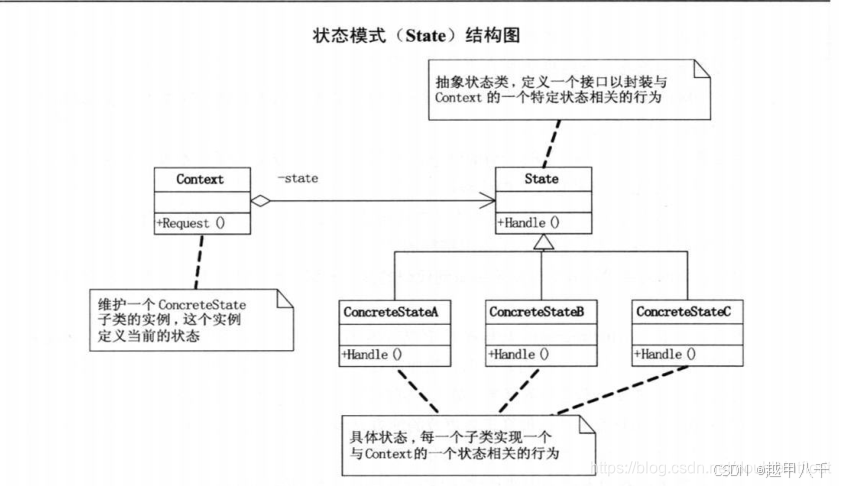
短字符串优化(SSO)
实现1

实现2

写时复制

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 引用计数存放的位置
// 1. 存放在栈上 --- 不行
// 2. 存放在全局静态区 --- 不行
// 3. 只能放在堆上
class String
{
public:
String();
String(const char* pstr);
String(const String& rhs);
String& operator=(const String& rhs);
~String();
const char* c_str() const;
int getRefCount()const;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& rhs);
char& operator[](size_t index);
private:
size_t size()const;
private:
char* _pstr;
};
String::String() :_pstr(new char[5] + 4)
{// 5: 引用计数+‘\0’ 4:让其直接指向数据的位置
//cout << "String()" << endl;
*(int*)(_pstr - 4) = 1;
}
String::String(const char* pstr):_pstr(new char[strlen(pstr) + 5]()+4)/*_pstr(new char(strlen(pstr)+1))*/
{
//cout << "String::String(const char* pstr)" << endl;
strcpy(_pstr,pstr);
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4)) = 1;
}
// String s2(s1)
String::String(const String& rhs):_pstr(rhs._pstr) // 浅拷贝
{
//cout << "String::String(const String& rhs)" << endl;
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))++;
}
String& String::operator=(const String& rhs)
{
if (&rhs != this) //1. 自赋值
{
// 2. 释放左操作
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
if (0 == (*(int*)(_pstr - 4)))
{
delete[](_pstr - 4);
}
// 3. 深拷贝(浅拷贝)
_pstr = rhs._pstr;
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))++;
}
return *this;
}
String::~String()
{
cout << "~String()" << endl;
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
if (0 == (*(int*)(_pstr - 4)))
{
delete[](_pstr - 4);
}
}
const char* String::c_str() const
{
return _pstr;
}
int String::getRefCount() const
{
return *(int*)(_pstr - 4);
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& rhs)
{
if (rhs._pstr != NULL) {
os << rhs._pstr << endl;
}
return os;
}
size_t String::size()const
{
return strlen(_pstr);
}
char& String::operator[](size_t index)
{
if (index > size()) {
static char charnull = '\0';
return charnull;
}
else {
if (getRefCount() > 1) { // 考虑是不是共享的
// 执行深拷贝
int len = size();
char* tmp = new char[len+5]()+4;
strcpy(tmp,_pstr);
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--; // 注意这里不需要看是否等于0,因为getRefCount() > 1
_pstr = tmp;
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4)) = 1;
/*return _pstr[index];*/ // 这个要写到括号之外,可能这个字符串没有被共享
}
return _pstr[index];
}
}
//std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, char ch)
//{
// os << "std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, char ch)" << endl;
// os << ch;
// return os;
//}
int main(void)
{
String s1("hello");
String s2(s1);
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n",s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n",s2.c_str());
String s3("world");
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << endl << "使用s3对s1进行赋值操作" << endl;
s3 = s1;
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s1 RefCount= " << s1.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n", s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3`address = %p\n", s3.c_str());
cout << endl << endl << "对s3[0]执行写操作" << endl;
s3[0] = 'H';
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s1 RefCount= " << s1.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n", s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3`address = %p\n", s3.c_str());
/*如何区分是对[] 读还是写
cout<<s[1] 是进行的读操作; 可以对[]进行重载
s[1] = '1' 是进行的写操作; 可以对=进行重载
*/
// 读操作
//cout << s1[1] << endl;
return 0;
}
-
如何区分什么什么时候读,什么时候写
- 通过一个中间类型CharProxy,并且重载他的operator=和operator<<函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstring>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 引用计数存放的位置
// 1. 存放在栈上 --- 不行
// 2. 存放在全局静态区 --- 不行
// 3. 只能放在堆上
class String
{
public:
String();
String(const char* pstr);
String(const String& rhs);
String& operator=(const String& rhs);
~String();
const char* c_str() const;
int getRefCount()const;
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& rhs);
private:
class CharProxy {
public:
CharProxy( String& self, size_t idx) :_self(self), _idx(idx) {}
char& operator = (const char& ch); // 写操作
/*{
_self[_idx] = ch;
return _self[_idx];
}*/
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const CharProxy& ch);
private:
String &_self; // 此时String是不完整类型
size_t _idx;
};
public:
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const CharProxy& ch);
//char& operator[](size_t index);
CharProxy operator[](size_t idx)
{
return CharProxy(*this,idx);
}
private:
void initRefCount();
void increaseRefCount();
void decreaseRefCount();
void release();
size_t size()const;
private:
char* _pstr;
};
String::String() :_pstr(new char[5] + 4)
{// 5: 引用计数+‘\0’ 4:让其直接指向数据的位置
//cout << "String()" << endl;
initRefCount();
}
String::String(const char* pstr):_pstr(new char[strlen(pstr) + 5]()+4)/*_pstr(new char(strlen(pstr)+1))*/
{
//cout << "String::String(const char* pstr)" << endl;
strcpy(_pstr,pstr);
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
initRefCount();
}
// String s2(s1)
String::String(const String& rhs):_pstr(rhs._pstr) // 浅拷贝
{
//cout << "String::String(const String& rhs)" << endl;
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))++;
increaseRefCount();
}
String& String::operator=(const String& rhs)
{
if (&rhs != this) //1. 自赋值
{
// 2. 释放左操作
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
/*decreaseRefCount();
if (0 == (*(int*)(_pstr - 4)))
{
delete[](_pstr - 4);
}*/
release();
// 3. 深拷贝(浅拷贝)
_pstr = rhs._pstr;
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))++;
increaseRefCount();
}
return *this;
}
String::~String()
{
//cout << "~String()" << endl;
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
//decreaseRefCount();
//if (0 == (*(int*)(_pstr - 4)))
//{
// delete[](_pstr - 4);
//}
release();
}
void String::initRefCount()
{
*(int*)(_pstr - 4) = 1;
}
void String::increaseRefCount()
{
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))++;
}
void String::decreaseRefCount()
{
(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--;
}
void String::release()
{
decreaseRefCount();
if (0 == (*(int*)(_pstr - 4)))
{
delete[](_pstr - 4);
}
}
const char* String::c_str() const
{
return _pstr;
}
int String::getRefCount() const
{
return *(int*)(_pstr - 4);
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& rhs)
{
if (rhs._pstr != NULL) {
os << rhs._pstr << endl;
}
return os;
}
size_t String::size()const
{
return strlen(_pstr);
}
char& String::CharProxy::operator = (const char& ch) // 写操作
{
if (_idx > _self.size())
{
static char charnull = '\0';
return charnull;
}
else
{
if (_self.getRefCount() > 1) { // 考虑是不是共享的
// 执行深拷贝
int len = _self.size();
char* tmp = new char[len+5]()+4;
strcpy(tmp, _self._pstr);
//(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--; // 注意这里不需要看是否等于0,因为getRefCount() > 1
_self.decreaseRefCount();
_self._pstr = tmp;
_self.initRefCount();
/*return _pstr[index];*/ // 这个要写到括号之外,可能这个字符串没有被共享
}
_self._pstr[_idx] = ch;
return _self._pstr[_idx];
}
}
//双友元的设置
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String::CharProxy& rhs)
// 注意这个函数既要左CharProxy的友元也要作为String的友元(不然上面的代码const String::CharProxy& ch处会报错)
{
os << rhs._self._pstr[rhs._idx];
return os;
}
//char& String::operator[](size_t index)
//{
// if (index > size()) {
// static char charnull = '\0';
// return charnull;
// }
// else {
// if (getRefCount() > 1) { // 考虑是不是共享的
// // 执行深拷贝
// int len = size();
// char* tmp = new char[len+5]()+4;
// strcpy(tmp,_pstr);
//
// //(*(int*)(_pstr - 4))--; // 注意这里不需要看是否等于0,因为getRefCount() > 1
// decreaseRefCount();
// _pstr = tmp;
// //(*(int*)(_pstr - 4)) = 1;
// initRefCount();
// /*return _pstr[index];*/ // 这个要写到括号之外,可能这个字符串没有被共享
// }
// return _pstr[index];
// }
//}
//std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, char ch)
//{
// os << "std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, char ch)" << endl;
// os << ch;
// return os;
//}
int main(void)
{
String s1("hello");
String s2(s1);
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n",s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n",s2.c_str());
String s3("world");
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << endl << "使用s3对s1进行赋值操作" << endl;
s3 = s1;
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s1 RefCount= " << s1.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n", s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3`address = %p\n", s3.c_str());
cout << endl << endl << "对s3[0]执行写操作" << endl;
s3[0] = 'H';
// 首先会调用s1.operator[](1)返回一个CharProxy对象,然后调用CharProxy的operatpr=()函数
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s1 RefCount= " << s1.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n", s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3`address = %p\n", s3.c_str());
/*如何区分是对[] 读还是写
cout<<s[1] 是进行的读操作; 可以对[]进行重载
s[1] = '1' 是进行的写操作; 可以对=进行重载
s[1] = '1' .
char = char 两个char是不能被重载的,因为 运算符重载的第一条规则,参数必须要有一个自定义类型或者enum
CharProxy = char就可以重载了
可以先重载一下[],让他返回一个CharProxy对象,然后重载CharProxy的operator=和operator<<函数
CharProxy operator[](size idx);
CharProxy = char;
*/
// 读操作
cout << endl << endl << "对s1[1]执行读操作操作" << endl;
cout << s1[1] << endl;
// 首先会调用s1.operator[](1)返回一个CharProxy对象,然后调用CharProxy的operator<<()函数
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
cout << "s1 RefCount= " << s1.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s2 RefCount= " << s2.getRefCount() << endl;
cout << "s3 RefCount= " << s3.getRefCount() << endl;
printf("s1`address = %p\n", s1.c_str());
printf("s2`address = %p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3`address = %p\n", s3.c_str());
return 0;
}
//https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1VM4m12754?t=1190.2&p=58
上面会出现,双友元声明,可以只重载operator=,不重载<< 和一个类型转换函数
-
//双友元的设置 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String::CharProxy& rhs) // 注意这个函数既要左CharProxy的友元也要作为String的友元(不然上面的代码const String::CharProxy& ch处会报错) { os << rhs._self._pstr[rhs._idx]; return os; } // cout<<s1[1] CharProxy-> char -
改为
-
String::CharProxy::operator char() // 注意类型转换函数在类外的定义的形式operator char都放在最后 { return _self._pstr[_idx]; }
-
string的实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class String
{
friend bool operator==(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend bool operator!=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend bool operator>(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend bool operator<(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend bool operator<=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend bool operator>=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& s);
friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, String& s);
public:
String();
String(const char* pstr);
String(const String& rhs);
String& operator=(const String& rhs);
String& operator=(const char* pstr);
String& operator+=(const String& rhs);
String& operator+=(const char* pstr);
char& operator[](std::size_t index); // 非const调用
char& operator[](std::size_t index) const;// const对象调用
std::size_t size()const;
const char* c_str()const;
private:
char* _pstr;
};
std::size_t String::size()const
{
return strlen(this->_pstr);
}
const char* String::c_str()const
{
return this->_pstr;
}
String::String() :_pstr(nullptr) // 后面的操作需要判空
{
cout << "String()" << endl;
}
String::String(const char* pstr) :_pstr(new char[strlen(pstr)+1]())
{
strcpy(this->_pstr,pstr);
}
String::String(const String& rhs) :_pstr(new char[strlen(rhs._pstr) + 1])
{
cout << "String(const String& rhs)" << endl;
strcpy(this->_pstr, rhs._pstr);
}
String& String::operator=(const String& rhs)
{
if (&rhs != this)
{
delete[] this->_pstr;
this->_pstr = nullptr;
this->_pstr = new char[strlen(rhs.c_str() + 1)]();
strcpy(this->_pstr, rhs.c_str());
}
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(const char* pstr)
{
String tmp(pstr);
*this = tmp; // 调用String的operator=()函数。
return tmp;
}
String& String::operator+=(const String& rhs)
{
int len = this->size() + rhs.size() + 1;
char* p = new char[len + 1] ();
strcpy(p,this->c_str());
strcat(p,rhs.c_str());
delete[] this->_pstr;
this->_pstr = p;
return *this;
}
String& String::operator+=(const char* pstr)
{
//char* p = new char[this->size()+strlen(pstr) + 1]();
//strcpy(p, this->c_str());
//strcat(p, pstr);
//delete[] this->_pstr;
//this->_pstr = p;
String tmp(pstr);
*this += tmp; // 调用operator+=(const String& rhs)
return *this;
}
char& String::operator[](std::size_t index)
{
if (index < this->size())
{
return this->_pstr[index];
}
else {
static char nullchar = '\0';
return nullchar;
}
}
char& String::operator[](std::size_t index) const
{
if (index < this->size())
{
return this->_pstr[index];
}
else {
static char nullchar = '\0';
return nullchar;
}
}
bool operator==(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return !strcmp(lhs.c_str(),rhs.c_str());
}
bool operator!=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str());
}
bool operator>(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return strcmp(lhs.c_str(),rhs.c_str());
}
bool operator<(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str());
}
bool operator<=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str());
}
bool operator>=(const String& lhs, const String& rhs)
{
return strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str());
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const String& s)
{
os << s.c_str();
}
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, String& s)
{
if (s._pstr)
{
delete s._pstr;
s._pstr = nullptr;
}
std::vector<char> buffer;
char ch;
while ((ch = is.get()) != '\n')
{
buffer.push_back(ch);
}
s._pstr = new char[buffer.size() + 1]();
strncpy(s._pstr,&buffer[0],buffer.size());
return is;
}