目录
fcntl
lseek
参数fd
参数offset
参数whence
返回值
应用场景
测试代码1
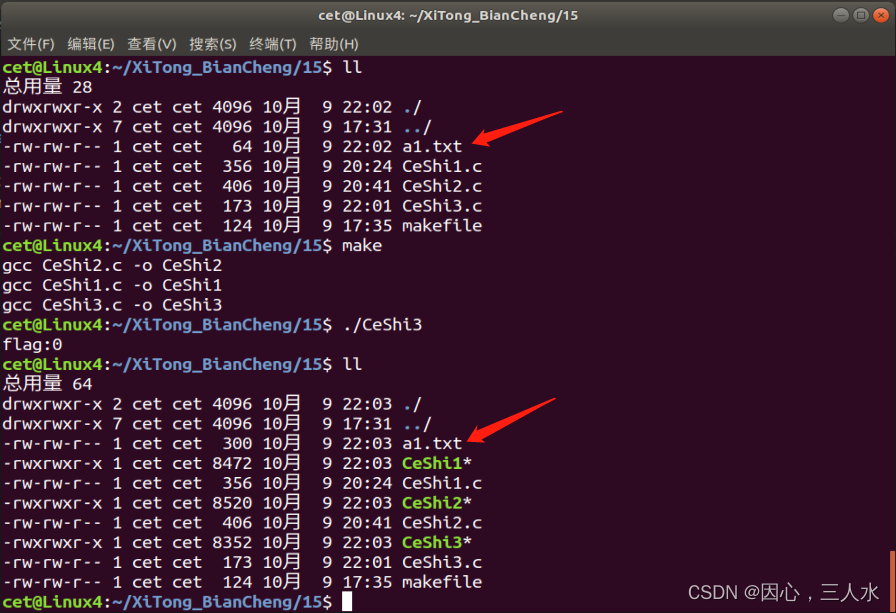
测试结果
测试代码2
测试结果
查看文件方式
truncate
参数path
参数length
测试代码3
测试结果
fcntl
获取文件属性、修改文件属性。
int flgs=fcntl(fd,F_GETFL); //获取
flgs|=O_NONBLOCK; //修改
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flgs); //设置
F_GETFL:获取文件状态
F_SETFL:设置文件状态
lseek
man 2 lseek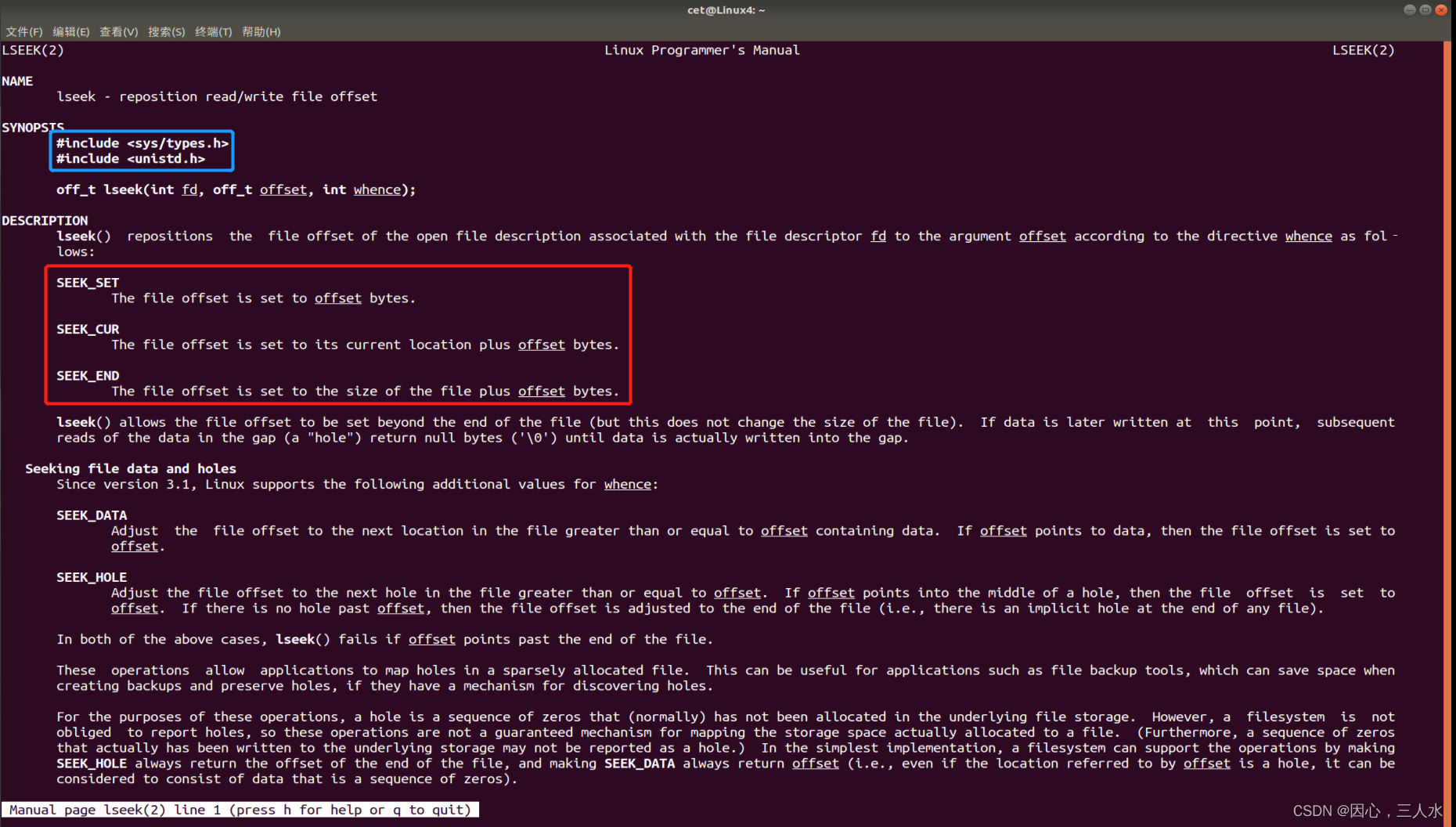
参数fd
文件描述符。
参数offset
偏移量。
参数whence
起始偏移位置。SEEK_SET、SEEK_CUR、SEER_END。
返回值
成功:较起始位置偏移量。
失败:-1。
应用场景
文件的“读”、“写”使用同一偏移位置。
使用lseek获取文件大小。
使用lseek拓展文件大小。想要文件的大小真正拓展,必须引起IO操作。也可以使用truncate函数,直接拓展文件。
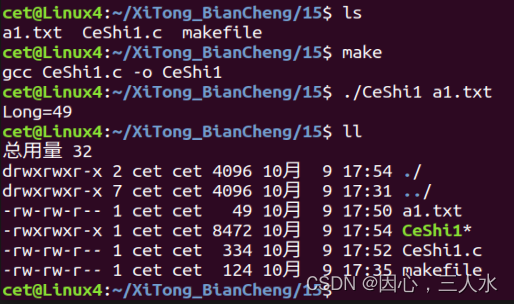
测试代码1
获取文件大小。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
int fd=open(argv[1],O_RDWR);
if(fd==-1){
perror("open error");
exit(1);
}
int Long=lseek(fd,0,SEEK_END);
printf("Long=%d\n",Long);
return 0;
}测试结果
测试代码2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
perror("open error");
exit(1);
}
int Long = lseek(fd,10, SEEK_END); //在内容末尾偏移10个字节
write(fd, "aaa", 3); //追加“aaa”
close(fd);
return 0;
}测试结果
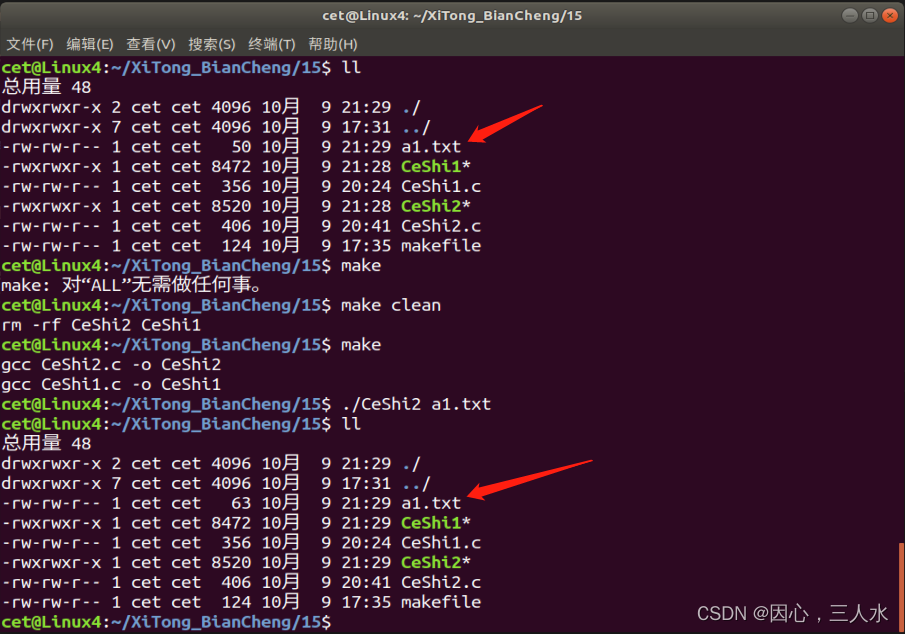
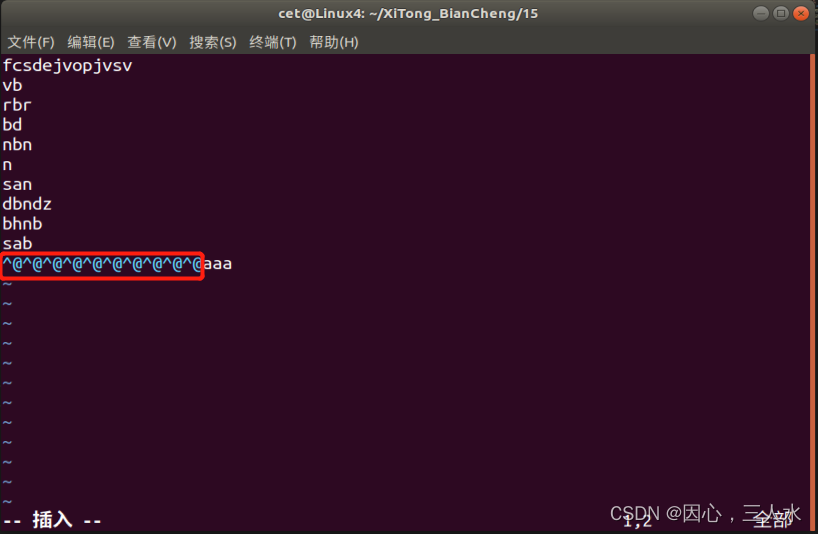
^@:文件空洞
查看文件方式
查看文件的16进制表示形式。
od -tcx 文件名od -tcx a1.txt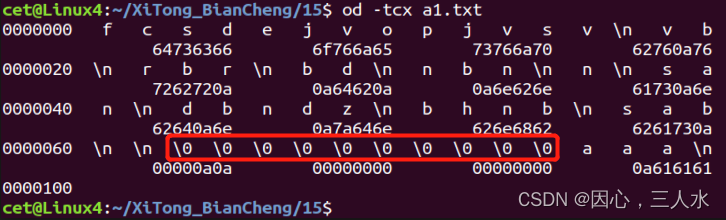
查看文件的10进制表示形式。
od -tcd 文件名od -tcd a1.txt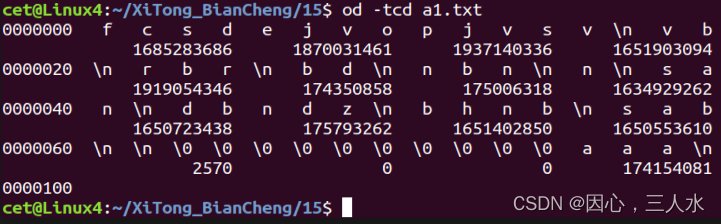
truncate
拓展文件大小。而且只能拓展现有文件的大小。
man 2 truncate
参数path
现有的文件或者文件路径。
参数length
拓展文件到的大小。
测试代码3
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int flag = truncate("a1.txt", 300);
printf("flag:%d\n", flag);
return 0;
}测试结果