Django类视图
一、知识要点概览表
| 类别 | 知识点 | 掌握程度要求 |
|---|---|---|
| 基础视图 | View、TemplateView、RedirectView | 深入理解 |
| 通用显示视图 | ListView、DetailView | 熟练应用 |
| 通用编辑视图 | CreateView、UpdateView、DeleteView | 熟练应用 |
| Mixin机制 | ContextMixin、LoginRequiredMixin | 理解原理 |
| 视图配置 | URL配置、参数传递、模板指定 | 熟练应用 |
二、基础视图实现
1. 基本View类
# views.py
from django.views import View
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.shortcuts import render
class HelloView(View):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return HttpResponse("Hello, Class-based Views!")
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return HttpResponse("POST request received")
class DashboardView(View):
template_name = 'dashboard.html'
def get(self, request):
context = {
'username': request.user.username,
'page_title': 'Dashboard'
}
return render(request, self.template_name, context)
2. TemplateView使用
# views.py
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
class HomePageView(TemplateView):
template_name = "home.html"
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['page_title'] = '首页'
context['features'] = [
'基于类的视图',
'通用视图',
'Mixin机制'
]
return context
3. RedirectView示例
# views.py
from django.views.generic import RedirectView
class GitHubRedirectView(RedirectView):
url = 'https://github.com'
permanent = False # 使用302临时重定向
query_string = True # 保留查询字符串
class OldPostRedirectView(RedirectView):
permanent = True # 使用301永久重定向
def get_redirect_url(self, *args, **kwargs):
post_id = kwargs['post_id']
return f'/blog/posts/{post_id}/'
三、通用显示视图
1. ListView实现
# models.py
from django.db import models
class Article(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
content = models.TextField()
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
is_published = models.BooleanField(default=False)
def __str__(self):
return self.title
# views.py
from django.views.generic import ListView
from .models import Article
class ArticleListView(ListView):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/article_list.html'
context_object_name = 'articles'
paginate_by = 10
def get_queryset(self):
"""只显示已发布的文章"""
return Article.objects.filter(
is_published=True
).order_by('-created_at')
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['total_articles'] = self.get_queryset().count()
return context
2. DetailView实现
# views.py
from django.views.generic import DetailView
from django.shortcuts import get_object_or_404
class ArticleDetailView(DetailView):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/article_detail.html'
context_object_name = 'article'
def get_object(self, queryset=None):
"""自定义获取对象的方法"""
obj = super().get_object(queryset=queryset)
# 增加访问次数
obj.views_count = obj.views_count + 1
obj.save()
return obj
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
# 添加相关文章
context['related_articles'] = Article.objects.filter(
is_published=True
).exclude(
id=self.object.id
)[:3]
return context
四、通用编辑视图
1. CreateView实现
# forms.py
from django import forms
from .models import Article
class ArticleForm(forms.ModelForm):
class Meta:
model = Article
fields = ['title', 'content', 'is_published']
def clean_title(self):
title = self.cleaned_data['title']
if len(title) < 5:
raise forms.ValidationError("标题长度不能少于5个字符")
return title
# views.py
from django.views.generic.edit import CreateView
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
from .forms import ArticleForm
class ArticleCreateView(CreateView):
model = Article
form_class = ArticleForm
template_name = 'articles/article_form.html'
success_url = reverse_lazy('article_list')
def form_valid(self, form):
"""表单验证成功时的处理"""
form.instance.author = self.request.user
response = super().form_valid(form)
# 可以在这里添加额外的处理逻辑
return response
def get_initial(self):
"""设置表单初始值"""
return {
'title': '新文章',
'is_published': False
}
2. UpdateView实现
# views.py
from django.views.generic.edit import UpdateView
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import LoginRequiredMixin
class ArticleUpdateView(LoginRequiredMixin, UpdateView):
model = Article
form_class = ArticleForm
template_name = 'articles/article_update.html'
def get_success_url(self):
return reverse_lazy(
'article_detail',
kwargs={'pk': self.object.pk}
)
def get_queryset(self):
"""确保用户只能编辑自己的文章"""
return Article.objects.filter(author=self.request.user)
3. DeleteView实现
# views.py
from django.views.generic.edit import DeleteView
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import UserPassesTestMixin
class ArticleDeleteView(LoginRequiredMixin, UserPassesTestMixin, DeleteView):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/article_confirm_delete.html'
success_url = reverse_lazy('article_list')
def test_func(self):
"""检查用户是否有权限删除文章"""
article = self.get_object()
return self.request.user == article.author
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""自定义删除逻辑"""
self.object = self.get_object()
success_url = self.get_success_url()
# 可以在这里添加其他清理工作
self.object.delete()
return HttpResponseRedirect(success_url)
五、类视图的URL配置
# urls.py
from django.urls import path
from . import views
app_name = 'articles'
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.ArticleListView.as_view(), name='article_list'),
path('<int:pk>/', views.ArticleDetailView.as_view(), name='article_detail'),
path('create/', views.ArticleCreateView.as_view(), name='article_create'),
path('<int:pk>/update/', views.ArticleUpdateView.as_view(), name='article_update'),
path('<int:pk>/delete/', views.ArticleDeleteView.as_view(), name='article_delete'),
]
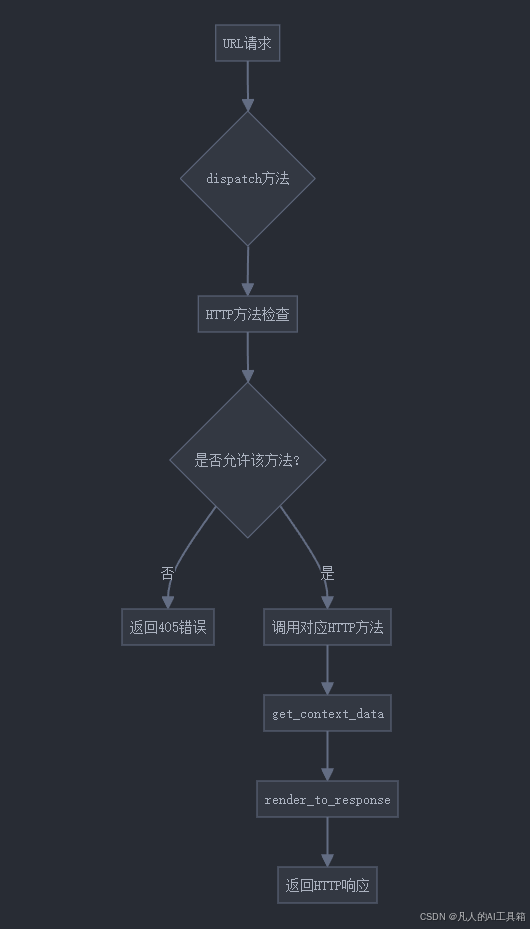
六、类视图执行流程图
七、Mixin的使用
1. 自定义Mixin
class TitleMixin:
title = ''
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['title'] = self.title
return context
class AuthorRequiredMixin:
"""确保用户是作者的Mixin"""
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
obj = self.get_object()
if obj.author != request.user:
raise PermissionDenied
return super().dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
class PageTitleMixin:
page_title = ''
def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):
context = super().get_context_data(**kwargs)
context['page_title'] = self.page_title
return context
# 使用Mixin
class ArticleDetailView(TitleMixin, PageTitleMixin, DetailView):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/article_detail.html'
title = '文章详情'
page_title = '查看文章'
2. 常用Mixin组合
from django.contrib.auth.mixins import (
LoginRequiredMixin,
PermissionRequiredMixin
)
class ArticleAdminView(
LoginRequiredMixin,
PermissionRequiredMixin,
ListView
):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/admin_list.html'
permission_required = 'articles.view_article'
def get_queryset(self):
return Article.objects.all().order_by('-created_at')
class StaffRequiredMixin(UserPassesTestMixin):
def test_func(self):
return self.request.user.is_staff
class ArticleStaffView(StaffRequiredMixin, ListView):
model = Article
template_name = 'articles/staff_list.html'
八、模板示例
<!-- templates/articles/article_list.html -->
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<div class="container">
<h1>{{ page_title }}</h1>
<div class="article-list">
{% for article in articles %}
<div class="article-item">
<h2>{{ article.title }}</h2>
<p>{{ article.content|truncatewords:30 }}</p>
<div class="article-meta">
<span>作者: {{ article.author }}</span>
<span>发布时间: {{ article.created_at|date:"Y-m-d" }}</span>
</div>
<div class="article-actions">
<a href="{% url 'articles:article_detail' article.pk %}"
class="btn btn-primary">
查看详情
</a>
{% if user == article.author %}
<a href="{% url 'articles:article_update' article.pk %}"
class="btn btn-secondary">
编辑
</a>
<a href="{% url 'articles:article_delete' article.pk %}"
class="btn btn-danger">
删除
</a>
{% endif %}
</div>
</div>
{% empty %}
<p>暂无文章</p>
{% endfor %}
</div>
{% if is_paginated %}
<nav aria-label="Page navigation">
<ul class="pagination">
{% if page_obj.has_previous %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.previous_page_number }}">
上一页
</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
{% for num in page_obj.paginator.page_range %}
<li class="page-item {% if page_obj.number == num %}active{% endif %}">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ num }}">{{ num }}</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
{% if page_obj.has_next %}
<li class="page-item">
<a class="page-link" href="?page={{ page_obj.next_page_number }}">
下一页
</a>
</li>
{% endif %}
</ul>
</nav>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% endblock %}
这就是关于Django类视图的详细内容。通过学习这些内容,将能够理解和使用Django的类视图系统,实现更加优雅和可维护的视图逻辑。如果有任何问题,欢迎随时提出!
怎么样今天的内容还满意吗?再次感谢朋友们的观看,关注GZH:凡人的AI工具箱,回复666,送您价值199的AI大礼包。最后,祝您早日实现财务自由,还请给个赞,谢谢!