PPQ量化工具库KLD算法解析
- 前言
- PPQ算法实现
- NVIDIA的PPT中KLD算法流程
- KLD算法PPQ实现版本
- PPQ与NVIDIA的区别:
前言
这是对PPQ库中KLD算法实现代码解析,关于PPQ库安装与使用详情见专栏上一篇博客。
PPQ算法实现
nvidia发布的PPT:8-bit Inference with TensorRT,百度可下载。下两图是KLD算法的实现伪代码:


下图是PPQ算法的实现过程:见https://github.com/openppl-public/ppq/blob/master/ppq/quantization/observer/range.py
def hist_to_scale_offset(
self, histogram: torch.Tensor, hist_bins: int, hist_scale: float,
config: TensorQuantizationConfig, computing_device: str = OBSERVER_KL_COMPUTING_DEVICE,
scale_threshold: float=OBSERVER_MIN_SCALE
) -> Tuple[float, int]:
"""
PPQ core quant parameter computing method - Histogram to scale & offset
With a pre-defined histogram,
this function will automatically search best clip value
to minimize KL divergence between quantized result and fp32 input.
only work for per-tensor symmetrical quantization policy for now.
see also https://on-demand.gputechconf.com/gtc/2017/presentation/s7310-8-bit-inference-with-tensorrt.pdf
Args:
histogram (torch.Tensor): histogram records activation's statistics.
hist_bins (int): how many bins are included in histogram(also known as histogram length)
hist_scale (float): histogram step size. it can be solved by histogram.max_val / histogram.bins
config (TensorQuantizationConfig): quantization config.
computing_device (str, optional): computing device. Defaults to 'cpu'.
Raises:
ValueError: given quantization config is invalid.
Returns:
Tuple[float, int]: scale(fp32) and offset(int).
"""
if config.policy.has_property(QuantizationProperty.ASYMMETRICAL):
raise PermissionError('KL observer is not designed for ASYMMETRICAL quantization')
if OBSERVER_MIN_SCALE_MANUL_OVERRIDE in config.detail:
scale_threshold = config.detail[OBSERVER_MIN_SCALE_MANUL_OVERRIDE]
# move histogram to cpu, speedup computation.
histogram = histogram.to(computing_device).float()
# compute symmtrical kl-divergence.
# Here is a simple example: reference distribution P consisting of 8 bins, we want to quantize into 2 bins:
# P = [ 1, 0, 2, 3, 5, 3, 1, 7]
# we merge into 2 bins (8 / 2 = 4 consecutive bins are merged into one bin)
# [1 + 0 + 2 + 3 , 5 + 3 + 1 + 7] = [6, 16]
# then proportionally expand back to 8 bins, we preserve empty bins from the original distribution P:
# Q = [ 6/3, 0, 6/3, 6/3, 16/4, 16/4, 16/4, 16/4] = [ 2, 0, 2, 2, 4, 4, 4, 4]
# now we should normalize both distributions, after that we can compute KL_divergence
# P /= sum(P) Q /= sum(Q)
# result = KL_divergence(P, Q)
# see also
# https://github.com/NVIDIA/TensorRT/blob/3835424af081db4dc8cfa3ff3c9f4a8b89844421/tools/pytorch-quantization/pytorch_quantization/calib/histogram.py#L147
losses, quant_bins = [], 2 ** (config.num_of_bits - 1)
# following code is curcial, do not move
histogram[: int(hist_bins * .002)] = 0
histogram[int(hist_bins * .002)] = 1
hist_sum = torch.sum(histogram)
for bin_range in range(quant_bins, hist_bins + quant_bins - 1, quant_bins):
p_hist = torch.zeros(size=(bin_range, ), dtype=torch.float, device=computing_device)
p_hist[: bin_range].copy_(histogram[: bin_range])
p_hist[bin_range - 1] += torch.sum(histogram[bin_range: ])
p_hist = p_hist / hist_sum
expand_ratio = int(bin_range / quant_bins)
q_hist = histogram[: bin_range].clone()
q_hist = q_hist.reshape((quant_bins, expand_ratio))
positive_map = q_hist > 0
positive_cnt = positive_map.sum(axis=1, keepdim=True)
positive_cnt[positive_cnt == 0] = 1
q_hist = torch.div(q_hist.sum(axis=1, keepdim=True), positive_cnt)
q_hist = q_hist.repeat([1, expand_ratio])
q_hist = q_hist * positive_map
q_hist = q_hist / torch.sum(q_hist)
q_hist = q_hist.flatten()
losses.append({
'kl': torch_KL_divergence(p_hist, q_hist),
'bin_range': bin_range
})
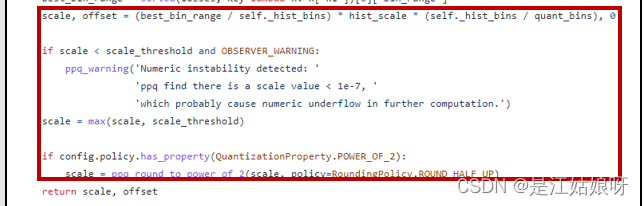
best_bin_range = sorted(losses, key=lambda x: x['kl'])[0]['bin_range']
scale, offset = (best_bin_range / self._hist_bins) * hist_scale * (self._hist_bins / quant_bins), 0
if scale < scale_threshold and OBSERVER_WARNING:
ppq_warning('Numeric instability detected: '
'ppq find there is a scale value < 1e-7, '
'which probably cause numeric underflow in further computation.')
scale = max(scale, scale_threshold)
if config.policy.has_property(QuantizationProperty.POWER_OF_2):
scale = ppq_round_to_power_of_2(scale, policy=RoundingPolicy.ROUND_HALF_UP)
return scale, offset
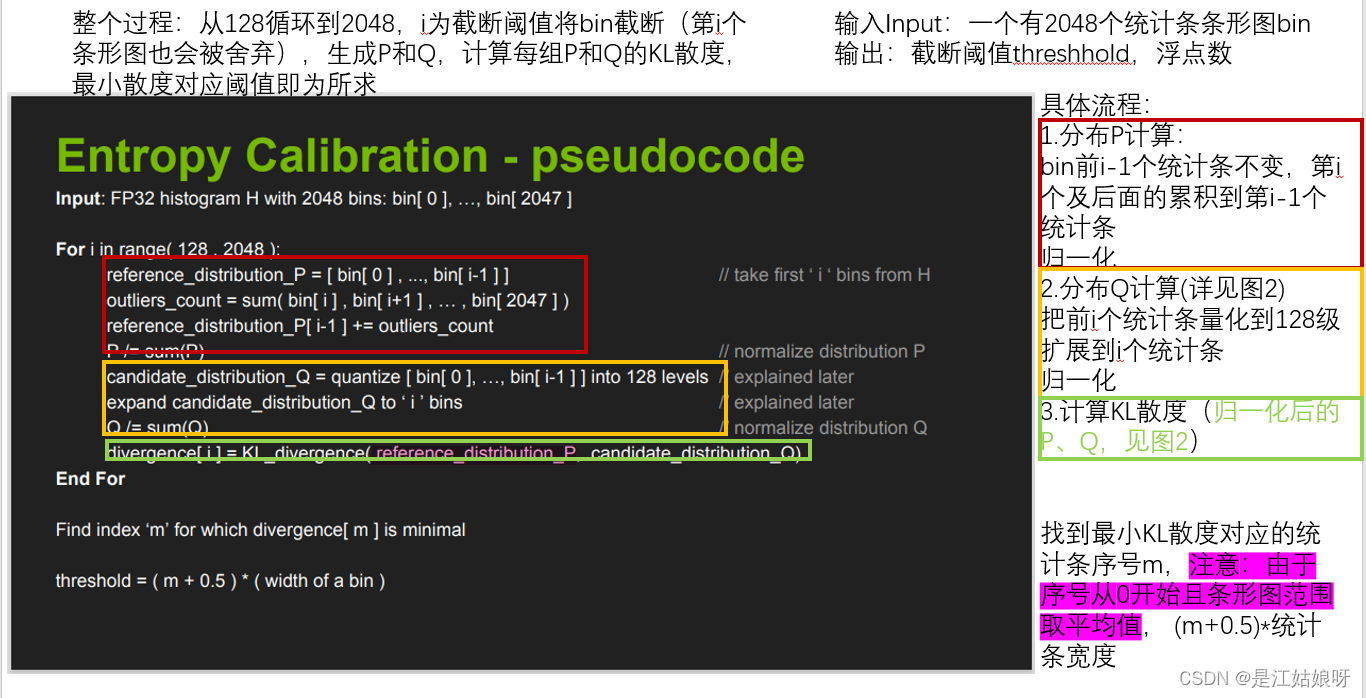
NVIDIA的PPT中KLD算法流程
整个过程:从128循环到2048,i为截断阈值将bin截断(第i个条形图也会被舍弃),生成P和Q,计算每组P和Q的KL散度,最小散度对应阈值即为所求
输入Input:一个有2048个统计条条形图bin
输出:截断阈值threshhold,浮点数

KLD算法PPQ实现版本
算法流程:
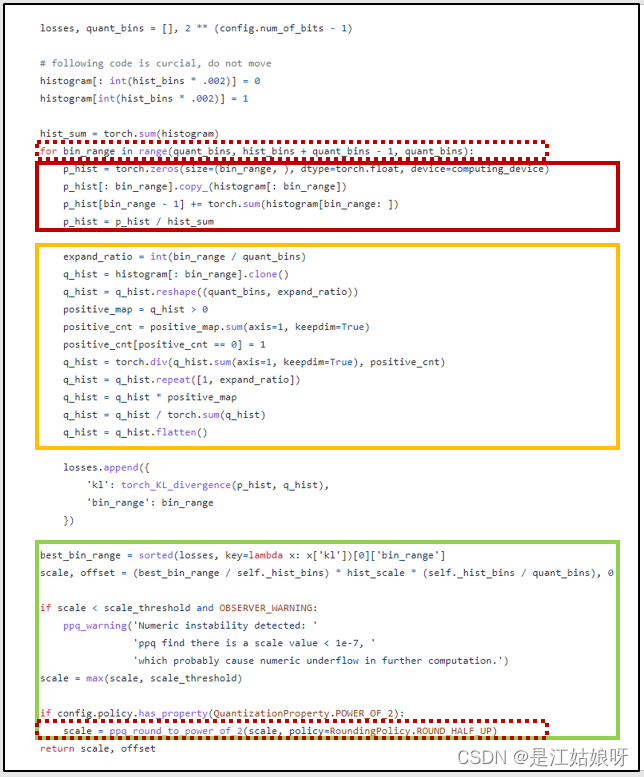
具体代码分析:

PPQ与NVIDIA的区别:
1.原始histogram条形图舍弃
NVIDIA是:不进行预处理
PPQ:前其千分之二置为零,第千分之二个条形置为1
2.for循环找截断阈值
NVIDIA是:for i in range(102,2048)
PPQ库是:for bin_range in range(quant_bins, hist_bins + quant_bins - 1, quant_bins):
3.阈值m转为实际浮点数
NVIDIA是:threshold = ( m + 0.5 ) * ( width of a bin )
PPQ库是: