Git 时间线管理
这一部分主要讲的是 取消(undo) 变化 和在不同的时间锚点跳来跳去,以 command 为主。
设计到的commits有:
- checkout
- restore
- reset
- revert
checkout
checkout 的一部分作用,即切换分枝在 git 分支操作 中有提到过,不过 checkout 本身的用途更多。有些开发甚至觉得 checkout 的功能太多了,最终将功能分割之后生成了新的 switch 和 restore。
除了分支管理之外,checkout 还能用来还原文件和 undo history。
checkout commit
下面会 checkout 一个 commit hash:
# 可以完整cv整个hash,或者截取前 7 位作为hash key
➜ basic git:(main) ✗ git checkout f8b2e15
Note: switching to 'f8b2e15'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example:
git switch -c <new-branch-name>
Or undo this operation with:
git switch -
Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false
HEAD is now at f8b2e15 start work on outline and characters
➜ basic git:(f8b2e15) ✗ git status
HEAD detached at f8b2e15
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
git.md
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
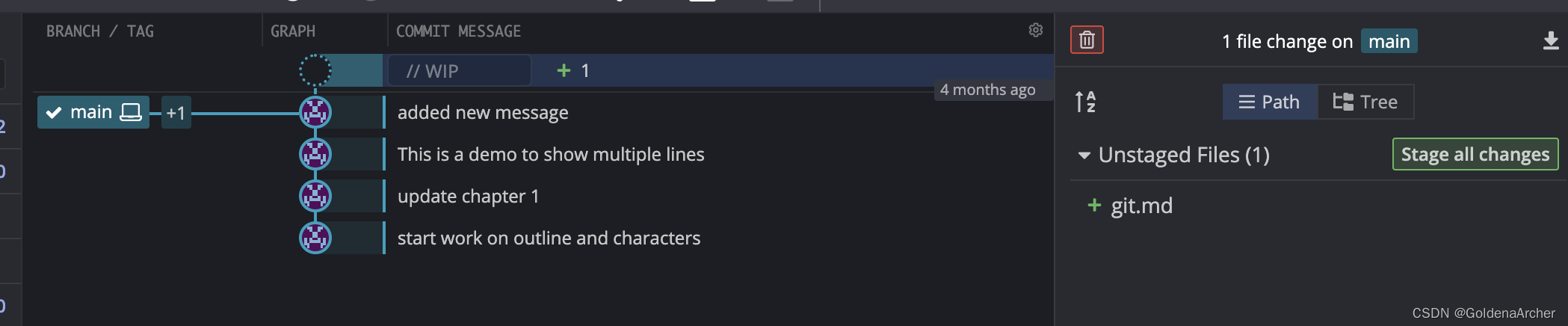
现在解释一下 detached HEAD 是什么意思,正常情况下,当前 branch 指向当前 commit,而当前 head 指向当前 branch,也就可以理解成是当前 commit 的 reference,这个时候的 head 是当前 commit 的 symlink:
软件上看起来是这样的:
但是当直接 checkout 到一个 commit 之后,当前的分支依旧之乡最后一个 commit,HEAD 则是只想当前的 commit:
也就是说 HEAD 从 branch 上分离(detach)了,软件上看起来是这样的:
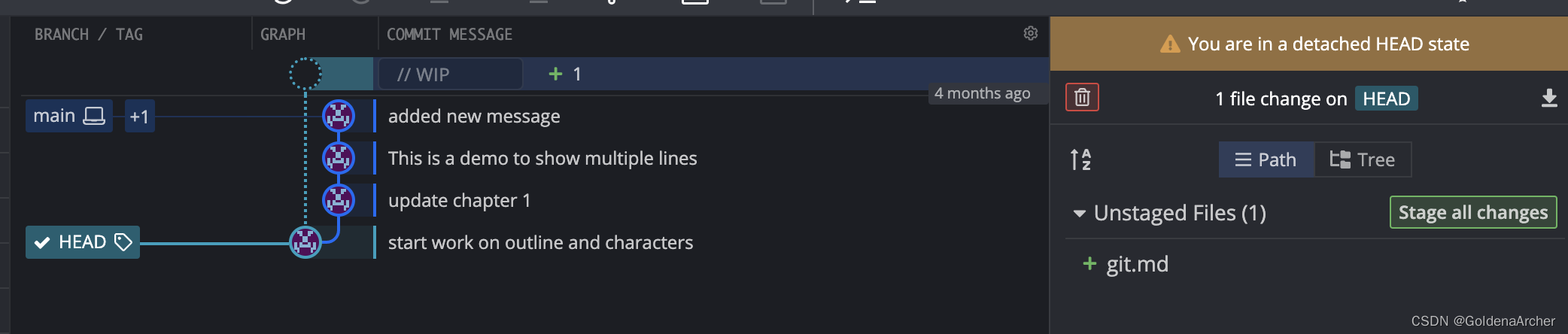
这时候的 HEAD 直接作为当前 commit 的 reference。
checkout commit 的用途有
-
查看原始文件
大多是时候发生在某个版本不工作了,然后要要 revert 到某一个版本
-
创建一个新的分支
就像 switch 到一个新的分支会创建一个新的历史一样,checkout 到某一个 commit 也会创建一个新的历史分支
➜ basic git:(main) ✗ git checkout f8b2e15 ➜ basic git:(f8b2e15) ✗ git switch -c new-ch2 Switched to a new branch 'new-ch2' ➜ basic git:(new-ch2) ✗ git commit -m "create new version of ch2" [new-ch2 12da43a] create new version of ch2 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) create mode 100644 ch2.txt ➜ basic git:(new-ch2) ✗此时的分支看起来如下:
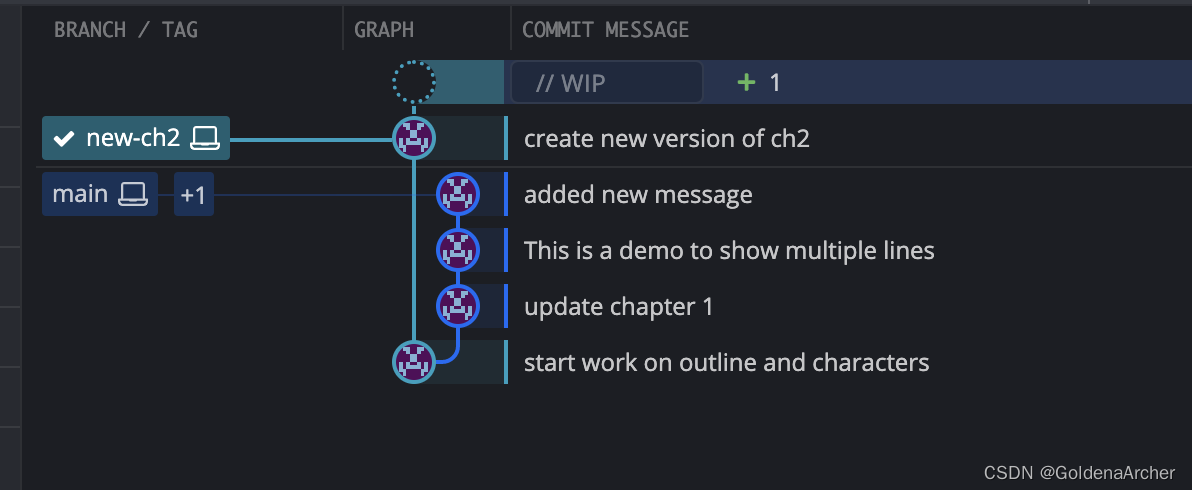
此时的 HEAD 不是一个 detached 状态,而是重新绑定到了新创建的
new-ch2分支上。而该分支没有保存的变化,依旧保存在另一个分支上。
如果没有做任何的变动,想要切换到原有的分支,可以直接使用 git checkout branchname 执行。
git checkout HEAD~
具体语法为:git checkout HEAD~1,其中 HEAD~ 后跟数字,如果是 1 就惠滚到上一个 commit,以此类推。
图解如下:
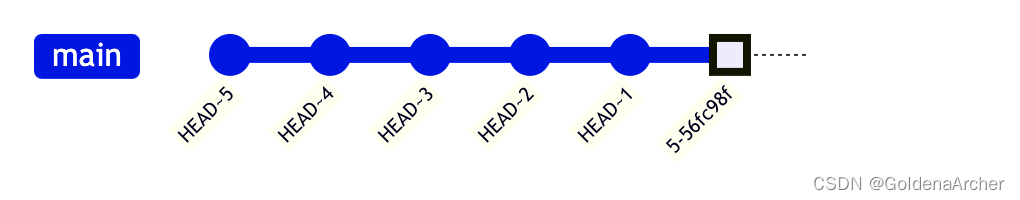
顺便上面的 mermaid 语法为:
gitGraph
commit id: "HEAD~5"
commit id: "HEAD~4"
commit id: "HEAD~3"
commit id: "HEAD~2"
commit id: "HEAD~1"
commit type: HIGHLIGHT
运行如下:
➜ basic git:(new-ch2) ✗ git checkout main
Switched to branch 'main'
➜ basic git:(main) ✗ git checkout HEAD~2
Note: switching to 'HEAD~2'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example:
git switch -c <new-branch-name>
Or undo this operation with:
git switch -
Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false
HEAD is now at b18e966 update chapter 1
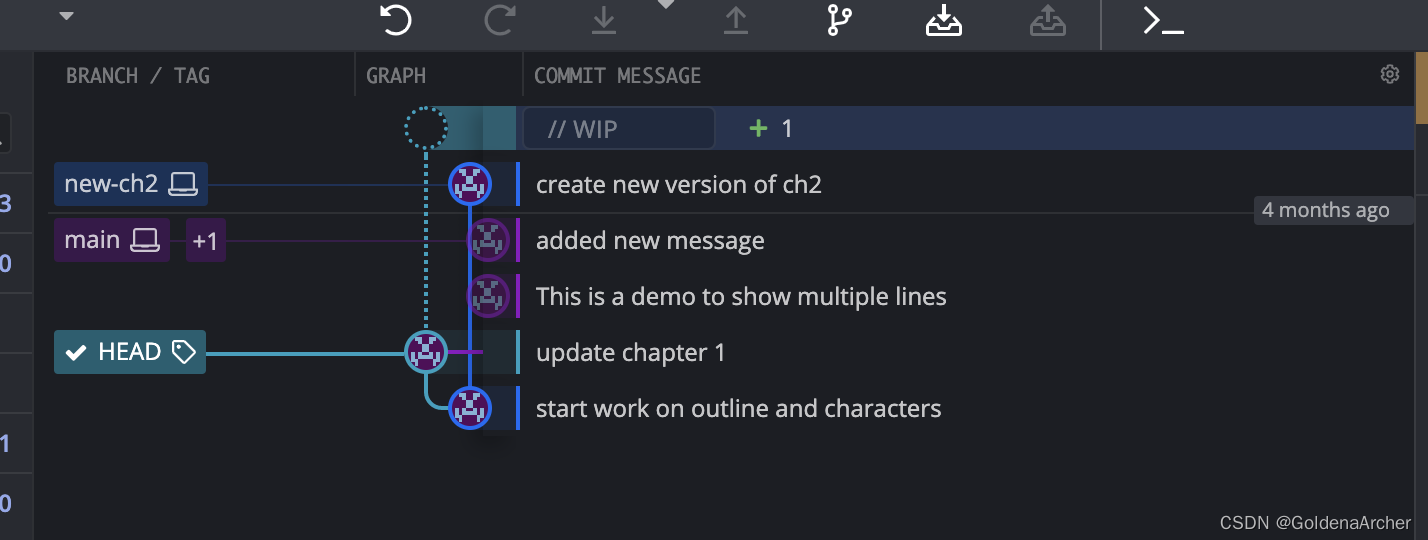
这个时候返回有两个方法:
-
记住原本分支
-
使用
git switch -,该指令会切换到上一个所在的分支,如:➜ basic git:(b18e966) ✗ git switch - Previous HEAD position was b18e966 update chapter 1 Switched to branch 'main'
git checkout HEAD
该指令可以用于重制已经修改的文件,这里会用一个新的 repo 做例子,初步设置如下:
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ touch cat.txt dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ echo "first commit" > cat.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ echo "first commit" > dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
cat.txt
dog.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git commit -m "first commits"
[main (root-commit) 6c98eb0] first commits
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
create mode 100644 cat.txt
create mode 100644 dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) cat cat.txt
first commit
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ echo 'second commit' >> cat.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ echo 'second commit' >> dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ cat cat.txt
first commit
second commit
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git commit -m "second commit"
[main 5a999a7] second commit
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
# 重复若干次
准备完了之后就可以用 git checkout HEAD <file>,缩写为 git checkout -- <filename> 去重制操作了,如:
➜ undo git:(main) git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: cat.txt
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git checkout HEAD cat.txt
Updated 1 path from 4899106
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: cat.txt
modified: dog.txt
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git checkout -- *.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
这个的使用场景可能在:
-
你真的搞砸了很多
-
重制 db 文件
比如说我们的项目就是从 csv 中读取 db 文件的,然后每天都必须要更新 csv 中的 ref date,这个时候更新分支就会因为 csv 不 match 导致 conflict。
restore
像上文提到的,restore 是一个比较新的命令,用于重置一些 checkout 的功能。
git restore
该指令可以用于重制已经修改的文件,对标 git checkout HEAD <file>。
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: dog.txt
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git restore dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: git.md
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗
restore --source
另一个 flag 可以用来将当前文件还原到几个 commit 之前,语法为:git restore --source <HEAD~1|hashedvalue> <filename>,还愿的方法使用上一条指令即可。
例:
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ cat dog.txt
first commit
second commit
third commit
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git restore --source HEAD~2 dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ cat dog.txt
first commit
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git restore dog.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ cat dog.txt
first commit
second commit
third commit
restore --staged
具体指令:git restore --staged <file>,这条指令可以将已经 staged 文件拉出来,如:
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ touch wrongfile.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: git.md
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
wrongfile.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: git.md
new file: wrongfile.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git restore --staged wrongfile.txt
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: git.md
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
wrongfile.txt
顺便,如果直接用 git status,git 会提示可以用什么指令进行操作,如 git restore --staged <file>... , git add <file>..., git restore <file>..。
reset
git reset 用于重置 commits,我主要用来将几个 commits squash 到一个 commits 里面去,使用 git rest 会保留当前的变化。
案例:
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
da7603f (HEAD -> main) mistake commit2
a34f0c8 mistake commit
50840de third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0 first commits
(END)
➜ undo git:(main) git reset 50840de
Unstaged changes after reset:
M cat.txt
M dog.txt
M git.md
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git status
On branch main
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: cat.txt
modified: dog.txt
modified: git.md
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
wrongfile.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git log --oneline
50840de (HEAD -> main) third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0 first commits
(END)
可以看到,本来的变化没有丢还在这里。
对于 git 来说,它会重新将 HEAD 指向提供的 commit hash 值,并且将中间的变化保存在 working directory 中。
我常用的做法就是清理分支上的 commits(尽量保证一个修 bug 的 MR/PR 一个 commits,功能性的保证有理由的 staging,一般来说小功能在 3 个以下,大功能 5 个一下这样),或者是将当前的变化带到其他的分支上。当然,后者用 git stash 也可以。
如果想要将当前的变化和修改的文件全都删除,可以加上 --hard 这个 flag,其语法为 git reset --hard <commit>,如:
➜ undo git:(main) git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git commit -m "mistake commit"
[main fa07782] mistake commit
2 files changed, 2 insertions(+)
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
fa07782 (HEAD -> main) mistake commit
0608200 fourth commit
50840de third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git reset --hard HEAD~1
HEAD is now at 0608200 fourth commit
➜ undo git:(main) git status
On branch main
nothing to commit, working tree clean
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
0608200 (HEAD -> main) fourth commit
50840de third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0 first commits
(END)
revert
revert 和 reset 有点像,但是 revert 会保留之前的 commit,将文件放到 working directory 中,并且创建一个新的 commit 说明之前的 commit 被 revert 了。
举例说明:
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
fbd7250 (HEAD -> main) mistake commit2
2f0f2ce mistake commit
0608200 fourth commit
50840de third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0 first commits
(END)
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git commit -m "mistake commit"
[main 2f0f2ce] mistake commit
3 files changed, 36 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
➜ undo git:(main) git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git commit -m "mistake commit2"
[main fbd7250] mistake commit2
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
➜ undo git:(main) git revert 0608200
error: Your local changes to the following files would be overwritten by merge:
git.md
Please commit your changes or stash them before you merge.
Aborting
fatal: revert failed
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git revert 0608200
Auto-merging cat.txt
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in cat.txt
Auto-merging dog.txt
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in dog.txt
Auto-merging git.md
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in git.md
error: could not revert 0608200... fourth commit
hint: After resolving the conflicts, mark them with
hint: "git add/rm <pathspec>", then run
hint: "git revert --continue".
hint: You can instead skip this commit with "git revert --skip".
hint: To abort and get back to the state before "git revert",
hint: run "git revert --abort".
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git add .
➜ undo git:(main) ✗ git revert --continue
[main 6c50464] Revert "fourth commit"
2 files changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
delete mode 100644 wrongfile.txt
➜ undo git:(main) git status
On branch main
nothing to commit, working tree clean
➜ undo git:(main) git log --oneline
6c50464 (HEAD -> main) Revert "fourth commit"
fbd7250 mistake commit2
2f0f2ce mistake commit
0608200 fourth commit
50840de third commit
5a999a7 second commit
6c98eb0 first commits
(END)
可以看到,working tree clean 标记修改的文件已经没有了,但是修改的 commits 还存在。
从个人经验上来说,我用 revert 就是为了修正某些已经实现的功能(by fixing one bug we created more bugs),但是别的同事机器上已经有了那个 commits,不可能说重改整个历史,这样别人做的 commits 也没有了。
即,如果所有的变化都是本地的,那么使用 reset 会方便些。如果变化推到了 remote,但是 没有其他的同事 使用这个 branch,使用 reset 也可以。否则就应该使用 reset。
reference
-
HEAD and ORIG_HEAD in Git
-
What is HEAD in Git?







![ubuntu20.04+x86_64+virtualbox6.7 环境下编译xenomai内核和实时性测试[详解]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5b174e89e1c549e88151fe928c39d3c0.png#pic_center)