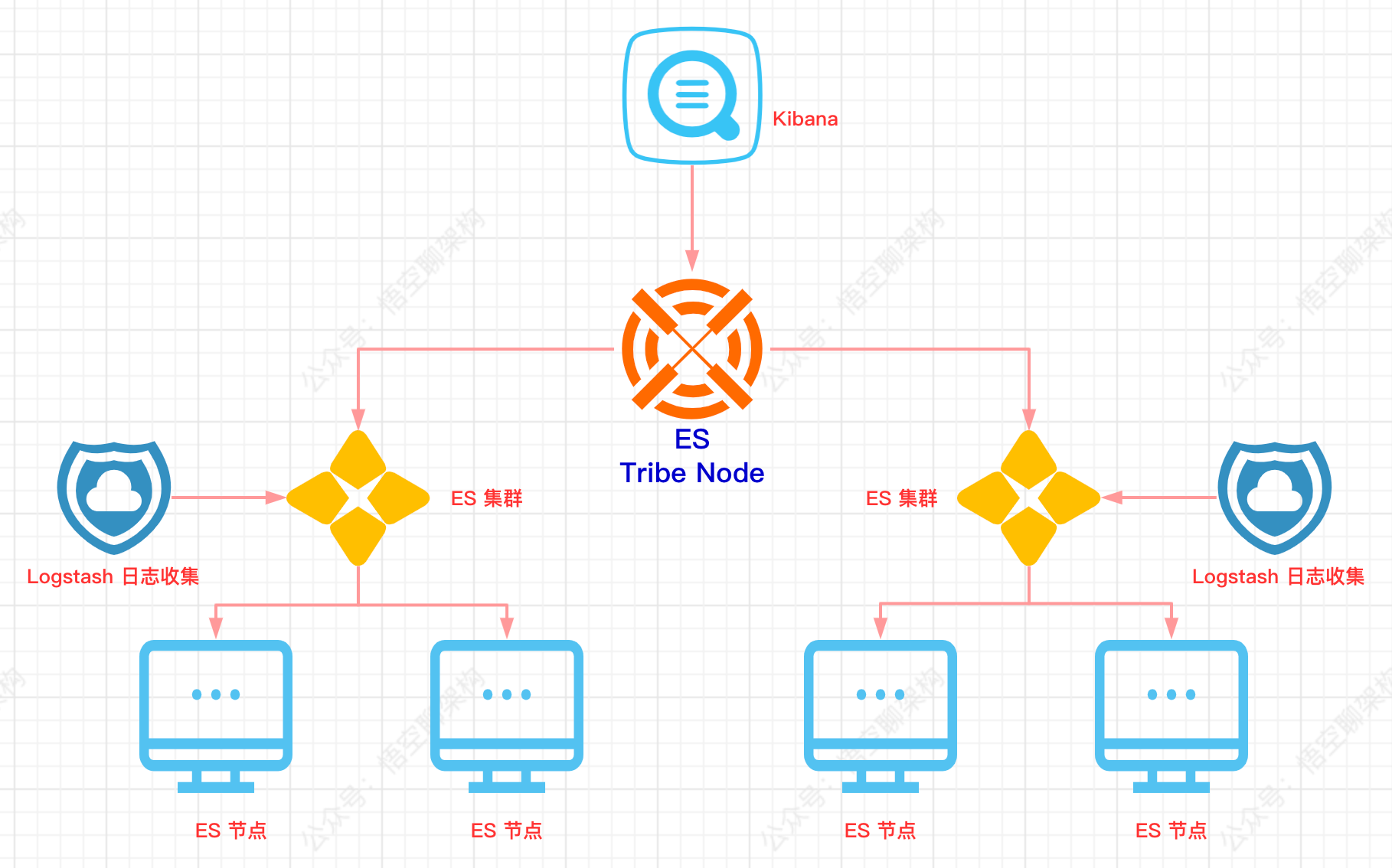
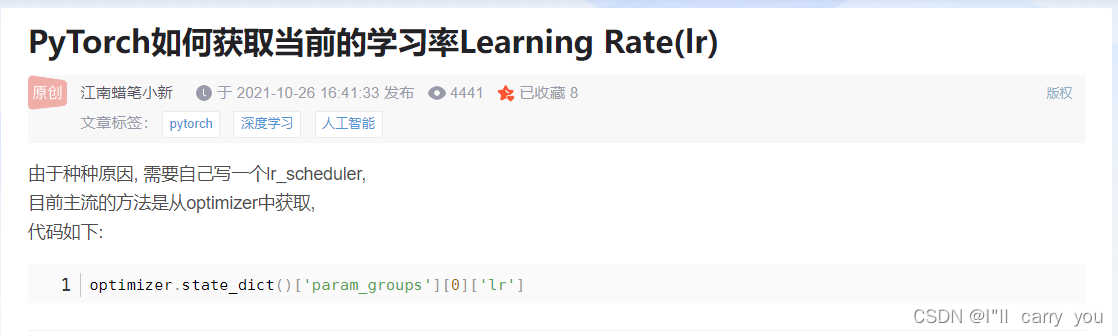
目录
一.前言
二.顺序表
1.概念及结构
2.顺序表结构体的定义
3.初始化顺序表,销毁顺序表和打印
3.接口
a.尾插 SepListpushback 头插 SepListpushfront
b.尾删 SepListpopback 头删 SepListpopfront
c.查询 SepListsearch
d.修改 SepListmodify
三.源码
SepList.h
SepList.c
test.c
四.顺序表的问题及思考
一.前言
其实顺序表的增删查改和前面的通讯录差不多,可以说通讯录的底层原理就是顺序表。如果你会写通讯录,那么顺序表也不是问题。所以这篇文章不会讲得太详细,如果你有不懂的地方,请看前面通讯录的实现过程,那里讲的非常详细。通讯录
二.顺序表
1.概念及结构
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储;
在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表分为静态顺序表和动态顺序表,由于静态顺序表的实用性不高,所以博主在此就不讲述了,主要讲解动态顺序表。
2.顺序表结构体的定义
#define INIT_CAPACITY 5 //顺序表的默认容量
typedef int SLdatatype; //使用 typedef 对类型重定义,方便后续修改
typedef struct SepList
{
SLdatatype* arr; //后续对 arr 进行动态内存开辟
int sz; //记录当前数据的个数
int capacity; //顺序表的容量
}SepList;3.初始化顺序表,销毁顺序表和打印
初始化
void download(SepList* ps) //从文件中读取数据
{
FILE* pf = fopen("SepList.txt", "r");
assert(pf);
while (fscanf(pf, "%d", &ps->arr[ps->sz]) != EOF)
{
ps->sz++;
expcapacity(ps);
}
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}
void SepListinit(SepList* ps)
{
ps->arr = (SLdatatype*)calloc(INIT_CAPACITY, sizeof(SLdatatype)); //动态内存开辟默认容量
assert(ps->arr); //判断是否开辟成功,若失败会直接报错,终止程序的运行
ps->sz = 0; //初始化当前数据量为1
ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY; //初始成默认容量
download(ps); //初始化时从文件中读取数据
}销毁
void SepListdestroy(SepList* ps) //销毁的同时将数据保存到文件中
{
int i = 0;
FILE* pf = fopen("SepList.txt", "w");
assert(pf);
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
fprintf(pf, "%d", ps->arr[i]);
}
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->sz = 0;
ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY;
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}打印
void SepListprint(SepList* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}3.接口
a.尾插 SepListpushback 头插 SepListpushfront
需要注意的是在插入数据前,需要判断顺序表是否已经满了,所以就需要写一个扩容函数,这和通讯录那里得逻辑是一致的。
扩容 expcapacity
void expcapacity(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == ps->capacity)
{
SLdatatype* tmp = (SLdatatype*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLdatatype) * 2 * ps->capacity); //使用realloc 函数扩容
assert(tmp);
ps->arr = tmp; //注意要把tmp赋给原来得指针,否则在一些情况下会出问题
ps->capacity = 2 * ps->capacity;
}
}尾插 SepListpushback
void SepListpushback(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x) //这个SLdatatype 是我们之前重定义得类型
{
expcapacity(ps); //判断顺序表是否已满
ps->arr[ps->sz] = x;
ps->sz++; //当前数据量 +1
}头插 SepListpushfront
头插就是把当前有的数据全部向后移1位,把第一个位置空出来,此时仍需判断顺序表是否已满。
void SepListpushfront(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
expcapacity(ps);
int end = ps->sz - 1; //注意这里要 -1
for (; end >= 0; end--)
{
ps->arr[end + 1] = ps->arr[end];
}
ps->arr[0] = x; 将数据赋给下标为0的位置,完成头插
ps->sz++;
}b.尾删 SepListpopback 头删 SepListpopfront
在删除前,我们需要判断顺序表中是否有数据,如果没有,那么则不需要删除。
尾删 SepListpopback
void SepListpopback(SepList* ps)
{
assert(ps->sz > 0); //判断顺序表中是否有数据,如果没有会直接报错,终止程序的运行
ps->sz--;
}头删 SepListpopfront
头删就是把所有数据向前移动1位
void SepListpopfront(SepList* ps)
{
assert(ps->sz > 0);
int begain = 0;
for (; begain < ps->sz-1; begain++)
{
ps->arr[begain] = ps->arr[begain + 1];
}
ps->sz--;
}c.查询 SepListsearch
查询前需要判断顺序表是否有数据。
void SepListsearch(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == 0)
{
printf("无数据可供查找\n");
return;
}
SLdatatype x = 0;
int count = 0;
SLdatatype* tmp = (SLdatatype*)calloc(ps->sz, sizeof(SLdatatype)); //要查询的数据可能有重复,所以定义一个数组来存储
assert(tmp);
printf("请输入要查询的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
int i = 0,flag = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
flag = 1;
tmp[count++] = i;
}
}
if (flag == 0)
printf("无此数据\n");
else
{
printf("查到了,下标是:> ");
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
printf("%d ", tmp[i]);
}
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
printf("\n");
}d.修改 SepListmodify
void SepListmodify(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == 0)
{
printf("无数据可供修改\n");
return;
}
SLdatatype x = 0;
again:
printf("请输入要修改的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
int i = 0, pos = 0;
int flag = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
flag = 1;
pos = i;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0)
{
printf("要修改的数据不存在,重新输入\n");
goto again;
}
else
{
printf("开始修改:>");
scanf("%d", &ps->arr[pos]);
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}三.源码
SepList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define INIT_CAPACITY 5
typedef int SLdatatype;
typedef struct SepList
{
SLdatatype* arr;
int sz;
int capacity;
}SepList;
//初始化
void SepListinit(SepList* ps);
//销毁
void SepListdestroy(SepList* ps);
//扩容
void expcapacity(SepList* ps);
//打印
void SepListprint(SepList* ps);
//尾插
void SepListpushback(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x);
//头插
void SepListpushfront(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x);
//尾删
void SepListpopback(SepList* ps);
//头删
void SepListpopfront(SepList* ps);
//查询
void SepListsearch(SepList* ps);
//修改
void SepListmodify(SepList* ps);SepList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SepList.h"
void download(SepList* ps)
{
FILE* pf = fopen("SepList.txt", "r");
assert(pf);
while (fscanf(pf, "%d", &ps->arr[ps->sz]) != EOF)
{
ps->sz++;
expcapacity(ps);
}
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}
void SepListinit(SepList* ps)
{
ps->arr = (SLdatatype*)calloc(INIT_CAPACITY, sizeof(SLdatatype));
assert(ps->arr);
ps->sz = 0;
ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY;
download(ps);
}
void SepListdestroy(SepList* ps)
{
int i = 0;
FILE* pf = fopen("SepList.txt", "w");
assert(pf);
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
fprintf(pf, "%d", ps->arr[i]);
}
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->sz = 0;
ps->capacity = INIT_CAPACITY;
fclose(pf);
pf = NULL;
}
void expcapacity(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == ps->capacity)
{
SLdatatype* tmp = (SLdatatype*)realloc(ps->arr, sizeof(SLdatatype) * 2 * ps->capacity);
assert(tmp);
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = 2 * ps->capacity;
}
}
void SepListprint(SepList* ps)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SepListpushback(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
expcapacity(ps);
ps->arr[ps->sz] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
void SepListpushfront(SepList* ps, SLdatatype x)
{
expcapacity(ps);
int end = ps->sz - 1;
for (; end >= 0; end--)
{
ps->arr[end + 1] = ps->arr[end];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->sz++;
}
void SepListpopback(SepList* ps)
{
assert(ps->sz > 0);
ps->sz--;
}
void SepListpopfront(SepList* ps)
{
assert(ps->sz > 0);
int begain = 0;
for (; begain < ps->sz-1; begain++)
{
ps->arr[begain] = ps->arr[begain + 1];
}
ps->sz--;
}
//#define
void SepListsearch(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == 0)
{
printf("无数据可供删除\n");
return;
}
SLdatatype x = 0;
int count = 0;
SLdatatype* tmp = (SLdatatype*)calloc(ps->sz, sizeof(SLdatatype));
assert(tmp);
printf("请输入要查询的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
int i = 0,flag = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
flag = 1;
tmp[count++] = i;
}
}
if (flag == 0)
{
printf("无此数据\n");
}
else
{
printf("查到了,下标是:> ");
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
printf("%d ", tmp[i]);
}
}
free(tmp);
tmp = NULL;
printf("\n");
}
void SepListmodify(SepList* ps)
{
if (ps->sz == 0)
{
printf("无数据可供修改\n");
return;
}
SLdatatype x = 0;
again:
printf("请输入要修改的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
int i = 0, pos = 0;
int flag = 0;
for (i = 0; i < ps->sz; i++)
{
if (ps->arr[i] == x)
{
flag = 1;
pos = i;
break;
}
}
if (flag == 0)
{
printf("要修改的数据不存在,重新输入\n");
goto again;
}
else
{
printf("开始修改:>");
scanf("%d", &ps->arr[pos]);
printf("修改成功\n");
}
}test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "SepList.h"
void menu()
{
printf("|----------------------顺序表----------------------|\n");
printf("||*********************************************** ||\n");
printf("||******* 1.尾插 2.头插 *******||\n");
printf("||******* 3.尾删 4.头删 *******||\n");
printf("||******* 5.查询 6.修改 *******||\n");
printf("||******* 7.打印 0.退出 *******||\n");
printf("||************************************************||\n");
printf("|--------------------------------------------------|\n");
}
int main()
{
SepList s;
SepListinit(&s);
int input = 0;
int x = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf("请输入要插入的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
SepListpushback(&s,x);
break;
case 2:
printf("请输入要插入的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &x);
SepListpushfront(&s, x);
break;
case 3:
SepListpopback(&s);
break;
case 4:
SepListpopfront(&s);
break;
case 5:
SepListsearch(&s);
break;
case 6:
SepListmodify(&s);
break;
case 7:
SepListprint(&s);
break;
case 0:
SepListdestroy(&s);
printf("退出顺序表\n期待您的下次使用\n");
break;
default :
printf("选择错误,重新选择\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}四.顺序表的问题及思考
问题:
1. 中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N);
2. 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间,会有不小的消耗;
3. 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
思考:如何解决以上问题呢?博主将在下一篇关于链表的文章中解决。
🐲👻关于顺序表的讲解就到这里了,若有错误或是建议欢迎小伙伴们指出。🐯🤖
🥰🤩希望小伙伴们可以多多支持博主哦。😍😃
😁😄谢谢你的阅读。😼😸