977 有序数组的平方
题目链接:203 移除链表元素
介绍
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个整数 val ,请你删除链表中所有满足 Node.val == val 的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。


思路一

如果要被删除的元素是非头节点,只需要找到前一个节点,然后让前一个节点的下一个指向当前元素的下一个节点。
如果要被删除的是头节点,将头节点head后移(head=head->next)

//先判断头节点不为空并且头节点指向的值是要删除的target
while(head!=NULL&&head->val=target){ //while是一个持续移动的过程
head=head->next;//删除头节点
//若是c++ 需要对删除的节点进行内存释放
}
cur = head; //每次检查cur->next是不是等于target
while(cur!=NULL&&cur-next!=NULL){
if(cur->next->value == target){
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
思路二—虚拟头节点

规则统一:只需要找到前一个节点,然后让前一个节点的下一个指向当前元素的下一个节点。
注意—遍历列表的时候,头节点的指针是不能改变的,要定义一个临时的指针对链表进行删除操作

//定义一个虚拟头节点
dummyhead = new (节点);
dummyhead->next = head;
cur = dummyhead;//若删除的是真实的头节点,必须要知道真实头节点的上一个元素,也就是虚拟头节点
while(cur->next!=NULL){
if(cur->next->val==target){
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}else{
cur = cur->next
}
}
return dummyhead->next;代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
while(head!=NULL&&head->val==val){
ListNode* tmp = head; //记录要删除的节点
head = head->next;
delete tmp;//释放内存
}
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur!=NULL&&cur->next!=NULL){
if(cur->next->val == val){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next; //记录要删除的节点
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;//释放内存
}else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//设立一个虚拟头节点
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyHead;
while(cur->next!=NULL){
if(cur->next->val == val){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
}else{
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};707 设计链表
题目链接:707设计链表
介绍
设计链表的实现。您可以选择使用单链表或双链表。单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next。val 是当前节点的值,next 是指向下一个节点的指针/引用。如果要使用双向链表,则还需要一个属性 prev 以指示链表中的上一个节点。假设链表中的所有节点都是 0-index 的。
在链表类中实现这些功能: n从0开始
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。获取第n个节点
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。头部插入节点
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。尾部插入节点
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。第n个节点前插入节点
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。删除第n个节点

思路
这里统一使用虚拟头节点的方式,从而更方便对链表进行增删改查操作。

获取第n个节点(n从0开始)
n<0不合法 n>size-1不合法
定义一个遍历指针cur指向头节点(操作完链表后要返回头节点head)
cur = dummyhead->next;
while(n){
cur = cur->next;
n--;
}
return cur->val头部插入节点

newNode = new node()
//dummyhead是虚拟头节点
newNode->next = dummyhead->next
dummyhead->next = newNode
size++尾部插入节点
newNode = new node() //定义newNode时,默认newNode->next=NULL
//找尾部的节点--当前遍历节点cur要指向尾部节点
cur = dummyhead
while(cur->next!=NULL){ //直到找到cur->next=NULL位置
cur = cur->next
}
//newNode->next = cur->next
cur->next = newNode
size++第n个结点前插入结点

//要找到第n个结点前一个的位置---cur
newNode = new node()
cur = dummyhead
while(n){
cur = cur->next
n--
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;删除第n个结点
//首先判断n的合法性
//然后还是要找到第n个节点前一个的位置
//第n个节点一定是curr->next
cur = dummyhead
while(n){
cur = cur->next
n--
}
curr->next = curr->next->next代码
class MyLinkedList {
public:
// 定义链表节点结构体
struct LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode* next;
LinkedNode(int val):val(val), next(nullptr){}
};
// 初始化链表
MyLinkedList() {
_dummyHead = new LinkedNode(0); // 这里定义的头结点 是一个虚拟头结点,而不是真正的链表头结点
_size = 0;
}
int get(int index) {
if(index >(_size-1)||index<0){
return -1;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while(index){
cur = cur->next;
index--;
}
return cur->val;
}
void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void addAtTail(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(cur->next!=nullptr){
cur =cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index >_size) return;
if(index<0) index=0;
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index){
cur = cur->next;
index--;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if(index >=_size || index < 0){
return;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index){
cur = cur->next;
index--;
}
LinkedNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
_size--;
}
private:
int _size;
LinkedNode* _dummyHead;
};
/**
* Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyLinkedList* obj = new MyLinkedList();
* int param_1 = obj->get(index);
* obj->addAtHead(val);
* obj->addAtTail(val);
* obj->addAtIndex(index,val);
* obj->deleteAtIndex(index);
*/206 反转链表
题目链接:206反转链表
介绍
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。


思路

思路一:双指针写法
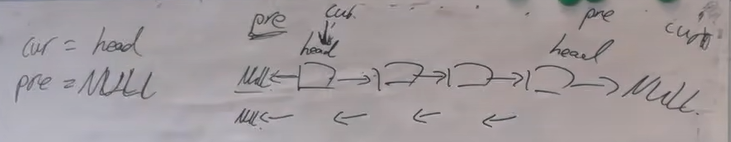
首先进行初始化:current=head pre=NULL 能够让翻转后的head->null
遍历链表: 遍历结束条件-->curr=NULL
while(curr!=NULL){
//使用一个临时指针在翻转赋值之前记录curr的下一个结点
temp = curr->next;
//翻转赋值
curr->next=pre;
//curr和pre整体后移
pre = curr;
curr = temp;
}
//跳出循环时,curr指向NULL,pre指向了新链表的头节点
return pre;思路二:递归写法
//206
reverseList(head){
return reverse(head,NULL)
}
reverse(curr,pre){
if(curr==NULL)
return pre;
temp = curr->next;
curr->next = pre;
revrse(temp,curr)
}代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* curr = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* tmp = nullptr;
while(curr!=nullptr){
tmp = curr->next;
curr->next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* curr,ListNode* pre){
if(curr==NULL) return pre;
ListNode* temp = curr->next;
curr->next = pre;
//pre = curr
//curr = temp
return reverse(temp,curr);
}
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
return reverse(head,NULL);
}
};