在开发过程中有时需要检查某个接口或者某个方法是否存在并发安全问题,我们会用到jmeter 、AB 等压测工具辅助我们完成代码测试,虽然这些工具功能很强大,也很好用,但是在开发过程中来使用还是不如直接执行@Test 或者main 方法来的方便,所以今天就顺便写了一个简单的并发执行任务工具类。
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* 并发执行任务工具
*
* @author Gavin
* @date 2024/11/21
*/
public class ConcurrencyDoTask {
/**
* 线程名称自增数
*/
private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 总耗时
*/
private StopWatch totalTime = new StopWatch();
/**
* 总求数
*/
private AtomicInteger requestTotal = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 成功求数
*/
private AtomicInteger successTotal = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 错误请求数
*/
private AtomicInteger errorTotal = new AtomicInteger(0);
private Supplier<Boolean> supplier;
private Integer threadCount;
private CountDownLatch complement;
private ConcurrencyDoTask() {}
/**
* 请求失败数
*/
private AtomicInteger requestErrorTotal = new AtomicInteger(0);
/**
* 创建线程
*
* @return
*/
private void createThread() {
if (threadCount == null || complement == null || supplier == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> doTask(countDownLatch));
thread.setName("thread--" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " 已就绪 ---- 时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
try {
System.out.println("---------" + threadCount + "个线程已全部就绪 ----5s后开始并发执行任务");
Thread.sleep(5000);
countDownLatch.countDown();
totalTime.start();
complement.await();
totalTime.stop();
System.out.println("总耗时:" + totalTime.getTotalTimeMillis() + "(毫秒) 总请求数 :" + requestTotal + " 成功总数:" + successTotal + " 服务拒绝错误总数:" + errorTotal + " 请求失败总数:" + requestErrorTotal);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("等待线程被中断" + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doTask(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
try {
countDownLatch.await();
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Boolean aBoolean = this.supplier.get();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("线程 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 任务执行成功-- 耗时 : " + stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis() + "(毫秒)");
requestTotal.getAndIncrement();
if (aBoolean) {
successTotal.getAndIncrement();
} else {
errorTotal.getAndIncrement();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
requestErrorTotal.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "任务执行失败");
} finally {
complement.countDown();
}
}
/**
* 初始化线程数量
*
* @param threadCount 线程的个数
* @return
*/
public static ConcurrencyDoTask init(int threadCount) {
if (threadCount <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数 threadCount 必须大于 0");
}
ConcurrencyDoTask multi = new ConcurrencyDoTask();
multi.complement = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
multi.threadCount = threadCount;
return multi;
}
/**
* 传入要执行的方法 返回 boolean
* true 成功 false 失败
*
* @param supplier
* @return
*/
public ConcurrencyDoTask execute(Supplier<Boolean> supplier) {
this.supplier = supplier;
return this;
}
/**
* 开始执行任务
*/
public void start() {
createThread();
}
}
工具的使用
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* ConcurrencyDoTaskTest
*
* @author Gavin
* @date 2024/11/21
*/
public class ConcurrencyDoTaskTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<Boolean> task = ()->{
// 要执行的任务
String result = HttpClientUtil.doGetString("http://xxx.xxx.x.xx/sm2/key");
// 返回是否成功 true 成功 false 失败
return result.contains("\"code\":200");
};
// 调用工具类初始化10个线程并发执行 task 的任务 最后调用 start() 开始执行
ConcurrencyDoTask.init(10).execute(task).start();
}
}
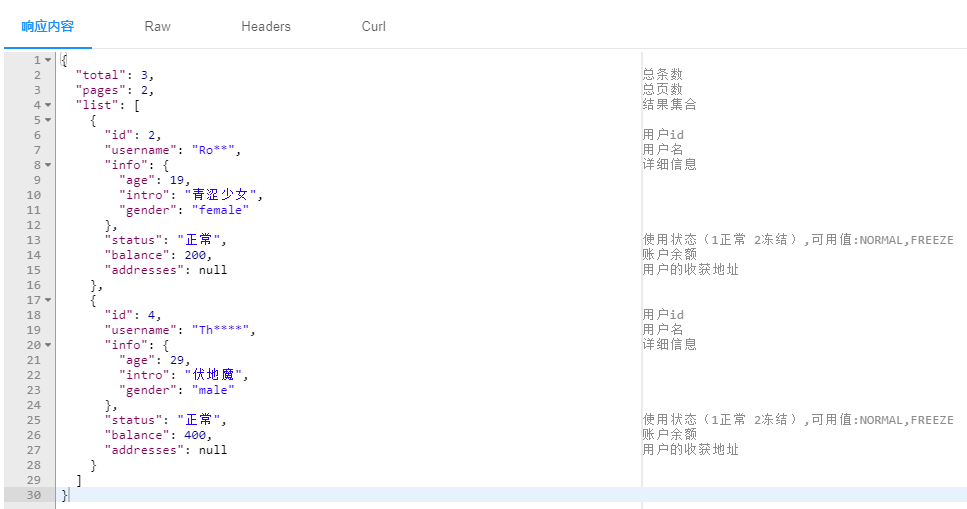
执行结果如下