结构体:属于用户自定义的数据类型,允许用户存储不同的数据类型
- 语法:struct 结构体名 {结构体成员列表};
- 通过结构体创建变量的三种方式:
- 1、struct 结构体名 变量名
- 2、struct 结构体名 变量名={成员1值,成员2值…}
- 3、定义结构体时顺便创建变量
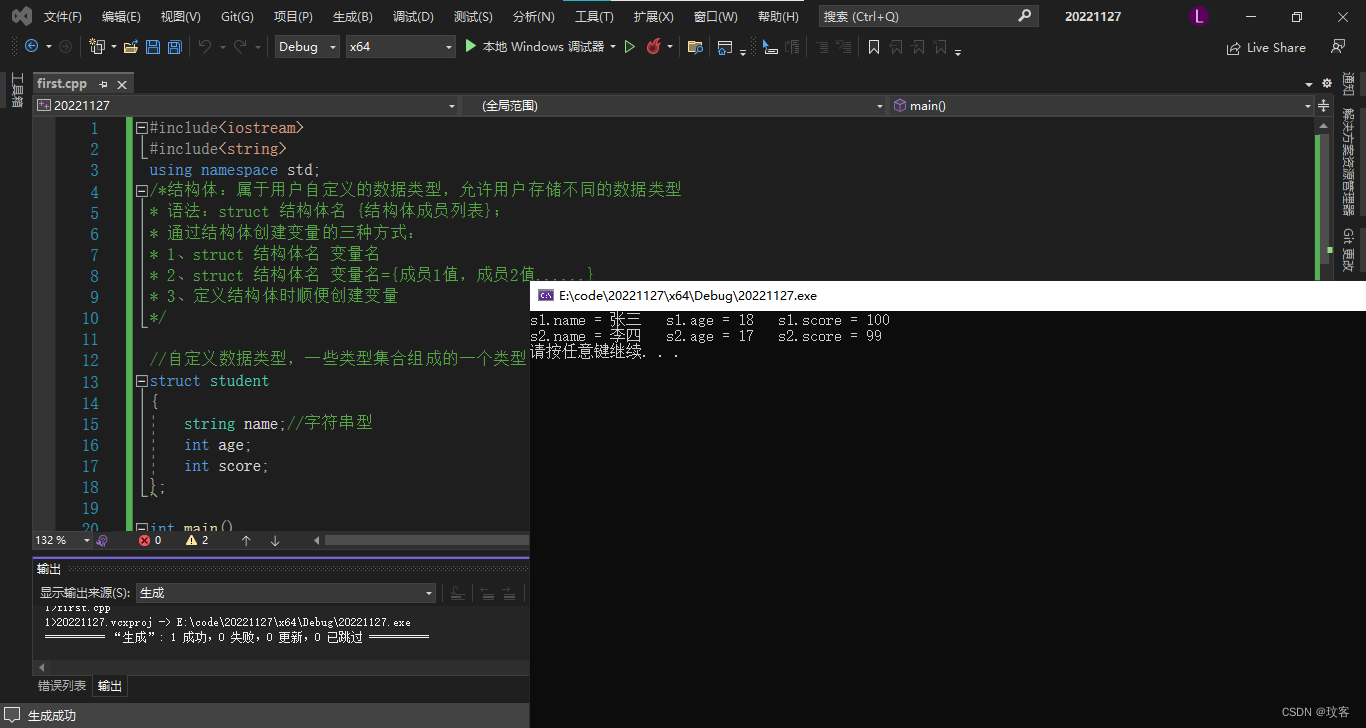
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//自定义数据类型,一些类型集合组成的一个类型
struct student
{
string name;//字符串型
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
//方法一:struct 结构体名 变量名
struct student s1;
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 18;
s1.score = 100;
cout << "s1.name = " << s1.name << " s1.age = " << s1.age << " s1.score = " << s1.score << endl;
//方法二:struct 结构体名 变量名={成员1值,成员2值......}
struct student s2 = { "李四",17,99 };
cout << "s2.name = " << s2.name << " s2.age = " << s2.age << " s2.score = " << s2.score << endl;
//方法三:定义结构体时顺便创建变量:通常不使用
system("pause");
return 0;
}
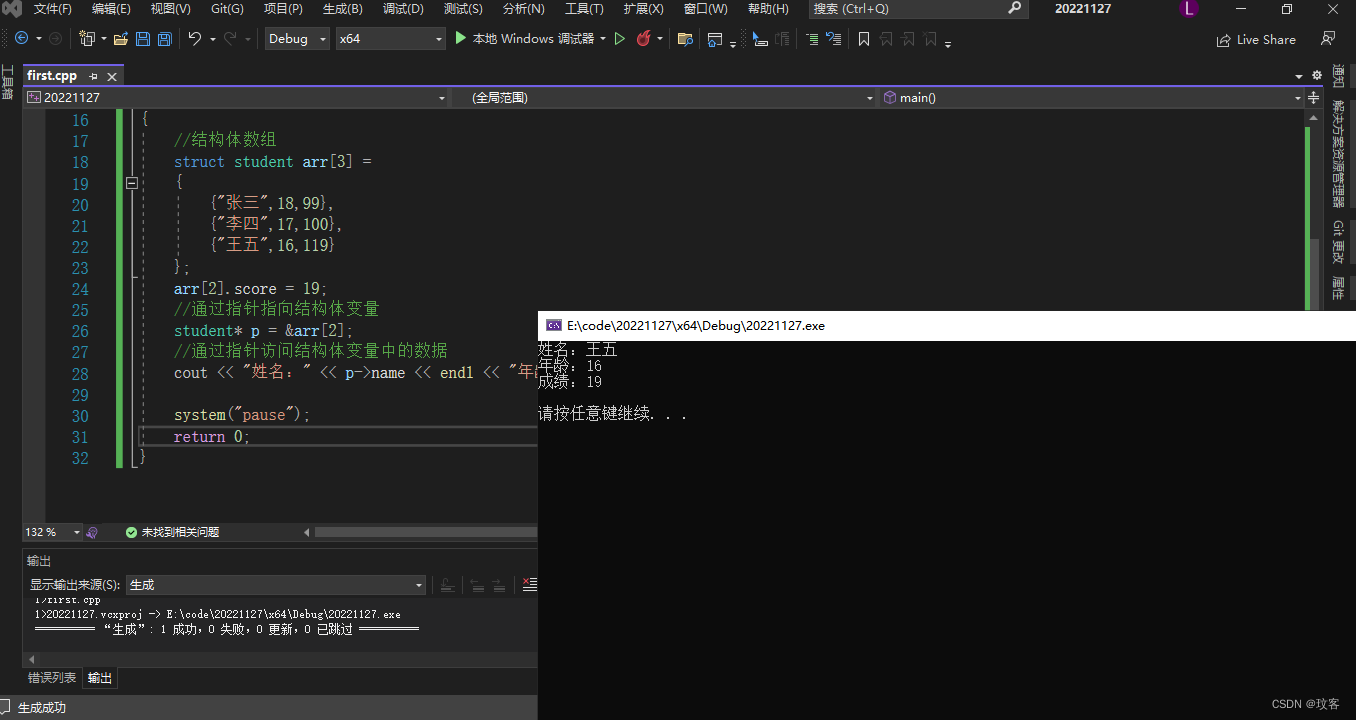
结构体数组
- 结构体数组:将自定义的结构体放入数组中方便维护
- 语法:struct 结构体名 数组名[元素个数] = {{} , {} , … ,{}}
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//自定义数据类型,一些类型集合组成的一个类型
struct student
{
string name;//字符串型
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
//结构体数组
struct student arr[3] =
{
{"张三",18,99},
{"李四",17,100},
{"王五",16,119}
};
arr[2].score = 19;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "第" << i + 1 << "个同学的信息为:" << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << arr[i].name << endl << "年龄:" << arr[i].age << endl << "成绩:" << arr[i].score << endl << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

结构体指针
- 通过指针访问结构体中的成员
- 利用操作符->可以通过结构体指针访问结构体属性
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
string name;//字符串型
int age;
int score;
};
int main()
{
//结构体数组
struct student arr[3] =
{
{"张三",18,99},
{"李四",17,100},
{"王五",16,119}
};
arr[2].score = 19;
//通过指针指向结构体变量
student* p = &arr[2];
//通过指针访问结构体变量中的数据
cout << "姓名:" << p->name << endl << "年龄:" << p->age << endl << "成绩:" << p->score << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
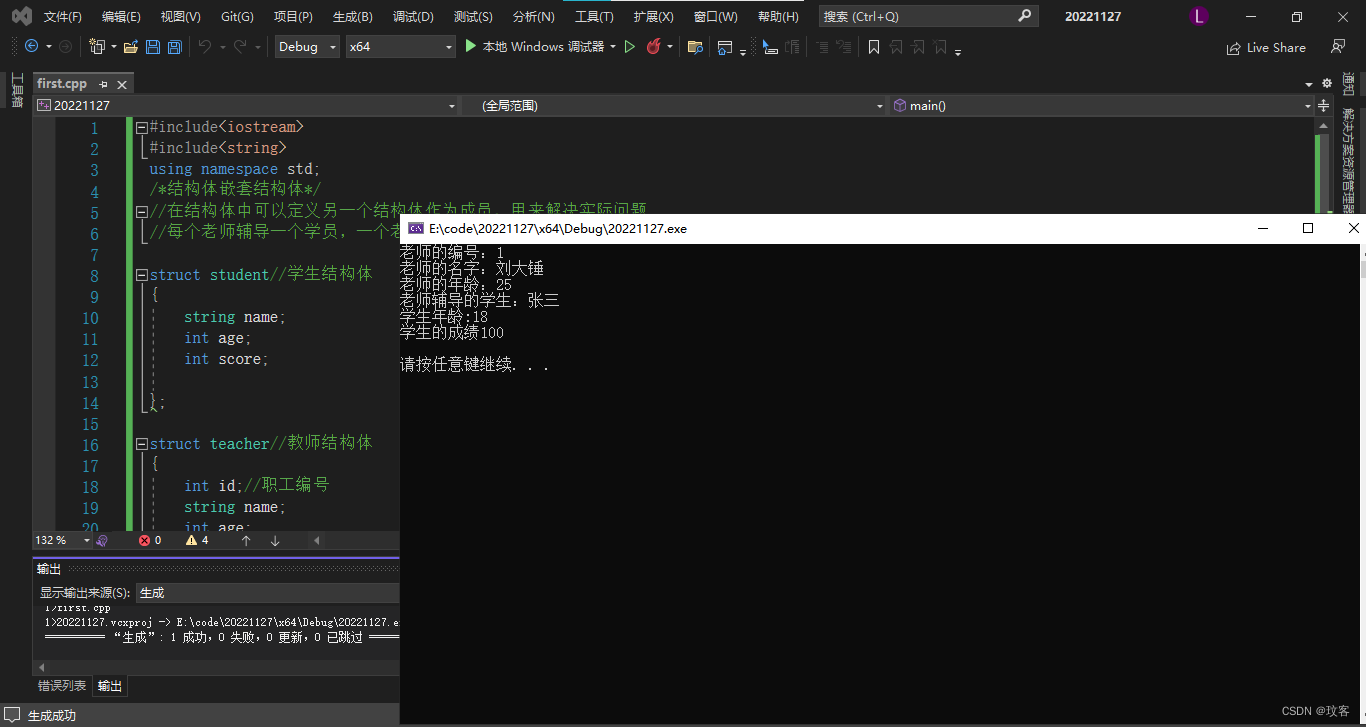
结构体嵌套结构体
- 在结构体中可以定义另一个结构体作为成员,用来解决实际问题
- 每个老师辅导一个学员,一个老师的结构体中,记录一个学生的结构体
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct student//学生结构体
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
struct teacher//教师结构体
{
int id;//职工编号
string name;
int age;
struct student stu;//老师辅导的学生
};
int main()
{
teacher one;
one.id = 1;
one.age = 25;
one.name = "刘大锤";
one.stu.age = 18;
one.stu.name = "张三";
one.stu.score = 100;
cout << "老师的编号:" << one.id << endl
<< "老师的名字:" << one.name << endl
<< "老师的年龄:" << one.age << endl
<< "老师辅导的学生:" << one.stu.name << endl
<< "学生年龄:" << one.stu.age << endl
<< "学生的成绩" << one.stu.score << endl << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结构体做函数参数
- 将结构体作为参数向函数中传递
- 传递方式有两种
- 1、值传递
- 2、地址传递
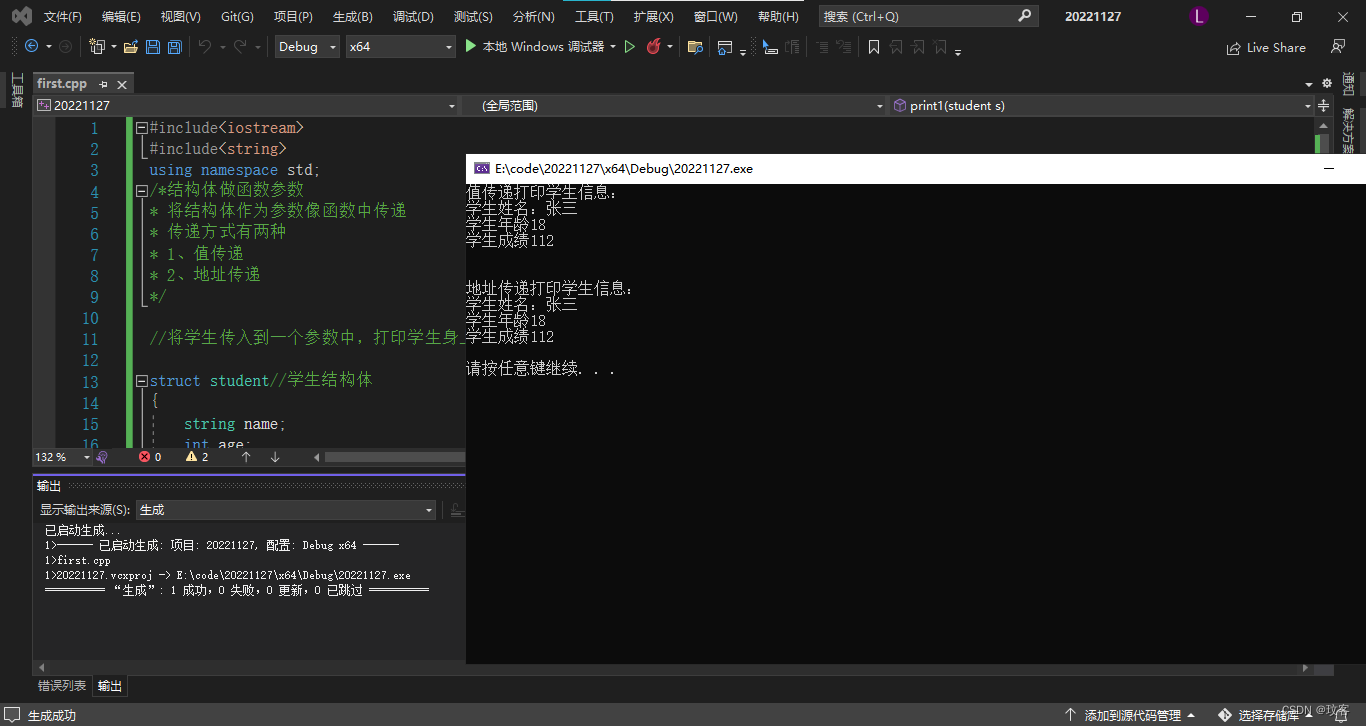
将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生的所有信息
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
/*结构体做函数参数
* 将结构体作为参数像函数中传递
* 传递方式有两种
* 1、值传递
* 2、地址传递
*/
//将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生的所有信息
struct student//学生结构体
{
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
//值传递
void print1(struct student s)
{
cout << "值传递打印学生信息:" << endl;
cout << "学生姓名:" << s.name << endl << "学生年龄" << s.age << endl << "学生成绩" << s.score << endl << endl;
}
//地址传递
void print2(struct student * p)
{
cout << endl << "地址传递打印学生信息:"<<endl;
cout << "学生姓名:" << p->name << endl << "学生年龄" << p->age << endl << "学生成绩" << p->score << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
struct student s;
s.name = "张三";
s.age = 18;
s.score = 112;
print1(s);
print2(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}