C++【类和对象】
- 1.运算符重载
- 2.赋值运算符重载
- 3.日期类的实现
1.运算符重载
(1).C++规定类类型运算符使用时,必须转换成调用运算符重载。
(2).运算符重载是具有特殊名字的函数,名字等于operator加需要使用的运算符,具有返回类型和参数列表及函数体。
(3).重载运算符函数的参数个数和该运算符作用的运算对象的个数保持一致,一元运算符有一个参数,二元运算符有两个参数,二元运算符左边的传给第一个参数,右边的传给第二个参数。
(4).如果一个重载运算符函数是成员函数,那么它的第一个函数参数是this指针,所以显示出来就少一个参数。
(5).运算符重载以后,其优先级和结合性与对应的内置类型运算符保持⼀致。
(6).不能通过连接语法中没有的符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
(7).
 这五个运算符不能重载。
这五个运算符不能重载。
(8).C++为了区分前置++和后置++运算符重载函数,规定前置为operator++(),后置++为operator++(int)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
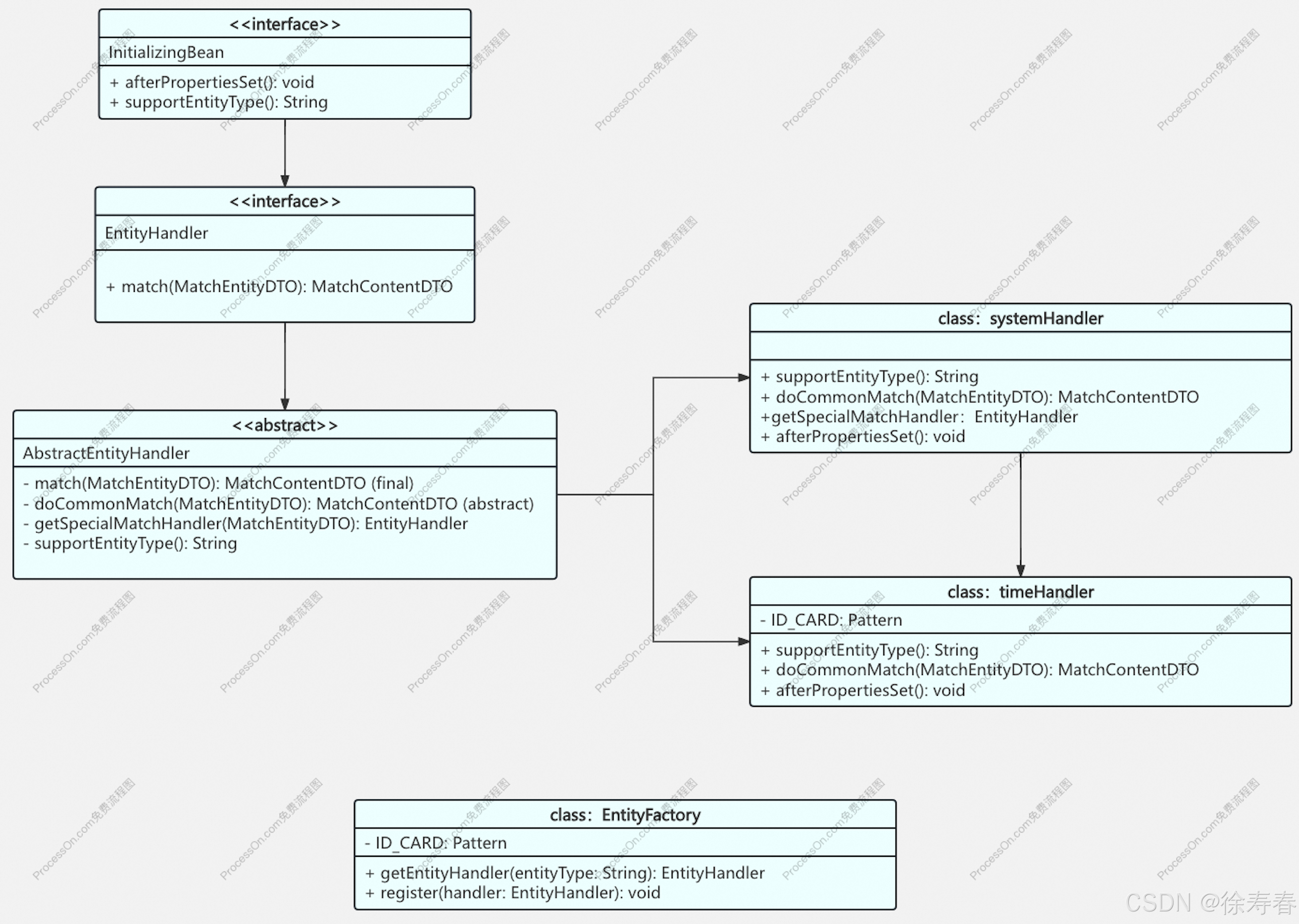
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
bool operator == (const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
//d1-d2
int operator-(const Date& d);
//日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2024, 3, 20);
Date d2(2025, 3, 18);
if (d1 == d2)
{
cout << "相等" << endl;
}
else
cout << "不相等" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.赋值运算符重载
赋值运算符重载是一个默认成员函数(不能重载到全局),用于完成两个已经存在的对象直接的拷贝赋值。
赋值运算符重载的特点:
(1).赋值运算符重载是一个函数重载,规定重载必须为成员函数,赋值运算重载的参数建议写成const 当前类类型引用,否则会传值传参会有拷贝。
(2).有返回值,且建议写成当前类类型引⽤,引⽤返回可以提高效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值场景。
(3).没有显式实现时,编译器会自动生成⼀个默认赋值运算符重载,默认赋值运算符重载行为跟默认拷贝构造函数类似,对内置类型成员变量会完成值拷贝/浅拷贝(⼀个字节⼀个字节的拷贝),对自定义类型成员变量会调用他的赋值重载函数。
(4).如果一个类显示实现析构并释放了资源,就需要我们显示实现赋值运算符重载,否则就不需要。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
Date& operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month =d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return*this;
}
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1(2004,8,18);
Date d2(d1);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
return 0;
}
3.日期类的实现
//Date.h
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
int GetMonthDay(int year,int month)
{
int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
else
return monthDayArray[month];
}
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator-(int day);
// ++d1 ->d1.operator++()
Date& operator++();
// d1++ ->d1.operator++(1);
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
bool operator<(const Date& d);
bool operator<=(const Date& d);
bool operator>(const Date& d);
bool operator>=(const Date& d);
bool operator==(const Date& d);
bool operator!=(const Date& d);
int operator-(const Date& d);
void Print();
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
//Date.cpp
#include"Date.h";
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
void Date::Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
// ++d1
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// d1++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year
&& _month < d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day < d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this < d);
}
//test.cpp
#include"Date.h"
void TestDate1()
{
Date d1(2025, 3, 9);
d1.Print();
Date d2 = d1 + 100;
d2.Print();
d1.Print();
Date d3 = d1 += 100;
d1.Print();
d3.Print();
}
void TestDate2()
{
Date d1(2025, 3, 9);
Date ret1 = ++d1;
//Date ret1 = d1.operator++();
d1.Print();
ret1.Print();
Date d2(2025, 3, 9);
Date ret2 = d2++;
//Date ret2 = d2.operator++(10000);
d2.Print();
ret2.Print();
}
int main()
{
TestDate2();
return 0;
}