目录
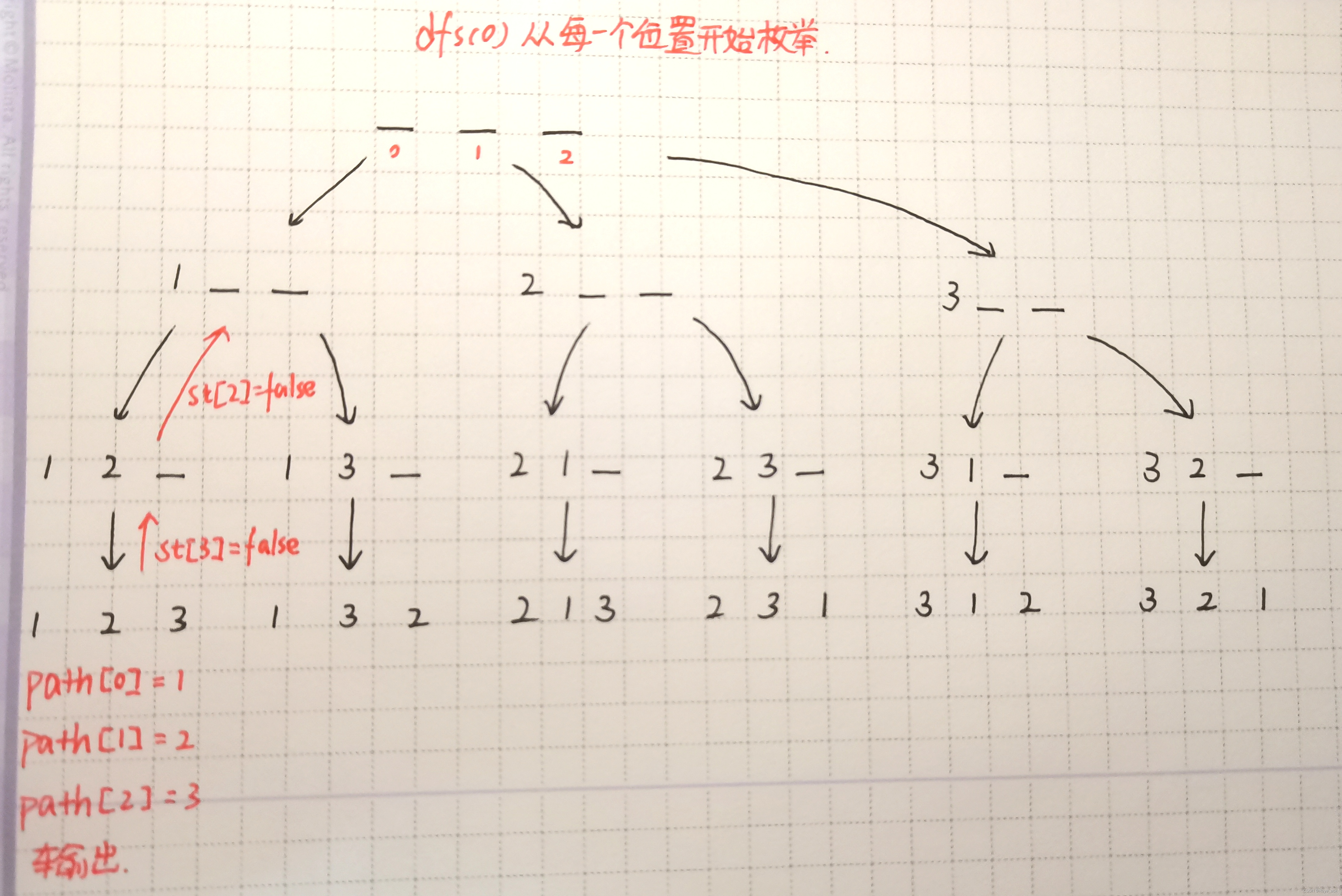
842. 排列数字 - DFS按位置枚举
843. n-皇后问题 - DFS按行枚举
165. 小猫爬山 - DFS枚举小猫
1209. 带分数 - DFS
3502. 不同路径数 -
842. 排列数字 - DFS按位置枚举
活动 - AcWing
题目:
给你一个整数n
要求将1~n的所有排列情况列出
比如:n=3
则123 132 213 231……
思路:
dfs从0位置开始枚举 层层深入 每枚举完一种情况就回溯
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=100010;
static int[] st=new int[N];
static int[] path=new int[N];
static int n;
static void dfs(int u) //枚举每一个位置
{
if(u==n) //位置从0 1 2……开始 如果u==n说明位置已经填满 需要输出
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) wt.print(path[i]+" ");
wt.println();
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(st[i]==0)
{
path[u]=i;
st[i]=1;
dfs(u+1);
st[i]=0; //还原现场
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
dfs(0);
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
843. n-皇后问题 - DFS按行枚举
活动 - AcWing
题目:
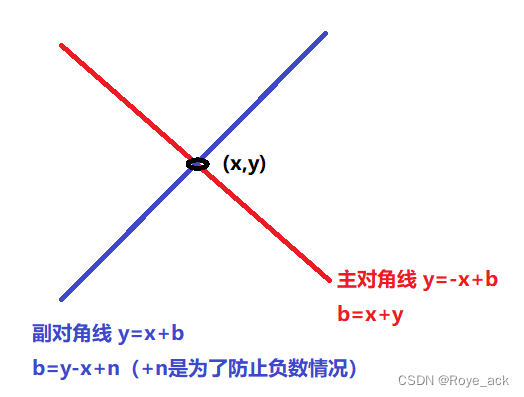
n−皇后问题是指将 n 个皇后放在 n×n 的国际象棋棋盘上,使得皇后不能相互攻击到,即任意两个皇后都不能处于同一行、同一列或同一斜线上
现在给定整数 n,请你输出所有的满足条件的棋子摆法
思路:
这题思路和排列的dfs思路如出一辙
从第0行开始按行枚举,这样保证每一行只有一个棋子
- 在某行情况下枚举每一列,如果该列、主对角线、副对角线上均没有棋子
- 则把棋子放在该位置,递归这种情况下 下一行的棋子摆放位置
- 当枚举行数==n时,因为是从第0行开始枚举,说明一个棋盘的棋子已经摆好
- 则输出这种情况,然后回溯还原现场,继续输出下一种情况
- 不断回溯递归,直到输出所有情况
对于主对角线和副对角线的标记
我们可以通过dg[x+y] udg[y-x+n]映射得到
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=20;
static int[] col=new int[N],dg=new int[N],udg=new int[N];
static char[][] g=new char[N][N];
static int n;
static void dfs(int u) //枚举每一个位置
{
if(u==n) //从0 1 2……行开始枚举 如果u==n说明棋盘已经摆满 需要输出
{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
wt.print(g[i][j]);
wt.println();
}
wt.println();
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(col[i]==0&&dg[i+u]==0&&udg[i-u+n]==0)
{
g[u][i]='Q';
col[i]=dg[i+u]=udg[i-u+n]=1;
dfs(u+1);
col[i]=dg[i+u]=udg[i-u+n]=0;
g[u][i]='.';
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) g[i][j]='.';
dfs(0);
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}165. 小猫爬山 - DFS枚举小猫
活动 - AcWing
题目:
一共n只小猫,每只小猫重wi
一辆缆车最大承重为m
问最少雇多少辆车能把所有猫都装上?
思路:
总思路就是枚举所有情况的车数,取最小值
从第0只小猫开始枚举,dfs(小猫数,当前车数)
每次塞猫分两种情况:
- 在已开好的车内,如果塞的下,塞进去,并递归这种情况下其他情况
- 开好的所有车都装不下,则开新车,车数+1,并递归这种情况下的其他情况
因为要枚举所有情况,所以每次递归完后,回溯时要还原现场
当所有小猫枚举完后,更新最小的车数
优化点1:想要车越少,则先让重的猫上车,这样不会遇到塞不下多开新车,能优化搜索速度
优化点2:如果搜索到的答案 ≥ 目前的res 则不用继续搜索,因为再搜索也不是最优解
/*
*道阻且长,行则将至*
author:Roye_ack
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class Main
{
static PrintWriter wt=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
static int N=20;
static int[] a=new int[N],car=new int[N];
static int n,w;
static int res=N;
public static void dfs(int cat,int bus)
{
if(bus>=res) return;
if(cat==n)
{
res=Math.min(res,bus);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<bus;i++) //如果当前车可以塞的下
if(car[i]+a[cat]<=w)
{
car[i]+=a[cat];
dfs(cat+1,bus);
car[i]-=a[cat];
}
//如果所有开好的车都塞不下 则开新车
car[bus]=a[cat];
dfs(cat+1,bus+1);
car[bus]=0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
n=rd.nextInt();
w=rd.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) a[i]=rd.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(a,0,n);
for(int i=0,j=n-1;i<j;i++,j--)
{
int t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
dfs(0,0); //dfs(小猫数,车数) 小猫和车都从0开始枚举
wt.print(res);
wt.flush();
}
static class rd
{
static BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringTokenizer tk=new StringTokenizer("");
static String nextLine() throws IOException
{
return bf.readLine();
}
static String next() throws IOException
{
while(!tk.hasMoreTokens()) tk=new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
return tk.nextToken();
}
static int nextInt() throws IOException
{
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
static double nextDouble() throws IOException
{
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
static long nextLong() throws IOException
{
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
static BigInteger nextBig() throws IOException
{
BigInteger d=new BigInteger(rd.nextLine());
return d;
}
}
}
class PII
{
int x,y;
PII(int x,int y)
{
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
1209. 带分数 - DFS
活动 - AcWing
题目:
思路:
3502. 不同路径数 -
3502. 不同路径数 - AcWing题库
题目:
思路: