
Springboot的第一个java文件
//SpringBoot项目启动入口类
@SpringBootApplication//springboot核心注解,主要用于开启spring自动配置
public class Springboot001Application {
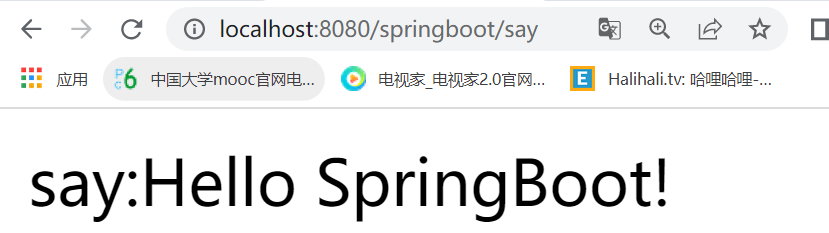
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot001Application.class, args);
}
}
2、Springboot集成mvc
编写Controller类
必须放在Springboot启动类所在的同级目录或者下级目录
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/springboot/say")
@ResponseBody
public String say(){
return "nihao";
}
}
启动并访问
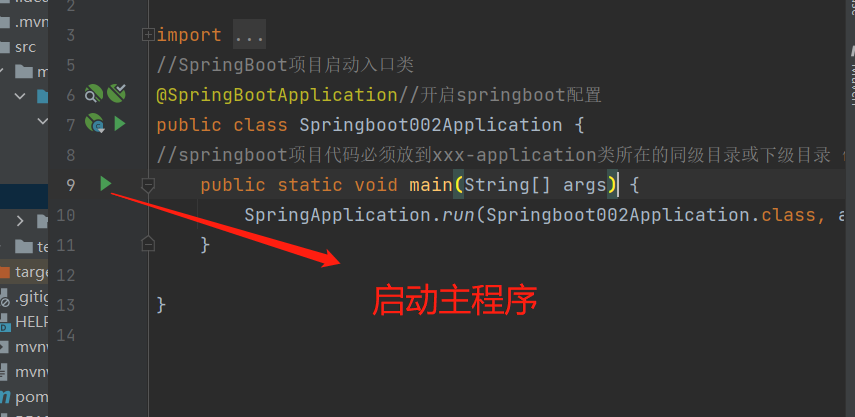
输出结果:

Springboot核心配置文件application.properties
设置端口号和上下文根

# 应用名称
spring.application.name=springboot_003
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口/设置内嵌Tomcat端口号
server.port=8080
#设置上下文根
server.servlet.context-path=/springboot
测试:
Springboot核心配置文件application.yml或者application.yaml
application.yml
添加配置,注意格式
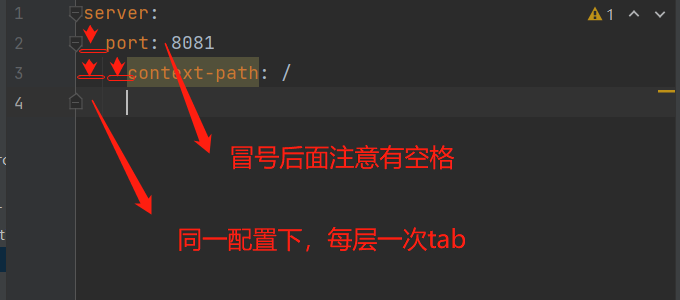
正确配置:
server:
port: 8081
servlet:
context-path: /
测试:

application.yaml
添加配置
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /666
测试

两种配置文件同时存在
如果两个文件同时存在,优先取的是properties文件内的
设置Maven私服仓库
如果项目出现问题,可以把maven镜像修改成我的(本地)
maven寻找依赖的时候,首先会去本地找,然后再到镜像仓库
<!--修改成阿里云的镜像-->
<mirror>
<id>nexus-aliyun</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<name>Nexus aliyun</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
三、多环境开发核心配置文件
多环境配置文件切换(properties)
一般情况我们的环境有:1开发环境 、2 测试环境、3 准生产环境 4 生产环境
有时候我们会在不同的环境对项目进行操作。但每个环境的配置不一样,比如IP端口、数据库等等。如果我们通过单一的配置文件进行反复的修改,会显得很麻烦。因此我们需要使用使用多环境开发模式对配置文件进行切换。
步骤:
1️⃣ 首先创建所需要的开发环境配置文件

我这里有dev:开发、product:生产、ready:准生产环境。你也可以根据自己的需求进行添加
下面是各个配置文件的详细内容
Dev:
#开发环境
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=springboot-properties-yal-yaml
# 应用服务 WEB 访问端口
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/dev
product:
#生产环境
server.port=9090
server.servlet.context-path=/product
ready:
#准生产环境
server.port=8082
server.servlet.context-path=/ready
test:
#测试环境
server.port=8081
server.servlet.context-path=/test
2️⃣我们还需要一个核心配置文件——application.properties
我们需要在这个文件里面激活需要的具体的环境配置文件

里面具体的操作:
使用spring.profiles.active激活我们想要使用的配置文件,“=”号后面只需要填写application-后面且,properties前面的内容。注意格式标准
#springboot主核心配置文件
#激活使用的配置文件
spring.profiles.active=dev
这是我们使用的是dev开发环境,开发环境的端口号是8080,此时我们启动程序查看日志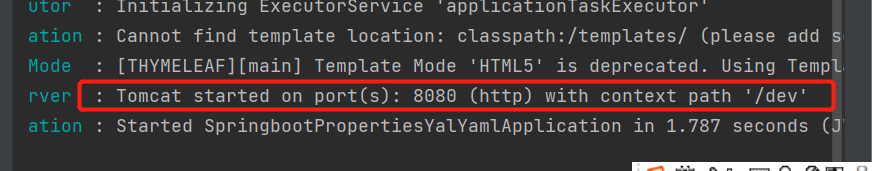
此时我们可以看到已经成功的切换到了开发环境,端口是8080
我们在换一个环境试试:换一个测试环境test,同样我们需要在核心配置文件里去激活
#springboot主核心配置文件
#激活使用的配置文件
spring.profiles.active=test
启动程序并查看日志
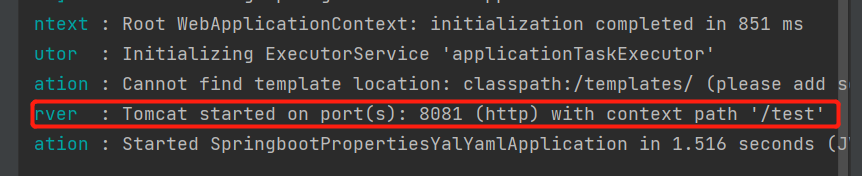
我们可以看到成功切换了
多环境配置文件切换(yaml/yml)
基本步骤和properties的配置相差不大
1️⃣
首先创建所需要的配置文件,这里我就只举一个例子了
dev

配置内容:
#开发环境
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /dev
2️⃣创建一个核心配置文件,这里的核心配置文件不是以.properties结尾的,而是以.yaml结尾的
激活配置文件
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
启动程序查看结果
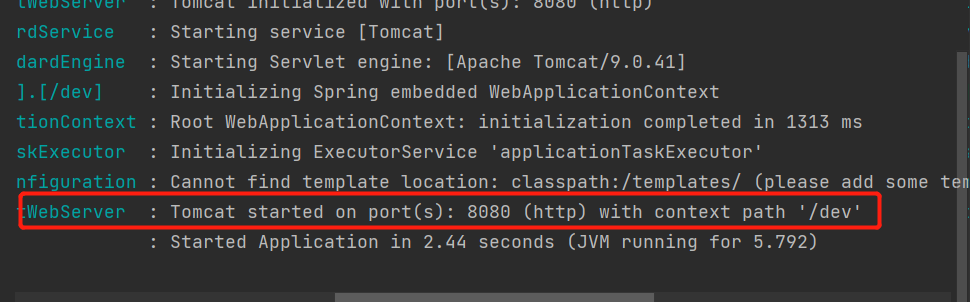
OK
获取自定义配置(单个值)
比如我们在配置文件中定义了数据
然后我们需要在外部获取
1️⃣我们首先在外部定义好数据
school.name=Sichuan Dachuan Middle School
websit=http://www.scdczx.en
2️⃣然后我们通过@Value注解来获取数据
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@Value("${school.name}")
private String schoolName;
@Value("${websit}")
private String websit;
@RequestMapping(value = "/say")
@ResponseBody
public String say(){
return "msg:"+schoolName+":"+websit;
}
}
运行结果:
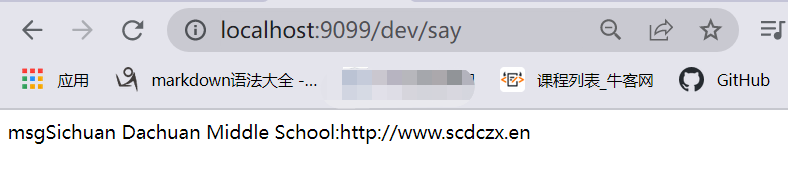
获取自定义配置(映射成对象)
1️⃣首先我们也设置好数据源
school.name=四川省达川中学
school.master=ObjectMan
school.websit=http://www.scdczx.en
2️⃣使用@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “”) 进行数据注入prefix的值为前数据源名称的前缀
@Component//将此类交给Spring容器管理
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "school")
public class School {
private String name;
private String master;
private String websit;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMaster() {
return master;
}
public void setMaster(String master) {
this.master = master;
}
public String getWebsit() {
return websit;
}
public void setWebsit(String websit) {
this.websit = websit;
}
}
获取对象
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@Autowired
private School school;
@RequestMapping(value = "/say")
@ResponseBody
public String say(){
return "学校:"+school.getName()+" "+"校长:"+school.getMaster()+" "+"学校官网:"+school.getWebsit();
}
四、SprigBoot集成Mybatis
步骤
1、添加mybatis依赖
2、添加Oracle驱动
3、使用Mybatis提供的逆向工程生成实体bean,映射文件,dao接口
<!--MySQL数据库驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--MyBatis整合SpringBoot框架起步依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
mybatis逆向工程1
我们可以通过配置文件和插件来自动生成我们需要的模块
插件
<!--mybatis 代码自动生成插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
<configuration>
<!--配置文件的位置-->
<configurationFile>GeneratorMapper.xml</configurationFile>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<overwrite>true</overwrite>
</configuration>
</plugin>
配置文件(在项目根目录创建)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<!-- 指定连接数据库的 JDBC 驱动包所在位置,指定到你本机的完整路径 -->
<classPathEntry location="D:\work_sduty\resource\mysql-connector-java-8.0.20.jar"/>
<!-- 配置 table 表信息内容体,targetRuntime 指定采用 MyBatis3 的版本 -->
<context id="tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<!-- 抑制生成注释,由于生成的注释都是英文的,可以不让它生成 -->
<commentGenerator>
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="true"/>
</commentGenerator>
<!-- 配置数据库连接信息 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dunv?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC&nullCatalogMeansCurrent=true"
userId="root"
password="654321">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- 生成 model 类,targetPackage 指定 model 类的包名, targetProject 指定
生成的 model 放在 eclipse 的哪个工程下面-->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.dunv.study.model"
targetProject="src/main/java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="false"/>
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- 生成 MyBatis 的 Mapper.xml 文件,targetPackage 指定 mapper.xml 文件的
包名, targetProject 指定生成的 mapper.xml 放在 eclipse 的哪个工程下面 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="mapper"
targetProject="src/main/resources/">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- 生成 MyBatis 的 Mapper 接口类文件,targetPackage 指定 Mapper 接口类的包
名, targetProject 指定生成的 Mapper 接口放在 eclipse 的哪个工程下面 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER"
targetPackage="com.dunv.study.mapper"
targetProject="src/main/java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- 数据库表名及对应的 Java 模型类名 -->
<table tableName="t_student" domainObjectName="Student"
enableCountByExample="false"
enableUpdateByExample="false"
enableDeleteByExample="false"
enableSelectByExample="false"
selectByExampleQueryId="false"/>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
运行:
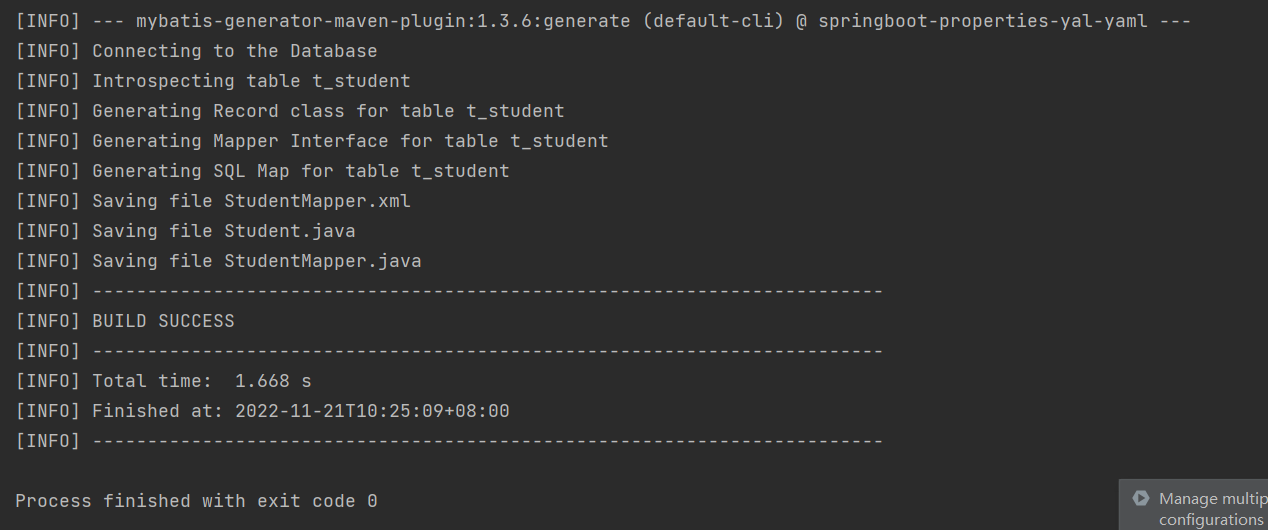
我们可以看到已经生成了
关于生成的Mapper映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.dunv.study.mapper.StudentMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.dunv.study.model.Student">
<!--id 标签只能修改主键字段-->
<!--result 除了主键以外的字段-->
<!--
column 数据库中的字段名称
property映射对象的属性名称
jdbcType 列中数据库字段的类型(可省略不写)
-->
<!--
resultMap作用:
1.当数据库中字段名称与实体类对象的属性名称不一致时,可以进行转换
2.当查询的结果没有一个对应表的时候,可以自定义一个结果集来映射查询结果
-->
<!--
数据库表字段名称 实体对象属性名称
name name
age age
-->
<!--
如果数据库中字段名称由多个单词构成,通过Mybatis逆向工程生成的对象属性
会按照驼峰命名法规则生成属性名称
其中:数据库中字段名称由多个单词的时候必须使用_下划线
-->
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id" />
<result column="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name" />
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age" />
</resultMap>
<!--
sql语句片段,将公共的部分抽取出来
通过include标签引用
-->
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id, name, age
</sql>
<!--
使用java.lang.Integer可以规避判断"" ,只需判断是否为null
-->
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List" />
from t_student
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</select>
<delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from t_student
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</delete>
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.dunv.study.model.Student">
insert into t_student (id, name, age
)
values (#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER}
)
</insert>
<!--
prefix:首拼接
suffix:尾拼接
suffixOverrides: 去除多余的逗号
-->
<insert id="insertSelective" parameterType="com.dunv.study.model.Student">
insert into t_student
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
id,
</if>
<if test="name != null">
name,
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="name != null">
#{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
#{age,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKeySelective" parameterType="com.dunv.study.model.Student">
update t_student
<set>
<if test="name != null">
name = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age = #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
<update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="com.dunv.study.model.Student">
update t_student
set name = #{name,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
age = #{age,jdbcType=INTEGER}
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
</update>
</mapper>
案例——springboot集成Mybatis
1、准备好实体类、mapper接口、mapper映射文件(由GeneratorMapper.xml使用mybatis逆向工程生成)
2、创建service层以及其实现层

service
package com.dunv.study.service;
import com.dunv.study.model.Student;
/**
* @author ZS
* @Description
* @date 2022/11/29 13:48
*/
public interface StudentService {
/**
* 根据学生ID查询详情
* @param id
* @return
*/
Student queryStudentById(Integer id);
}
serviceImpl
为StudentServiceImpl 添加@Service注解
package com.dunv.study.service.impl;
import com.dunv.study.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.dunv.study.model.Student;
import com.dunv.study.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @author ZS
* @Description
* @date 2022/11/29 13:49
*/
@Service //为StudentServiceImpl 添加@Service注解
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Override
public Student queryStudentById(Integer id) {
Student student = studentMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
return student;
}
}
2、创建控制层的StudentController
package com.dunv.study.controller;
import com.dunv.study.model.Student;
import com.dunv.study.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
/**
* @author ZS
* @Description
* @date 2022/11/29 13:45
*/
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/student")
@ResponseBody
public Object student(Integer id){
Student student = studentService.queryStudentById(id);
return student;
}
}
3、为mapper接口添加mapper扫描
package com.dunv.study;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author 28259
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.dunv.study.mapper")//开启扫描mapper接口的包以及子目录
class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
4、在pom.xml的build中指定文件夹为resource
<!--手动指定文件夹为resource-->
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
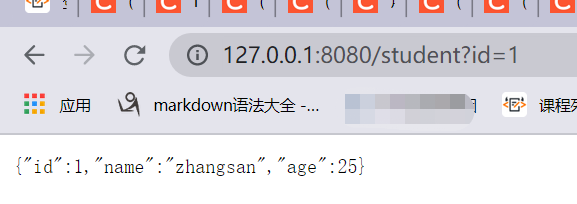
5、运行并访问
数据库信息

查询结果
Mapper映射文件存放位置(不在pom文件中指定资源目录)
1、把mapper.xml映射文件放到resource/mapper目录下

2、在核心配置文件application.properties中指定
#设置数据库连接
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dunv?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&nullCatalogMeansCurrent=true
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=654321
#指定mybatis映射文件的位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
3、运行并访问
springboot集成mybatis总结
1️⃣Springboot集成Mybatis
- 添加mybatis依赖,Mysql/Oracle驱动
- 使用Mybatis提供的逆向工程生成实体bean,映射文件,DAO接口
2️⃣Springboot集成mybatis,最主要的两个注解是@Mapper和@MapperScan
- @Maper 需要在每一个Mapper接口类上添加,作用扫描dao/mapper接口
- @MapperScan是在SpringBoot启动入口类添加的,它是扫描所有得1包
3️⃣关于映射文件存放的位置
1、将Mapper接口和Mapper映射文件存放到src.mian/java同一目录下,
还需要在pom文件中手动指定资源文件夹的路径resource
2、将Mapper接口和Mapper映射文件分开存放,需要在核心配置文件中指定mapper映射文件存放的位置
五、 SpringBoot支持事物
前言
事物是一个完整的功能,也叫一个完整的业务
事物只跟什么SQL语句有关系?(DML【数据操纵语言】:增、删、改)
上面说了,事物是一个完整的业务,里面包含了多个执行单元。由于事物的一致性原则——这些执行单元要么全部执行,要么全不执行
我们以数据修改为例
public int updateStudentById(Student student) {
//修改成功
int i = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
//失败
int a = 10/0;
return i;
}
在上面的方法中,就可以把这个方法看成是一个事务,里面包含了两个执行单位
- int i = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
- int a = 10/0;
第二个 int a = 10/0 肯定会报错
现在我们要把数据库里面的哈哈修改成啦啦,如果不添加事务,我们可以看看结果是什么样的。
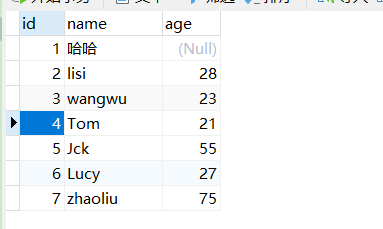
我们可以看到页面上报错了

后端控制台也报错了,正是第二个错误
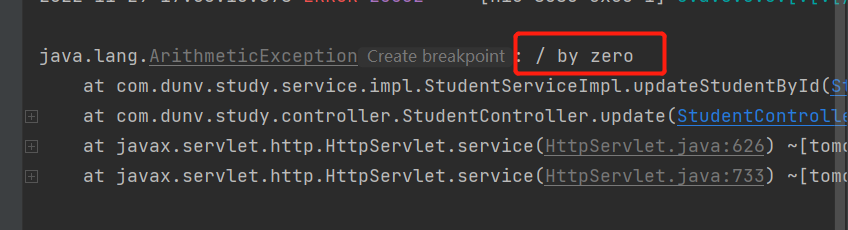
此时我们再看数据库
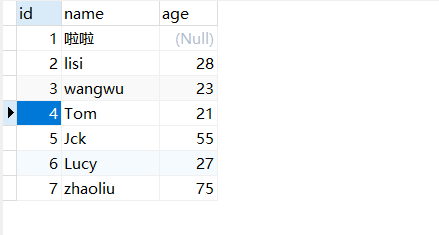
数据被修改了!,也就是说int i = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);执行成功了,但是int a = 10/0执行失败了。这违反了事务的一致性原则
此时我们应该添加事务
添加事务
在对应的业务上添加 @Transactional(Springboot2.0以上)注解即可,这样就不会保持事务的一致性原则
@Transactional
@Override
public int updateStudentById(Student student) {
//修改成功
int i = studentMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(student);
//失败
int a = 10/0;
return i;
}
}




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot高校流浪动物领养网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b74a57108a924235853f9c868a770ed8.png)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot高校学生摄影作品展示平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/72ee6c7b7bac4876b608f6b112b741ee.png)

![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计校园征兵及退役复原管理系统JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d49e0e3d68fc4550a3c7c8d3e9e6ed40.png)