1、 目标检测比赛中的tricks
DOTAv2遥感图像旋转目标检测竞赛经验分享(Swin Transformer + Anchor free/based方案)
目标检测比赛中的tricks(已更新更多代码解析)
水下目标检测算法赛解决方案分享 | 2020年全国水下机器人(湛江)大赛 -
0.78的baseline config和SWA单模型集成,需要的兄弟自取
天池酒瓶瑕疵检测数据集分析及完整baseline
BaseLine开源mmdetection(2020/012/05,submit.sh
数智重庆.全球产业赋能创新大赛(创新应用赛:工业智能化升级)总决赛极客奖比赛攻略_Spring队
数智重庆.全球产业赋能创新大赛总决赛极客奖队伍比赛攻略_球球君
数智重庆.全球产业赋能创新大赛总决赛极客奖队伍比赛攻略_吹风磁暴救救我
2、数据分析
1、统计类别
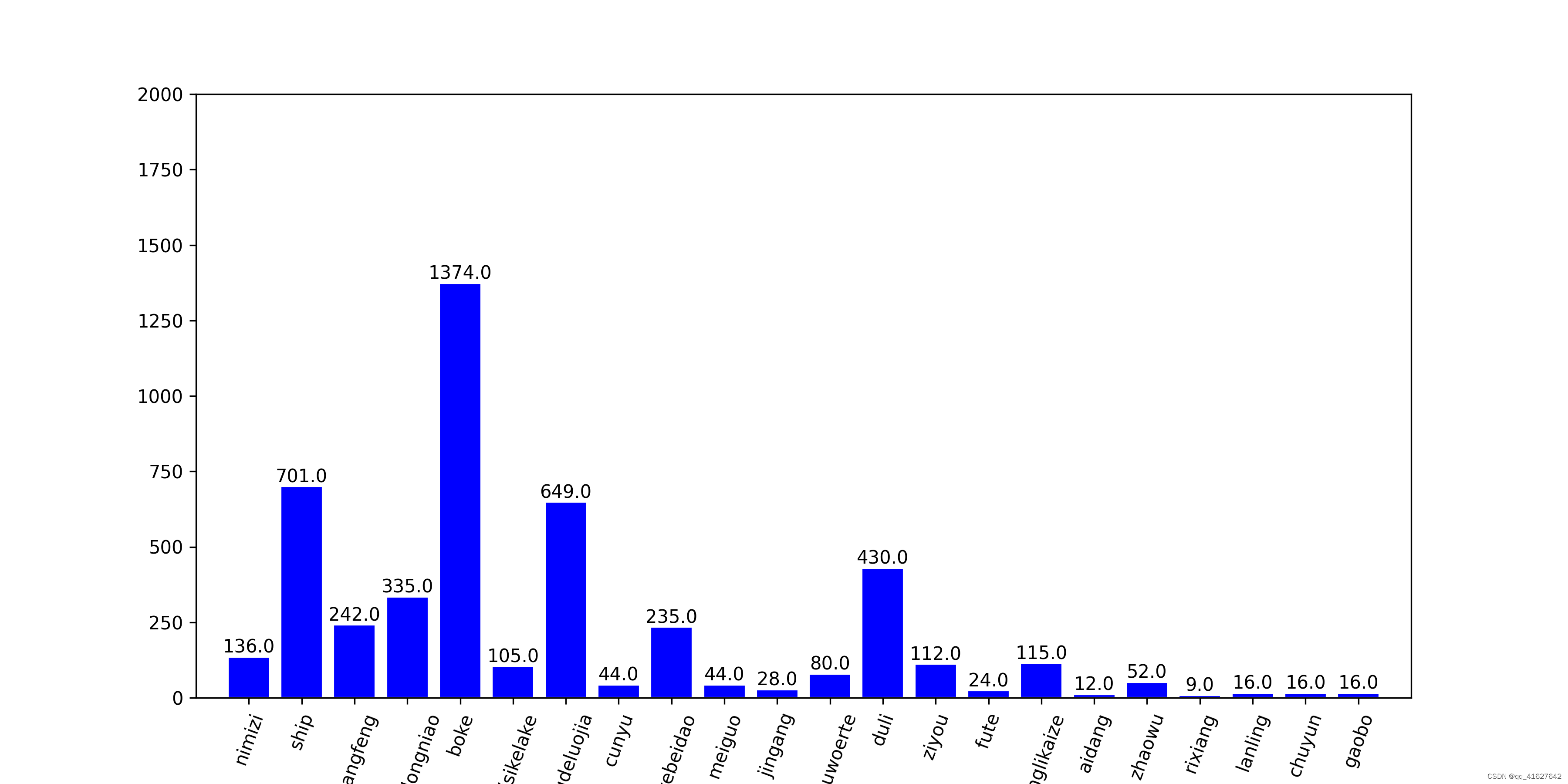

1、发现:
模型数据集的类别极不均衡,呈现长尾分布,需要应用focalloss,ohem等trick平衡正负以及困难样本
2、分类的损失函数focalloss平衡正负样本
cascade_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x.py(放到rpn_head中的 loss_cls)
# model settings
model = dict(
type='CascadeRCNN',
num_stages=3,
pretrained='torchvision://resnet50',
backbone=dict(
type='ResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
frozen_stages=1,
style='pytorch',
#dcn=dict( #在最后三个block加入可变形卷积
# modulated=False, deformable_groups=1, fallback_on_stride=False),
# stage_with_dcn=(False, True, True, True)
),
neck=dict(
type='FPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
num_outs=5),
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_scales=[8],
anchor_ratios=[0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0], # 添加了0.2,5,过两天发图
anchor_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64],
target_means=[.0, .0, .0, .0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
loss_cls=dict(
type='FocalLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0), # 修改了loss,为了调控难易样本与正负样本比例
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0 / 9.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', out_size=7, sample_num=2),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=[
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.05, 0.05, 0.1, 0.1],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.033, 0.033, 0.067, 0.067],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0))
])
3、OHEM 在线难例挖掘
OHEM(Online Hard negative Example Mining,在线难例挖掘)见于[5]。两阶段检测模型中,提出的RoI Proposal在输入R-CNN子网络前,我们有机会对正负样本(背景类和前景类)的比例进行调整。通常,背景类的RoI Proposal个数要远远多于前景类,Fast R-CNN的处理方式是随机对两种样本进行上采样和下采样,以使每一batch的正负样本比例保持在1:3,这一做法缓解了类别比例不均衡的问题,是两阶段方法相比单阶段方法具有优势的地方,也被后来的大多数工作沿用。
论文中把OHEM应用在Fast R-CNN,是因为Fast R-CNN相当于目标检测各大框架的母体,很多框架都是它的变形,所以作者在Fast R-CNN上应用很有说明性。
1、MMDetection中,OHEM(online hard example mining):(源码解析)
rcnn=[
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.4, # 更换
neg_iou_thr=0.4,
min_pos_iou=0.4,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.5,
neg_iou_thr=0.5,
min_pos_iou=0.5,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler', # 解决难易样本,也解决了正负样本比例问题。
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.6,
neg_iou_thr=0.6,
min_pos_iou=0.6,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False)
],
stage_loss_weights=[1, 0.5, 0.25])
2、配置文件添加OHEM
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.7,
neg_iou_thr=0.3,
min_pos_iou=0.3,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',#默认使用的是随机采样RandomSampler,这里可替换成OHEM采样,引入在线难样本学习
num=256,
pos_fraction=0.5,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=False),
allowed_border=0,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
rpn_proposal=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=2000,
nms_post=2000,
max_num=2000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.5,
neg_iou_thr=0.5,
min_pos_iou=0.5,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False))
test_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=1000,
nms_post=1000,
max_num=1000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
score_thr=0.05, nms=dict(type='nms', iou_thr=0.5), max_per_img=100)
# soft-nms is also supported for rcnn testing
# e.g., nms=dict(type='soft_nms', iou_thr=0.5, min_score=0.05) )
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.7,
neg_iou_thr=0.3,
min_pos_iou=0.3,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=256,
pos_fraction=0.5,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=False),
allowed_border=0,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
rpn_proposal=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=2000,
nms_post=2000,
max_num=2000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=[
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.4, # 更换
neg_iou_thr=0.4,
min_pos_iou=0.4,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.5,
neg_iou_thr=0.5,
min_pos_iou=0.5,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler', # 解决难易样本,也解决了正负样本比例问题。
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.6,
neg_iou_thr=0.6,
min_pos_iou=0.6,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='OHEMSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False)
],
stage_loss_weights=[1, 0.5, 0.25])
4、样本增强
统计切割后DOTAv2图像中的类别数量占比和分布情况。DOTAv2数据集中类别严重失衡,最大类别失衡比≈2000:1,网络的训练会被头部类别主导。且这种失衡比单纯采用过/欠采样和调节各类别的loss权重效果都不会太好,所以选择为部分类别单独训练一个检测器是性价比极高的做法。同时为了平衡各个类别的分布,一些多样本数据增强策略是可以尝试的。
1、图像增强
1、引入albumentations数据增强库进行增强
1、mmdet/datasets/pipelines/transforms.py的源码
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
import copy
import inspect
import math
import warnings
import cv2
import mmcv
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
from mmdet.core import BitmapMasks, PolygonMasks, find_inside_bboxes
from mmdet.core.evaluation.bbox_overlaps import bbox_overlaps
from mmdet.utils import log_img_scale
from ..builder import PIPELINES
try:
from imagecorruptions import corrupt
except ImportError:
corrupt = None
try:
import albumentations
from albumentations import Compose
except ImportError:
albumentations = None
Compose = None
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Resize:
"""Resize images & bbox & mask.
This transform resizes the input image to some scale. Bboxes and masks are
then resized with the same scale factor. If the input dict contains the key
"scale", then the scale in the input dict is used, otherwise the specified
scale in the init method is used. If the input dict contains the key
"scale_factor" (if MultiScaleFlipAug does not give img_scale but
scale_factor), the actual scale will be computed by image shape and
scale_factor.
`img_scale` can either be a tuple (single-scale) or a list of tuple
(multi-scale). There are 3 multiscale modes:
- ``ratio_range is not None``: randomly sample a ratio from the ratio \
range and multiply it with the image scale.
- ``ratio_range is None`` and ``multiscale_mode == "range"``: randomly \
sample a scale from the multiscale range.
- ``ratio_range is None`` and ``multiscale_mode == "value"``: randomly \
sample a scale from multiple scales.
Args:
img_scale (tuple or list[tuple]): Images scales for resizing.
multiscale_mode (str): Either "range" or "value".
ratio_range (tuple[float]): (min_ratio, max_ratio)
keep_ratio (bool): Whether to keep the aspect ratio when resizing the
image.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether to clip the objects outside
the border of the image. In some dataset like MOT17, the gt bboxes
are allowed to cross the border of images. Therefore, we don't
need to clip the gt bboxes in these cases. Defaults to True.
backend (str): Image resize backend, choices are 'cv2' and 'pillow'.
These two backends generates slightly different results. Defaults
to 'cv2'.
interpolation (str): Interpolation method, accepted values are
"nearest", "bilinear", "bicubic", "area", "lanczos" for 'cv2'
backend, "nearest", "bilinear" for 'pillow' backend.
override (bool, optional): Whether to override `scale` and
`scale_factor` so as to call resize twice. Default False. If True,
after the first resizing, the existed `scale` and `scale_factor`
will be ignored so the second resizing can be allowed.
This option is a work-around for multiple times of resize in DETR.
Defaults to False.
"""
def __init__(self,
img_scale=None,
multiscale_mode='range',
ratio_range=None,
keep_ratio=True,
bbox_clip_border=True,
backend='cv2',
interpolation='bilinear',
override=False):
if img_scale is None:
self.img_scale = None
else:
if isinstance(img_scale, list):
self.img_scale = img_scale
else:
self.img_scale = [img_scale]
assert mmcv.is_list_of(self.img_scale, tuple)
if ratio_range is not None:
# mode 1: given a scale and a range of image ratio
assert len(self.img_scale) == 1
else:
# mode 2: given multiple scales or a range of scales
assert multiscale_mode in ['value', 'range']
self.backend = backend
self.multiscale_mode = multiscale_mode
self.ratio_range = ratio_range
self.keep_ratio = keep_ratio
# TODO: refactor the override option in Resize
self.interpolation = interpolation
self.override = override
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
@staticmethod
def random_select(img_scales):
"""Randomly select an img_scale from given candidates.
Args:
img_scales (list[tuple]): Images scales for selection.
Returns:
(tuple, int): Returns a tuple ``(img_scale, scale_dix)``, \
where ``img_scale`` is the selected image scale and \
``scale_idx`` is the selected index in the given candidates.
"""
assert mmcv.is_list_of(img_scales, tuple)
scale_idx = np.random.randint(len(img_scales))
img_scale = img_scales[scale_idx]
return img_scale, scale_idx
@staticmethod
def random_sample(img_scales):
"""Randomly sample an img_scale when ``multiscale_mode=='range'``.
Args:
img_scales (list[tuple]): Images scale range for sampling.
There must be two tuples in img_scales, which specify the lower
and upper bound of image scales.
Returns:
(tuple, None): Returns a tuple ``(img_scale, None)``, where \
``img_scale`` is sampled scale and None is just a placeholder \
to be consistent with :func:`random_select`.
"""
assert mmcv.is_list_of(img_scales, tuple) and len(img_scales) == 2
img_scale_long = [max(s) for s in img_scales]
img_scale_short = [min(s) for s in img_scales]
long_edge = np.random.randint(
min(img_scale_long),
max(img_scale_long) + 1)
short_edge = np.random.randint(
min(img_scale_short),
max(img_scale_short) + 1)
img_scale = (long_edge, short_edge)
return img_scale, None
@staticmethod
def random_sample_ratio(img_scale, ratio_range):
"""Randomly sample an img_scale when ``ratio_range`` is specified.
A ratio will be randomly sampled from the range specified by
``ratio_range``. Then it would be multiplied with ``img_scale`` to
generate sampled scale.
Args:
img_scale (tuple): Images scale base to multiply with ratio.
ratio_range (tuple[float]): The minimum and maximum ratio to scale
the ``img_scale``.
Returns:
(tuple, None): Returns a tuple ``(scale, None)``, where \
``scale`` is sampled ratio multiplied with ``img_scale`` and \
None is just a placeholder to be consistent with \
:func:`random_select`.
"""
assert isinstance(img_scale, tuple) and len(img_scale) == 2
min_ratio, max_ratio = ratio_range
assert min_ratio <= max_ratio
ratio = np.random.random_sample() * (max_ratio - min_ratio) + min_ratio
scale = int(img_scale[0] * ratio), int(img_scale[1] * ratio)
return scale, None
def _random_scale(self, results):
"""Randomly sample an img_scale according to ``ratio_range`` and
``multiscale_mode``.
If ``ratio_range`` is specified, a ratio will be sampled and be
multiplied with ``img_scale``.
If multiple scales are specified by ``img_scale``, a scale will be
sampled according to ``multiscale_mode``.
Otherwise, single scale will be used.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from :obj:`dataset`.
Returns:
dict: Two new keys 'scale` and 'scale_idx` are added into \
``results``, which would be used by subsequent pipelines.
"""
if self.ratio_range is not None:
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample_ratio(
self.img_scale[0], self.ratio_range)
elif len(self.img_scale) == 1:
scale, scale_idx = self.img_scale[0], 0
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'range':
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample(self.img_scale)
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'value':
scale, scale_idx = self.random_select(self.img_scale)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
results['scale'] = scale
results['scale_idx'] = scale_idx
def _resize_img(self, results):
"""Resize images with ``results['scale']``."""
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
if self.keep_ratio:
img, scale_factor = mmcv.imrescale(
results[key],
results['scale'],
return_scale=True,
interpolation=self.interpolation,
backend=self.backend)
# the w_scale and h_scale has minor difference
# a real fix should be done in the mmcv.imrescale in the future
new_h, new_w = img.shape[:2]
h, w = results[key].shape[:2]
w_scale = new_w / w
h_scale = new_h / h
else:
img, w_scale, h_scale = mmcv.imresize(
results[key],
results['scale'],
return_scale=True,
interpolation=self.interpolation,
backend=self.backend)
results[key] = img
scale_factor = np.array([w_scale, h_scale, w_scale, h_scale],
dtype=np.float32)
results['img_shape'] = img.shape
# in case that there is no padding
results['pad_shape'] = img.shape
results['scale_factor'] = scale_factor
results['keep_ratio'] = self.keep_ratio
def _resize_bboxes(self, results):
"""Resize bounding boxes with ``results['scale_factor']``."""
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
bboxes = results[key] * results['scale_factor']
if self.bbox_clip_border:
img_shape = results['img_shape']
bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 0::2], 0, img_shape[1])
bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 1::2], 0, img_shape[0])
results[key] = bboxes
def _resize_masks(self, results):
"""Resize masks with ``results['scale']``"""
for key in results.get('mask_fields', []):
if results[key] is None:
continue
if self.keep_ratio:
results[key] = results[key].rescale(results['scale'])
else:
results[key] = results[key].resize(results['img_shape'][:2])
def _resize_seg(self, results):
"""Resize semantic segmentation map with ``results['scale']``."""
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
if self.keep_ratio:
gt_seg = mmcv.imrescale(
results[key],
results['scale'],
interpolation='nearest',
backend=self.backend)
else:
gt_seg = mmcv.imresize(
results[key],
results['scale'],
interpolation='nearest',
backend=self.backend)
results[key] = gt_seg
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to resize images, bounding boxes, masks, semantic
segmentation map.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Resized results, 'img_shape', 'pad_shape', 'scale_factor', \
'keep_ratio' keys are added into result dict.
"""
if 'scale' not in results:
if 'scale_factor' in results:
img_shape = results['img'].shape[:2]
scale_factor = results['scale_factor']
assert isinstance(scale_factor, float)
results['scale'] = tuple(
[int(x * scale_factor) for x in img_shape][::-1])
else:
self._random_scale(results)
else:
if not self.override:
assert 'scale_factor' not in results, (
'scale and scale_factor cannot be both set.')
else:
results.pop('scale')
if 'scale_factor' in results:
results.pop('scale_factor')
self._random_scale(results)
self._resize_img(results)
self._resize_bboxes(results)
self._resize_masks(results)
self._resize_seg(results)
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(img_scale={self.img_scale}, '
repr_str += f'multiscale_mode={self.multiscale_mode}, '
repr_str += f'ratio_range={self.ratio_range}, '
repr_str += f'keep_ratio={self.keep_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'bbox_clip_border={self.bbox_clip_border})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class RandomFlip:
"""Flip the image & bbox & mask.
If the input dict contains the key "flip", then the flag will be used,
otherwise it will be randomly decided by a ratio specified in the init
method.
When random flip is enabled, ``flip_ratio``/``direction`` can either be a
float/string or tuple of float/string. There are 3 flip modes:
- ``flip_ratio`` is float, ``direction`` is string: the image will be
``direction``ly flipped with probability of ``flip_ratio`` .
E.g., ``flip_ratio=0.5``, ``direction='horizontal'``,
then image will be horizontally flipped with probability of 0.5.
- ``flip_ratio`` is float, ``direction`` is list of string: the image will
be ``direction[i]``ly flipped with probability of
``flip_ratio/len(direction)``.
E.g., ``flip_ratio=0.5``, ``direction=['horizontal', 'vertical']``,
then image will be horizontally flipped with probability of 0.25,
vertically with probability of 0.25.
- ``flip_ratio`` is list of float, ``direction`` is list of string:
given ``len(flip_ratio) == len(direction)``, the image will
be ``direction[i]``ly flipped with probability of ``flip_ratio[i]``.
E.g., ``flip_ratio=[0.3, 0.5]``, ``direction=['horizontal',
'vertical']``, then image will be horizontally flipped with probability
of 0.3, vertically with probability of 0.5.
Args:
flip_ratio (float | list[float], optional): The flipping probability.
Default: None.
direction(str | list[str], optional): The flipping direction. Options
are 'horizontal', 'vertical', 'diagonal'. Default: 'horizontal'.
If input is a list, the length must equal ``flip_ratio``. Each
element in ``flip_ratio`` indicates the flip probability of
corresponding direction.
"""
def __init__(self, flip_ratio=None, direction='horizontal'):
if isinstance(flip_ratio, list):
assert mmcv.is_list_of(flip_ratio, float)
assert 0 <= sum(flip_ratio) <= 1
elif isinstance(flip_ratio, float):
assert 0 <= flip_ratio <= 1
elif flip_ratio is None:
pass
else:
raise ValueError('flip_ratios must be None, float, '
'or list of float')
self.flip_ratio = flip_ratio
valid_directions = ['horizontal', 'vertical', 'diagonal']
if isinstance(direction, str):
assert direction in valid_directions
elif isinstance(direction, list):
assert mmcv.is_list_of(direction, str)
assert set(direction).issubset(set(valid_directions))
else:
raise ValueError('direction must be either str or list of str')
self.direction = direction
if isinstance(flip_ratio, list):
assert len(self.flip_ratio) == len(self.direction)
def bbox_flip(self, bboxes, img_shape, direction):
"""Flip bboxes horizontally.
Args:
bboxes (numpy.ndarray): Bounding boxes, shape (..., 4*k)
img_shape (tuple[int]): Image shape (height, width)
direction (str): Flip direction. Options are 'horizontal',
'vertical'.
Returns:
numpy.ndarray: Flipped bounding boxes.
"""
assert bboxes.shape[-1] % 4 == 0
flipped = bboxes.copy()
if direction == 'horizontal':
w = img_shape[1]
flipped[..., 0::4] = w - bboxes[..., 2::4]
flipped[..., 2::4] = w - bboxes[..., 0::4]
elif direction == 'vertical':
h = img_shape[0]
flipped[..., 1::4] = h - bboxes[..., 3::4]
flipped[..., 3::4] = h - bboxes[..., 1::4]
elif direction == 'diagonal':
w = img_shape[1]
h = img_shape[0]
flipped[..., 0::4] = w - bboxes[..., 2::4]
flipped[..., 1::4] = h - bboxes[..., 3::4]
flipped[..., 2::4] = w - bboxes[..., 0::4]
flipped[..., 3::4] = h - bboxes[..., 1::4]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid flipping direction '{direction}'")
return flipped
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to flip bounding boxes, masks, semantic segmentation
maps.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Flipped results, 'flip', 'flip_direction' keys are added \
into result dict.
"""
if 'flip' not in results:
if isinstance(self.direction, list):
# None means non-flip
direction_list = self.direction + [None]
else:
# None means non-flip
direction_list = [self.direction, None]
if isinstance(self.flip_ratio, list):
non_flip_ratio = 1 - sum(self.flip_ratio)
flip_ratio_list = self.flip_ratio + [non_flip_ratio]
else:
non_flip_ratio = 1 - self.flip_ratio
# exclude non-flip
single_ratio = self.flip_ratio / (len(direction_list) - 1)
flip_ratio_list = [single_ratio] * (len(direction_list) -
1) + [non_flip_ratio]
cur_dir = np.random.choice(direction_list, p=flip_ratio_list)
results['flip'] = cur_dir is not None
if 'flip_direction' not in results:
results['flip_direction'] = cur_dir
if results['flip']:
# flip image
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
results[key] = mmcv.imflip(
results[key], direction=results['flip_direction'])
# flip bboxes
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
results[key] = self.bbox_flip(results[key],
results['img_shape'],
results['flip_direction'])
# flip masks
for key in results.get('mask_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key].flip(results['flip_direction'])
# flip segs
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
results[key] = mmcv.imflip(
results[key], direction=results['flip_direction'])
return results
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + f'(flip_ratio={self.flip_ratio})'
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class RandomShift:
"""Shift the image and box given shift pixels and probability.
Args:
shift_ratio (float): Probability of shifts. Default 0.5.
max_shift_px (int): The max pixels for shifting. Default 32.
filter_thr_px (int): The width and height threshold for filtering.
The bbox and the rest of the targets below the width and
height threshold will be filtered. Default 1.
"""
def __init__(self, shift_ratio=0.5, max_shift_px=32, filter_thr_px=1):
assert 0 <= shift_ratio <= 1
assert max_shift_px >= 0
self.shift_ratio = shift_ratio
self.max_shift_px = max_shift_px
self.filter_thr_px = int(filter_thr_px)
# The key correspondence from bboxes to labels.
self.bbox2label = {
'gt_bboxes': 'gt_labels',
'gt_bboxes_ignore': 'gt_labels_ignore'
}
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to random shift images, bounding boxes.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Shift results.
"""
if random.random() < self.shift_ratio:
img_shape = results['img'].shape[:2]
random_shift_x = random.randint(-self.max_shift_px,
self.max_shift_px)
random_shift_y = random.randint(-self.max_shift_px,
self.max_shift_px)
new_x = max(0, random_shift_x)
ori_x = max(0, -random_shift_x)
new_y = max(0, random_shift_y)
ori_y = max(0, -random_shift_y)
# TODO: support mask and semantic segmentation maps.
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
bboxes = results[key].copy()
bboxes[..., 0::2] += random_shift_x
bboxes[..., 1::2] += random_shift_y
# clip border
bboxes[..., 0::2] = np.clip(bboxes[..., 0::2], 0, img_shape[1])
bboxes[..., 1::2] = np.clip(bboxes[..., 1::2], 0, img_shape[0])
# remove invalid bboxes
bbox_w = bboxes[..., 2] - bboxes[..., 0]
bbox_h = bboxes[..., 3] - bboxes[..., 1]
valid_inds = (bbox_w > self.filter_thr_px) & (
bbox_h > self.filter_thr_px)
# If the shift does not contain any gt-bbox area, skip this
# image.
if key == 'gt_bboxes' and not valid_inds.any():
return results
bboxes = bboxes[valid_inds]
results[key] = bboxes
# label fields. e.g. gt_labels and gt_labels_ignore
label_key = self.bbox2label.get(key)
if label_key in results:
results[label_key] = results[label_key][valid_inds]
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
img = results[key]
new_img = np.zeros_like(img)
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
new_h = img_h - np.abs(random_shift_y)
new_w = img_w - np.abs(random_shift_x)
new_img[new_y:new_y + new_h, new_x:new_x + new_w] \
= img[ori_y:ori_y + new_h, ori_x:ori_x + new_w]
results[key] = new_img
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(max_shift_px={self.max_shift_px}, '
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Pad:
"""Pad the image & masks & segmentation map.
There are two padding modes: (1) pad to a fixed size and (2) pad to the
minimum size that is divisible by some number.
Added keys are "pad_shape", "pad_fixed_size", "pad_size_divisor",
Args:
size (tuple, optional): Fixed padding size.
size_divisor (int, optional): The divisor of padded size.
pad_to_square (bool): Whether to pad the image into a square.
Currently only used for YOLOX. Default: False.
pad_val (dict, optional): A dict for padding value, the default
value is `dict(img=0, masks=0, seg=255)`.
"""
def __init__(self,
size=None,
size_divisor=None,
pad_to_square=False,
pad_val=dict(img=0, masks=0, seg=255)):
self.size = size
self.size_divisor = size_divisor
if isinstance(pad_val, float) or isinstance(pad_val, int):
warnings.warn(
'pad_val of float type is deprecated now, '
f'please use pad_val=dict(img={pad_val}, '
f'masks={pad_val}, seg=255) instead.', DeprecationWarning)
pad_val = dict(img=pad_val, masks=pad_val, seg=255)
assert isinstance(pad_val, dict)
self.pad_val = pad_val
self.pad_to_square = pad_to_square
if pad_to_square:
assert size is None and size_divisor is None, \
'The size and size_divisor must be None ' \
'when pad2square is True'
else:
assert size is not None or size_divisor is not None, \
'only one of size and size_divisor should be valid'
assert size is None or size_divisor is None
def _pad_img(self, results):
"""Pad images according to ``self.size``."""
pad_val = self.pad_val.get('img', 0)
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
if self.pad_to_square:
max_size = max(results[key].shape[:2])
self.size = (max_size, max_size)
if self.size is not None:
padded_img = mmcv.impad(
results[key], shape=self.size, pad_val=pad_val)
elif self.size_divisor is not None:
padded_img = mmcv.impad_to_multiple(
results[key], self.size_divisor, pad_val=pad_val)
results[key] = padded_img
results['pad_shape'] = padded_img.shape
results['pad_fixed_size'] = self.size
results['pad_size_divisor'] = self.size_divisor
def _pad_masks(self, results):
"""Pad masks according to ``results['pad_shape']``."""
pad_shape = results['pad_shape'][:2]
pad_val = self.pad_val.get('masks', 0)
for key in results.get('mask_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key].pad(pad_shape, pad_val=pad_val)
def _pad_seg(self, results):
"""Pad semantic segmentation map according to
``results['pad_shape']``."""
pad_val = self.pad_val.get('seg', 255)
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
results[key] = mmcv.impad(
results[key], shape=results['pad_shape'][:2], pad_val=pad_val)
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to pad images, masks, semantic segmentation maps.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Updated result dict.
"""
self._pad_img(results)
self._pad_masks(results)
self._pad_seg(results)
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(size={self.size}, '
repr_str += f'size_divisor={self.size_divisor}, '
repr_str += f'pad_to_square={self.pad_to_square}, '
repr_str += f'pad_val={self.pad_val})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Normalize:
"""Normalize the image.
Added key is "img_norm_cfg".
Args:
mean (sequence): Mean values of 3 channels.
std (sequence): Std values of 3 channels.
to_rgb (bool): Whether to convert the image from BGR to RGB,
default is true.
"""
def __init__(self, mean, std, to_rgb=True):
self.mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32)
self.std = np.array(std, dtype=np.float32)
self.to_rgb = to_rgb
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to normalize images.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Normalized results, 'img_norm_cfg' key is added into
result dict.
"""
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
results[key] = mmcv.imnormalize(results[key], self.mean, self.std,
self.to_rgb)
results['img_norm_cfg'] = dict(
mean=self.mean, std=self.std, to_rgb=self.to_rgb)
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(mean={self.mean}, std={self.std}, to_rgb={self.to_rgb})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class RandomCrop:
"""Random crop the image & bboxes & masks.
The absolute `crop_size` is sampled based on `crop_type` and `image_size`,
then the cropped results are generated.
Args:
crop_size (tuple): The relative ratio or absolute pixels of
height and width.
crop_type (str, optional): one of "relative_range", "relative",
"absolute", "absolute_range". "relative" randomly crops
(h * crop_size[0], w * crop_size[1]) part from an input of size
(h, w). "relative_range" uniformly samples relative crop size from
range [crop_size[0], 1] and [crop_size[1], 1] for height and width
respectively. "absolute" crops from an input with absolute size
(crop_size[0], crop_size[1]). "absolute_range" uniformly samples
crop_h in range [crop_size[0], min(h, crop_size[1])] and crop_w
in range [crop_size[0], min(w, crop_size[1])]. Default "absolute".
allow_negative_crop (bool, optional): Whether to allow a crop that does
not contain any bbox area. Default False.
recompute_bbox (bool, optional): Whether to re-compute the boxes based
on cropped instance masks. Default False.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether clip the objects outside
the border of the image. Defaults to True.
Note:
- If the image is smaller than the absolute crop size, return the
original image.
- The keys for bboxes, labels and masks must be aligned. That is,
`gt_bboxes` corresponds to `gt_labels` and `gt_masks`, and
`gt_bboxes_ignore` corresponds to `gt_labels_ignore` and
`gt_masks_ignore`.
- If the crop does not contain any gt-bbox region and
`allow_negative_crop` is set to False, skip this image.
"""
def __init__(self,
crop_size,
crop_type='absolute',
allow_negative_crop=False,
recompute_bbox=False,
bbox_clip_border=True):
if crop_type not in [
'relative_range', 'relative', 'absolute', 'absolute_range'
]:
raise ValueError(f'Invalid crop_type {crop_type}.')
if crop_type in ['absolute', 'absolute_range']:
assert crop_size[0] > 0 and crop_size[1] > 0
assert isinstance(crop_size[0], int) and isinstance(
crop_size[1], int)
else:
assert 0 < crop_size[0] <= 1 and 0 < crop_size[1] <= 1
self.crop_size = crop_size
self.crop_type = crop_type
self.allow_negative_crop = allow_negative_crop
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
self.recompute_bbox = recompute_bbox
# The key correspondence from bboxes to labels and masks.
self.bbox2label = {
'gt_bboxes': 'gt_labels',
'gt_bboxes_ignore': 'gt_labels_ignore'
}
self.bbox2mask = {
'gt_bboxes': 'gt_masks',
'gt_bboxes_ignore': 'gt_masks_ignore'
}
def _crop_data(self, results, crop_size, allow_negative_crop):
"""Function to randomly crop images, bounding boxes, masks, semantic
segmentation maps.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
crop_size (tuple): Expected absolute size after cropping, (h, w).
allow_negative_crop (bool): Whether to allow a crop that does not
contain any bbox area. Default to False.
Returns:
dict: Randomly cropped results, 'img_shape' key in result dict is
updated according to crop size.
"""
assert crop_size[0] > 0 and crop_size[1] > 0
for key in results.get('img_fields', ['img']):
img = results[key]
margin_h = max(img.shape[0] - crop_size[0], 0)
margin_w = max(img.shape[1] - crop_size[1], 0)
offset_h = np.random.randint(0, margin_h + 1)
offset_w = np.random.randint(0, margin_w + 1)
crop_y1, crop_y2 = offset_h, offset_h + crop_size[0]
crop_x1, crop_x2 = offset_w, offset_w + crop_size[1]
# crop the image
img = img[crop_y1:crop_y2, crop_x1:crop_x2, ...]
img_shape = img.shape
results[key] = img
results['img_shape'] = img_shape
# crop bboxes accordingly and clip to the image boundary
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
# e.g. gt_bboxes and gt_bboxes_ignore
bbox_offset = np.array([offset_w, offset_h, offset_w, offset_h],
dtype=np.float32)
bboxes = results[key] - bbox_offset
if self.bbox_clip_border:
bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 0::2], 0, img_shape[1])
bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 1::2], 0, img_shape[0])
valid_inds = (bboxes[:, 2] > bboxes[:, 0]) & (
bboxes[:, 3] > bboxes[:, 1])
# If the crop does not contain any gt-bbox area and
# allow_negative_crop is False, skip this image.
if (key == 'gt_bboxes' and not valid_inds.any()
and not allow_negative_crop):
return None
results[key] = bboxes[valid_inds, :]
# label fields. e.g. gt_labels and gt_labels_ignore
label_key = self.bbox2label.get(key)
if label_key in results:
results[label_key] = results[label_key][valid_inds]
# mask fields, e.g. gt_masks and gt_masks_ignore
mask_key = self.bbox2mask.get(key)
if mask_key in results:
results[mask_key] = results[mask_key][
valid_inds.nonzero()[0]].crop(
np.asarray([crop_x1, crop_y1, crop_x2, crop_y2]))
if self.recompute_bbox:
results[key] = results[mask_key].get_bboxes()
# crop semantic seg
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key][crop_y1:crop_y2, crop_x1:crop_x2]
return results
def _get_crop_size(self, image_size):
"""Randomly generates the absolute crop size based on `crop_type` and
`image_size`.
Args:
image_size (tuple): (h, w).
Returns:
crop_size (tuple): (crop_h, crop_w) in absolute pixels.
"""
h, w = image_size
if self.crop_type == 'absolute':
return (min(self.crop_size[0], h), min(self.crop_size[1], w))
elif self.crop_type == 'absolute_range':
assert self.crop_size[0] <= self.crop_size[1]
crop_h = np.random.randint(
min(h, self.crop_size[0]),
min(h, self.crop_size[1]) + 1)
crop_w = np.random.randint(
min(w, self.crop_size[0]),
min(w, self.crop_size[1]) + 1)
return crop_h, crop_w
elif self.crop_type == 'relative':
crop_h, crop_w = self.crop_size
return int(h * crop_h + 0.5), int(w * crop_w + 0.5)
elif self.crop_type == 'relative_range':
crop_size = np.asarray(self.crop_size, dtype=np.float32)
crop_h, crop_w = crop_size + np.random.rand(2) * (1 - crop_size)
return int(h * crop_h + 0.5), int(w * crop_w + 0.5)
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to randomly crop images, bounding boxes, masks,
semantic segmentation maps.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Randomly cropped results, 'img_shape' key in result dict is
updated according to crop size.
"""
image_size = results['img'].shape[:2]
crop_size = self._get_crop_size(image_size)
results = self._crop_data(results, crop_size, self.allow_negative_crop)
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(crop_size={self.crop_size}, '
repr_str += f'crop_type={self.crop_type}, '
repr_str += f'allow_negative_crop={self.allow_negative_crop}, '
repr_str += f'bbox_clip_border={self.bbox_clip_border})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class SegRescale:
"""Rescale semantic segmentation maps.
Args:
scale_factor (float): The scale factor of the final output.
backend (str): Image rescale backend, choices are 'cv2' and 'pillow'.
These two backends generates slightly different results. Defaults
to 'cv2'.
"""
def __init__(self, scale_factor=1, backend='cv2'):
self.scale_factor = scale_factor
self.backend = backend
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to scale the semantic segmentation map.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with semantic segmentation map scaled.
"""
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
if self.scale_factor != 1:
results[key] = mmcv.imrescale(
results[key],
self.scale_factor,
interpolation='nearest',
backend=self.backend)
return results
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + f'(scale_factor={self.scale_factor})'
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class PhotoMetricDistortion:
"""Apply photometric distortion to image sequentially, every transformation
is applied with a probability of 0.5. The position of random contrast is in
second or second to last.
1. random brightness
2. random contrast (mode 0)
3. convert color from BGR to HSV
4. random saturation
5. random hue
6. convert color from HSV to BGR
7. random contrast (mode 1)
8. randomly swap channels
Args:
brightness_delta (int): delta of brightness.
contrast_range (tuple): range of contrast.
saturation_range (tuple): range of saturation.
hue_delta (int): delta of hue.
"""
def __init__(self,
brightness_delta=32,
contrast_range=(0.5, 1.5),
saturation_range=(0.5, 1.5),
hue_delta=18):
self.brightness_delta = brightness_delta
self.contrast_lower, self.contrast_upper = contrast_range
self.saturation_lower, self.saturation_upper = saturation_range
self.hue_delta = hue_delta
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to perform photometric distortion on images.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with images distorted.
"""
if 'img_fields' in results:
assert results['img_fields'] == ['img'], \
'Only single img_fields is allowed'
img = results['img']
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# random brightness
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.brightness_delta,
self.brightness_delta)
img += delta
# mode == 0 --> do random contrast first
# mode == 1 --> do random contrast last
mode = random.randint(2)
if mode == 1:
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.contrast_lower,
self.contrast_upper)
img *= alpha
# convert color from BGR to HSV
img = mmcv.bgr2hsv(img)
# random saturation
if random.randint(2):
img[..., 1] *= random.uniform(self.saturation_lower,
self.saturation_upper)
# random hue
if random.randint(2):
img[..., 0] += random.uniform(-self.hue_delta, self.hue_delta)
img[..., 0][img[..., 0] > 360] -= 360
img[..., 0][img[..., 0] < 0] += 360
# convert color from HSV to BGR
img = mmcv.hsv2bgr(img)
# random contrast
if mode == 0:
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.contrast_lower,
self.contrast_upper)
img *= alpha
# randomly swap channels
if random.randint(2):
img = img[..., random.permutation(3)]
results['img'] = img
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(\nbrightness_delta={self.brightness_delta},\n'
repr_str += 'contrast_range='
repr_str += f'{(self.contrast_lower, self.contrast_upper)},\n'
repr_str += 'saturation_range='
repr_str += f'{(self.saturation_lower, self.saturation_upper)},\n'
repr_str += f'hue_delta={self.hue_delta})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Expand:
"""Random expand the image & bboxes.
Randomly place the original image on a canvas of 'ratio' x original image
size filled with mean values. The ratio is in the range of ratio_range.
Args:
mean (tuple): mean value of dataset.
to_rgb (bool): if need to convert the order of mean to align with RGB.
ratio_range (tuple): range of expand ratio.
prob (float): probability of applying this transformation
"""
def __init__(self,
mean=(0, 0, 0),
to_rgb=True,
ratio_range=(1, 4),
seg_ignore_label=None,
prob=0.5):
self.to_rgb = to_rgb
self.ratio_range = ratio_range
if to_rgb:
self.mean = mean[::-1]
else:
self.mean = mean
self.min_ratio, self.max_ratio = ratio_range
self.seg_ignore_label = seg_ignore_label
self.prob = prob
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to expand images, bounding boxes.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with images, bounding boxes expanded
"""
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.prob:
return results
if 'img_fields' in results:
assert results['img_fields'] == ['img'], \
'Only single img_fields is allowed'
img = results['img']
h, w, c = img.shape
ratio = random.uniform(self.min_ratio, self.max_ratio)
# speedup expand when meets large image
if np.all(self.mean == self.mean[0]):
expand_img = np.empty((int(h * ratio), int(w * ratio), c),
img.dtype)
expand_img.fill(self.mean[0])
else:
expand_img = np.full((int(h * ratio), int(w * ratio), c),
self.mean,
dtype=img.dtype)
left = int(random.uniform(0, w * ratio - w))
top = int(random.uniform(0, h * ratio - h))
expand_img[top:top + h, left:left + w] = img
results['img'] = expand_img
# expand bboxes
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key] + np.tile(
(left, top), 2).astype(results[key].dtype)
# expand masks
for key in results.get('mask_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key].expand(
int(h * ratio), int(w * ratio), top, left)
# expand segs
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
gt_seg = results[key]
expand_gt_seg = np.full((int(h * ratio), int(w * ratio)),
self.seg_ignore_label,
dtype=gt_seg.dtype)
expand_gt_seg[top:top + h, left:left + w] = gt_seg
results[key] = expand_gt_seg
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(mean={self.mean}, to_rgb={self.to_rgb}, '
repr_str += f'ratio_range={self.ratio_range}, '
repr_str += f'seg_ignore_label={self.seg_ignore_label})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class MinIoURandomCrop:
"""Random crop the image & bboxes, the cropped patches have minimum IoU
requirement with original image & bboxes, the IoU threshold is randomly
selected from min_ious.
Args:
min_ious (tuple): minimum IoU threshold for all intersections with
bounding boxes
min_crop_size (float): minimum crop's size (i.e. h,w := a*h, a*w,
where a >= min_crop_size).
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether clip the objects outside
the border of the image. Defaults to True.
Note:
The keys for bboxes, labels and masks should be paired. That is, \
`gt_bboxes` corresponds to `gt_labels` and `gt_masks`, and \
`gt_bboxes_ignore` to `gt_labels_ignore` and `gt_masks_ignore`.
"""
def __init__(self,
min_ious=(0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9),
min_crop_size=0.3,
bbox_clip_border=True):
# 1: return ori img
self.min_ious = min_ious
self.sample_mode = (1, *min_ious, 0)
self.min_crop_size = min_crop_size
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
self.bbox2label = {
'gt_bboxes': 'gt_labels',
'gt_bboxes_ignore': 'gt_labels_ignore'
}
self.bbox2mask = {
'gt_bboxes': 'gt_masks',
'gt_bboxes_ignore': 'gt_masks_ignore'
}
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to crop images and bounding boxes with minimum IoU
constraint.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with images and bounding boxes cropped, \
'img_shape' key is updated.
"""
if 'img_fields' in results:
assert results['img_fields'] == ['img'], \
'Only single img_fields is allowed'
img = results['img']
assert 'bbox_fields' in results
boxes = [results[key] for key in results['bbox_fields']]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes, 0)
h, w, c = img.shape
while True:
mode = random.choice(self.sample_mode)
self.mode = mode
if mode == 1:
return results
min_iou = mode
for i in range(50):
new_w = random.uniform(self.min_crop_size * w, w)
new_h = random.uniform(self.min_crop_size * h, h)
# h / w in [0.5, 2]
if new_h / new_w < 0.5 or new_h / new_w > 2:
continue
left = random.uniform(w - new_w)
top = random.uniform(h - new_h)
patch = np.array(
(int(left), int(top), int(left + new_w), int(top + new_h)))
# Line or point crop is not allowed
if patch[2] == patch[0] or patch[3] == patch[1]:
continue
overlaps = bbox_overlaps(
patch.reshape(-1, 4), boxes.reshape(-1, 4)).reshape(-1)
if len(overlaps) > 0 and overlaps.min() < min_iou:
continue
# center of boxes should inside the crop img
# only adjust boxes and instance masks when the gt is not empty
if len(overlaps) > 0:
# adjust boxes
def is_center_of_bboxes_in_patch(boxes, patch):
center = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2
mask = ((center[:, 0] > patch[0]) *
(center[:, 1] > patch[1]) *
(center[:, 0] < patch[2]) *
(center[:, 1] < patch[3]))
return mask
mask = is_center_of_bboxes_in_patch(boxes, patch)
if not mask.any():
continue
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
boxes = results[key].copy()
mask = is_center_of_bboxes_in_patch(boxes, patch)
boxes = boxes[mask]
if self.bbox_clip_border:
boxes[:, 2:] = boxes[:, 2:].clip(max=patch[2:])
boxes[:, :2] = boxes[:, :2].clip(min=patch[:2])
boxes -= np.tile(patch[:2], 2)
results[key] = boxes
# labels
label_key = self.bbox2label.get(key)
if label_key in results:
results[label_key] = results[label_key][mask]
# mask fields
mask_key = self.bbox2mask.get(key)
if mask_key in results:
results[mask_key] = results[mask_key][
mask.nonzero()[0]].crop(patch)
# adjust the img no matter whether the gt is empty before crop
img = img[patch[1]:patch[3], patch[0]:patch[2]]
results['img'] = img
results['img_shape'] = img.shape
# seg fields
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
results[key] = results[key][patch[1]:patch[3],
patch[0]:patch[2]]
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(min_ious={self.min_ious}, '
repr_str += f'min_crop_size={self.min_crop_size}, '
repr_str += f'bbox_clip_border={self.bbox_clip_border})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Corrupt:
"""Corruption augmentation.
Corruption transforms implemented based on
`imagecorruptions <https://github.com/bethgelab/imagecorruptions>`_.
Args:
corruption (str): Corruption name.
severity (int, optional): The severity of corruption. Default: 1.
"""
def __init__(self, corruption, severity=1):
self.corruption = corruption
self.severity = severity
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to corrupt image.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict from loading pipeline.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with images corrupted.
"""
if corrupt is None:
raise RuntimeError('imagecorruptions is not installed')
if 'img_fields' in results:
assert results['img_fields'] == ['img'], \
'Only single img_fields is allowed'
results['img'] = corrupt(
results['img'].astype(np.uint8),
corruption_name=self.corruption,
severity=self.severity)
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(corruption={self.corruption}, '
repr_str += f'severity={self.severity})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Albu:
"""Albumentation augmentation.
Adds custom transformations from Albumentations library.
Please, visit `https://albumentations.readthedocs.io`
to get more information.
An example of ``transforms`` is as followed:()
.. code-block::
[
dict(
type='ShiftScaleRotate',
shift_limit=0.0625,
scale_limit=0.0,
rotate_limit=0,
interpolation=1,
p=0.5),
dict(
type='RandomBrightnessContrast',
brightness_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
contrast_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
p=0.2),
dict(type='ChannelShuffle', p=0.1),
dict(
type='OneOf',
transforms=[
dict(type='Blur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0),
dict(type='MedianBlur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0)
],
p=0.1),
]
Args:
transforms (list[dict]): A list of albu transformations
bbox_params (dict): Bbox_params for albumentation `Compose`
keymap (dict): Contains {'input key':'albumentation-style key'}
skip_img_without_anno (bool): Whether to skip the image if no ann left
after aug
"""
def __init__(self,
transforms,
bbox_params=None,
keymap=None,
update_pad_shape=False,
skip_img_without_anno=False):
if Compose is None:
raise RuntimeError('albumentations is not installed')
# Args will be modified later, copying it will be safer
transforms = copy.deepcopy(transforms)
if bbox_params is not None:
bbox_params = copy.deepcopy(bbox_params)
if keymap is not None:
keymap = copy.deepcopy(keymap)
self.transforms = transforms
self.filter_lost_elements = False
self.update_pad_shape = update_pad_shape
self.skip_img_without_anno = skip_img_without_anno
# A simple workaround to remove masks without boxes
if (isinstance(bbox_params, dict) and 'label_fields' in bbox_params
and 'filter_lost_elements' in bbox_params):
self.filter_lost_elements = True
self.origin_label_fields = bbox_params['label_fields']
bbox_params['label_fields'] = ['idx_mapper']
del bbox_params['filter_lost_elements']
self.bbox_params = (
self.albu_builder(bbox_params) if bbox_params else None)
self.aug = Compose([self.albu_builder(t) for t in self.transforms],
bbox_params=self.bbox_params)
if not keymap:
self.keymap_to_albu = {
'img': 'image',
'gt_masks': 'masks',
'gt_bboxes': 'bboxes'
}
else:
self.keymap_to_albu = keymap
self.keymap_back = {v: k for k, v in self.keymap_to_albu.items()}
def albu_builder(self, cfg):
"""Import a module from albumentations.
It inherits some of :func:`build_from_cfg` logic.
Args:
cfg (dict): Config dict. It should at least contain the key "type".
Returns:
obj: The constructed object.
"""
assert isinstance(cfg, dict) and 'type' in cfg
args = cfg.copy()
obj_type = args.pop('type')
if mmcv.is_str(obj_type):
if albumentations is None:
raise RuntimeError('albumentations is not installed')
obj_cls = getattr(albumentations, obj_type)
elif inspect.isclass(obj_type):
obj_cls = obj_type
else:
raise TypeError(
f'type must be a str or valid type, but got {type(obj_type)}')
if 'transforms' in args:
args['transforms'] = [
self.albu_builder(transform)
for transform in args['transforms']
]
return obj_cls(**args)
@staticmethod
def mapper(d, keymap):
"""Dictionary mapper. Renames keys according to keymap provided.
Args:
d (dict): old dict
keymap (dict): {'old_key':'new_key'}
Returns:
dict: new dict.
"""
updated_dict = {}
for k, v in zip(d.keys(), d.values()):
new_k = keymap.get(k, k)
updated_dict[new_k] = d[k]
return updated_dict
def __call__(self, results):
# dict to albumentations format
results = self.mapper(results, self.keymap_to_albu)
# TODO: add bbox_fields
if 'bboxes' in results:
# to list of boxes
if isinstance(results['bboxes'], np.ndarray):
results['bboxes'] = [x for x in results['bboxes']]
# add pseudo-field for filtration
if self.filter_lost_elements:
results['idx_mapper'] = np.arange(len(results['bboxes']))
# TODO: Support mask structure in albu
if 'masks' in results:
if isinstance(results['masks'], PolygonMasks):
raise NotImplementedError(
'Albu only supports BitMap masks now')
ori_masks = results['masks']
if albumentations.__version__ < '0.5':
results['masks'] = results['masks'].masks
else:
results['masks'] = [mask for mask in results['masks'].masks]
results = self.aug(**results)
if 'bboxes' in results:
if isinstance(results['bboxes'], list):
results['bboxes'] = np.array(
results['bboxes'], dtype=np.float32)
results['bboxes'] = results['bboxes'].reshape(-1, 4)
# filter label_fields
if self.filter_lost_elements:
for label in self.origin_label_fields:
results[label] = np.array(
[results[label][i] for i in results['idx_mapper']])
if 'masks' in results:
results['masks'] = np.array(
[results['masks'][i] for i in results['idx_mapper']])
results['masks'] = ori_masks.__class__(
results['masks'], results['image'].shape[0],
results['image'].shape[1])
if (not len(results['idx_mapper'])
and self.skip_img_without_anno):
return None
if 'gt_labels' in results:
if isinstance(results['gt_labels'], list):
results['gt_labels'] = np.array(results['gt_labels'])
results['gt_labels'] = results['gt_labels'].astype(np.int64)
# back to the original format
results = self.mapper(results, self.keymap_back)
# update final shape
if self.update_pad_shape:
results['pad_shape'] = results['img'].shape
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__ + f'(transforms={self.transforms})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class RandomCenterCropPad:
"""Random center crop and random around padding for CornerNet.
This operation generates randomly cropped image from the original image and
pads it simultaneously. Different from :class:`RandomCrop`, the output
shape may not equal to ``crop_size`` strictly. We choose a random value
from ``ratios`` and the output shape could be larger or smaller than
``crop_size``. The padding operation is also different from :class:`Pad`,
here we use around padding instead of right-bottom padding.
The relation between output image (padding image) and original image:
.. code:: text
output image
+----------------------------+
| padded area |
+------|----------------------------|----------+
| | cropped area | |
| | +---------------+ | |
| | | . center | | | original image
| | | range | | |
| | +---------------+ | |
+------|----------------------------|----------+
| padded area |
+----------------------------+
There are 5 main areas in the figure:
- output image: output image of this operation, also called padding
image in following instruction.
- original image: input image of this operation.
- padded area: non-intersect area of output image and original image.
- cropped area: the overlap of output image and original image.
- center range: a smaller area where random center chosen from.
center range is computed by ``border`` and original image's shape
to avoid our random center is too close to original image's border.
Also this operation act differently in train and test mode, the summary
pipeline is listed below.
Train pipeline:
1. Choose a ``random_ratio`` from ``ratios``, the shape of padding image
will be ``random_ratio * crop_size``.
2. Choose a ``random_center`` in center range.
3. Generate padding image with center matches the ``random_center``.
4. Initialize the padding image with pixel value equals to ``mean``.
5. Copy the cropped area to padding image.
6. Refine annotations.
Test pipeline:
1. Compute output shape according to ``test_pad_mode``.
2. Generate padding image with center matches the original image
center.
3. Initialize the padding image with pixel value equals to ``mean``.
4. Copy the ``cropped area`` to padding image.
Args:
crop_size (tuple | None): expected size after crop, final size will
computed according to ratio. Requires (h, w) in train mode, and
None in test mode.
ratios (tuple): random select a ratio from tuple and crop image to
(crop_size[0] * ratio) * (crop_size[1] * ratio).
Only available in train mode.
border (int): max distance from center select area to image border.
Only available in train mode.
mean (sequence): Mean values of 3 channels.
std (sequence): Std values of 3 channels.
to_rgb (bool): Whether to convert the image from BGR to RGB.
test_mode (bool): whether involve random variables in transform.
In train mode, crop_size is fixed, center coords and ratio is
random selected from predefined lists. In test mode, crop_size
is image's original shape, center coords and ratio is fixed.
test_pad_mode (tuple): padding method and padding shape value, only
available in test mode. Default is using 'logical_or' with
127 as padding shape value.
- 'logical_or': final_shape = input_shape | padding_shape_value
- 'size_divisor': final_shape = int(
ceil(input_shape / padding_shape_value) * padding_shape_value)
test_pad_add_pix (int): Extra padding pixel in test mode. Default 0.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether clip the objects outside
the border of the image. Defaults to True.
"""
def __init__(self,
crop_size=None,
ratios=(0.9, 1.0, 1.1),
border=128,
mean=None,
std=None,
to_rgb=None,
test_mode=False,
test_pad_mode=('logical_or', 127),
test_pad_add_pix=0,
bbox_clip_border=True):
if test_mode:
assert crop_size is None, 'crop_size must be None in test mode'
assert ratios is None, 'ratios must be None in test mode'
assert border is None, 'border must be None in test mode'
assert isinstance(test_pad_mode, (list, tuple))
assert test_pad_mode[0] in ['logical_or', 'size_divisor']
else:
assert isinstance(crop_size, (list, tuple))
assert crop_size[0] > 0 and crop_size[1] > 0, (
'crop_size must > 0 in train mode')
assert isinstance(ratios, (list, tuple))
assert test_pad_mode is None, (
'test_pad_mode must be None in train mode')
self.crop_size = crop_size
self.ratios = ratios
self.border = border
# We do not set default value to mean, std and to_rgb because these
# hyper-parameters are easy to forget but could affect the performance.
# Please use the same setting as Normalize for performance assurance.
assert mean is not None and std is not None and to_rgb is not None
self.to_rgb = to_rgb
self.input_mean = mean
self.input_std = std
if to_rgb:
self.mean = mean[::-1]
self.std = std[::-1]
else:
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
self.test_mode = test_mode
self.test_pad_mode = test_pad_mode
self.test_pad_add_pix = test_pad_add_pix
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
def _get_border(self, border, size):
"""Get final border for the target size.
This function generates a ``final_border`` according to image's shape.
The area between ``final_border`` and ``size - final_border`` is the
``center range``. We randomly choose center from the ``center range``
to avoid our random center is too close to original image's border.
Also ``center range`` should be larger than 0.
Args:
border (int): The initial border, default is 128.
size (int): The width or height of original image.
Returns:
int: The final border.
"""
k = 2 * border / size
i = pow(2, np.ceil(np.log2(np.ceil(k))) + (k == int(k)))
return border // i
def _filter_boxes(self, patch, boxes):
"""Check whether the center of each box is in the patch.
Args:
patch (list[int]): The cropped area, [left, top, right, bottom].
boxes (numpy array, (N x 4)): Ground truth boxes.
Returns:
mask (numpy array, (N,)): Each box is inside or outside the patch.
"""
center = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2
mask = (center[:, 0] > patch[0]) * (center[:, 1] > patch[1]) * (
center[:, 0] < patch[2]) * (
center[:, 1] < patch[3])
return mask
def _crop_image_and_paste(self, image, center, size):
"""Crop image with a given center and size, then paste the cropped
image to a blank image with two centers align.
This function is equivalent to generating a blank image with ``size``
as its shape. Then cover it on the original image with two centers (
the center of blank image and the random center of original image)
aligned. The overlap area is paste from the original image and the
outside area is filled with ``mean pixel``.
Args:
image (np array, H x W x C): Original image.
center (list[int]): Target crop center coord.
size (list[int]): Target crop size. [target_h, target_w]
Returns:
cropped_img (np array, target_h x target_w x C): Cropped image.
border (np array, 4): The distance of four border of
``cropped_img`` to the original image area, [top, bottom,
left, right]
patch (list[int]): The cropped area, [left, top, right, bottom].
"""
center_y, center_x = center
target_h, target_w = size
img_h, img_w, img_c = image.shape
x0 = max(0, center_x - target_w // 2)
x1 = min(center_x + target_w // 2, img_w)
y0 = max(0, center_y - target_h // 2)
y1 = min(center_y + target_h // 2, img_h)
patch = np.array((int(x0), int(y0), int(x1), int(y1)))
left, right = center_x - x0, x1 - center_x
top, bottom = center_y - y0, y1 - center_y
cropped_center_y, cropped_center_x = target_h // 2, target_w // 2
cropped_img = np.zeros((target_h, target_w, img_c), dtype=image.dtype)
for i in range(img_c):
cropped_img[:, :, i] += self.mean[i]
y_slice = slice(cropped_center_y - top, cropped_center_y + bottom)
x_slice = slice(cropped_center_x - left, cropped_center_x + right)
cropped_img[y_slice, x_slice, :] = image[y0:y1, x0:x1, :]
border = np.array([
cropped_center_y - top, cropped_center_y + bottom,
cropped_center_x - left, cropped_center_x + right
],
dtype=np.float32)
return cropped_img, border, patch
def _train_aug(self, results):
"""Random crop and around padding the original image.
Args:
results (dict): Image infomations in the augment pipeline.
Returns:
results (dict): The updated dict.
"""
img = results['img']
h, w, c = img.shape
boxes = results['gt_bboxes']
while True:
scale = random.choice(self.ratios)
new_h = int(self.crop_size[0] * scale)
new_w = int(self.crop_size[1] * scale)
h_border = self._get_border(self.border, h)
w_border = self._get_border(self.border, w)
for i in range(50):
center_x = random.randint(low=w_border, high=w - w_border)
center_y = random.randint(low=h_border, high=h - h_border)
cropped_img, border, patch = self._crop_image_and_paste(
img, [center_y, center_x], [new_h, new_w])
mask = self._filter_boxes(patch, boxes)
# if image do not have valid bbox, any crop patch is valid.
if not mask.any() and len(boxes) > 0:
continue
results['img'] = cropped_img
results['img_shape'] = cropped_img.shape
results['pad_shape'] = cropped_img.shape
x0, y0, x1, y1 = patch
left_w, top_h = center_x - x0, center_y - y0
cropped_center_x, cropped_center_y = new_w // 2, new_h // 2
# crop bboxes accordingly and clip to the image boundary
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
mask = self._filter_boxes(patch, results[key])
bboxes = results[key][mask]
bboxes[:, 0:4:2] += cropped_center_x - left_w - x0
bboxes[:, 1:4:2] += cropped_center_y - top_h - y0
if self.bbox_clip_border:
bboxes[:, 0:4:2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 0:4:2], 0, new_w)
bboxes[:, 1:4:2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 1:4:2], 0, new_h)
keep = (bboxes[:, 2] > bboxes[:, 0]) & (
bboxes[:, 3] > bboxes[:, 1])
bboxes = bboxes[keep]
results[key] = bboxes
if key in ['gt_bboxes']:
if 'gt_labels' in results:
labels = results['gt_labels'][mask]
labels = labels[keep]
results['gt_labels'] = labels
if 'gt_masks' in results:
raise NotImplementedError(
'RandomCenterCropPad only supports bbox.')
# crop semantic seg
for key in results.get('seg_fields', []):
raise NotImplementedError(
'RandomCenterCropPad only supports bbox.')
return results
def _test_aug(self, results):
"""Around padding the original image without cropping.
The padding mode and value are from ``test_pad_mode``.
Args:
results (dict): Image infomations in the augment pipeline.
Returns:
results (dict): The updated dict.
"""
img = results['img']
h, w, c = img.shape
results['img_shape'] = img.shape
if self.test_pad_mode[0] in ['logical_or']:
# self.test_pad_add_pix is only used for centernet
target_h = (h | self.test_pad_mode[1]) + self.test_pad_add_pix
target_w = (w | self.test_pad_mode[1]) + self.test_pad_add_pix
elif self.test_pad_mode[0] in ['size_divisor']:
divisor = self.test_pad_mode[1]
target_h = int(np.ceil(h / divisor)) * divisor
target_w = int(np.ceil(w / divisor)) * divisor
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
'RandomCenterCropPad only support two testing pad mode:'
'logical-or and size_divisor.')
cropped_img, border, _ = self._crop_image_and_paste(
img, [h // 2, w // 2], [target_h, target_w])
results['img'] = cropped_img
results['pad_shape'] = cropped_img.shape
results['border'] = border
return results
def __call__(self, results):
img = results['img']
assert img.dtype == np.float32, (
'RandomCenterCropPad needs the input image of dtype np.float32,'
' please set "to_float32=True" in "LoadImageFromFile" pipeline')
h, w, c = img.shape
assert c == len(self.mean)
if self.test_mode:
return self._test_aug(results)
else:
return self._train_aug(results)
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(crop_size={self.crop_size}, '
repr_str += f'ratios={self.ratios}, '
repr_str += f'border={self.border}, '
repr_str += f'mean={self.input_mean}, '
repr_str += f'std={self.input_std}, '
repr_str += f'to_rgb={self.to_rgb}, '
repr_str += f'test_mode={self.test_mode}, '
repr_str += f'test_pad_mode={self.test_pad_mode}, '
repr_str += f'bbox_clip_border={self.bbox_clip_border})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class CutOut:
"""CutOut operation.
Randomly drop some regions of image used in
`Cutout <https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.04552>`_.
Args:
n_holes (int | tuple[int, int]): Number of regions to be dropped.
If it is given as a list, number of holes will be randomly
selected from the closed interval [`n_holes[0]`, `n_holes[1]`].
cutout_shape (tuple[int, int] | list[tuple[int, int]]): The candidate
shape of dropped regions. It can be `tuple[int, int]` to use a
fixed cutout shape, or `list[tuple[int, int]]` to randomly choose
shape from the list.
cutout_ratio (tuple[float, float] | list[tuple[float, float]]): The
candidate ratio of dropped regions. It can be `tuple[float, float]`
to use a fixed ratio or `list[tuple[float, float]]` to randomly
choose ratio from the list. Please note that `cutout_shape`
and `cutout_ratio` cannot be both given at the same time.
fill_in (tuple[float, float, float] | tuple[int, int, int]): The value
of pixel to fill in the dropped regions. Default: (0, 0, 0).
"""
def __init__(self,
n_holes,
cutout_shape=None,
cutout_ratio=None,
fill_in=(0, 0, 0)):
assert (cutout_shape is None) ^ (cutout_ratio is None), \
'Either cutout_shape or cutout_ratio should be specified.'
assert (isinstance(cutout_shape, (list, tuple))
or isinstance(cutout_ratio, (list, tuple)))
if isinstance(n_holes, tuple):
assert len(n_holes) == 2 and 0 <= n_holes[0] < n_holes[1]
else:
n_holes = (n_holes, n_holes)
self.n_holes = n_holes
self.fill_in = fill_in
self.with_ratio = cutout_ratio is not None
self.candidates = cutout_ratio if self.with_ratio else cutout_shape
if not isinstance(self.candidates, list):
self.candidates = [self.candidates]
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to drop some regions of image."""
h, w, c = results['img'].shape
n_holes = np.random.randint(self.n_holes[0], self.n_holes[1] + 1)
for _ in range(n_holes):
x1 = np.random.randint(0, w)
y1 = np.random.randint(0, h)
index = np.random.randint(0, len(self.candidates))
if not self.with_ratio:
cutout_w, cutout_h = self.candidates[index]
else:
cutout_w = int(self.candidates[index][0] * w)
cutout_h = int(self.candidates[index][1] * h)
x2 = np.clip(x1 + cutout_w, 0, w)
y2 = np.clip(y1 + cutout_h, 0, h)
results['img'][y1:y2, x1:x2, :] = self.fill_in
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(n_holes={self.n_holes}, '
repr_str += (f'cutout_ratio={self.candidates}, ' if self.with_ratio
else f'cutout_shape={self.candidates}, ')
repr_str += f'fill_in={self.fill_in})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class Mosaic:
"""Mosaic augmentation.
Given 4 images, mosaic transform combines them into
one output image. The output image is composed of the parts from each sub-
image.
.. code:: text
mosaic transform
center_x
+------------------------------+
| pad | pad |
| +-----------+ |
| | | |
| | image1 |--------+ |
| | | | |
| | | image2 | |
center_y |----+-------------+-----------|
| | cropped | |
|pad | image3 | image4 |
| | | |
+----|-------------+-----------+
| |
+-------------+
The mosaic transform steps are as follows:
1. Choose the mosaic center as the intersections of 4 images
2. Get the left top image according to the index, and randomly
sample another 3 images from the custom dataset.
3. Sub image will be cropped if image is larger than mosaic patch
Args:
img_scale (Sequence[int]): Image size after mosaic pipeline of single
image. The shape order should be (height, width).
Default to (640, 640).
center_ratio_range (Sequence[float]): Center ratio range of mosaic
output. Default to (0.5, 1.5).
min_bbox_size (int | float): The minimum pixel for filtering
invalid bboxes after the mosaic pipeline. Default to 0.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether to clip the objects outside
the border of the image. In some dataset like MOT17, the gt bboxes
are allowed to cross the border of images. Therefore, we don't
need to clip the gt bboxes in these cases. Defaults to True.
skip_filter (bool): Whether to skip filtering rules. If it
is True, the filter rule will not be applied, and the
`min_bbox_size` is invalid. Default to True.
pad_val (int): Pad value. Default to 114.
prob (float): Probability of applying this transformation.
Default to 1.0.
"""
def __init__(self,
img_scale=(640, 640),
center_ratio_range=(0.5, 1.5),
min_bbox_size=0,
bbox_clip_border=True,
skip_filter=True,
pad_val=114,
prob=1.0):
assert isinstance(img_scale, tuple)
assert 0 <= prob <= 1.0, 'The probability should be in range [0,1]. '\
f'got {prob}.'
log_img_scale(img_scale, skip_square=True)
self.img_scale = img_scale
self.center_ratio_range = center_ratio_range
self.min_bbox_size = min_bbox_size
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
self.skip_filter = skip_filter
self.pad_val = pad_val
self.prob = prob
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to make a mosaic of image.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with mosaic transformed.
"""
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.prob:
return results
results = self._mosaic_transform(results)
return results
def get_indexes(self, dataset):
"""Call function to collect indexes.
Args:
dataset (:obj:`MultiImageMixDataset`): The dataset.
Returns:
list: indexes.
"""
indexes = [random.randint(0, len(dataset)) for _ in range(3)]
return indexes
def _mosaic_transform(self, results):
"""Mosaic transform function.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict.
Returns:
dict: Updated result dict.
"""
assert 'mix_results' in results
mosaic_labels = []
mosaic_bboxes = []
if len(results['img'].shape) == 3:
mosaic_img = np.full(
(int(self.img_scale[0] * 2), int(self.img_scale[1] * 2), 3),
self.pad_val,
dtype=results['img'].dtype)
else:
mosaic_img = np.full(
(int(self.img_scale[0] * 2), int(self.img_scale[1] * 2)),
self.pad_val,
dtype=results['img'].dtype)
# mosaic center x, y
center_x = int(
random.uniform(*self.center_ratio_range) * self.img_scale[1])
center_y = int(
random.uniform(*self.center_ratio_range) * self.img_scale[0])
center_position = (center_x, center_y)
loc_strs = ('top_left', 'top_right', 'bottom_left', 'bottom_right')
for i, loc in enumerate(loc_strs):
if loc == 'top_left':
results_patch = copy.deepcopy(results)
else:
results_patch = copy.deepcopy(results['mix_results'][i - 1])
img_i = results_patch['img']
h_i, w_i = img_i.shape[:2]
# keep_ratio resize
scale_ratio_i = min(self.img_scale[0] / h_i,
self.img_scale[1] / w_i)
img_i = mmcv.imresize(
img_i, (int(w_i * scale_ratio_i), int(h_i * scale_ratio_i)))
# compute the combine parameters
paste_coord, crop_coord = self._mosaic_combine(
loc, center_position, img_i.shape[:2][::-1])
x1_p, y1_p, x2_p, y2_p = paste_coord
x1_c, y1_c, x2_c, y2_c = crop_coord
# crop and paste image
mosaic_img[y1_p:y2_p, x1_p:x2_p] = img_i[y1_c:y2_c, x1_c:x2_c]
# adjust coordinate
gt_bboxes_i = results_patch['gt_bboxes']
gt_labels_i = results_patch['gt_labels']
if gt_bboxes_i.shape[0] > 0:
padw = x1_p - x1_c
padh = y1_p - y1_c
gt_bboxes_i[:, 0::2] = \
scale_ratio_i * gt_bboxes_i[:, 0::2] + padw
gt_bboxes_i[:, 1::2] = \
scale_ratio_i * gt_bboxes_i[:, 1::2] + padh
mosaic_bboxes.append(gt_bboxes_i)
mosaic_labels.append(gt_labels_i)
if len(mosaic_labels) > 0:
mosaic_bboxes = np.concatenate(mosaic_bboxes, 0)
mosaic_labels = np.concatenate(mosaic_labels, 0)
if self.bbox_clip_border:
mosaic_bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(mosaic_bboxes[:, 0::2], 0,
2 * self.img_scale[1])
mosaic_bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(mosaic_bboxes[:, 1::2], 0,
2 * self.img_scale[0])
if not self.skip_filter:
mosaic_bboxes, mosaic_labels = \
self._filter_box_candidates(mosaic_bboxes, mosaic_labels)
# remove outside bboxes
inside_inds = find_inside_bboxes(mosaic_bboxes, 2 * self.img_scale[0],
2 * self.img_scale[1])
mosaic_bboxes = mosaic_bboxes[inside_inds]
mosaic_labels = mosaic_labels[inside_inds]
results['img'] = mosaic_img
results['img_shape'] = mosaic_img.shape
results['gt_bboxes'] = mosaic_bboxes
results['gt_labels'] = mosaic_labels
return results
def _mosaic_combine(self, loc, center_position_xy, img_shape_wh):
"""Calculate global coordinate of mosaic image and local coordinate of
cropped sub-image.
Args:
loc (str): Index for the sub-image, loc in ('top_left',
'top_right', 'bottom_left', 'bottom_right').
center_position_xy (Sequence[float]): Mixing center for 4 images,
(x, y).
img_shape_wh (Sequence[int]): Width and height of sub-image
Returns:
tuple[tuple[float]]: Corresponding coordinate of pasting and
cropping
- paste_coord (tuple): paste corner coordinate in mosaic image.
- crop_coord (tuple): crop corner coordinate in mosaic image.
"""
assert loc in ('top_left', 'top_right', 'bottom_left', 'bottom_right')
if loc == 'top_left':
# index0 to top left part of image
x1, y1, x2, y2 = max(center_position_xy[0] - img_shape_wh[0], 0), \
max(center_position_xy[1] - img_shape_wh[1], 0), \
center_position_xy[0], \
center_position_xy[1]
crop_coord = img_shape_wh[0] - (x2 - x1), img_shape_wh[1] - (
y2 - y1), img_shape_wh[0], img_shape_wh[1]
elif loc == 'top_right':
# index1 to top right part of image
x1, y1, x2, y2 = center_position_xy[0], \
max(center_position_xy[1] - img_shape_wh[1], 0), \
min(center_position_xy[0] + img_shape_wh[0],
self.img_scale[1] * 2), \
center_position_xy[1]
crop_coord = 0, img_shape_wh[1] - (y2 - y1), min(
img_shape_wh[0], x2 - x1), img_shape_wh[1]
elif loc == 'bottom_left':
# index2 to bottom left part of image
x1, y1, x2, y2 = max(center_position_xy[0] - img_shape_wh[0], 0), \
center_position_xy[1], \
center_position_xy[0], \
min(self.img_scale[0] * 2, center_position_xy[1] +
img_shape_wh[1])
crop_coord = img_shape_wh[0] - (x2 - x1), 0, img_shape_wh[0], min(
y2 - y1, img_shape_wh[1])
else:
# index3 to bottom right part of image
x1, y1, x2, y2 = center_position_xy[0], \
center_position_xy[1], \
min(center_position_xy[0] + img_shape_wh[0],
self.img_scale[1] * 2), \
min(self.img_scale[0] * 2, center_position_xy[1] +
img_shape_wh[1])
crop_coord = 0, 0, min(img_shape_wh[0],
x2 - x1), min(y2 - y1, img_shape_wh[1])
paste_coord = x1, y1, x2, y2
return paste_coord, crop_coord
def _filter_box_candidates(self, bboxes, labels):
"""Filter out bboxes too small after Mosaic."""
bbox_w = bboxes[:, 2] - bboxes[:, 0]
bbox_h = bboxes[:, 3] - bboxes[:, 1]
valid_inds = (bbox_w > self.min_bbox_size) & \
(bbox_h > self.min_bbox_size)
valid_inds = np.nonzero(valid_inds)[0]
return bboxes[valid_inds], labels[valid_inds]
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'img_scale={self.img_scale}, '
repr_str += f'center_ratio_range={self.center_ratio_range}, '
repr_str += f'pad_val={self.pad_val}, '
repr_str += f'min_bbox_size={self.min_bbox_size}, '
repr_str += f'skip_filter={self.skip_filter})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class MixUp:
"""MixUp data augmentation.
.. code:: text
mixup transform
+------------------------------+
| mixup image | |
| +--------|--------+ |
| | | | |
|---------------+ | |
| | | |
| | image | |
| | | |
| | | |
| |-----------------+ |
| pad |
+------------------------------+
The mixup transform steps are as follows:
1. Another random image is picked by dataset and embedded in
the top left patch(after padding and resizing)
2. The target of mixup transform is the weighted average of mixup
image and origin image.
Args:
img_scale (Sequence[int]): Image output size after mixup pipeline.
The shape order should be (height, width). Default: (640, 640).
ratio_range (Sequence[float]): Scale ratio of mixup image.
Default: (0.5, 1.5).
flip_ratio (float): Horizontal flip ratio of mixup image.
Default: 0.5.
pad_val (int): Pad value. Default: 114.
max_iters (int): The maximum number of iterations. If the number of
iterations is greater than `max_iters`, but gt_bbox is still
empty, then the iteration is terminated. Default: 15.
min_bbox_size (float): Width and height threshold to filter bboxes.
If the height or width of a box is smaller than this value, it
will be removed. Default: 5.
min_area_ratio (float): Threshold of area ratio between
original bboxes and wrapped bboxes. If smaller than this value,
the box will be removed. Default: 0.2.
max_aspect_ratio (float): Aspect ratio of width and height
threshold to filter bboxes. If max(h/w, w/h) larger than this
value, the box will be removed. Default: 20.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether to clip the objects outside
the border of the image. In some dataset like MOT17, the gt bboxes
are allowed to cross the border of images. Therefore, we don't
need to clip the gt bboxes in these cases. Defaults to True.
skip_filter (bool): Whether to skip filtering rules. If it
is True, the filter rule will not be applied, and the
`min_bbox_size` and `min_area_ratio` and `max_aspect_ratio`
is invalid. Default to True.
"""
def __init__(self,
img_scale=(640, 640),
ratio_range=(0.5, 1.5),
flip_ratio=0.5,
pad_val=114,
max_iters=15,
min_bbox_size=5,
min_area_ratio=0.2,
max_aspect_ratio=20,
bbox_clip_border=True,
skip_filter=True):
assert isinstance(img_scale, tuple)
log_img_scale(img_scale, skip_square=True)
self.dynamic_scale = img_scale
self.ratio_range = ratio_range
self.flip_ratio = flip_ratio
self.pad_val = pad_val
self.max_iters = max_iters
self.min_bbox_size = min_bbox_size
self.min_area_ratio = min_area_ratio
self.max_aspect_ratio = max_aspect_ratio
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
self.skip_filter = skip_filter
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to make a mixup of image.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with mixup transformed.
"""
results = self._mixup_transform(results)
return results
def get_indexes(self, dataset):
"""Call function to collect indexes.
Args:
dataset (:obj:`MultiImageMixDataset`): The dataset.
Returns:
list: indexes.
"""
for i in range(self.max_iters):
index = random.randint(0, len(dataset))
gt_bboxes_i = dataset.get_ann_info(index)['bboxes']
if len(gt_bboxes_i) != 0:
break
return index
def _mixup_transform(self, results):
"""MixUp transform function.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict.
Returns:
dict: Updated result dict.
"""
assert 'mix_results' in results
assert len(
results['mix_results']) == 1, 'MixUp only support 2 images now !'
if results['mix_results'][0]['gt_bboxes'].shape[0] == 0:
# empty bbox
return results
retrieve_results = results['mix_results'][0]
retrieve_img = retrieve_results['img']
jit_factor = random.uniform(*self.ratio_range)
is_filp = random.uniform(0, 1) > self.flip_ratio
if len(retrieve_img.shape) == 3:
out_img = np.ones(
(self.dynamic_scale[0], self.dynamic_scale[1], 3),
dtype=retrieve_img.dtype) * self.pad_val
else:
out_img = np.ones(
self.dynamic_scale, dtype=retrieve_img.dtype) * self.pad_val
# 1. keep_ratio resize
scale_ratio = min(self.dynamic_scale[0] / retrieve_img.shape[0],
self.dynamic_scale[1] / retrieve_img.shape[1])
retrieve_img = mmcv.imresize(
retrieve_img, (int(retrieve_img.shape[1] * scale_ratio),
int(retrieve_img.shape[0] * scale_ratio)))
# 2. paste
out_img[:retrieve_img.shape[0], :retrieve_img.shape[1]] = retrieve_img
# 3. scale jit
scale_ratio *= jit_factor
out_img = mmcv.imresize(out_img, (int(out_img.shape[1] * jit_factor),
int(out_img.shape[0] * jit_factor)))
# 4. flip
if is_filp:
out_img = out_img[:, ::-1, :]
# 5. random crop
ori_img = results['img']
origin_h, origin_w = out_img.shape[:2]
target_h, target_w = ori_img.shape[:2]
padded_img = np.zeros(
(max(origin_h, target_h), max(origin_w,
target_w), 3)).astype(np.uint8)
padded_img[:origin_h, :origin_w] = out_img
x_offset, y_offset = 0, 0
if padded_img.shape[0] > target_h:
y_offset = random.randint(0, padded_img.shape[0] - target_h)
if padded_img.shape[1] > target_w:
x_offset = random.randint(0, padded_img.shape[1] - target_w)
padded_cropped_img = padded_img[y_offset:y_offset + target_h,
x_offset:x_offset + target_w]
# 6. adjust bbox
retrieve_gt_bboxes = retrieve_results['gt_bboxes']
retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] * scale_ratio
retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] * scale_ratio
if self.bbox_clip_border:
retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2],
0, origin_w)
retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2],
0, origin_h)
if is_filp:
retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = (
origin_w - retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2][:, ::-1])
# 7. filter
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes = retrieve_gt_bboxes.copy()
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = \
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] - x_offset
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = \
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] - y_offset
if self.bbox_clip_border:
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 0::2], 0, target_w)
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[:, 1::2], 0, target_h)
# 8. mix up
ori_img = ori_img.astype(np.float32)
mixup_img = 0.5 * ori_img + 0.5 * padded_cropped_img.astype(np.float32)
retrieve_gt_labels = retrieve_results['gt_labels']
if not self.skip_filter:
keep_list = self._filter_box_candidates(retrieve_gt_bboxes.T,
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes.T)
retrieve_gt_labels = retrieve_gt_labels[keep_list]
cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes = cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes[keep_list]
mixup_gt_bboxes = np.concatenate(
(results['gt_bboxes'], cp_retrieve_gt_bboxes), axis=0)
mixup_gt_labels = np.concatenate(
(results['gt_labels'], retrieve_gt_labels), axis=0)
# remove outside bbox
inside_inds = find_inside_bboxes(mixup_gt_bboxes, target_h, target_w)
mixup_gt_bboxes = mixup_gt_bboxes[inside_inds]
mixup_gt_labels = mixup_gt_labels[inside_inds]
results['img'] = mixup_img.astype(np.uint8)
results['img_shape'] = mixup_img.shape
results['gt_bboxes'] = mixup_gt_bboxes
results['gt_labels'] = mixup_gt_labels
return results
def _filter_box_candidates(self, bbox1, bbox2):
"""Compute candidate boxes which include following 5 things:
bbox1 before augment, bbox2 after augment, min_bbox_size (pixels),
min_area_ratio, max_aspect_ratio.
"""
w1, h1 = bbox1[2] - bbox1[0], bbox1[3] - bbox1[1]
w2, h2 = bbox2[2] - bbox2[0], bbox2[3] - bbox2[1]
ar = np.maximum(w2 / (h2 + 1e-16), h2 / (w2 + 1e-16))
return ((w2 > self.min_bbox_size)
& (h2 > self.min_bbox_size)
& (w2 * h2 / (w1 * h1 + 1e-16) > self.min_area_ratio)
& (ar < self.max_aspect_ratio))
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'dynamic_scale={self.dynamic_scale}, '
repr_str += f'ratio_range={self.ratio_range}, '
repr_str += f'flip_ratio={self.flip_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'pad_val={self.pad_val}, '
repr_str += f'max_iters={self.max_iters}, '
repr_str += f'min_bbox_size={self.min_bbox_size}, '
repr_str += f'min_area_ratio={self.min_area_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'max_aspect_ratio={self.max_aspect_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'skip_filter={self.skip_filter})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class RandomAffine:
"""Random affine transform data augmentation.
This operation randomly generates affine transform matrix which including
rotation, translation, shear and scaling transforms.
Args:
max_rotate_degree (float): Maximum degrees of rotation transform.
Default: 10.
max_translate_ratio (float): Maximum ratio of translation.
Default: 0.1.
scaling_ratio_range (tuple[float]): Min and max ratio of
scaling transform. Default: (0.5, 1.5).
max_shear_degree (float): Maximum degrees of shear
transform. Default: 2.
border (tuple[int]): Distance from height and width sides of input
image to adjust output shape. Only used in mosaic dataset.
Default: (0, 0).
border_val (tuple[int]): Border padding values of 3 channels.
Default: (114, 114, 114).
min_bbox_size (float): Width and height threshold to filter bboxes.
If the height or width of a box is smaller than this value, it
will be removed. Default: 2.
min_area_ratio (float): Threshold of area ratio between
original bboxes and wrapped bboxes. If smaller than this value,
the box will be removed. Default: 0.2.
max_aspect_ratio (float): Aspect ratio of width and height
threshold to filter bboxes. If max(h/w, w/h) larger than this
value, the box will be removed.
bbox_clip_border (bool, optional): Whether to clip the objects outside
the border of the image. In some dataset like MOT17, the gt bboxes
are allowed to cross the border of images. Therefore, we don't
need to clip the gt bboxes in these cases. Defaults to True.
skip_filter (bool): Whether to skip filtering rules. If it
is True, the filter rule will not be applied, and the
`min_bbox_size` and `min_area_ratio` and `max_aspect_ratio`
is invalid. Default to True.
"""
def __init__(self,
max_rotate_degree=10.0,
max_translate_ratio=0.1,
scaling_ratio_range=(0.5, 1.5),
max_shear_degree=2.0,
border=(0, 0),
border_val=(114, 114, 114),
min_bbox_size=2,
min_area_ratio=0.2,
max_aspect_ratio=20,
bbox_clip_border=True,
skip_filter=True):
assert 0 <= max_translate_ratio <= 1
assert scaling_ratio_range[0] <= scaling_ratio_range[1]
assert scaling_ratio_range[0] > 0
self.max_rotate_degree = max_rotate_degree
self.max_translate_ratio = max_translate_ratio
self.scaling_ratio_range = scaling_ratio_range
self.max_shear_degree = max_shear_degree
self.border = border
self.border_val = border_val
self.min_bbox_size = min_bbox_size
self.min_area_ratio = min_area_ratio
self.max_aspect_ratio = max_aspect_ratio
self.bbox_clip_border = bbox_clip_border
self.skip_filter = skip_filter
def __call__(self, results):
img = results['img']
height = img.shape[0] + self.border[0] * 2
width = img.shape[1] + self.border[1] * 2
# Rotation
rotation_degree = random.uniform(-self.max_rotate_degree,
self.max_rotate_degree)
rotation_matrix = self._get_rotation_matrix(rotation_degree)
# Scaling
scaling_ratio = random.uniform(self.scaling_ratio_range[0],
self.scaling_ratio_range[1])
scaling_matrix = self._get_scaling_matrix(scaling_ratio)
# Shear
x_degree = random.uniform(-self.max_shear_degree,
self.max_shear_degree)
y_degree = random.uniform(-self.max_shear_degree,
self.max_shear_degree)
shear_matrix = self._get_shear_matrix(x_degree, y_degree)
# Translation
trans_x = random.uniform(-self.max_translate_ratio,
self.max_translate_ratio) * width
trans_y = random.uniform(-self.max_translate_ratio,
self.max_translate_ratio) * height
translate_matrix = self._get_translation_matrix(trans_x, trans_y)
warp_matrix = (
translate_matrix @ shear_matrix @ rotation_matrix @ scaling_matrix)
img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img,
warp_matrix,
dsize=(width, height),
borderValue=self.border_val)
results['img'] = img
results['img_shape'] = img.shape
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
bboxes = results[key]
num_bboxes = len(bboxes)
if num_bboxes:
# homogeneous coordinates
xs = bboxes[:, [0, 0, 2, 2]].reshape(num_bboxes * 4)
ys = bboxes[:, [1, 3, 3, 1]].reshape(num_bboxes * 4)
ones = np.ones_like(xs)
points = np.vstack([xs, ys, ones])
warp_points = warp_matrix @ points
warp_points = warp_points[:2] / warp_points[2]
xs = warp_points[0].reshape(num_bboxes, 4)
ys = warp_points[1].reshape(num_bboxes, 4)
warp_bboxes = np.vstack(
(xs.min(1), ys.min(1), xs.max(1), ys.max(1))).T
if self.bbox_clip_border:
warp_bboxes[:, [0, 2]] = \
warp_bboxes[:, [0, 2]].clip(0, width)
warp_bboxes[:, [1, 3]] = \
warp_bboxes[:, [1, 3]].clip(0, height)
# remove outside bbox
valid_index = find_inside_bboxes(warp_bboxes, height, width)
if not self.skip_filter:
# filter bboxes
filter_index = self.filter_gt_bboxes(
bboxes * scaling_ratio, warp_bboxes)
valid_index = valid_index & filter_index
results[key] = warp_bboxes[valid_index]
if key in ['gt_bboxes']:
if 'gt_labels' in results:
results['gt_labels'] = results['gt_labels'][
valid_index]
if 'gt_masks' in results:
raise NotImplementedError(
'RandomAffine only supports bbox.')
return results
def filter_gt_bboxes(self, origin_bboxes, wrapped_bboxes):
origin_w = origin_bboxes[:, 2] - origin_bboxes[:, 0]
origin_h = origin_bboxes[:, 3] - origin_bboxes[:, 1]
wrapped_w = wrapped_bboxes[:, 2] - wrapped_bboxes[:, 0]
wrapped_h = wrapped_bboxes[:, 3] - wrapped_bboxes[:, 1]
aspect_ratio = np.maximum(wrapped_w / (wrapped_h + 1e-16),
wrapped_h / (wrapped_w + 1e-16))
wh_valid_idx = (wrapped_w > self.min_bbox_size) & \
(wrapped_h > self.min_bbox_size)
area_valid_idx = wrapped_w * wrapped_h / (origin_w * origin_h +
1e-16) > self.min_area_ratio
aspect_ratio_valid_idx = aspect_ratio < self.max_aspect_ratio
return wh_valid_idx & area_valid_idx & aspect_ratio_valid_idx
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(max_rotate_degree={self.max_rotate_degree}, '
repr_str += f'max_translate_ratio={self.max_translate_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'scaling_ratio={self.scaling_ratio_range}, '
repr_str += f'max_shear_degree={self.max_shear_degree}, '
repr_str += f'border={self.border}, '
repr_str += f'border_val={self.border_val}, '
repr_str += f'min_bbox_size={self.min_bbox_size}, '
repr_str += f'min_area_ratio={self.min_area_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'max_aspect_ratio={self.max_aspect_ratio}, '
repr_str += f'skip_filter={self.skip_filter})'
return repr_str
@staticmethod
def _get_rotation_matrix(rotate_degrees):
radian = math.radians(rotate_degrees)
rotation_matrix = np.array(
[[np.cos(radian), -np.sin(radian), 0.],
[np.sin(radian), np.cos(radian), 0.], [0., 0., 1.]],
dtype=np.float32)
return rotation_matrix
@staticmethod
def _get_scaling_matrix(scale_ratio):
scaling_matrix = np.array(
[[scale_ratio, 0., 0.], [0., scale_ratio, 0.], [0., 0., 1.]],
dtype=np.float32)
return scaling_matrix
@staticmethod
def _get_share_matrix(scale_ratio):
scaling_matrix = np.array(
[[scale_ratio, 0., 0.], [0., scale_ratio, 0.], [0., 0., 1.]],
dtype=np.float32)
return scaling_matrix
@staticmethod
def _get_shear_matrix(x_shear_degrees, y_shear_degrees):
x_radian = math.radians(x_shear_degrees)
y_radian = math.radians(y_shear_degrees)
shear_matrix = np.array([[1, np.tan(x_radian), 0.],
[np.tan(y_radian), 1, 0.], [0., 0., 1.]],
dtype=np.float32)
return shear_matrix
@staticmethod
def _get_translation_matrix(x, y):
translation_matrix = np.array([[1, 0., x], [0., 1, y], [0., 0., 1.]],
dtype=np.float32)
return translation_matrix
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class YOLOXHSVRandomAug:
"""Apply HSV augmentation to image sequentially. It is referenced from
https://github.com/Megvii-
BaseDetection/YOLOX/blob/main/yolox/data/data_augment.py#L21.
Args:
hue_delta (int): delta of hue. Default: 5.
saturation_delta (int): delta of saturation. Default: 30.
value_delta (int): delat of value. Default: 30.
"""
def __init__(self, hue_delta=5, saturation_delta=30, value_delta=30):
self.hue_delta = hue_delta
self.saturation_delta = saturation_delta
self.value_delta = value_delta
def __call__(self, results):
img = results['img']
hsv_gains = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [
self.hue_delta, self.saturation_delta, self.value_delta
]
# random selection of h, s, v
hsv_gains *= np.random.randint(0, 2, 3)
# prevent overflow
hsv_gains = hsv_gains.astype(np.int16)
img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV).astype(np.int16)
img_hsv[..., 0] = (img_hsv[..., 0] + hsv_gains[0]) % 180
img_hsv[..., 1] = np.clip(img_hsv[..., 1] + hsv_gains[1], 0, 255)
img_hsv[..., 2] = np.clip(img_hsv[..., 2] + hsv_gains[2], 0, 255)
cv2.cvtColor(img_hsv.astype(img.dtype), cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=img)
results['img'] = img
return results
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'(hue_delta={self.hue_delta}, '
repr_str += f'saturation_delta={self.saturation_delta}, '
repr_str += f'value_delta={self.value_delta})'
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module()
class CopyPaste:
"""Simple Copy-Paste is a Strong Data Augmentation Method for Instance
Segmentation The simple copy-paste transform steps are as follows:
1. The destination image is already resized with aspect ratio kept,
cropped and padded.
2. Randomly select a source image, which is also already resized
with aspect ratio kept, cropped and padded in a similar way
as the destination image.
3. Randomly select some objects from the source image.
4. Paste these source objects to the destination image directly,
due to the source and destination image have the same size.
5. Update object masks of the destination image, for some origin objects
may be occluded.
6. Generate bboxes from the updated destination masks and
filter some objects which are totally occluded, and adjust bboxes
which are partly occluded.
7. Append selected source bboxes, masks, and labels.
Args:
max_num_pasted (int): The maximum number of pasted objects.
Default: 100.
bbox_occluded_thr (int): The threshold of occluded bbox.
Default: 10.
mask_occluded_thr (int): The threshold of occluded mask.
Default: 300.
selected (bool): Whether select objects or not. If select is False,
all objects of the source image will be pasted to the
destination image.
Default: True.
"""
def __init__(
self,
max_num_pasted=100,
bbox_occluded_thr=10,
mask_occluded_thr=300,
selected=True,
):
self.max_num_pasted = max_num_pasted
self.bbox_occluded_thr = bbox_occluded_thr
self.mask_occluded_thr = mask_occluded_thr
self.selected = selected
def get_indexes(self, dataset):
"""Call function to collect indexes.s.
Args:
dataset (:obj:`MultiImageMixDataset`): The dataset.
Returns:
list: Indexes.
"""
return random.randint(0, len(dataset))
def __call__(self, results):
"""Call function to make a copy-paste of image.
Args:
results (dict): Result dict.
Returns:
dict: Result dict with copy-paste transformed.
"""
assert 'mix_results' in results
num_images = len(results['mix_results'])
assert num_images == 1, \
f'CopyPaste only supports processing 2 images, got {num_images}'
if self.selected:
selected_results = self._select_object(results['mix_results'][0])
else:
selected_results = results['mix_results'][0]
return self._copy_paste(results, selected_results)
def _select_object(self, results):
"""Select some objects from the source results."""
bboxes = results['gt_bboxes']
labels = results['gt_labels']
masks = results['gt_masks']
max_num_pasted = min(bboxes.shape[0] + 1, self.max_num_pasted)
num_pasted = np.random.randint(0, max_num_pasted)
selected_inds = np.random.choice(
bboxes.shape[0], size=num_pasted, replace=False)
selected_bboxes = bboxes[selected_inds]
selected_labels = labels[selected_inds]
selected_masks = masks[selected_inds]
results['gt_bboxes'] = selected_bboxes
results['gt_labels'] = selected_labels
results['gt_masks'] = selected_masks
return results
def _copy_paste(self, dst_results, src_results):
"""CopyPaste transform function.
Args:
dst_results (dict): Result dict of the destination image.
src_results (dict): Result dict of the source image.
Returns:
dict: Updated result dict.
"""
dst_img = dst_results['img']
dst_bboxes = dst_results['gt_bboxes']
dst_labels = dst_results['gt_labels']
dst_masks = dst_results['gt_masks']
src_img = src_results['img']
src_bboxes = src_results['gt_bboxes']
src_labels = src_results['gt_labels']
src_masks = src_results['gt_masks']
if len(src_bboxes) == 0:
return dst_results
# update masks and generate bboxes from updated masks
composed_mask = np.where(np.any(src_masks.masks, axis=0), 1, 0)
updated_dst_masks = self.get_updated_masks(dst_masks, composed_mask)
updated_dst_bboxes = updated_dst_masks.get_bboxes()
assert len(updated_dst_bboxes) == len(updated_dst_masks)
# filter totally occluded objects
bboxes_inds = np.all(
np.abs(
(updated_dst_bboxes - dst_bboxes)) <= self.bbox_occluded_thr,
axis=-1)
masks_inds = updated_dst_masks.masks.sum(
axis=(1, 2)) > self.mask_occluded_thr
valid_inds = bboxes_inds | masks_inds
# Paste source objects to destination image directly
img = dst_img * (1 - composed_mask[..., np.newaxis]
) + src_img * composed_mask[..., np.newaxis]
bboxes = np.concatenate([updated_dst_bboxes[valid_inds], src_bboxes])
labels = np.concatenate([dst_labels[valid_inds], src_labels])
masks = np.concatenate(
[updated_dst_masks.masks[valid_inds], src_masks.masks])
dst_results['img'] = img
dst_results['gt_bboxes'] = bboxes
dst_results['gt_labels'] = labels
dst_results['gt_masks'] = BitmapMasks(masks, masks.shape[1],
masks.shape[2])
return dst_results
def get_updated_masks(self, masks, composed_mask):
assert masks.masks.shape[-2:] == composed_mask.shape[-2:], \
'Cannot compare two arrays of different size'
masks.masks = np.where(composed_mask, 0, masks.masks)
return masks
def __repr__(self):
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += f'max_num_pasted={self.max_num_pasted}, '
repr_str += f'bbox_occluded_thr={self.bbox_occluded_thr}, '
repr_str += f'mask_occluded_thr={self.mask_occluded_thr}, '
repr_str += f'selected={self.selected}, '
return repr_str
2、mmdet/datasets/pipelines/init.py源码
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
from .auto_augment import (AutoAugment, BrightnessTransform, ColorTransform,
ContrastTransform, EqualizeTransform, Rotate, Shear,
Translate)
from .compose import Compose
from .formatting import (Collect, DefaultFormatBundle, ImageToTensor,
ToDataContainer, ToTensor, Transpose, to_tensor)
from .instaboost import InstaBoost
from .loading import (LoadAnnotations, LoadImageFromFile, LoadImageFromWebcam,
LoadMultiChannelImageFromFiles, LoadPanopticAnnotations,
LoadProposals)
from .test_time_aug import MultiScaleFlipAug
from .transforms import (Albu, CopyPaste, CutOut, Expand, MinIoURandomCrop,
MixUp, Mosaic, Normalize, Pad, PhotoMetricDistortion,
RandomAffine, RandomCenterCropPad, RandomCrop,
RandomFlip, RandomShift, Resize, SegRescale,
YOLOXHSVRandomAug)
__all__ = [
'Compose', 'to_tensor', 'ToTensor', 'ImageToTensor', 'ToDataContainer',
'Transpose', 'Collect', 'DefaultFormatBundle', 'LoadAnnotations',
'LoadImageFromFile', 'LoadImageFromWebcam', 'LoadPanopticAnnotations',
'LoadMultiChannelImageFromFiles', 'LoadProposals', 'MultiScaleFlipAug',
'Resize', 'RandomFlip', 'Pad', 'RandomCrop', 'Normalize', 'SegRescale',
'MinIoURandomCrop', 'Expand', 'PhotoMetricDistortion', 'Albu',
'InstaBoost', 'RandomCenterCropPad', 'AutoAugment', 'CutOut', 'Shear',
'Rotate', 'ColorTransform', 'EqualizeTransform', 'BrightnessTransform',
'ContrastTransform', 'Translate', 'RandomShift', 'Mosaic', 'MixUp',
'RandomAffine', 'YOLOXHSVRandomAug', 'CopyPaste'
]
3、配置文件引入albumentations数据增强库进行增强
#只需要将albu的transform定义出来放到train_pipeline即可
albu_train_transforms = [
dict(
type='ShiftScaleRotate',
shift_limit=0.0625,
scale_limit=0.0,
rotate_limit=0,
interpolation=1,
p=0.5),
dict(
type='RandomBrightnessContrast',
brightness_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
contrast_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
p=0.2),
dict(
type='OneOf',
transforms=[
dict(
type='RGBShift',
r_shift_limit=10,
g_shift_limit=10,
b_shift_limit=10,
p=1.0),
dict(
type='HueSaturationValue',
hue_shift_limit=20,
sat_shift_limit=30,
val_shift_limit=20,
p=1.0)
],
p=0.1),
dict(type='JpegCompression', quality_lower=85, quality_upper=95, p=0.2),
dict(type='ChannelShuffle', p=0.1),
dict(
type='OneOf',
transforms=[
dict(type='Blur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0),
dict(type='MedianBlur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0)
],
p=0.1),
]
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True, with_mask=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(
type='Albu',
transforms=albu_train_transforms,
bbox_params=dict(
type='BboxParams',
format='pascal_voc',
label_fields=['gt_labels'],
min_visibility=0.0,
filter_lost_elements=True),
keymap={
'img': 'image',
'gt_masks': 'masks',
'gt_bboxes': 'bboxes'
},
update_pad_shape=False,
skip_img_without_anno=True),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(
type='Collect',
keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels', 'gt_masks'],
meta_keys=('filename', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape', 'img_norm_cfg',
'pad_shape', 'scale_factor'))
]
data = dict(train=dict(pipeline=train_pipeline))
albu_train_transforms = [
# dict(
# type='HorizontalFlip',
# p=0.5),
# dict(
# type='VerticalFlip',
# p=0.5),
dict(
type='ShiftScaleRotate',
shift_limit=0.0625,
scale_limit=0.0,
rotate_limit=180,
interpolation=1,
p=0.5),
# dict(
# type='RandomBrightnessContrast',
# brightness_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
# contrast_limit=[0.1, 0.3],
# p=0.2),
# dict(
# type='OneOf',
# transforms=[
# dict(
# type='RGBShift',
# r_shift_limit=10,
# g_shift_limit=10,
# b_shift_limit=10,
# p=1.0),
# dict(
# type='HueSaturationValue',
# hue_shift_limit=20,
# sat_shift_limit=30,
# val_shift_limit=20,
# p=1.0)
# ],
# p=0.1),
# # dict(type='JpegCompression', quality_lower=85, quality_upper=95, p=0.2),
#
# dict(type='ChannelShuffle', p=0.1),
# dict(
# type='OneOf',
# transforms=[
# dict(type='Blur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0),
# dict(type='MedianBlur', blur_limit=3, p=1.0)
# ],
# p=0.1),
]
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=[(4096, 800), (4096, 1200)], keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(
type='Albu',
transforms=albu_train_transforms,
bbox_params=dict(
type='BboxParams',
format='pascal_voc',
label_fields=['gt_labels'],
min_visibility=0.0,
filter_lost_elements=True),
keymap={
'img': 'image',
'gt_bboxes': 'bboxes'
},
update_pad_shape=False,
skip_img_without_anno=True),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(
type='Collect',
keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels'],
meta_keys=('filename', 'ori_shape', 'img_shape', 'img_norm_cfg',
'pad_shape', 'scale_factor')
)
]
2、MMDetection自带数据增强进行增强
源码在mmdet\datasets\pipelines里面,包括RandomCrop、brightness、contrast、saturation、ExtraAugmentation等等图像增强方法。
添加位置是train_pipeline或test_pipeline这个地方(一般train进行增强而test不需要),例如数据增强RandomFlip,flip_ratio代表随机翻转的概率:
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 800),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
3、MMDetection自定义数据增强进行增强
MMDetection 系列之(自定义数据管道处理增强管道)
数据增强这部分的操作比较多,主要用了有监督数据增强方式中的单样本数据增强以及多样本数据增强(其实就是把yolov5的数据增强tricks全搬过来了)。
单样本数据增强:HSV色域增强、仿射变换(Center/Perspective/Rotation/Scale/ Shear/Translate,其实只用到了Translate)、随机裁剪、随机旋转、随机尺度变换、随机翻转;
多样本数据增强:Mosaic + Mixup;(Mixup这里采用的不是贴图的方式而是普通意义上的图像融合,主要是poly标注得抠像素,不想自己写代码)
上述代码均在mmdetection框架下完成,大家可以根据具体场景任意组合train_pipeline并更改先后顺序,我在比赛时使用的train_pipeline顺序为:
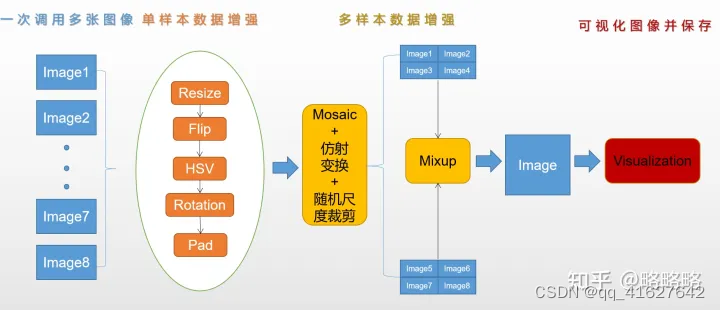
以上Tricks全部生效后的数据增强可视化图。
注意1:Mosaic + Rotation两者会相互抑制,如下图所示Mosaic的输出图像中间有一大片像素缺失区域,比赛中我的处理方式是触发Mosaic时必定触发Mixup。
注意2:Mosaic + Mixup会改变原始数据的输入分布,因此训练时可以参考YoloX的做法,在训练后期关闭多样本数据增强继续训练,此时的精度提升就十分明显。(具体提升多少确实忘了,表格数据在内网,而且此次比赛没用上,因为YoloX是我比赛后才看的,在安检数据集上测试了下,resume权重并以数据原始分布再训几个epoch的精度提升大概在0.5)
在mmdet\datasets\pipelines新建poly_transforms.py(旋转框目标检测增强方法)
import numpy as np
from ..registry import PIPELINES
import cv2
import mmcv
import random
from mmdet.core import poly2rbox, rbox2poly
import math
from collections import Counter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import copy
plt.set_loglevel('WARNING')
@PIPELINES.register_module
class CorrectRBBox(object):
"""
Correct gt_bboxes, turn gt_bboxes(n, 8) to rotate rectangle(n, 8).
Args:
correct_rbbox (bool): Whether to shape the gt_bboxes(n, 8) to be rotate rectangle(n, 8).
refine_rbbox(bool): Whether to keep the original points order.
"""
def __init__(self, correct_rbbox=True, refine_rbbox=False):
self.correct_rbbox = correct_rbbox
self.refine_rbbox = refine_rbbox
# correct_rbbox: 是否将任意四点坐标correct成最小外界矩形 refine_rbbox: 是否更改四点坐标的先后顺序
def _correct_rbbox(self, gt_rbboxes_points, refine_rbbox=False): # gt_rbboxes_points:(n, 8)
gt_bboxes_points_correct = []
for rbbox_points in gt_rbboxes_points: # rbbox_points:array.shape(8)
rbbox_points_4x2 = rbbox_points.astype(np.int64).reshape(4, 2)
rbbox_xywht = cv2.minAreaRect(rbbox_points_4x2)
x_ctr, y_ctr, width, height, theta = rbbox_xywht[0][0], rbbox_xywht[0][1], \
rbbox_xywht[1][0], rbbox_xywht[1][1], rbbox_xywht[2]
rbbox_points = cv2.boxPoints(((x_ctr, y_ctr), (width, height), theta)).reshape(-1) # rbbox_points:(8)
if refine_rbbox:
min_dist = 1e8
for i, rbbox_point in enumerate(rbbox_points.reshape(4, 2)):
ori_x1, ori_y1 = rbbox_points_4x2[0]
cur_x1, cur_y1 = rbbox_point
dist = np.sqrt((ori_x1 - cur_x1) ** 2 + (ori_y1 - cur_y1) ** 2)
if dist <= min_dist:
min_dist = dist
index = i
gt_bboxes_correct = np.array([ # gt_bboxes_correct: array.shape(8)
rbbox_points[2 * (index % 4)], rbbox_points[2 * (index % 4) + 1],
rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 1) % 4)], rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 1) % 4) + 1],
rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 2) % 4)], rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 2) % 4) + 1],
rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 3) % 4)], rbbox_points[2 * ((index + 3) % 4) + 1],
])
gt_bboxes_points_correct.append(gt_bboxes_correct)
else:
gt_bboxes_points_correct.append(rbbox_points)
return np.array(gt_bboxes_points_correct) # return array.shape(n, 8)
def normal_call(self, results):
gt_rbboxes_points = results['gt_bboxes'] # results['gt_bboxes'] (n, 8)
gt_rbboxes_points_correct = self._correct_rbbox(gt_rbboxes_points, self.refine_rbbox) # gt_rbboxes_points_correct: array.shape(n, 8)
results['gt_bboxes'] = gt_rbboxes_points_correct.astype(np.float32)
return results
def multi_img_call(self, results_4or9):
for results in results_4or9:
gt_rbboxes_points = results['gt_bboxes'] # results['gt_bboxes'] (n, 8)
gt_rbboxes_points_correct = self._correct_rbbox(gt_rbboxes_points, self.refine_rbbox) # gt_rbboxes_points_correct: array.shape(n, 8)
results['gt_bboxes'] = gt_rbboxes_points_correct.astype(np.float32)
return results_4or9
def __call__(self, results):
if self.correct_rbbox:
if not isinstance(results, list):
results = self.normal_call(results)
else:
results = self.multi_img_call(results)
return results
def __repr__(self): # 实例化对象时,可以获得自我描述信息
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += ('(correct_rbbox={}, refine_rbbox={})').format(self.correct_rbbox,
self.refine_rbbox)
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module
class PolyResize(object):
def __init__(self,
img_scale=None,
multiscale_mode='range',
ratio_range=None,
keep_ratio=True,
clamp_rbbox=True, # False
interpolation='bilinear'):
"""
Resize poly format labels(n, 8) and images.
Args:
img_scale (tuple or list[tuple]): Images scales for resizing.
multiscale_mode (str): Either "range" or "value".
ratio_range (tuple[float]): (min_ratio, max_ratio)
keep_ratio (bool): Whether to keep the aspect ratio when resizing the
image. Defaults to True.
clamp_rbbox(bool, optional): Whether clip the objects outside
the border of the image. Defaults to True.
interpolation: Interpolation method, accepted values are
"nearest", "bilinear", "bicubic", "area", "lanczos".
"""
self.clamp_rbbox = clamp_rbbox
self.interpolation = interpolation
if img_scale is None:
self.img_scale = None
else:
if isinstance(img_scale, list): # img_scale=[(1333, 768), (1333, 1280)]
self.img_scale = img_scale
else:
self.img_scale = [img_scale]
assert mmcv.is_list_of(self.img_scale, tuple)
if ratio_range is not None:
# mode 1: given a scale and a range of image ratio
assert len(self.img_scale) == 1
else:
# mode 2: given multiple scales or a range of scales
assert multiscale_mode in ['value', 'range']
self.multiscale_mode = multiscale_mode
self.ratio_range = ratio_range
self.keep_ratio = keep_ratio
@staticmethod
def random_select(img_scales):
assert mmcv.is_list_of(img_scales, tuple)
scale_idx = np.random.randint(len(img_scales))
img_scale = img_scales[scale_idx]
return img_scale, scale_idx
@staticmethod
def random_sample(img_scales): # img_scale=[(1333, 768), (1333, 1280)]
assert mmcv.is_list_of(img_scales, tuple) and len(img_scales) == 2
img_scale_long = [max(s) for s in img_scales] # 最大边 [max, max]
# print('##############')
# print('img_scale_long', img_scale_long)
img_scale_short = [min(s) for s in img_scales] # 最小边 [min, min]
# print('img_scale_short', img_scale_short)
long_edge = np.random.randint(
min(img_scale_long),
max(img_scale_long) + 1)
# print('long_edge', long_edge)
short_edge = np.random.randint(
min(img_scale_short),
max(img_scale_short) + 1)
# print('short_edge', short_edge)
img_scale = (long_edge, short_edge)
# print('img_scale', img_scale)
return img_scale, None
@staticmethod
def random_sample_ratio(img_scale, ratio_range):
assert isinstance(img_scale, tuple) and len(img_scale) == 2
min_ratio, max_ratio = ratio_range
assert min_ratio <= max_ratio
ratio = np.random.random_sample() * (max_ratio - min_ratio) + min_ratio
scale = int(img_scale[0] * ratio), int(img_scale[1] * ratio)
return scale, None
def _random_scale(self, results):
if self.ratio_range is not None:
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample_ratio(
self.img_scale[0], self.ratio_range)
elif len(self.img_scale) == 1: # img_scale=[(1333, 768), (1333, 1280)]
scale, scale_idx = self.img_scale[0], 0
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'range':
scale, scale_idx = self.random_sample(self.img_scale) # return img_scale = (long_edge, short_edge), None
elif self.multiscale_mode == 'value':
scale, scale_idx = self.random_select(self.img_scale)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
results['scale'] = scale # results['scale'] = (long_edge, short_edge)
results['scale_idx'] = scale_idx # results['scale_idx'] = None
def _resize_img(self, results):
if self.keep_ratio:
img, scale_factor = mmcv.imrescale(
results['img'], results['scale'], return_scale=True, interpolation=self.interpolation)
else:
img, w_scale, h_scale = mmcv.imresize(
results['img'], results['scale'], return_scale=True, interpolation=self.interpolation)
scale_factor = np.array([w_scale, h_scale, w_scale, h_scale],
dtype=np.float32)
results['img'] = img
results['img_shape'] = img.shape
results['pad_shape'] = img.shape # in case that there is no padding
results['scale_factor'] = scale_factor
results['keep_ratio'] = self.keep_ratio
def _resize_bboxes(self, results, clamp_rbbox=True):
img_shape = results['img_shape']
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
bboxes = results[key] * results['scale_factor']
if clamp_rbbox:
bboxes[:, 0::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 0::2], 0, img_shape[1] - 1)
bboxes[:, 1::2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 1::2], 0, img_shape[0] - 1)
results[key] = bboxes
def normal_call(self, results):
if 'scale' not in results:
self._random_scale(results) # 给results['scale_idx'] 和 results['scale']赋值
else: # test_aug
assert len(results['scale']) == 2 # (2048, 1333)
edge1 = np.random.randint(
min(results['scale']),
max(results['scale']) + 1)
edge2 = np.random.randint(
min(results['scale']),
max(results['scale']) + 1)
results['scale'] = (max(edge1, edge2)+1, min(edge1, edge2))
self._resize_img(results)
self._resize_bboxes(results, self.clamp_rbbox)
return results
def multi_img_call(self, results_4or9):
for results in results_4or9:
if 'scale' not in results:
self._random_scale(results) # 随机采样scale并给results['scale_idx'] 和 results['scale']赋值
self._resize_img(results) # 等ratio的随机比例缩放
self._resize_bboxes(results, self.clamp_rbbox) #
return results_4or9
def __call__(self, results):
if not isinstance(results, list):
results = self.normal_call(results)
else:
results = self.multi_img_call(results)
return results
def __repr__(self): # 实例化对象时,可以获得自我描述信息
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += ('(img_scale={}, multiscale_mode={}, ratio_range={}, '
'keep_ratio={}, clamp_rbbox={}, interpolation={})').format(self.img_scale,
self.multiscale_mode,
self.ratio_range,
self.keep_ratio,
self.clamp_rbbox,
self.interpolation)
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module
class PolyRandomFlip(object):
"""Flip the image & bbox(n, 8)
If the input dict contains the key "flip", then the flag will be used,
otherwise it will be randomly decided by a ratio specified in the init
method.
Args:
flip_ratio (float, optional): The flipping probability.
Default: None.
direction (list[str]): The flipping direction. Options
are 'horizontal', 'vertical'.
"""
def __init__(self, flip_ratio=None, direction=['horizontal', 'vertical']):
self.flip_ratio = flip_ratio
self.direction = direction
# assert isinstance(direction, list)
if flip_ratio is not None:
assert flip_ratio >= 0 and flip_ratio <= 1
for d in self.direction:
assert d in ['horizontal', 'vertical']
# assert direction in ['horizontal', 'vertical']
def rbbox_flip(self, rbboxes, img_shape, direction):
"""Flip bboxes horizontally.
Args:
rbboxes(ndarray): shape (..., 8*k)
img_shape(tuple): (height, width)
"""
assert rbboxes.shape[-1] % 8 == 0
flipped = rbboxes.copy()
if direction == 'horizontal':
w = img_shape[1]
flipped[..., 0::8] = w - rbboxes[..., 0::8] - 1
flipped[..., 2::8] = w - rbboxes[..., 2::8] - 1
flipped[..., 4::8] = w - rbboxes[..., 4::8] - 1
flipped[..., 6::8] = w - rbboxes[..., 6::8] - 1
elif direction == 'vertical':
h = img_shape[0]
flipped[..., 1::8] = h - rbboxes[..., 1::8] - 1
flipped[..., 3::8] = h - rbboxes[..., 3::8] - 1
flipped[..., 5::8] = h - rbboxes[..., 5::8] - 1
flipped[..., 7::8] = h - rbboxes[..., 7::8] - 1
else:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid flipping direction "{}"'.format(direction))
return flipped
def normal_call(self, results):
if 'flip' not in results:
flip = True if np.random.rand() < self.flip_ratio else False
results['flip'] = flip
#if 'flip_direction' not in results:
results['flip_direction'] = random.sample(self.direction, 1)[0]
# results['flip_direction'] = self.direction
if results['flip']:
# flip image
results['img'] = mmcv.imflip(
results['img'], direction=results['flip_direction'])
# flip bboxes
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
results[key] = self.rbbox_flip(results[key],
results['img_shape'],
results['flip_direction'])
return results
def multi_img_call(self, results_4or9):
for results in results_4or9:
if 'flip' not in results:
flip = True if np.random.rand() < self.flip_ratio else False
results['flip'] = flip
#if 'flip_direction' not in results:
results['flip_direction'] = random.sample(self.direction, 1)[0]
# results['flip_direction'] = self.direction
if results['flip']:
# flip image
results['img'] = mmcv.imflip(
results['img'], direction=results['flip_direction'])
# flip bboxes
for key in results.get('bbox_fields', []):
results[key] = self.rbbox_flip(results[key],
results['img_shape'],
results['flip_direction'])
return results_4or9
def __call__(self, results):
if not isinstance(results, list):
results = self.normal_call(results)
else:
results = self.multi_img_call(results)
return results
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(flip_ratio={}, direction={})'.format(
self.flip_ratio, self.direction)
@PIPELINES.register_module
class PolyRandomRotate(object):
"""
Rotate img & bbox(n, 8).
Args:
rate (bool): (float, optional): The rotating probability.
Default: 0.5.
angles_range(int): The rotate angle defined by random(-angles_range, +angles_range).
auto_bound(bool): whether to find the new width and height bounds.
"""
def __init__(self,
rotate_ratio=0.5,
angles_range=180, # random(-180, 180)
auto_bound=False):
self.rotate_ratio = rotate_ratio
self.auto_bound = auto_bound
self.angles_range = angles_range
self.discrete_range = [90, 180, -90, -180] # 水平框物体时的旋转角度
@property
def is_rotate(self):
return np.random.rand() < self.rotate_ratio
def apply_image(self, img, bound_h, bound_w, interp=cv2.INTER_LINEAR):
"""
img should be a numpy array, formatted as Height * Width * Nchannels
"""
if len(img) == 0:
return img
return cv2.warpAffine(img, self.rm_image, (bound_w, bound_h), flags=interp)
def apply_coords(self, coords):
"""
coords should be a N * 2 array-like, containing N couples of (x, y) points
"""
if len(coords) == 0:
return coords
coords = np.asarray(coords, dtype=float)
return cv2.transform(coords[:, np.newaxis, :], self.rm_coords)[:, 0, :]
def apply_segmentation(self, segmentation):
segmentation = self.apply_image(segmentation, interp=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
return segmentation
def create_rotation_matrix(self, center, angle, bound_h, bound_w, offset=0):
center = (center[0] + offset, center[1] + offset)
rm = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(tuple(center), angle, 1)
if self.auto_bound:
# Find the coordinates of the center of rotation in the new image
# The only point for which we know the future coordinates is the center of the image
rot_im_center = cv2.transform(
center[None, None, :] + offset, rm)[0, 0, :]
new_center = np.array(
[bound_w / 2, bound_h / 2]) + offset - rot_im_center
# shift the rotation center to the new coordinates
rm[:, 2] += new_center
return rm
def filter_border(self, bboxes, h, w): # bboxes: (n, 5)
x_ctr, y_ctr = bboxes[:, 0], bboxes[:, 1]
w_bbox, h_bbox = bboxes[:, 2], bboxes[:, 3]
keep_inds = (x_ctr > 0) & (x_ctr < w) & (y_ctr > 0) & (y_ctr < h) & (w_bbox > 5) & (h_bbox > 5)
return keep_inds
def normal_call(self, results):
# return the results directly if not rotate
if not self.is_rotate:
results['rotate'] = False
angle = 0
else:
angle = random.uniform( -self.angles_range, self.angles_range)
results['rotate'] = True
# 图中物体类别为'storage-tank' 'roundabout' 'airport'时只进行90°的旋转
# class_labels = results['gt_labels'] # (n)
# for classid in class_labels:
# if classid == 10 or classid == 12 or classid ==17: # class_num=18时
# random.shuffle(self.discrete_range)
# angle = self.discrete_range[0]
# break
h, w, c = results['img_shape']
img = results['img']
# angle for rotate
# angle = random.uniform( -self.angles_range, self.angles_range)
# results['rotate'] = True
results['rotate_angle'] = angle
image_center = np.array((w / 2, h / 2))
abs_cos, abs_sin = abs(np.cos(angle)), abs(np.sin(angle))
if self.auto_bound:
# find the new width and height bounds
bound_w, bound_h = np.rint(
[h * abs_sin + w * abs_cos, h * abs_cos + w * abs_sin]
).astype(int)
else:
bound_w, bound_h = w, h
self.rm_coords = self.create_rotation_matrix(
image_center, angle, bound_h, bound_w)
# Needed because of this problem https://github.com/opencv/opencv/issues/11784
self.rm_image = self.create_rotation_matrix(
image_center, angle, bound_h, bound_w, offset=-0.5)
# rotate img
img = self.apply_image(img, bound_h, bound_w)
results['img'] = img
results['img_shape'] = (bound_h, bound_w, c)
gt_bboxes = results.get('gt_bboxes', [])
labels = results.get('gt_labels', [])
polys = gt_bboxes.reshape(-1,2)
polys = self.apply_coords(polys).reshape(-1, 8)
gt_bboxes = poly2rbox(polys)
keep_inds = self.filter_border(gt_bboxes, bound_h, bound_w)
gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes[keep_inds, :]
labels = labels[keep_inds]
if len(gt_bboxes) == 0:
return None
results['gt_bboxes'] = rbox2poly(gt_bboxes).astype(np.float32)
results['gt_labels'] = labels
return results
def multi_img_call(self, results_4or9):
for results in results_4or9:
# return the results directly if not rotate
if not self.is_rotate:
results['rotate'] = False
angle = 0
else:
angle = random.uniform( -self.angles_range, self.angles_range)
results['rotate'] = True
# 图中物体类别为'storage-tank' 'roundabout' 'airport'时只进行90°的旋转
# class_labels = results['gt_labels'] # (n)
# for classid in class_labels:
# if classid == 12 or classid == 16 or classid ==17: # class_num=18时
# random.shuffle(self.discrete_range)
# angle = self.discrete_range[0]
# break
h, w, c = results['img_shape']
img = results['img']
# angle for rotate
#angle = self.rand_angle
# angle = random.uniform( -self.angles_range, self.angles_range)
# results['rotate'] = True
results['rotate_angle'] = angle
image_center = np.array((w / 2, h / 2))
abs_cos, abs_sin = abs(np.cos(angle)), abs(np.sin(angle))
if self.auto_bound:
# find the new width and height bounds
bound_w, bound_h = np.rint(
[h * abs_sin + w * abs_cos, h * abs_cos + w * abs_sin]
).astype(int)
else:
bound_w, bound_h = w, h
self.rm_coords = self.create_rotation_matrix(
image_center, angle, bound_h, bound_w)
# Needed because of this problem https://github.com/opencv/opencv/issues/11784
self.rm_image = self.create_rotation_matrix(
image_center, angle, bound_h, bound_w, offset=-0.5)
# rotate img
img = self.apply_image(img, bound_h, bound_w)
results['img'] = img
results['img_shape'] = (bound_h, bound_w, c)
gt_bboxes = results.get('gt_bboxes', [])
labels = results.get('gt_labels', [])
polys = gt_bboxes.reshape(-1,2)
polys = self.apply_coords(polys).reshape(-1, 8)
gt_bboxes = poly2rbox(polys)
keep_inds = self.filter_border(gt_bboxes, bound_h, bound_w)
gt_bboxes = gt_bboxes[keep_inds, :]
labels = labels[keep_inds]
if len(gt_bboxes) == 0:
results = None
continue
results['gt_bboxes'] = rbox2poly(gt_bboxes).astype(np.float32)
results['gt_labels'] = labels
return results_4or9
def __call__(self, results):
if not isinstance(results, list):
results = self.normal_call(results)
else:
results = self.multi_img_call(results)
return results
def __repr__(self): # 实例化对象时,可以获得自我描述信息
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += ('(rotate_ratio={}, angles_range={}, auto_bound={})').format(self.rotate_ratio,
self.angles_range,
self.auto_bound)
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module
class Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective(object):
"""
Mosaic augmentation.
Given 4 or 9 images, mosaic combine them into one output image
output Mosaic4_mode image
cut_x
+------------------------------+
| | |
| image 0 | image 1 |
cut_y |-----------------|------------|
| | |
| image 2 | image3 |
| | |
| | |
+------------------------------|
output Mosaic9_mode image
+-------------------------------------------+
| | | |
| | image 1 | image 2 |
| image 8 | | |
| |---------------------|---------|
| | | |
|-----------| | image 3 |
| | image 0 | |
| image 7 | |---------|
| | | |
|-----------|---------------------| image 4 |
| | | |
| image 6 | image 5 | |
| | | |
+-------------------------------------------+
Args:
degrees(int) : The rotate augmentation after mosaic, the rotate angle defined by random.uniform(-degrees, degrees).
Default: 0.
translate(int) : The translate augmentation after mosaic.
Default: 0.
scale(int) : Resize mosaic to random(1-scale, 1+scale) size-ratio.
Default: 0.
shear(int) : The shear augmentation after mosaic, the shear angle(°) defined by random.uniform(-degrees, degrees).
Default: 0.
perspective(float) : The perspective augmentation after mosaic.
Default: 0.
Mosaic_Crop(bool) : Whether to crop mosaic, the size of crop output is defined by the max size of inputs.
Default: True
rate: The mosaic implement probability.
Default: 0.5
About output size:
Given 4 images, which sizes are (1024, 1024), (1280, 1280), (1536, 1536), (768, 768).
if Mosaic4_mode and not Mosaic_Crop:
The output size is (3072, 3072)
if Mosaic9_mode and not Mosaic_Crop:
The output size is (4608, 4608)
if Mosaic?_mode and Mosaic_Crop:
The output size is (1536, 1536)
if Mixup_mode:
The output is List[mosaic_output1, mosaic_output2]
"""
def __init__(self,
degrees=0,
translate=0,
scale=0,
shear=0,
perspective=0.0,
ifcrop=True,
mosaic_ratio=0.5
):
self.degrees = degrees
self.translate = translate
self.scale = scale
self.shear = shear
self.perspective = perspective
self.random_perspective_flag = ifcrop
self.mosaic_ratio = mosaic_ratio
def load_mosaic4(self, results_4):
labels4 = []
gt_bboxes4 = []
s = self.img_size
# 随机取mosaic中心点
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(-x, 2 * s + x)) for x in self.mosaic_border] # mosaic center x, y
for i, results in enumerate(results_4):
# Load image
# img.size = (height, width, 3)
img = results['img']
h, w = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
# place img in img4
if i == 0: # top left
img4 = np.full((s * 2, s * 2, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles img4.shape(2048, 2048, 3)
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), max(yc - h, 0), xc, yc # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (large image) 用于确定原图片在img4左上角的坐标(左上右下)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (small image) 用于确定原图片剪裁进img4中的图像内容范围
elif i == 1: # top right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, max(yc - h, 0), min(xc + w, s * 2), yc
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
elif i == 2: # bottom left
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(xc - w, 0), yc, xc, min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h)
elif i == 3: # bottom right
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = xc, yc, min(xc + w, s * 2), min(s * 2, yc + h)
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h)
# img4.size = [resized_height,resized_ width, 3]
img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # img4[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
padw = x1a - x1b # 原图片未剪裁进img4中的宽度
padh = y1a - y1b # 原图片未剪裁进img4中的高度
# Labels
x = results['gt_bboxes'] # x.shape(n, [x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4])
labels = results['gt_labels'] # labels.shape (n)
gt_bboxes = x.copy()
if x.size > 0:
gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = x[:, 0::2] + padw
gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = x[:, 1::2] + padh
gt_bboxes4.append(gt_bboxes) # labels4:[array.size(n1, 8), array.size(n2, 8), array.size(n3, 8), array.size(n4, 8)]
labels4.append(labels)
# Concat/clip labels
if len(gt_bboxes4):
# 即labels4.shape=(一张mosaic图片中的GT数量, [x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4])
gt_bboxes4 = np.concatenate(gt_bboxes4, 0) # 将第一个维度取消
labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0)
np.clip(gt_bboxes4[:, :], 0, 2 * s, out=gt_bboxes4[:, :]) # 限定labels4[:, :]中最小值只能为0,最大值只能为2*self.size
return img4, gt_bboxes4, labels4
def load_mosaic9(self, results_9):
labels9 = []
gt_bboxes9 = []
s = self.img_size
for i, results in enumerate(results_9):
# Load image
# img.size = (height, width, 3)
img = results['img']
h, w = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
# place img in img9
if i == 0: # center
img9 = np.full((s * 3, s * 3, img.shape[2]), 114, dtype=np.uint8) # base image with 4 tiles
h0, w0 = h, w
c = s, s, s + w, s + h # xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax (base) coordinates
elif i == 1: # top
c = s, s - h, s + w, s
elif i == 2: # top right
c = s + wp, s - h, s + wp + w, s
elif i == 3: # right
c = s + w0, s, s + w0 + w, s + h
elif i == 4: # bottom right
c = s + w0, s + hp, s + w0 + w, s + hp + h
elif i == 5: # bottom
c = s + w0 - w, s + h0, s + w0, s + h0 + h
elif i == 6: # bottom left
c = s + w0 - wp - w, s + h0, s + w0 - wp, s + h0 + h
elif i == 7: # left
c = s - w, s + h0 - h, s, s + h0
elif i == 8: # top left
c = s - w, s + h0 - hp - h, s, s + h0 - hp
padx, pady = c[:2]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [max(x, 0) for x in c] # allocate coords
# Image
img9[y1:y2, x1:x2] = img[y1 - pady:, x1 - padx:] # img9[ymin:ymax, xmin:xmax]
hp, wp = h, w # height, width previous
# Labels
x = results['gt_bboxes'] # x.shape(n, [x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4])
labels = results['gt_labels'] # labels.shape (n)
gt_bboxes = x.copy()
if x.size > 0:
gt_bboxes[:, 0::2] = x[:, 0::2] + padx
gt_bboxes[:, 1::2] = x[:, 1::2] + pady
gt_bboxes9.append(gt_bboxes) # gt_bboxes9 :[array.size(n1, 8), array.size(n2, 8), array.size(n3, 8), array.size(n4, 8)]
labels9.append(labels)
# # Offset
yc, xc = [int(random.uniform(0, s)) for _ in self.mosaic_border] # mosaic center x, y
img9 = img9[yc:yc + 2 * s, xc:xc + 2 * s] # 截取2s * 2s的图像区域
# Concat/clip labels
if len(gt_bboxes9):
# 即labels4.shape=(一张mosaic图片中的GT数量, [x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4])
gt_bboxes9 = np.concatenate(gt_bboxes9, 0) # 将第一个维度取消
labels9 = np.concatenate(labels9, 0)
gt_bboxes9[:, 0::2] -= xc
gt_bboxes9[:, 1::2] -= yc
np.clip(gt_bboxes9[:, :], 0, 2 * s, out=gt_bboxes9[:, :]) # 限定labels9[:, :]中最小值只能为0,最大值只能为2*self.size
return img9, gt_bboxes9, labels9
def random_perspective(self, img, bboxes=(), labels=(), degrees=0, translate=0, scale=0, shear=0, perspective=0.0, border=(0, 0)):
'''
遍性数据增强:
进行随机旋转,缩放,错切,平移,center,perspective数据增强
Args:
img: shape=(height_mosaic, width_mosaic, 3)
targets :size = (n, 8) 未归一化 (归一化的数据无法处理)
Returns:
img:shape=(height, width, 3)
targets = (n, 8)
'''
height = img.shape[0] + border[0] * 2 # shape(h,w,c) 用于将Mosaic图像剪裁至要求的大小 相当于2*img_size - img_size
width = img.shape[1] + border[1] * 2
# Center
C = np.eye(3)
C[0, 2] = -img.shape[1] / 2 # x translation (pixels)
C[1, 2] = -img.shape[0] / 2 # y translation (pixels)
# Perspective
P = np.eye(3)
P[2, 0] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # x perspective (about y)
P[2, 1] = random.uniform(-perspective, perspective) # y perspective (about x)
# 设置旋转和缩放的仿射矩阵并进行旋转和缩放
# Rotation and Scale
R = np.eye(3) # 行数为3,对角线为1,其余为0的矩阵
a = random.uniform(-degrees, degrees) # 随机生成[-degrees, degrees)的实数 即为旋转角度 负数则代表逆时针旋转
# a += random.choice([-180, -90, 0, 90]) # add 90deg rotations to small rotations
s = random.uniform(1 - scale, 1 + scale)
# s = 2 ** random.uniform(-scale, scale)
R[:2] = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(angle=a, center=(0, 0), scale=s) # 获得以(0,0)为中心的旋转仿射变化矩阵
# 设置裁剪的仿射矩阵系数
# Shear
S = np.eye(3)
S[0, 1] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # x shear (deg)
S[1, 0] = math.tan(random.uniform(-shear, shear) * math.pi / 180) # y shear (deg)
# 设置平移的仿射系数
# Translation
T = np.eye(3)
T[0, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * width # x translation (pixels)
T[1, 2] = random.uniform(0.5 - translate, 0.5 + translate) * height # y translation (pixels)
# Combined rotation matrix
# 融合仿射矩阵并作用在图片上
M = T @ S @ R @ P @ C # order of operations (right to left) is IMPORTANT
if (border[0] != 0) or (border[1] != 0) or (M != np.eye(3)).any(): # image changed
if perspective:
img = cv2.warpPerspective(img, M, dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
else: # affine
img = cv2.warpAffine(img, M[:2], dsize=(width, height), borderValue=(114, 114, 114))
# Transform label coordinates
# 调整框的标签
n = len(bboxes) # targets.size = (n, 8)
if n:
# warp points
xy = np.ones((n * 4, 3))
xy[:, :2] = bboxes[:, :].reshape(n * 4, 2) # x1y1, ,x2y2 , x3y3, x4y4
xy = xy @ M.T # transform
if perspective:
xy = (xy[:, :2] / xy[:, 2:3]).reshape(n, 8) # rescale
else: # affine
xy = xy[:, :2].reshape(n, 8)
# # clip boxes
# xy_ = xy.copy() # (n, 8)
# xy_[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]] = xy[:, [0, 2, 4, 6]].clip(0, width)
# xy_[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]] = xy[:, [1, 3, 5, 7]].clip(0, height)
# filter candidates
rbboxes = poly2rbox(xy) # (n,5)
keep_inds = self.filter_border(rbboxes, height, width)
xy = xy[keep_inds, :]
bboxes = xy
labels = labels[keep_inds]
return img, bboxes, labels
def filter_border(self, bboxes, h, w): # bboxes.size(n,5)
x_ctr, y_ctr = bboxes[:, 0], bboxes[:, 1]
w_bboxes, h_bboxes = bboxes[:, 2], bboxes[:, 3]
keep_inds = (x_ctr > 0) & (x_ctr < w) & (y_ctr > 0) & (y_ctr < h) & (w_bboxes > 5) & (h_bboxes > 5)
return keep_inds
def normal_call(self, results):
return results
def mosaic4_call(self, results_4):
img_mosaic4, gt_bboxes_mosaic4, gt_labels_mosaic4 = self.load_mosaic4(results_4)
if self.random_perspective_flag:
img_mosaic4, gt_bboxes_mosaic4, gt_labels_mosaic4= self.random_perspective(
img=img_mosaic4,
bboxes= gt_bboxes_mosaic4,
labels=gt_labels_mosaic4,
degrees=self.degrees,
translate=self.translate,
scale=self.scale,
shear=self.shear,
perspective=self.perspective,
border=self.mosaic_border
)
else:
# filter candidates
rbboxes = poly2rbox(gt_bboxes_mosaic4) # (n, 8) -> (n,5)
keep_inds = self.filter_border(rbboxes, img_mosaic4.shape[0], img_mosaic4.shape[1])
gt_bboxes_mosaic4 = gt_bboxes_mosaic4[keep_inds, :]
gt_labels_mosaic4 = gt_labels_mosaic4[keep_inds]
results = results_4[0]
results['img'] = img_mosaic4
results['gt_bboxes'] = gt_bboxes_mosaic4.astype(np.float32)
results['gt_labels'] = gt_labels_mosaic4
return results
def mosaic9_call(self, results_9):
img_mosaic9, gt_bboxes_mosaic9, gt_labels_mosaic9 = self.load_mosaic9(results_9)
if self.random_perspective_flag:
img_mosaic9, gt_bboxes_mosaic9, gt_labels_mosaic9= self.random_perspective(
img=img_mosaic9,
bboxes= gt_bboxes_mosaic9,
labels=gt_labels_mosaic9,
degrees=self.degrees,
translate=self.translate,
scale=self.scale,
shear=self.shear,
perspective=self.perspective,
border=self.mosaic_border
)
else:
# filter candidates
rbboxes = poly2rbox(gt_bboxes_mosaic9) # (n, 8) -> (n,5)
keep_inds = self.filter_border(rbboxes, img_mosaic9.shape[0], img_mosaic9.shape[1])
gt_bboxes_mosaic9 = gt_bboxes_mosaic9[keep_inds, :]
gt_labels_mosaic9 = gt_labels_mosaic9[keep_inds]
results = results_9[0]
results['img'] = img_mosaic9
results['gt_bboxes'] = gt_bboxes_mosaic9.astype(np.float32)
results['gt_labels'] = gt_labels_mosaic9
return results
def mixup_mosaic(self, results_x2):
if len(results_x2) == 2: # Normal + Mixup
return results_x2
results_pre = []
results_last = []
results_mixups = []
for i, results in enumerate(results_x2):
if i < (len(results_x2) / 2):
results_pre.append(results)
else:
results_last.append(results)
if results_x2[0]['Mosaic_mode'] == 'Mosaic4': # Mosaic4 + Mixup
results_mixup1 = self.mosaic4_call(results_pre)
results_mixup2 = self.mosaic4_call(results_last)
results_mixups.append(results_mixup1)
results_mixups.append(results_mixup2)
elif results_x2[0]['Mosaic_mode'] == 'Mosaic9': # Mosaic9 + Mixup
results_mixup1 = self.mosaic9_call(results_pre)
results_mixup2 = self.mosaic9_call(results_last)
results_mixups.append(results_mixup1)
results_mixups.append(results_mixup2)
return results_mixups
def __call__(self, results):
if not isinstance(results, list): # 1 img
results = self.normal_call(results)
return results
self.img_size = 0
for result in results:
# img.size = (height, width, 3)
img = result['img']
img_max_size = max(img.shape[0], img.shape[1])
self.img_size = max(self.img_size, img_max_size)
self.mosaic_border = [-self.img_size // 2, -self.img_size // 2]
if results[0]['Mixup_mode']: # mixup = True
if random.random() > self.mosaic_ratio: # with no mosaic process
results_ = []
results1 = results[0]
results2 = results[int(len(results) / 2)]
results_.append(results1)
results_.append(results2)
return results_
else:
results = self.mixup_mosaic(results)
return results
else: # mixup = False
if random.random() > self.mosaic_ratio: # with no mosaic process
results1 = results[0]
return results1
else:
if results[0]['Mosaic_mode'] == 'Mosaic4':
results = self.mosaic4_call(results)
return results
if results[0]['Mosaic_mode'] == 'Mosaic9':
results = self.mosaic9_call(results)
return results
def __repr__(self): # 实例化对象时,可以获得自我描述信息
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += ('(degrees={}, translate={}, scale={}, shear={}'
'perspective={}, ifcrop={}, mosaic_ratio={})').format(self.degrees,
self.translate,
self.scale,
self.shear,
self.perspective,
self.random_perspective_flag,
self.mosaic_ratio)
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module
class MixUp(object):
"""mix 2 imgs
Args:
rate(float): the mixup rate
"""
def __init__(self,
mixup_ratio=0.5
):
self.mixup_ratio = mixup_ratio
def mixup_imgs(self, results2):
results_1 = results2[0]
results_2 = results2[1]
img1, gt_bboxes1, gt_labels1 = results_1['img'], results_1['gt_bboxes'], results_1['gt_labels']
img2, gt_bboxes2, gt_labels2 = results_2['img'], results_2['gt_bboxes'], results_2['gt_labels']
max_h, max_w = max(img2.shape[0], img1.shape[0]), max(img2.shape[1], img1.shape[1])
img1 = mmcv.impad(img1, (max_h, max_w), 0)
img2 = mmcv.impad(img2, (max_h, max_w), 0)
r = np.random.beta(8.0, 8.0) # mixup ratio, alpha=beta=8.0
img_mixed = img1 * r + img2 * (1 - r)
gt_bboxes = np.concatenate((gt_bboxes1, gt_bboxes2), 0)
gt_labels = np.concatenate((gt_labels1, gt_labels2), 0)
results_1['img'] = img_mixed
results_1['gt_bboxes'] = gt_bboxes
results_1['gt_labels'] = gt_labels
return results_1
def __call__(self, results):
if not isinstance(results, list): # only 1 img
return results
if random.random() < self.mixup_ratio: # 2 img
results = self.mixup_imgs(results)
return results
else:
return results[0]
def __repr__(self): # 实例化对象时,可以获得自我描述信息
repr_str = self.__class__.__name__
repr_str += ('(mixup_ratio={})').format(self.mixup_ratio)
return repr_str
@PIPELINES.register_module
class PolyImgPlot(object):
"""visualize the poly-format img after augmentation.
Args:
img_save_path (str): where to save the visualized img.
"""
def __init__(self, img_save_path='work_dirs/', save_img_num=4, class_num=18, thickness=2):
self.img_aug_id = 0
self.img_save_path = img_save_path
self.save_img_num = save_img_num
# 设置画框的颜色 colors = [[178, 63, 143], [25, 184, 176], [238, 152, 129],....,[235, 137, 120]]随机设置RGB颜色
self.colors = [[random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(class_num)]
self.thickness = thickness
self.dict_class_img_distribution = {}
self.dict_class_num_distribution = {}
self.img_num = 0
def __call__(self, results):
dict_label_thisimg = Counter(results['gt_labels'])
for i in range(1, len(self.colors)+1): # 1 ~ classnum
if i in dict_label_thisimg: # 该类别id在本次迭代中中出现
# 对应类别id对应的键值自增,表示该类别存在的图片数量
if i not in self.dict_class_img_distribution:
self.dict_class_img_distribution[i] = 1
else:
self.dict_class_img_distribution[i] += 1
# 对应类别id对应的键值 + 本次迭代的频数,表示该目标类别的数量
if i not in self.dict_class_num_distribution:
self.dict_class_num_distribution[i] = dict_label_thisimg[i]
else:
self.dict_class_num_distribution[i] += dict_label_thisimg[i]
if (results['Mosaic_mode'] != 'Normal') and (results['Mixup_mode'] == True):
class_distribution_name = 'mixup+mosaic_mode_class_distribution.jpg'
objects_distribution_name = 'mixup+mosaic_mode_objects_distribution.jpg'
elif results['Mixup_mode'] == True:
class_distribution_name = 'mixup_mode_class_distribution.jpg'
objects_distribution_name = 'mixup_mode_objects_distribution.jpg'
elif results['Mosaic_mode'] != 'Normal':
class_distribution_name = 'mosaic_mode_class_distribution.jpg'
objects_distribution_name = 'mosaic_mode_objects_distribution.jpg'
else:
class_distribution_name = 'normal_mode_class_distribution.jpg'
objects_distribution_name = 'normal_mode_objects_distribution.jpg'
# 各个类别的分布图绘制
plt_x = []
plt_y = []
self.img_num += 1
for i in range(1, len(self.colors)+1): #i: 1 ~ classnum
if i in self.dict_class_img_distribution:
plt_x.append('%g' % i)
plt_y.append(self.dict_class_img_distribution[i] / self.img_num)
fig = plt.figure(0)
plt.bar(plt_x, plt_y)
for classid, distribution_ratio in zip(plt_x, plt_y):
plt.text(classid, distribution_ratio, '{:.2f}%'.format(distribution_ratio*100), ha='center', va='bottom') # 在(classid, distribution_ratio)显示具体数值
plt.title('every class distribution')
plt.xlabel('classid')
plt.ylabel('distribution ratio')
plt.savefig(self.img_save_path + class_distribution_name)
plt.close(0)
# 各个类别的数量占比绘制
plt_x = []
plt_y = []
object_num = 0
for i in self.dict_class_num_distribution:
object_num += self.dict_class_num_distribution[i]
for i in range(1, len(self.colors)+1): #i: 1 ~ classnum
if i in self.dict_class_num_distribution:
plt_x.append('%g' % i)
plt_y.append(self.dict_class_num_distribution[i] / object_num)
fig = plt.figure(0)
plt.bar(plt_x, plt_y)
for classid, distribution_ratio in zip(plt_x, plt_y):
plt.text(classid, distribution_ratio, '{:.2f}%'.format(distribution_ratio*100), ha='center', va='bottom') # 在(classid, distribution_ratio)显示具体数值
plt.title('objects distribution')
plt.xlabel('classid')
plt.ylabel('distribution ratio')
plt.savefig(self.img_save_path + objects_distribution_name)
plt.close(0)
if self.img_aug_id < self.save_img_num:
filename = self.img_save_path + ('img_augment%g.jpg' % self.img_aug_id) # filename
self.img_aug_id += 1
img = copy.deepcopy(results['img']) # img(h, w, 3) 未归一化
polys = results['gt_bboxes'] # results['gt_bboxes'] (n, 8)
labels = results['gt_labels'] # results['gt_labels'] (n)
# visulize the oriented boxes
for i, bbox in enumerate(polys):
cls_index = labels[i] - 1
# box_list.size(4, 2)
box_list = np.array([(bbox[0], bbox[1]), (bbox[2], bbox[3]), (bbox[4], bbox[5]), (bbox[6], bbox[7])], np.int32)
cv2.drawContours(image=img, contours=[box_list], contourIdx=-1, color=self.colors[int(cls_index)], thickness=self.thickness)
cv2.imwrite(filename, img)
return results
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(img_save_path={})'.format(
self.img_save_path,
self.save_img_num,
self.colors)
from .compose import Compose
from .formating import (Collect, ImageToTensor, ToDataContainer, ToTensor,
Transpose, to_tensor)
from .instaboost import InstaBoost
from .loading import LoadAnnotations, LoadImageFromFile, LoadProposals
from .test_aug import MultiScaleFlipAug
from .transforms import (Albu, Expand, MinIoURandomCrop, Normalize, Pad,
PhotoMetricDistortion, RandomCrop, RandomFlip, Resize,
SegRescale, ColorJitter, HSVAugment)
from .poly_transforms import (CorrectRBBox, PolyResize, PolyRandomFlip, PolyRandomRotate,
Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective, MixUp, PolyImgPlot)
__all__ = [
'Compose', 'to_tensor', 'ToTensor', 'ImageToTensor', 'ToDataContainer',
'Transpose', 'Collect', 'LoadAnnotations', 'LoadImageFromFile',
'LoadProposals', 'MultiScaleFlipAug', 'Resize', 'RandomFlip', 'Pad',
'RandomCrop', 'Normalize', 'SegRescale', 'MinIoURandomCrop', 'Expand',
'PhotoMetricDistortion', 'Albu', 'InstaBoost', 'ColorJitter',
'HSVAugment', 'CorrectRBBox', 'PolyResize', 'PolyRandomFlip', 'PolyRandomRotate',
'Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective', 'MixUp', 'PolyImgPlot'
]
在mmdet/datasets/pipelines/init.py添加新增的数据增强
from .compose import Compose
from .formating import (Collect, ImageToTensor, ToDataContainer, ToTensor,
Transpose, to_tensor)
from .instaboost import InstaBoost
from .loading import LoadAnnotations, LoadImageFromFile, LoadProposals
from .test_aug import MultiScaleFlipAug
from .transforms import (Albu, Expand, MinIoURandomCrop, Normalize, Pad,
PhotoMetricDistortion, RandomCrop, RandomFlip, Resize,
SegRescale, ColorJitter, HSVAugment)
from .poly_transforms import (CorrectRBBox, PolyResize, PolyRandomFlip, PolyRandomRotate,
Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective, MixUp, PolyImgPlot)
__all__ = [
'Compose', 'to_tensor', 'ToTensor', 'ImageToTensor', 'ToDataContainer',
'Transpose', 'Collect', 'LoadAnnotations', 'LoadImageFromFile',
'LoadProposals', 'MultiScaleFlipAug', 'Resize', 'RandomFlip', 'Pad',
'RandomCrop', 'Normalize', 'SegRescale', 'MinIoURandomCrop', 'Expand',
'PhotoMetricDistortion', 'Albu', 'InstaBoost', 'ColorJitter',
'HSVAugment', 'CorrectRBBox', 'PolyResize', 'PolyRandomFlip', 'PolyRandomRotate',
'Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective', 'MixUp', 'PolyImgPlot'
]
配置文件导入新增的数据增强方法
# model settings
norm_cfg = dict(type='GN', num_groups=32, requires_grad=True)
work_dir = 'work_dirs/ReRes_ReFPN_dotav2/'
model = dict(
type='OrientedRepPointsDetector',
pretrained='/ReDet_mmcls/re_resnet50_c8_batch256/re_resnet50_c8_batch256-25b16846.pth',
backbone=dict(
type='ReResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
frozen_stages=1,
style='pytorch'),
neck=dict(
type='ReFPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
start_level=1,
add_extra_convs=True,
num_outs=5,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg
),
bbox_head=dict(
type='OrientedRepPointsHead',
num_classes=19,
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
point_feat_channels=256,
stacked_convs=3,
num_points=9,
gradient_mul=0.3,
point_strides=[8, 16, 32, 64, 128],
point_base_scale=2,
norm_cfg=norm_cfg,
loss_cls=dict(type='FocalLoss', use_sigmoid=True, gamma=2.0, alpha=0.25, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_rbox_init=dict(type='GIoULoss', loss_weight=0.375),
loss_rbox_refine=dict(type='GIoULoss', loss_weight=1.0),
loss_spatial_init=dict(type='SpatialBorderLoss', loss_weight=0.05),
loss_spatial_refine=dict(type='SpatialBorderLoss', loss_weight=0.1),
top_ratio=0.4,))
# training and testing settings
train_cfg = dict(
init=dict(
assigner=dict(type='PointAssigner', scale=4, pos_num=1), # 每个gtbox仅选一个正样本
allowed_border=-1,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
refine=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner', #pre-assign to select more samples for samples selection
pos_iou_thr=0.1,
neg_iou_thr=0.1,
min_pos_iou=0,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
allowed_border=-1,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False))
test_cfg = dict(
nms_pre=2000,
min_bbox_size=0,
score_thr=0.05,
nms=dict(type='rnms', iou_thr=0.4),
max_per_img=2000)
# dataset settings
dataset_type = 'DotaDatasetv2'
data_root = '/media/test/4d846cae-2315-4928-8d1b-ca6d3a61a3c6/DOTA/DOTAv2.0/'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='CorrectRBBox', correct_rbbox=True, refine_rbbox=True),
dict(type='PolyResize',
img_scale=[(1333, 768), (1333, 1280)], # 建议根据显存来确定长边的值,在线多尺度缩放幅度控制在25%左右为佳
keep_ratio=True,
multiscale_mode='range',
clamp_rbbox=False),
dict(type='PolyRandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
# dict(type='HSVAugment', hgain=0.015, sgain=0.7, vgain=0.4),
dict(type='PolyRandomRotate', rotate_ratio=0.5, angles_range=180, auto_bound=False),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
# dict(type='Poly_Mosaic_RandomPerspective', mosaic_ratio=0, ifcrop=True, degrees=0, translate=0.1, scale=0.2, shear=0, perspective=0.0),
# dict(type='MixUp', mixup_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='PolyImgPlot', img_save_path=work_dir, save_img_num=16, class_num=18, thickness=2),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels'])]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1024, 1024),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='PolyResize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='PolyRandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
imgs_per_gpu=2,
workers_per_gpu=2,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'trainval_split_1024/Train_dotav2_trainval1024_poly.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'trainval_split_1024/images/',
pipeline=train_pipeline,
Mosaic4=False,
Mosaic9=False,
Mixup=False),
val=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'trainval_split_1024/Train_dotav2_trainval1024_poly.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'trainval_split_1024/images/',
pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'test-dev_split/Test_datav2_test1024.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'test-dev_split/images/',
pipeline=test_pipeline))
evaluation = dict(interval=1, metric='bbox')
# optimizer
optimizer = dict(type='AdamW', lr=0.0001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), weight_decay=0.05,
paramwise_cfg=dict(custom_keys={'absolute_pos_embed': dict(decay_mult=0.),
'relative_position_bias_table': dict(decay_mult=0.),
'norm': dict(decay_mult=0.)}))
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(
policy='step',
warmup='linear',
warmup_iters=500,
warmup_ratio=0.001,
step=[27, 33])
runner = dict(type='EpochBasedRunnerAmp', max_epochs=36)
total_epochs = 36
checkpoint_config = dict(interval=12)
# yapf:disable
log_config = dict(
interval=20, # 迭代n次时打印一次
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook')
])
# yapf:enable
# runtime settings
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
load_from = None
resume_from = None
workflow = [('train', 1)]
# do not use mmdet version fp16
fp16 = None
optimizer_config = dict(grad_clip=dict(max_norm=35, norm_type=2))
# optimizer_config = dict(
# # type="DistOptimizerHook",
# # update_interval=1,
# grad_clip=None,
# coalesce=True,
# bucket_size_mb=-1,
# # use_fp16=True,
# )
2、Bbox增强
albumentations数据增强(同上)
源码在mmdet/datasets/custom.py里面,增强源码为:
def pre_pipeline(self, results):
"""Prepare results dict for pipeline."""
results['img_prefix'] = self.img_prefix
results['seg_prefix'] = self.seg_prefix
results['proposal_file'] = self.proposal_file
results['bbox_fields'] = []
results['mask_fields'] = []
results['seg_fields'] = []
3、增强后训练样本数据的可视化
python tools/misc/browse_dataset.py ${CONFIG} [-h] [--skip-type ${SKIP_TYPE[SKIP_TYPE...]}] [--output-dir ${OUTPUT_DIR}] [--not-show] [--show-interval ${SHOW_INTERVAL}]
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
import argparse
import os
from collections import Sequence
from pathlib import Path
import mmcv
from mmcv import Config, DictAction
from mmdet.datasets.builder import build_dataset
from mmrotate.core.visualization import imshow_det_rbboxes
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Browse a dataset')
parser.add_argument('--config',type=str,default='./work_dirs/runs/redet_hrsc/redet_re50_refpn_3x_hrsc_le90.py', help='train config file path')
parser.add_argument('--skip-type',type=str, nargs='+', default=['DefaultFormatBundle', 'Normalize', 'Collect'],help='skip some useless pipeline')
parser.add_argument('--output-dir',default='data/hrsc/AnnBoxsVisual/', type=str,help='If there is no display interface, you can save it')
parser.add_argument('--not-show', default=False, action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--show-interval',type=float,default=2, help='the interval of show (s)')
parser.add_argument('--cfg-options',nargs='+',action=DictAction,help='override some settings in the used config, the key-value pair ''in xxx=yyy format will be merged into config file. If the value to ''be overwritten is a list, it should be like key="[a,b]" or key=a,b ''It also allows nested list/tuple values, e.g. key="[(a,b),(c,d)]" '
'Note that the quotation marks are necessary and that no white space '
'is allowed.')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def retrieve_data_cfg(config_path, skip_type, cfg_options):
"""Retrieve the dataset config file.
Args:
config_path (str): Path of the config file.
skip_type (list[str]): List of the useless pipeline to skip.
cfg_options (dict): dict of configs to merge from.
"""
def skip_pipeline_steps(config):
config['pipeline'] = [
x for x in config.pipeline if x['type'] not in skip_type
]
cfg = Config.fromfile(config_path)
if cfg_options is not None:
cfg.merge_from_dict(cfg_options)
train_data_cfg = cfg.data.train
while 'dataset' in train_data_cfg and train_data_cfg[
'type'] != 'MultiImageMixDataset':
train_data_cfg = train_data_cfg['dataset']
if isinstance(train_data_cfg, Sequence):
[skip_pipeline_steps(c) for c in train_data_cfg]
else:
skip_pipeline_steps(train_data_cfg)
return cfg
def main():
args = parse_args()
cfg = retrieve_data_cfg(args.config, args.skip_type, args.cfg_options)
dataset = build_dataset(cfg.data.train)
progress_bar = mmcv.ProgressBar(len(dataset))
for item in dataset:
filename = os.path.join(args.output_dir,
Path(item['filename']).name
) if args.output_dir is not None else None
gt_bboxes = item['gt_bboxes']#获取数据增强后的框
gt_labels = item['gt_labels']#获取数据增强后的标签
imshow_det_rbboxes(
item['img'],
gt_bboxes,
gt_labels,
class_names=dataset.CLASSES,
score_thr=0,
show=not args.not_show,
wait_time=args.show_interval,
out_file=filename,
bbox_color=dataset.PALETTE,
text_color=(200, 200, 200))
progress_bar.update()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()


2、统计图像分辨率(训练和测试多尺度)
训练和测试多尺度:增强模型鲁棒性,同时小图被放大后能利于被模型捕捉到
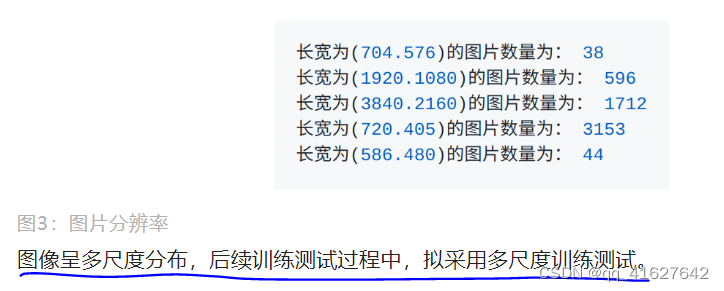



train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=(1333, 800), keep_ratio=True), #这里可以更换多尺度[(),()]
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 800), #这里可以更换多尺度[(),()]
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
3、统计目标长宽比
目标检测数据可视化,分析anchor_ratio的设置问题
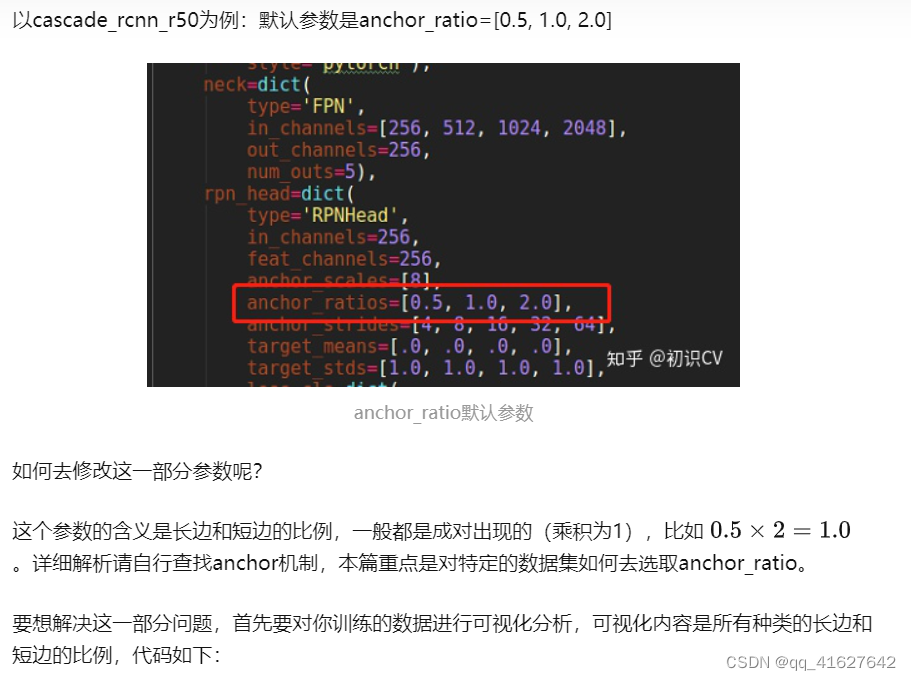
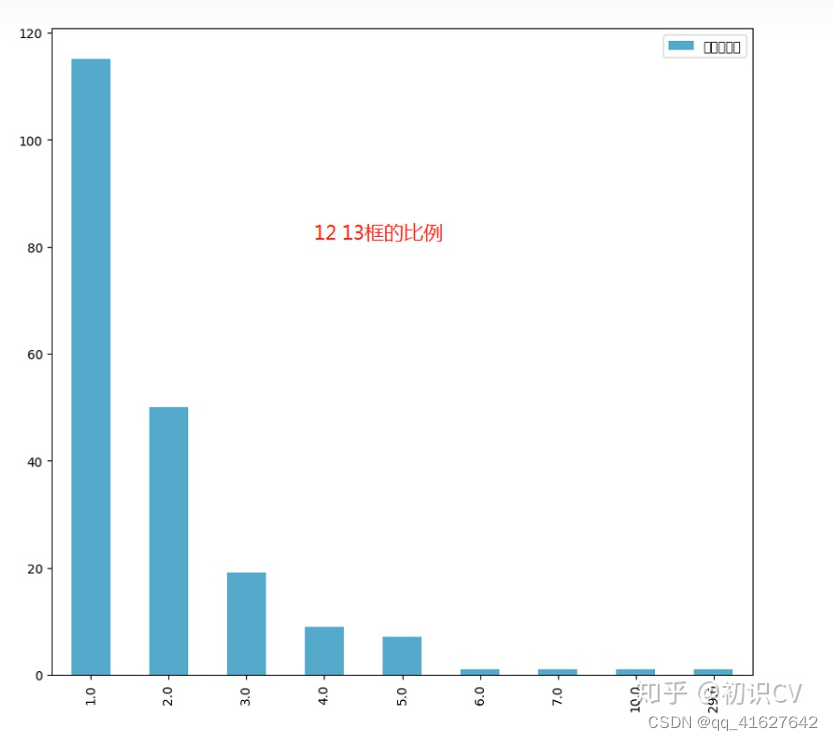
分析:
由上图中我们可知长边和短边的比例为:1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、10.0、29.0,此时anchor_ratios可选择为anchor_ratios=[0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, 10]。
有人该问为什么不选择3.0、4.0、6.0、7.0、29.0呢?
选取时得保证一个原则:不能选择极端比例。意思就是,不是有什么比例就选择什么比例,而是用一个近似比例代替其他的比例。就好像3.0可以近似的看做2.0,4.0、6.0、7.0可以近似的看为5.0,29.0可以近似的看为10.0。
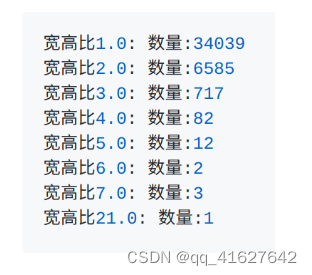
1、修改anchor ratios参数
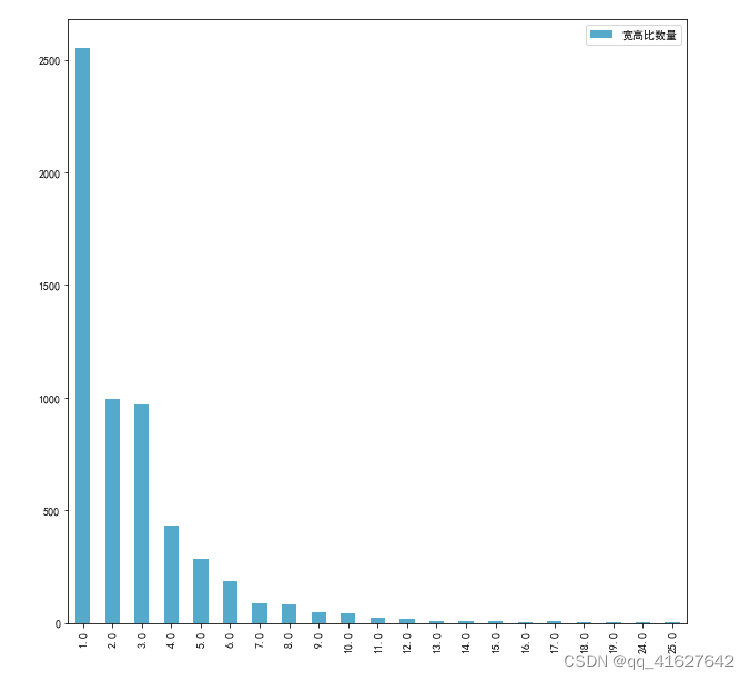
基于anchor的目标检测任务,需要分析目标长宽比,以选择最优的anchor比例。在考虑计算消耗的前提下,尽可能扩大感受野,保证anchor的分布尽可能与目标分布保持一致。所以最初我们选择anchor的ratio为[0.2,0.5,1,2,5]。
统计切割后DOTAv2图像中的目标边框长宽比的分布,可以发现水平框和旋转框的长宽比范围也非常广,长宽比例最大接近6:1。
——因此anchor based检测器中的anchor scale和anchor ratios参数也需要重新调整。另外可变形卷积网络DCN的使用在应对长宽比变化较剧烈的目标识别任务时可能会有不错的效果。(可在backbone中添加dcn结构或使用dcn类型的检测算法)
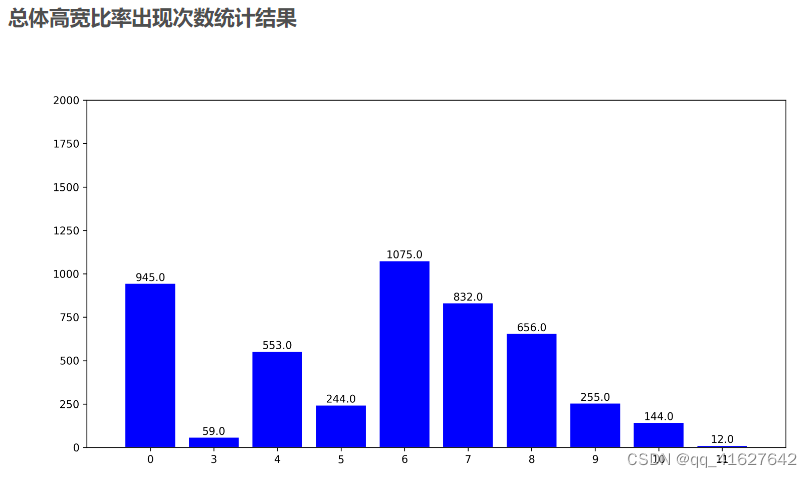
model = dict(
type='CascadeRCNN',
num_stages=3,
pretrained='torchvision://resnet50',
backbone=dict(
type='ResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
frozen_stages=1,
style='pytorch',
#dcn=dict( #在最后三个block加入可变形卷积
# modulated=False, deformable_groups=1, fallback_on_stride=False),
# stage_with_dcn=(False, True, True, True)
),
neck=dict(
type='FPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
num_outs=5),
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_scales=[8],
anchor_ratios=[0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 5.0], # 添加了0.2,5,过两天发图
anchor_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64],
target_means=[.0, .0, .0, .0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
loss_cls=dict(
type='FocalLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0), # 修改了loss,为了调控难易样本与正负样本比例
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0 / 9.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', out_size=7, sample_num=2),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=[
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.05, 0.05, 0.1, 0.1],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.033, 0.033, 0.067, 0.067],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0))
])
2、添加DCN(采用dcn减少不同尺度目标的差异性带来的影响,提高检测性能)
1、配置文件案例DCN放到backbone中
# fp16
fp16 = dict(loss_scale=512.)
# model settings
model = dict(
type='CascadeRCNN',
num_stages=3,
pretrained='torchvision://resnet50',
backbone=dict(
type='ResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3),
frozen_stages=1,
style='pytorch',
#添加DCN,在最后三个block加入可变形卷积
dcn=dict(
modulated=False, deformable_groups=1, fallback_on_stride=False),
stage_with_dcn=(False, True, True, True)),
neck=dict(
type='FPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
num_outs=5),
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_scales=[8],
anchor_ratios=[0.5, 1.0, 2.0],
anchor_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64],
target_means=[.0, .0, .0, .0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0 / 9.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', out_size=7, sample_num=2),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=[
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.05, 0.05, 0.1, 0.1],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0)),
dict(
type='SharedFCBBoxHead',
num_fcs=2,
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=11,
target_means=[0., 0., 0., 0.],
target_stds=[0.033, 0.033, 0.067, 0.067],
reg_class_agnostic=True,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='SmoothL1Loss', beta=1.0, loss_weight=1.0))
])
# model training and testing settings
train_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.7,
neg_iou_thr=0.3,
min_pos_iou=0.3,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=256,
pos_fraction=0.5,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=False),
allowed_border=0,
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
rpn_proposal=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=2000,
nms_post=2000,
max_num=2000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=[
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.5,
neg_iou_thr=0.5,
min_pos_iou=0.5,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.6,
neg_iou_thr=0.6,
min_pos_iou=0.6,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False),
dict(
assigner=dict(
type='MaxIoUAssigner',
pos_iou_thr=0.7,
neg_iou_thr=0.7,
min_pos_iou=0.7,
ignore_iof_thr=-1),
sampler=dict(
type='RandomSampler',
num=512,
pos_fraction=0.25,
neg_pos_ub=-1,
add_gt_as_proposals=True),
pos_weight=-1,
debug=False)
],
stage_loss_weights=[1, 0.5, 0.25])
test_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=1000,
nms_post=1000,
max_num=1000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
score_thr=0.05, nms=dict(type='nms', iou_thr=0.5), max_per_img=100))
# dataset settings
dataset_type = 'CocoDataset'
data_root = '/chongqingAI/chongqing1_round1_train1_20191223/'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True),
dict(type='Resize', img_scale=[(1333, 800), (1333, 1200)], multiscale_mode='range', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(1333, 1000),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
imgs_per_gpu=5,
workers_per_gpu=6,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file='/chongqing1_round1_train1_20191223/annotations.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'images/',
pipeline=train_pipeline),
test=dict(
pipeline=test_pipeline)
)
# optimizer
# single gpu and autoscale
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.05 , momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
optimizer_config = dict(grad_clip=dict(max_norm=35, norm_type=2))
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(
policy='step',
warmup='linear',
warmup_iters=500,
warmup_ratio=1.0 / 3,
step=[8, 11])
checkpoint_config = dict(interval=1)
# yapf:disable
log_config = dict(
interval=50,
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook'),
# dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')
])
# yapf:enable
# runtime settings
total_epochs = 12
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
work_dir = '../work_dirs/cascade_rcnn_dconv_c3-c5_r50_fpn_1x'
load_from = '../checkpoints/cascade_rcnn_r50_fpn_1x_20190501-3b6211ab.pth'
resume_from = None
workflow = [
('train', 1)]
2、how to use DCN in other backbones
I’m looking for the code that implements Deformable Conv (DCN or DCNv2), where is it? I have researched the backbone code in mmdet and it seems that DCN is only used in the resnet series. How can I apply DCN to other backbone networks? (like CSPDarkNet)
the configs are at here:
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/master/configs/dcn
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/tree/master/configs/dcnv2

dcn=dict(type='DCNv2', deform_groups=1, fallback_on_stride=False),
stage_with_dcn=(False, False, True, True)))
3、回归框损失函数设置GIoU Loss、DIoU Loss
Cascade-rcnn中如何使用GIoU Loss、DIoU Loss?
GIoU是源自IoU的一种边框预测的损失计算方法,在目标检测等领域,需要对预测边框(pre BBox)与实际标注边框(ground truth BBox)进行对比,计算损失。在Yolo算法中,给定预测值与ground truth的 (x, y, w, h) 进行预测,采用回归损失。但实际上,回归损失并不是该问题的最好损失函数,因为其只关注 (x, y, w, h) 对应的“距离”,而本质上我们想要得到 IoU 值比较大的预测框,两者联系并不大。那么为什么不直接采用IoU值作为损失函数呢? 因为一旦预测框与真实框不相交,那么IoU都为0,也就是说,在很大的范围内(不相交的区域),损失函数是没有梯度的,因此才有了GIoU Loss(Generalized Intersection over Union)。
Some questions about iou loss and other variants
一般情况下,用GIoULoss代替L1Loss后会涨点。
原版用的配置文件(使用L1Loss)如下:
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_generator=dict(
type='AnchorGenerator',
scales=[8],
ratios=[0.5, 1.0, 2.0],
strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64]),
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]),
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='L1Loss', loss_weight=1.0)),
roi_head=dict(
type='StandardRoIHead',
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', out_size=7, sample_num=0),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=dict(
type='Shared2FCBBoxHead',
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=10,
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]),
reg_class_agnostic=False,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
loss_bbox=dict(type='L1Loss', loss_weight=1.0))))
添加GIoULoss后的配置文件如下:
rpn_head=dict(
type='RPNHead',
in_channels=256,
feat_channels=256,
anchor_generator=dict(
type='AnchorGenerator',
scales=[8],
ratios=[0.5, 1.0, 2.0],
strides=[4, 8, 16, 32, 64]),
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
target_stds=[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0]),
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=True, loss_weight=1.0),
reg_decoded_bbox=True, # 使用GIoUI时注意添加
loss_bbox=dict(type='GIoULoss', loss_weight=5.0)),
roi_head=dict(
type='StandardRoIHead',
bbox_roi_extractor=dict(
type='SingleRoIExtractor',
roi_layer=dict(type='RoIAlign', out_size=7, sample_num=0),
out_channels=256,
featmap_strides=[4, 8, 16, 32]),
bbox_head=dict(
type='Shared2FCBBoxHead',
in_channels=256,
fc_out_channels=1024,
roi_feat_size=7,
num_classes=10,
bbox_coder=dict(
type='DeltaXYWHBBoxCoder',
target_means=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
target_stds=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]),
reg_class_agnostic=False,
loss_cls=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss', use_sigmoid=False, loss_weight=1.0),
reg_decoded_bbox=True, # 使用GIoUI时注意添加
loss_bbox=dict(type='GIoULoss', loss_weight=5.0))))
4、Soft NMS 软化非极大抑制
Softnms更适合密集的场景,一般性能会更好,但不是绝对的。
MMDetection中,Soft NMS 软化非极大抑制:(源码解析)
test_cfg = dict(
rpn=dict(
nms_across_levels=False,
nms_pre=1000,
nms_post=1000,
max_num=1000,
nms_thr=0.7,
min_bbox_size=0),
rcnn=dict(
score_thr=0.05, nms=dict(type='nms', iou_thr=0.5), max_per_img=100) # max_per_img表示最终输出的det bbox数量
# soft-nms is also supported for rcnn testing
# e.g., nms=dict(type='soft_nms', iou_thr=0.5, min_score=0.001) # soft_nms参数
)
5、超参数的调整:部分工作也发现如NMS中IoU阈值的调整(从0.3到0.5)也有利于精度的提升,但这一方面尚无最佳配置参照
6、使用FP16
mmcv/runner/hooks/optimizer.py
fp16 = dict(loss_scale=512.)
you need to set mode=‘dynamic’ if you are using pytorch<=1.5.0
FP16=yes
If models do not support fp16 by default, they cannot be run in this mode after. At least I didn’t see that option.
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/ca11860f4f3c3ca2ce8340e2686eeaec05b29111/configs/swin/mask_rcnn_swin-t-p4-w7_fpn_fp16_ms-crop-3x_coco.py
https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmdetection/blob/ca11860f4f3c3ca2ce8340e2686eeaec05b29111/configs/swin/README.md