先谈论校验方法,本人腾讯云大数据工程师。
1、hdfs的校验
这个通常就是distcp校验,hdfs通过distcp迁移到另一个集群,怎么校验你的对不对。
有人会说,默认会有校验CRC校验。我们关闭了,为什么关闭?全量迁移,如果当前表再写数据,开自动校验就会失败。数据量大(PB级)迁移流程是先迁移全量,后面在定时补最近几天增量,再找个时间点,进行业务割接
那么怎么知道你迁移的hdfs是否有问题呢?
2个文件,一个是脚本,一个是需要校验的目录
data_checksum.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2025/1/16 22:52
# @Author : fly-wlx
# @Email : xxx@163.com
# @File : data_compare.py
# @Software: PyCharm
import subprocess
#output_file = 'data_checksum_result.txt'
def load_file_paths_from_conf(conf_file):
file_list = []
with open(conf_file, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
for line in lines:
path = line.strip()
if path and not path.startswith('#'): # 跳过空行和注释
full_path = f"{path}"
file_list.append(full_path)
return file_list
#def write_sizes_to_file(filepath,source_namenode,source_checksum,target_namenode,target_checksum,status, output_file):
# with open(output_file, 'w') as file:
#file.write(f"{source_namenode}/{filepath},{source_checksum},{target_namenode}/{filepath},{target_checksum},{status}\n")
def write_sizes_to_file(source_path, src_info, destination_path, target_info, status,output_file):
with open(output_file, 'a') as file:
file.write(f"{source_path},{src_info},{destination_path}, {target_info}, {status}\n")
def run_hadoop_command(command):
"""运行 Hadoop 命令并返回输出"""
try:
result = subprocess.check_output(command, shell=True, text=True)
return result.strip()
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print(f"Command failed: {e}")
return None
def get_hdfs_count(hdfs_filepath):
"""获取 HDFS 路径的文件和目录统计信息"""
command = f"hadoop fs -count {hdfs_filepath}"
output = run_hadoop_command(command)
if output:
parts = output.split()
if len(parts) >= 3:
dir_count, file_count, content_size = parts[-3:]
return dir_count, file_count, content_size
return None, None, None
def get_hdfs_size(hdfs_filepath):
"""获取 HDFS 路径的总文件大小"""
command = f"hadoop fs -du -s {hdfs_filepath}"
output = run_hadoop_command(command)
if output:
parts = output.split()
if len(parts) >= 1:
return parts[0]
return None
def validate_hdfs_data(source_namenode, target_namenode,filepath):
output_file = 'data_checksum_result.txt'
source_path=f"{source_namenode}/{filepath}"
destination_path = f"{target_namenode}/{filepath}"
"""校验 HDFS 源路径和目标路径的数据一致性"""
print("Fetching source path statistics...")
src_dir_count, src_file_count, src_content_size = get_hdfs_count(source_path)
src_total_size = get_hdfs_size(source_path)
print("Fetching destination path statistics...")
dest_dir_count, dest_file_count, dest_content_size = get_hdfs_count(destination_path)
dest_total_size = get_hdfs_size(destination_path)
src_info={}
src_info["src_dir_count"] = src_dir_count
src_info["src_file_count"] = src_file_count
#src_info["src_content_size"] = src_content_size
src_info["src_total_size"] = src_total_size
target_info = {}
target_info["src_dir_count"] = dest_dir_count
target_info["src_file_count"] = dest_file_count
#target_info["src_content_size"] = dest_content_size
target_info["src_total_size"] = dest_total_size
print("\nValidation Results:")
if (src_dir_count == dest_dir_count and
src_file_count == dest_file_count and
# src_content_size == dest_content_size and
src_total_size == dest_total_size):
print("✅ Source and destination paths are consistent!")
write_sizes_to_file(source_path, src_info, destination_path,target_info, 0,
output_file)
else:
print("❌ Source and destination paths are inconsistent!")
write_sizes_to_file(source_path, src_info, destination_path, target_info, 1,
output_file)
#print(f"Source: DIR_COUNT={src_dir_count}, FILE_COUNT={src_file_count}, CONTENT_SIZE={src_content_size}, TOTAL_SIZE={src_total_size}")
#print(f"Destination: DIR_COUNT={dest_dir_count}, FILE_COUNT={dest_file_count}, CONTENT_SIZE={dest_content_size}, TOTAL_SIZE={dest_total_size}")
# 设置源路径和目标路径
#source_path = "hdfs://namenode1:8020/"
#destination_path = "hdfs://namenode2:8020/path/to/destination"
# 定义源和目标集群的 namenode 地址
source_namenode = "hdfs://10.xx.xx.6:8020"
target_namenode= "hdfs://10.xx.xx.106:4007"
def main():
# 配置文件路径和输出文件路径
conf_file = 'distcp_paths.conf'
# 定义源和目标集群的 namenode 地址
# 设置源路径和目标路径
#source_namenode = "hdfs://source-namenode:8020"
#target_namenode = "hdfs://target-namenode:8020"
# 文件列表
file_paths = load_file_paths_from_conf(conf_file)
# 对每个目录进行校验
for filepath in file_paths:
validate_hdfs_data(source_namenode, target_namenode, filepath)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# 执行校验
#validate_hdfs_data(source_path, destination_path)distcp_paths.conf
/apps/hive/warehouse/xx.db/dws_ixx_features
/apps/hive/warehouse/xx.db/dwd_xx_df用法
直接python3 data_checksum.py(需要改为自己的)
他会实时打印对比结果,并且将结果生成到一个文件中(data_checksum_result.txt)

2、hive文件内容比对
最终客户要的是任务的数据对得上,而不是管你迁移怎么样,所以验证任务的方式:两边同时跑同多个Hive任务流的任务,查看表数据内容是否一致。(因为跑出来的hdfs的文件大小由于mapreduce原因,肯定是不一致的,校验实际数据一致就行了)
方法是先对比表字段,然后对比count数,然后将每行拼起来对比md5
涉及3个文件,单检测脚本,批量入口脚本,需要批量检测的表文件
check_script.sh
#!/bin/bash
#owner:clark.shi
#date:2025/1/22
#背景:用于hive从源端任务和目标端任务,两边跑完结果表的内容校验(因为mapreduce和小文件不同,所以要用数据内容校验)
# --用trino(presto)会更好,因为可以跨集群使用,目前客户因为资源情况没装,此为使用hive引擎,将数据放到本地进行比对
#输入:源端表,目标表,分区名,分区值
#$0是脚本本身,最低从1开始
#限制脚本运行内存大小,30gb
#ulimit -v 30485760
#---注意,要保证,2个表的字段顺序是一样的(md5是根据顺序拼接的)
echo "================"
echo "注意"
echo "要保证,2个表的字段顺序是一样的(md5是根据顺序拼接的)"
echo "要保证,这2个表是存在的"
echo "要保证,双端是可以互相访问"
echo "要保证,2个hive集群的MD5算法相同"
echo "禁止表,一个分区数据量超过本地磁盘,此脚本会写入本地磁盘(双端数据),对比后删除"
echo "注意,如果分区字段是数字不用加引号,如果是字符串需要加引号,搜partition_value,这里分区是int如20250122是没有引号"
echo "================"
a_table=$1
b_table=$2
partition_column=$3
partition_value=$4
if [ $# -ne 4 ]; then
echo "错误:必须输入 4 个参数,源端表,目标表,分区名,分区值"
exit 1
fi
#------------函数
check_value() {
# 第一个参数是布尔值,第二个参数是要 echo 的内容
local value=$1
local message=$2
# 检查第一个参数的值
if [ "$value" == "false" ]; then
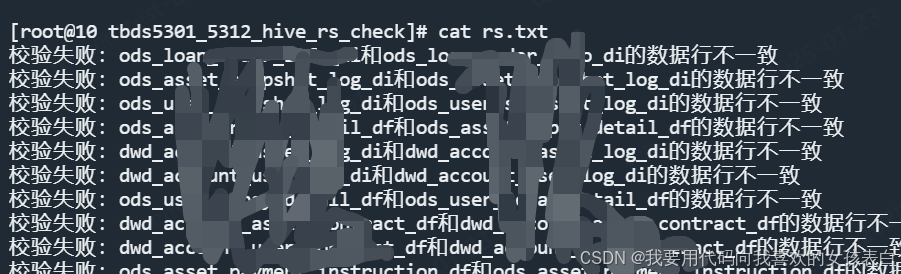
echo "校验失败:$message" >> rs.txt
exit
fi
}
#-----------函数结束
echo "需要对比表的数据内容是$a_table和$b_table--,需要对比分区$partition_column是$partition_value--"
sleep 2
echo "===============开始校验============="
#todo改成自己的,kerbers互信认证(也可以用ldap)
`kinit -kt /root/s_xx_tbds.keytab s_xx_tbds@TBDS-V12X10CS`
#校验字段类型
echo "1.开始校验字段类型"
#todo这里要改成自己的
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.4:10001/XXdatabase;principal=hive/tbds-10-xx-xx-4.hadooppdt.xxjin.srv@TBDS-V12X10CS;transportMode=http;httpPath=cliservice" -e "DESCRIBE $b_table" > 1_a_column.txt
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.104:7001/XXdatabase;principal=hadoop/10.xx.xx.104@TBDS-09T7KXLE" -e "DESCRIBE $a_table" > 1_b_column.txt
if diff 1_a_column.txt 1_b_column.txt > /dev/null; then
echo "表结构一致"
else
echo "表结构不一致"
check_value false "$a_table和$b_table字段类型不一致"
fi
echo "------------1.表字段,校验完毕,通过-------------"
#校验count数
echo "2.开始count校验"
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.4:10001/XXdatabase;principal=hive/tbds-10-xx-xx-4.hadooppdt.xxjin.srv@TBDS-V12X10CS;transportMode=http;httpPath=cliservice" -e "select count(*) from $b_table where $partition_column=$partition_value" > 2_a_count.txt
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.104:7001/XXdatabase;principal=hadoop/10.xx.xx.104@TBDS-09T7KXLE" -e "select count(*) from $a_table where $partition_column=$partition_value" > 2_b_count.txt
if diff 2_a_count.txt 2_b_count.txt > /dev/null; then
echo "数据行一致"
else
echo "数据行不一致"
check_value false "$a_table和$b_table的数据行不一致"
fi
echo "------------2.数据行,校验完毕,通过-------------"
#拼接每一行的值,作为唯一值,创建2个临时表
echo "3.生成每条数据唯一标识"
#1.获取表列名
#使用awk,去除第一行字段名,,删除#字号以及他后面的内容(一般是分区的描述),根据分隔符|取第一列数据,去掉空的行
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.104:7001/XXdatabase;principal=hadoop/10.xx.xx.104@TBDS-09T7KXLE" --outputformat=dsv -e "DESCRIBE $a_table" |awk 'NR > 1' |awk '!/^#/ {print} /^#/ {exit}'|awk 'BEGIN {FS="|"} {print $1}'|awk 'NF > 0' > 3_table_field_name.txt
#2.拼接表列名,生成md5的表 (第一步已经检测过双方的表结构了,这里用同一个拼接字段即可)
# 使用 while 循环逐行读取文件内容
name_fields=""
while IFS= read -r line; do
if [ -z "$name_fields" ]; then
name_fields="$line"
else
name_fields="$name_fields,$line"
fi
done < "3_table_field_name.txt"
echo "$name_fields"
#将每行数据进行拼接,并且生成含一个字段的md5表
md5_sql="SELECT distinct(MD5(CONCAT($name_fields))) AS md5_value "
a_md5_sql="$md5_sql from (select * from dim_user_profile_df where $partition_column=$partition_value limit 100)a;"
b_md5_sql="$md5_sql from $a_table where $partition_column=$partition_value;"
echo "a表的sql是:$a_md5_sql"
echo "b表的sql是:$b_md5_sql"
#源端是生产环境,这里做了特殊处理,源端就取100条(没使用order by rand(),客户主要是检测函数,order by 会占用他们集群资源)
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.4:10001/XXdatabase;principal=hive/tbds-10-xx-xx-4.hadooppdt.xxjin.srv@TBDS-V12X10CS;transportMode=http;httpPath=cliservice" --outputformat=dsv -e "$a_md5_sql" > 4_a_md5_data.txt
beeline -u "jdbc:hive2://10.xx.xx.104:7001/XXdatabase;principal=hadoop/10.xx.xx.104@TBDS-09T7KXLE" --outputformat=dsv -e "$b_md5_sql" > 4_b_md5_data.txt
#3.(由于不是同集群,需要下载到本地,再进行导入--如果耗费资源时长太长,再导入到hive,否则直接shell脚本搞定)
# 设置large_file和small_file的路径
large_file="4_b_md5_data.txt"
small_file="4_a_md5_data.txt"
# 遍历small_file中的每一行
while IFS= read -r line; do
# 检查line是否存在于large_file中
if grep -qxF "$line" "$large_file"; then
# 如果line存在于large_file中,输出1
#echo "1"
a=1
else
# 如果line不存在于large_file中,输出2
echo "2"
check_value false "$a_table和$b_table抽样存在数据内容不一致"
fi
done < "$small_file"
echo echo "------------3.数据内容,校验完毕,通过-------------"
#抽样核对md5(取数据时已抽样,否则数据太大容易跑挂生产环境)
input_file.txt需要校验的表文件
源端表名,目标端表名,分区字段(写1级分区就可以),分区值
ods_xxnfo_di ods_xxnfo_dii dt 20250106
ods_asxx_log_di ods_asxx_log_dii dt 20250106
ods_xxog_di ods_xxog_di dt 20250106
dwd_xxx dwd_xxx dt 20250106
run.sh
#!/bin/bash
# 设置文件路径
input_file="input_file.txt"
# 遍历文件中的每一行
while IFS= read -r line; do
# 调用另一个脚本并传递当前行的参数
echo $line
./check_script.sh $line
# 在每次执行完后间隔一小段时间,避免系统过载(可选)
sleep 1
done < "$input_file"使用方法
sh run.sh(需要把check_scripe和run里的内容改成自己的哈)
他会把不通过的,生成一个rs.txt