basysKom GmbH | How to run Flutter on an Embedded Device
https://github.com/sony/flutter-embedded-linux/wiki/Building-Flutter-Engine-from-source
flutter源码下载(最新)-CSDN博客
flutter_engine 交叉编译【自定义编译器(最新)】_flutter。engine 修改-CSDN博客
flutter移植arm32位板子_flutter框架 移植-CSDN博客
Essential Summary
In this blog we will cross compile Flutter for a generic ARMv7 Embedded Linux target. We will prepare the sdk, compile flutter and in the end run some demos.
Implementing cross platform HMIs is something we at basysKom do on a daily basis. Usually we use either Qt/QML or Web Technologies, but we are always looking at a broader spectrum of options to provide our customers the best possible solution.
Flutter is one of those other options. It is an UI Framework based on Dart, made by Google. While the primary focus of Flutter are mobile platforms like iOS and Android with a growing support for the Web, Flutter is also heading towards Linux and Windows. Interesting to know is that Google uses Flutter to provide the HMI for their own embedded devices and that it will become even more important once Fuchsia does succeed Android, since it will be the primary Ui Framework of Fuchsia.
So I wondered if it is possible to run Flutter on an UX-Gruppe MACH platform (which is an iMX.6 SOC). The short answer is: Yes it is possible.
In this blog I will explain how you can setup everything to compile and run Flutter for and on a generic ARMv7 Embedded Linux target. Since I do not know which hardware you may have at hand, I need to assume that you will be able to fill the gaps. An i.MX6 with a recent Buildroot or Yocto BSP is a good starting point.
I will show you the basic dependencies and command lines you need in order to cross-compile Flutter for ARMv7. What you can also expect is a general instruction of what needs to be done in order to finally run a Flutter App on your platform (after you compiled the engine).
Hardware Requirements
The mentioned specs are simply the spec of the hardware I used, they are not necessarily the minimum hardware requirements of Flutter on Embedded.
As mentioned, I use our own UX-Gruppe Hardware, an Ultratronic Mach Platform evaluation board with a single core iMX.6 and 1 GB of Memory. The ARMv7 iMX.6 comes with an integrated graphic chip. The touch-display draws in 1280x800px with 60hz.
SDK Requirements
All my work is done on a Thinkpad X1, running Windows 10 with an Ubuntu 18.04 executed within the Windows Linux Subsystem Version 1.0. You can of course simply run Linux natively, it’s your choice.
The UX-Gruppe hardware comes with a Buildroot Embedded Linux and an SDK/cross-toolchain for ARMv7 containing Clang/LLVM.
Make sure you have an SDK in place that is, in general, able to cross-compile to ARMv7. Ideally your SDK already supports Clang/LLVM, if not, you can of course try to build it on your own, including the required build-tools. Though this is not a trivial task and it may take you a moment or two.
Preparing Clang/LLVM Toolchain for your SDK
This is a little sidetrack since I didn’t actually needed to do it. This is something that you may only need to follow in case your SDK does either not come with any, or a not a recent enough Clang/LLVM support. Expect some stormy weather here, it all depends on the state of the SDK you are using to do this. You should know what you do since I can only give you orientation but not the path.
Get and build Clang/LLVM
To be sure you use the latest instructions, you can find them here. Ensure your host fulfills the general dependencies. Of course you need cmake, git, ssh,… .
#Setup working directory
cd ~
mkdir flutter-exp
cd flutter-exp
#Clone llvm
git clone https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project.git
cd llvm-project
#create build directory
mkdir build
cd build
#Build the TOOLCHAIN
cmake ../llvm \
-DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD=ARM \
-DLLVM_DEFAULT_TARGET_TRIPLE=arm-linux-gnueabihf \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK
make # consider some -j
make install Get and compile Bintools
#Setup working directory
cd ~
#mkdir flutter-exp
cd flutter-exp
git clone git://sourceware.org/git/binutils-gdb.git
cd binutils-gdb
./configure --prefix="/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK" \
--enable-ld \
--target=arm-linux-gnueabihf
make
make install
Get and compile libcxx and libcxxabi
This might be the most troublesome part. In order to avoid issues you want to be sure that the libc you are using to build the engine is new enough to support the requirements of the flutter engine.
In order to avoid breaking your embedded system by introducing a new libc I recommend to compile and link and provide them as static lib.
You already have checked out sources for both together with llvm-project.
Build libcxxabi
cd ~
cd flutter-exp
cd llvm-project
cd build
cmake ../llvm/projects/libcxxabi \
-DCMAKE_CROSSCOMPILING=True \
-DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD=ARM \
-DCMAKE_SYSROOT=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/sysroot #NOTICE SYSROOT HERE! \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME=Linux \
-DCMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR=ARM \
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/bin/clang \
-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/bin/clang++ \
-DLIBCXX_ENABLE_SHARED=False \
-DLIBCXXABI_ENABLE_EXCEPTIONS=False
make # consider some -j
make check-cxx # Test
make install-cxxabi
Build libcxx
cd ~
cd flutter-exp
cd llvm-project
cd build
# you may have trouble here because __cxxabi_config.h
# and cxxabi.h are not placed in /PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/include/c++/v1
# find them and copy them there.
cmake ../llvm/projects/libcxx \
-DCMAKE_CROSSCOMPILING=True \
-DLLVM_TARGETS_TO_BUILD=ARM \
-DCMAKE_SYSROOT=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/sysroot #NOTICE SYSROOT HERE! \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK \
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \
-DCMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME=Linux \
-DCMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR=ARM \
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/bin/clang \
-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/bin/clang++
-DLIBCXX_ENABLE_SHARED=False \
-DLIBCXX_ENABLE_EXCEPTIONS=False \
-DLIBCXX_CXX_ABI=libcxxabi \
-DLIBCXX_CXX_ABI_INCLUDE_PATHS=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/include/c++/v1 \
-DLIBCXX_CXX_ABI_LIBRARY_PATH=/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/lib \
-DLIBCXX_ENABLE_STATIC_ABI_LIBRARY=True
make # consider some -j
make check-cxx # Test
make install-cxx
Congrats! If you managed to get here with(out) trouble, you are all set to build your own Flutter-Engine.
Cross Compiling Flutter for ARM
Setup your Environment
First, get the Chromium depot tools.
cd ~
mkdir flutter-exp
git clone https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/tools/depot_tools.git
#consider this to be added to your ~/.bashrc
export PATH=~/flutter-exp/depot_tools:$PATH
Then, follow the instructions of the setup development environment page of Flutter.
You have to follow Step 1 up to Step 6. Ignore Step 7, 8, 9. The last step you should do is to add a remote for the upstream repository.
Compile the Engine
Following along the instructions for desktop Linux we will now compile the engine.
cd engine
cd src
./flutter/tools/gn \
--target-toolchain /PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK \
--target-sysroot /PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/sysroot \
--target-triple arm-linux-gnueabihf \
--arm-float-abi hard \
--linux-cpu arm \
--runtime-mode debug \
--embedder-for-target \
--no-lto \
--target-os linux
ninja -C out/linux_debug_arm If you run into issue like missing *.o files during linking you do experience an issue most likely caused by libgcc not being installed correctly within the sysroot of the sdk.
You may want to make a coffee (or two) while it compiles…
Once you are done and everything is built, create a good and save location on your disk and copy
libflutter_engine.so,icudtl.datandflutter_embedder.h
from out/linux_debug_arm to your target disk.
You can check with file libflutter_engine.so that you have created an ARM ELF file.
The Embedder
The application which provides the flutter engine an opengl context and access to system resources is called “the embedder”.
A very light-weight starting point can be found here. The instructions are made for a raspberry pi + compiling on the pi. I will point out what we need to cross-compile in our more general case.
Make sure the compiler and linker can find libflutter_engine.so and flutter_embedded.h.
git clone https://github.com/andyjjones28/flutter-pi.git
cd flutter-pi
mkdir out
/PATH/TO/YOUR/SDK/bin/arm-linux-gnueabihf-cc -D_GNU_SOURCE \
-lEGL \
-ldrm \
-lgbm \
-lGLESv2 \
-lrt \
-lflutter_engine \
-lpthread \
-ldl \
-I./include \
-I/usr/include \
-I/usr/include/libdrm \
./src/flutter-pi.c \
./src/platformchannel.c \
./src/pluginregistry.c \
./src/plugins/services-plugin.c \
-o out/flutter-pi How to run your Flutter App
Now that you have built it, you sure want to verify its working, right?
Prepare your device
First you have to copy the libflutter_engine.so and the icudtl.dat along with the flutter-pi to your target hardware.
Prepare the app code
For some samples, take a look here in the sample repository. Please note that many of them require deeper support, support that the sample embedder does not provide to them. You may also (depending on your system) experience some ssl certificate issues on some demos.
What should work with the embedder is the nice background particle demo.
Once you got the sources you will have to patch the main function in ./lib/main.dart. By adding debugDefaultTargetPlatformOverride = TargetPlatform.fuchsia;
before the runApp call.
// ADD THIS IMPORT
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
// ......
void main() {
debugDefaultTargetPlatformOverride = TargetPlatform.fuchsia;
runApp(MyApp());
}
Bundle the app
For this step you have to install flutter on your host system (if you have not done this already). It’s a really awesome experience, don’t worry.
If you have a flutter dev setup on your host. Go to your sample directory and call:
# cd flutter-example
flutter build bundle And now copy it to your target, next to your embedder.
Run the app
The time has come to flutter on your target. For more detailed instructions just take a look in the README of the runner repo. You can also pass flutter engine flags along by adding them after the bundle directory.
/path/to/assets/bundle/directory is the path of the flutter asset bundle directory (i.e. the directory containing the kernel_blob.bin) of the flutter app you’re trying to run.
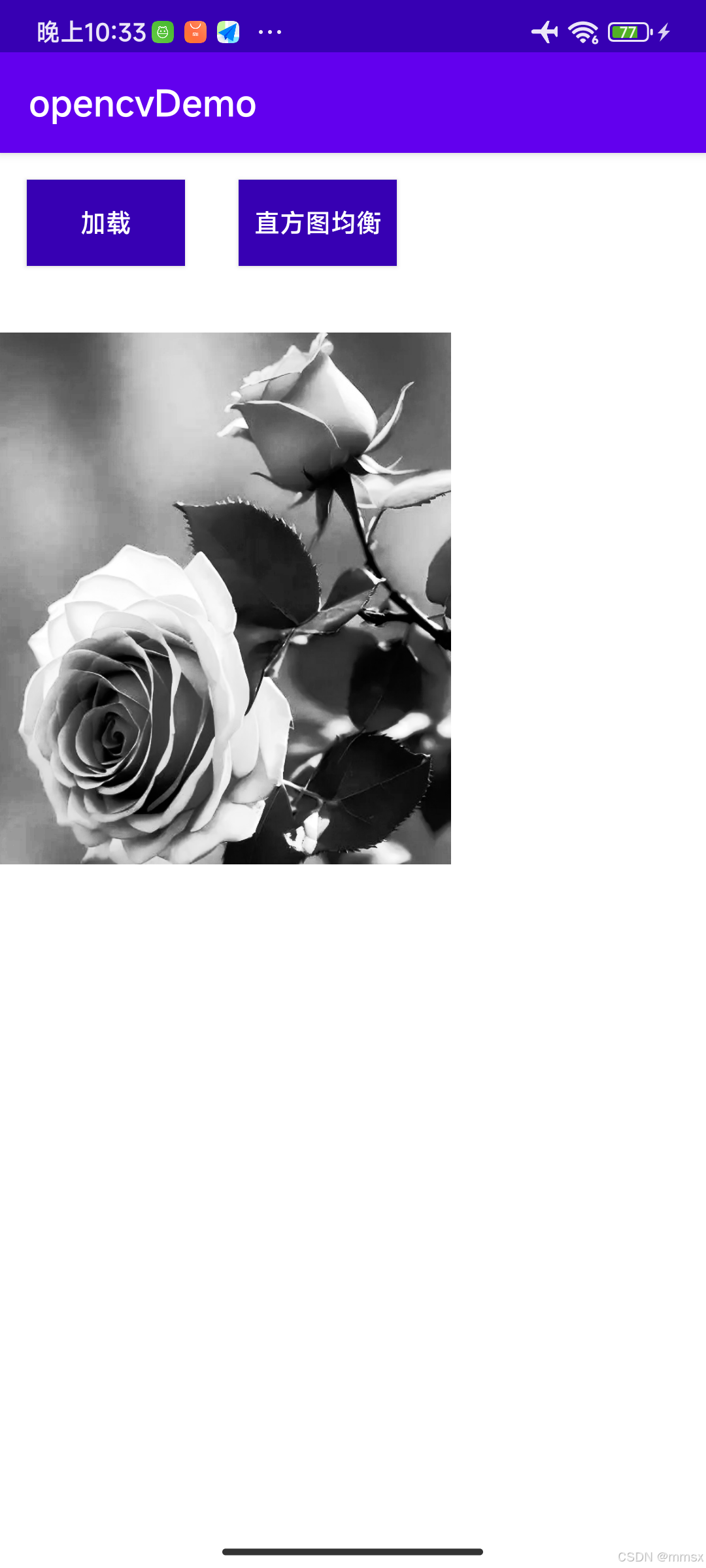
./flutter-pi -t /dev/input0 /path/to/assets/bundle/directory And now you should see your Flutter App on your target device display, along with many additional information on your terminal.
Live capture
Add Your Heading Text Here
Conclusion
After testing and experimenting with Flutter on the iMX.6, I was really surprised by the performance you get with an unoptimized embedder within a debug build. I did not spent much time on profiling, so I can not provide you hard numbers, but it really feels like a very good start.
On the negative side, creating and maintaining an embedder with the required features is hard groundwork. This is definitely not something for juniors, since you have to get down into some dirt where even experienced developers will need to take a sip of coffee first.
On the plus side, you will get a very light-weight, fast and flexible environment to run your app in. This app can run on iOS, Android, Desktop, the Web (Javascript!) and of course on your device.
Together with the ability to use the SKIA backend and render in software Flutter should be able to run on very low end devices and render even there some basic HMI’s.
Flutter is definitely an option to take into consideration if you plan to build a multi platform HMI with a relative small dependency footprint and a very friendly BSD-3 open source license.
I hope you enjoyed this adventure into the world of Flutter like I did. If you have any suggestion or question just drop a comment down below.
Further reads
There are some great resources found in the internet that helped me to put down this article.
- Flutter on RaspberryPi
- Flutter on Toradex
- Flutter Pi