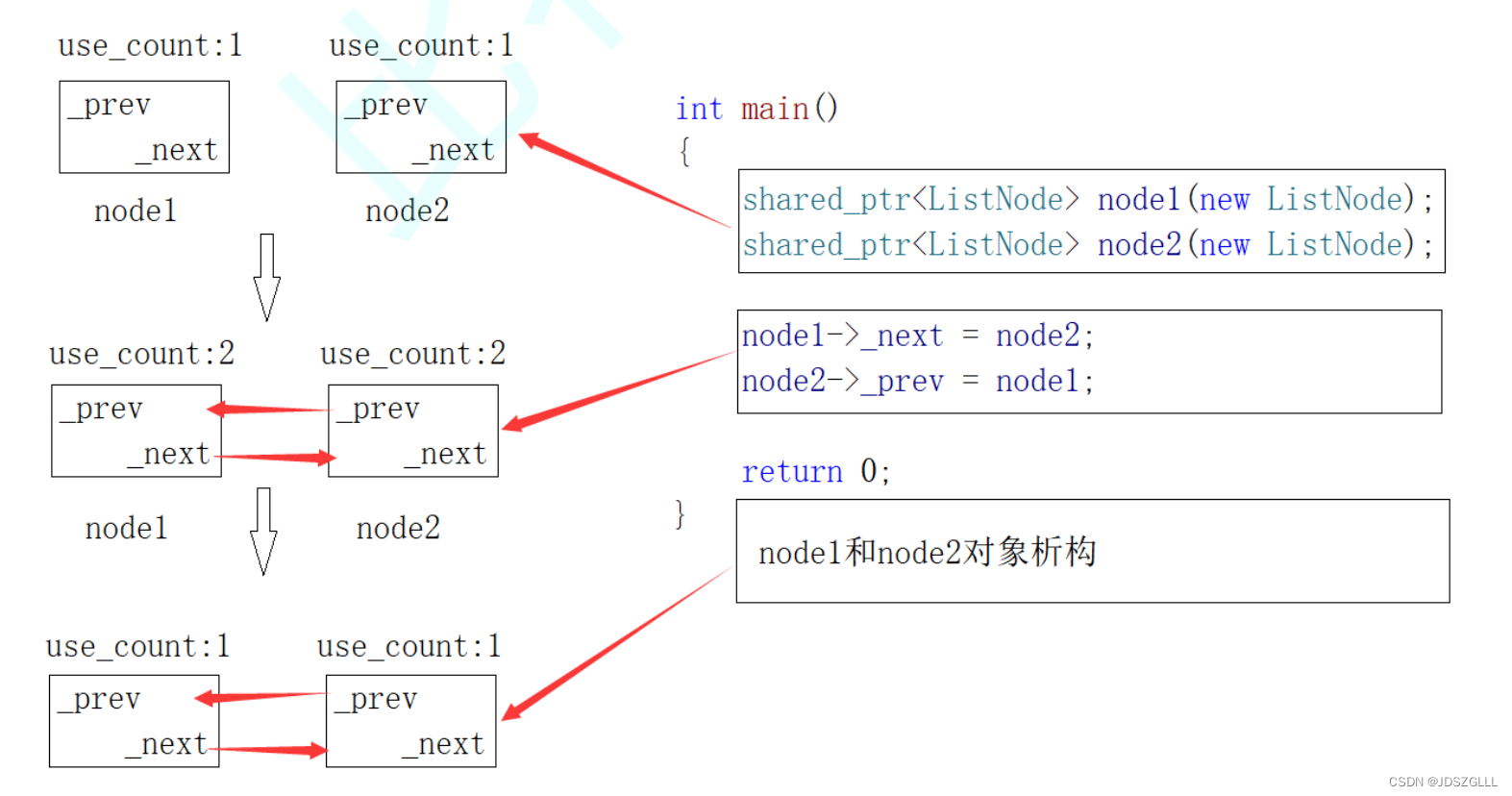
介绍
所谓类的单例模式 就是采取一定的方法保证在整个软件系统中对某个类只能存在一个对象实例,并且该类只提供一个取得其对象实例的方法(静态方法)
比如 Hibemate的SessionFactory 它充当数据存储源的代理 并负责创建Session对象 SessionFactory并不是轻量级的 一般情况下 一个 项目通常只需要一个SessionFactory就够 这样就需要用到单例模式了
单例模式的八种实现方式
饿汉式(静态常量)
public class HungryMan1 {
//1 构造器私有话 外部不能直接new对象调用
private HungryMan1(){}
//2 本类内部创建对象实例
private final static HungryMan1 instance = new HungryMan1();
//3 提供一个公有的静态方法 返回实例对象
public static HungryMan1 getInstance(){
return instance;
}
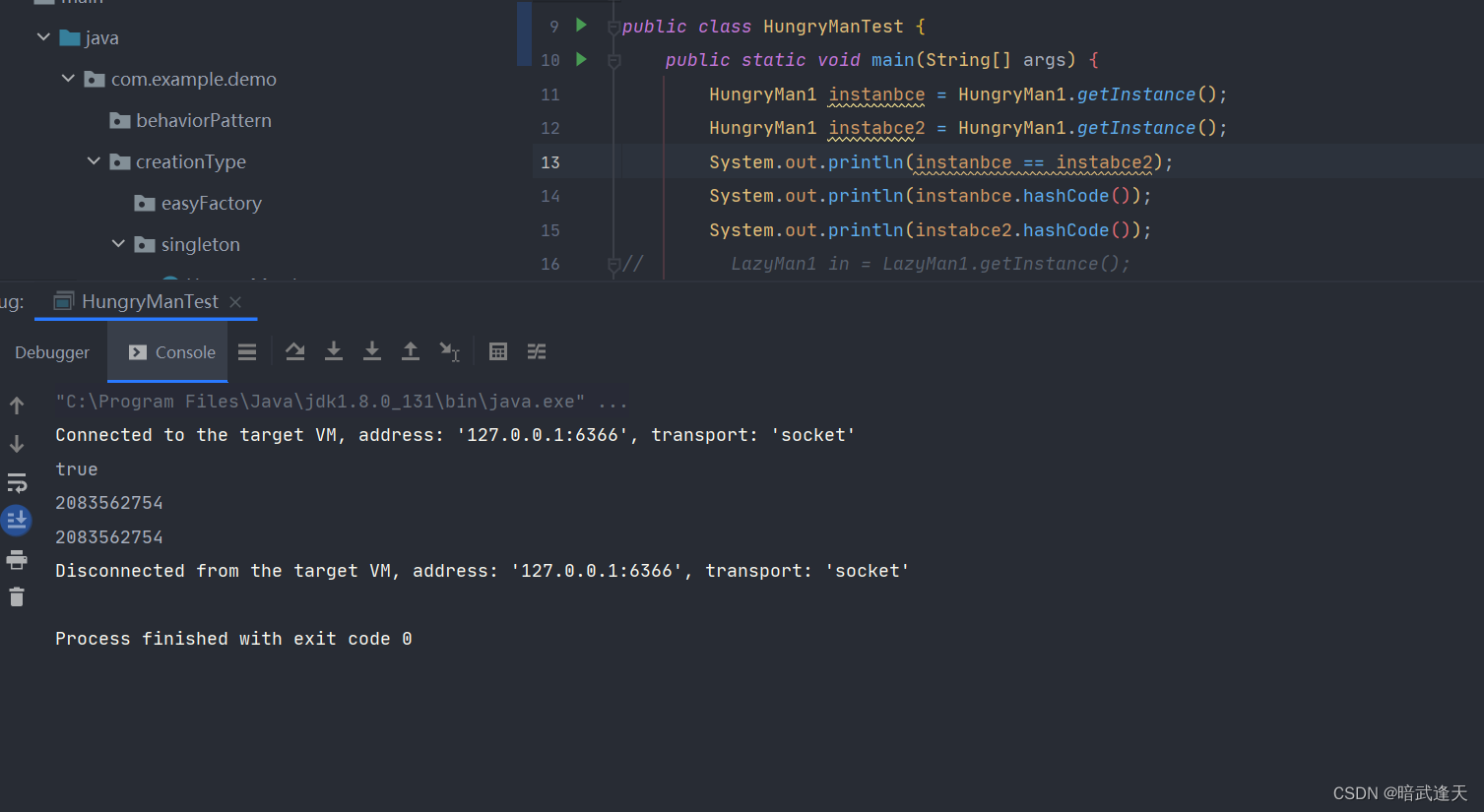
}public class HungryManTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HungryMan1 instanbce = HungryMan1.getInstance();
HungryMan1 instabce2 = HungryMan1.getInstance();
System.out.println(instanbce == instabce2);
System.out.println(instanbce.hashCode());
System.out.println(instabce2.hashCode());
}
}测试结果
饿汉式(静态代码块)
public class HungryMan2 {
private HungryMan2(){}
//在静态代码块中 创建单例对象
static {
instance = new HungryMan2();
}
//2 本类内部创建对象实例
private final static HungryMan2 instance;
//3 提供一个公有的静态方法 返回实例对象
public static HungryMan2 getInstance(){
return instance;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
懒汉式(线程不安全)
public class LazyMan1 {
private static LazyMan1 instance;
private LazyMan1(){};
//提供一个静态的公有方法 当使用到该方法时 才会去创建 instance
public static LazyMan1 getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
instance = new LazyMan1();
}
//等价于 jdk8 Optional写法
// Optional.ofNullable(instance).orElseGet(()->new LazyMan1());
return instance;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
懒汉式(线程安全 同步方法)
public class LazyMan2 {
private static LazyMan2 instance;
private LazyMan2(){};
//提供一个静态的公有方法 加入同步处理的代码 解决线程安全问题
public static synchronized LazyMan2 getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
instance = new LazyMan2();
}
return instance;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
懒汉式(线程安全 同步代码块)
public class LazyMan3 {
private static LazyMan3 instance;
private LazyMan3(){};
//提供一个静态的公有方法 加入同步处理的代码 解决线程安全问题
public static LazyMan3 getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
synchronized(LazyMan3.class){
instance = new LazyMan3();
}
}
return instance;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
双重检查
public class LazyMan4 {
private static volatile LazyMan4 instance;
private LazyMan4(){};
//提供一个静态的公有方法 加入双重检查代码 解决线程安全问题 同时解决懒加载问题
public static synchronized LazyMan4 getInstance(){
if(instance==null){
synchronized(LazyMan4.class){
if(instance==null){
instance = new LazyMan4();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
静态内部类
public class LazyMan5 {
private LazyMan5(){};
//书写静态内部类 该类中有一个静态属性 LazyManInstance
private static class LasyManInstance{
private static final LazyMan5 INSTANCE = new LazyMan5();
}
//提供一个静态公有方法 直接返回LazyManInstance.INSTANCE
public static synchronized LazyMan5 getInstance(){
return LasyManInstance.INSTANCE;
}
}测试同 "饿汉式静态常量"一致
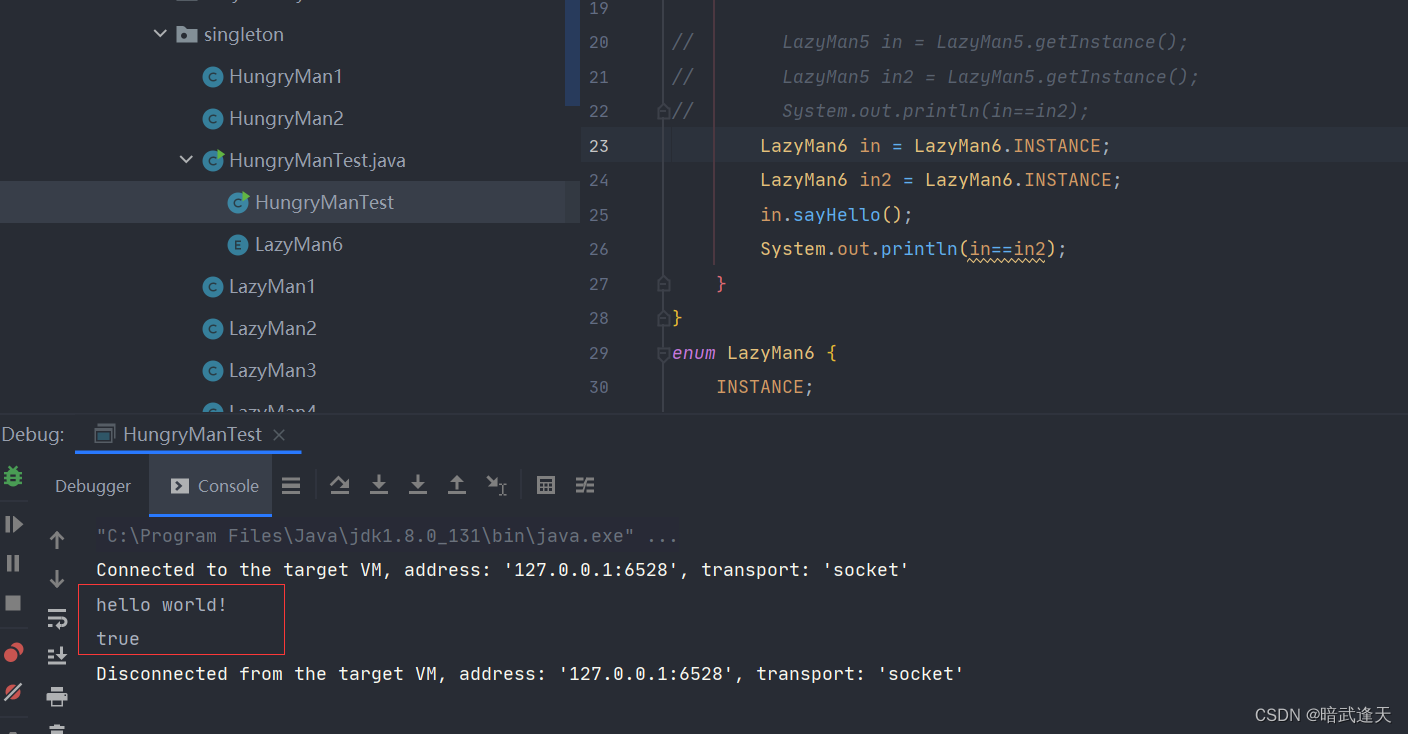
枚举
public class HungryManTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LazyMan6 in = LazyMan6.INSTANCE;
LazyMan6 in2 = LazyMan6.INSTANCE;
in.sayHello();
System.out.println(in==in2);
}
}
enum LazyMan6 {
INSTANCE;
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}测试: