目录
概述
List和Queue
Map和Set
HashTable和HashMap的区别
Queue和Deque
BlockingQueue
并发集合
概述
写程序免不了处理一些批量数据,不同数据结构和算法,会带来不同的性能效果。大学的计算机课程中就有一门叫《数据结构》的课程,这门课程就是研究处理批量数据的结构和算法。Java中的集合类型就是数据结构和算法的具体实现,我们直接拿来用就行了。不过,在用之前需要了解不同集合类型的具体数据结构定义和操作,了解其算法特点和性能,这样在实际开发中才能得心应手。我们先看一下,Java中的集合类型有哪些。官方教程给了一张图:
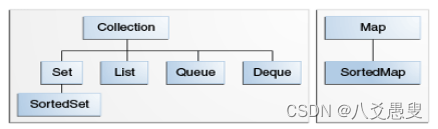
图中Queue和Deque可以算一种,SortedSet是在Set的基础增加了排序存储和算法也是一回事,Set在具体实现类中用的散列表存储的,和Map也算是一回事。所以总结下来,实际就三种集合:List、Queue、Map。
有了初步映像后,接下来我们再一一比较它们的具体实现类型间的区别。
List和Queue
List有两个具体实现,一个是ArrayList,另一个是LinkedList,按照字面差不多就知道这两个类型分别对应数据结构中的线性表和链表。线性表是以数据方式存放数据,链表是以链接方式存放数据,其区别是线性的数据是连续的,而链表是分散的。因为这种差别,在频繁的增改操作上,链表的性能要好于线性表,而且性能表容易造成空间浪费。
我们看一下ArrayList的数据增加方式:
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData,
newCapacity(minCapacity));
}从代码中可以看出,当元素的个数超过存放数据的数组容量的时候,就会计算新的长度,重新生成创建一个数组,这样就增加了性能的开销。
再看ArrayList的移除操作,其实就是把后边的数据往前移,但这个Array的长度还在,造成空间浪费:
private void fastRemove(Object[] es, int i) {
modCount++;
final int newSize;
if ((newSize = size - 1) > i)
System.arraycopy(es, i + 1, es, i, newSize - i);
es[size = newSize] = null;
}LinkList增删元素只要修改相应的前后驱引用就行了,明显性能会好很多,移除的元素也会被JVM回收,不会造成空间浪费。
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}但对于只读数据来讲,线性表反倒优于链表。链表不能通过索引值直接定位到具体元素,而线性表可以。
ArrayList获取元素,通过索引值直接得到数组中的元素:
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}LinkedList获取元素,通过计算元素在链接中的位置,返回相应的元素:
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}Map和Set
Map有三个实现:HashMap, TreeMap 及 LinkedHashMap。对应的Set也有三个实现:HashSet, TreeSet, 和 LinkedHashSet。Map和Set区别是Set使用元素自身做索引键,Map需要显式给定键和值。
往HashSet中添加元素的实现代码:
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}往HashMap中添加元素:
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}知道了Map和Set是一回事之后,我们区分出Map三种具体实现的差别,就知道如何应用了。
HashMap是创建了一个二维表格,每一行数据由哈稀值做id,存放位置也是根据哈稀值得到,因为是一个顺序不可控的数据集合,另外相同的对象获取的哈稀值是一样的,所以集合中不会出现两个相同的键,因为HashSet可以用于数据的去重:
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}TreeMap用的树存储,通过比较前后键内容从上到下,从左到右顺序摆放:
public V put(K key, V value) {
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}LinkedHashMap在HashMap的基础上,为键值对增加了前后驱,这样就可以按插入顺序进行元素查找。
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}HashTable和HashMap的区别
这两个类大同小异,只不过HashTable不允许空值,如果放入空值则直接抛出异常,同时写入方法上加了同步锁,所以是线程安全的,但默认加锁可能带来一些不必要的性能开销:
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}Queue和Deque
Queue本是个List,定义这个类是为了实现FIFO的效果,于是在LinkedList上直接实现了标准队列效果。Deque继承了Queue,并增加了插队的功能,及两端都可以push和pop。
BlockingQueue<E>
JDK1.5之后,增加了java.util.concurrent 包 ,里边增加了一些同步集合。
顾名思义,这是个阻塞队列,即当队列为空的时候,从队列中取元素的线程就会挂在那里,直到队列不为空为止。
//此线程往队列里塞对象
class Producer implements Runnable {
private final BlockingQueue queue;
Producer(BlockingQueue q) { queue = q; }
public void run() {
try {
while (true) { queue.put(produce()); }
} catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ...}
}
Object produce() { ... }
}
//此线程从队列里取对象
class Consumer implements Runnable {
private final BlockingQueue queue;
Consumer(BlockingQueue q) { queue = q; }
public void run() {
try {
//如果队列中没有对象,则会挂起
while (true) { consume(queue.take()); }
} catch (InterruptedException ex) { ... handle ...}
}
void consume(Object x) { ... }
}
class Setup {
void main() {
BlockingQueue q = new SomeQueueImplementation();
Producer p = new Producer(q);
Consumer c1 = new Consumer(q);
Consumer c2 = new Consumer(q);
new Thread(p).start();
new Thread(c1).start();
new Thread(c2).start();
}
}并发集合
并发有关的集合有:ConcurrentHashMap, ConcurrentSkipListMap, ConcurrentSkipListSet, CopyOnWriteArrayList, 及CopyOnWriteArraySet
这个类跟相应的非并发类类似,只是在集合修改的时候,其它线程访问此类集合不会报集合被修改的异常(ConcurrentModificationException),这些类的目标并不是为了保证集合内容的同步,如果想保持集合数据访问一致,那就需要用 Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap())来生成同步集合。