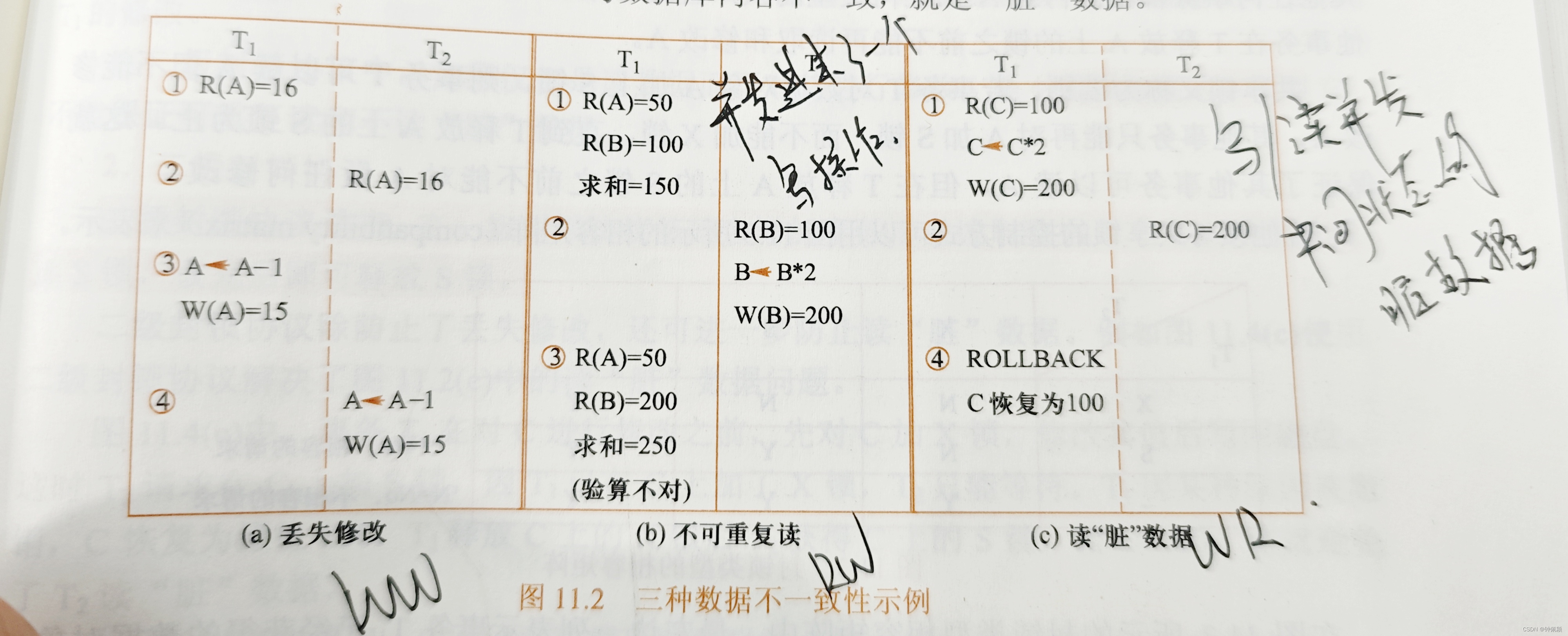
算法思想
深度优先搜索(DFS):
- 使用递归从节点 0 开始,探索所有从当前节点到终点 n−1 的路径。
- 每次访问一个节点时,将该节点加入当前路径 path。
回溯法: 在递归返回时,通过 path.pop_back() 撤销当前节点的选择,回到上一层状态,避免影响其他分支。
路径保存: 当递归到达终点 n−1 时,将当前路径加入结果集 result。
递归终止条件: 当前节点为终点 n−1 时,结束递归。
复杂度: 针对有向无环图(DAG)的特性,确保路径无环,且不重复访问节点。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
vector<vector<int>> result; // 存储所有路径
vector<int> path; // 当前路径
dfs(graph, 0, path, result); // 从节点0开始搜索
return result;
}
private:
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int node, vector<int>& path, vector<vector<int>>& result) {
path.push_back(node); // 将当前节点加入路径
if (node == graph.size() - 1) {
// 如果到达目标节点,将路径加入结果
result.push_back(path);
}
else {
// 遍历当前节点的所有邻居
for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {
dfs(graph, neighbor, path, result);
}
}
path.pop_back(); // 回溯,移除当前节点
}
};
int main() {
// 输入图
vector<vector<int>> graph = { {1, 2}, {3}, {3}, {} };
Solution solution;
vector<vector<int>> result = solution.allPathsSourceTarget(graph);
// 输出结果
cout << "[" << endl;
for (const auto& path : result) {
cout << " [";
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i) {
cout << path[i];
if (i != path.size() - 1) cout << ", ";
}
cout << "]" << endl;
}
cout << "]" << endl;
return 0;
}