文章目录
- 前言
- 一、什么是链表?
- 二、单向链表
- 2.1 单向链表的个人实现
- 2.2 单向链表的例题
- 三、双向链表
- 3.1 双向链表的个人实现
- 3.2 关于真正的java中提供的链表的使用
- 总结
前言
提示:概念来源于:>>LinkedList<<
一、什么是链表?
链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的地址。
链表可分为单向链表和双向链表。
一个单向链表包含两个值: 当前节点的值和一个指向下一个节点的链接。
一个双向链表有三个整数值: 数值、向后的节点链接、向前的节点链接。
二、单向链表
一个单向链表包含两个值: 当前节点的值和一个指向下一个节点的链接。

2.1 单向链表的个人实现
先定义一个接口,让个人实现的单向链表实现这个接口中的方法,感兴趣可以直接复制这段代码,然后自己试试实现。
public interface ILinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
public int size();
//用来显示自己的链表,便于编写代码
public void display();
//清空链表
public void clear();
}
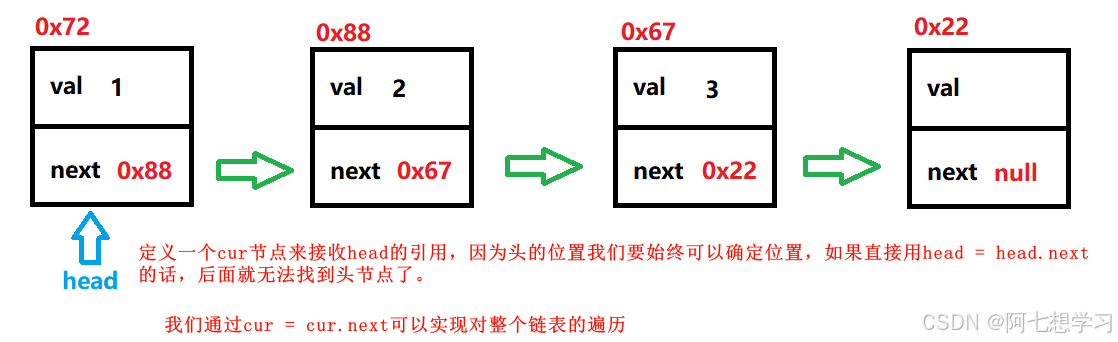
display() — 显示链表中所有内容
//显示链表中所有内容
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
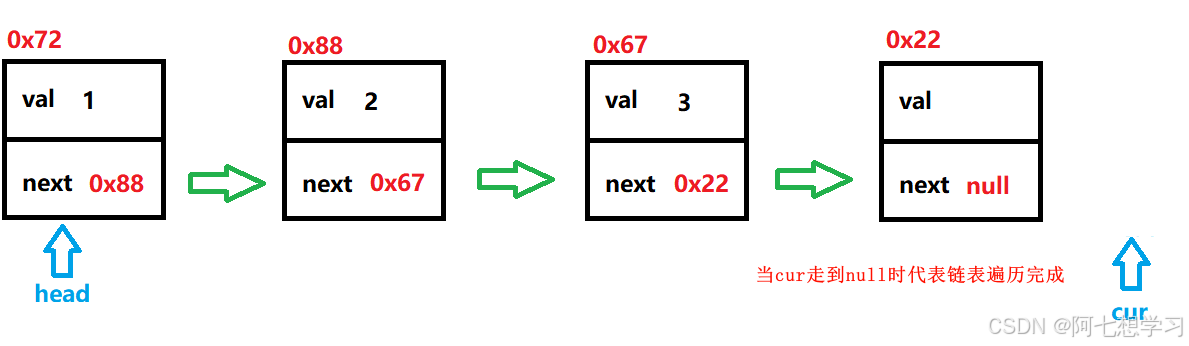
size() — 得到单链表的长度
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int size = 0;
while (cur != null){
size++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return size;
}
和上面的显示链表相似,就是遍历链表
定义一个私有方法,专门用来判断是不是空链表
private boolean isEmpty(MySingleLinkedList mySingleLinkedList){
return 0 == mySingleLinkedList.size();
}
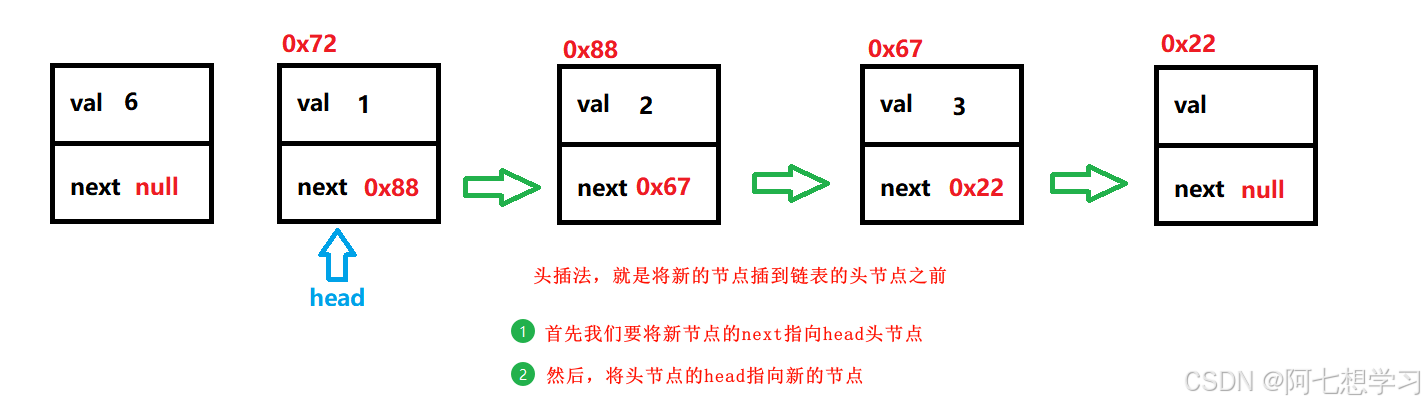
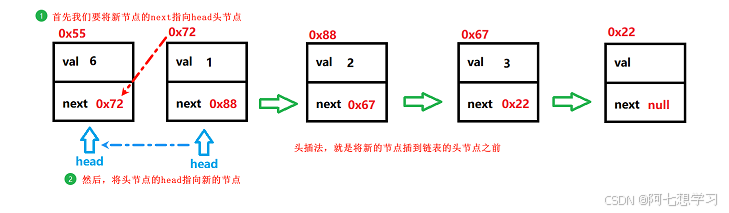
addFirst() — 头插法
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
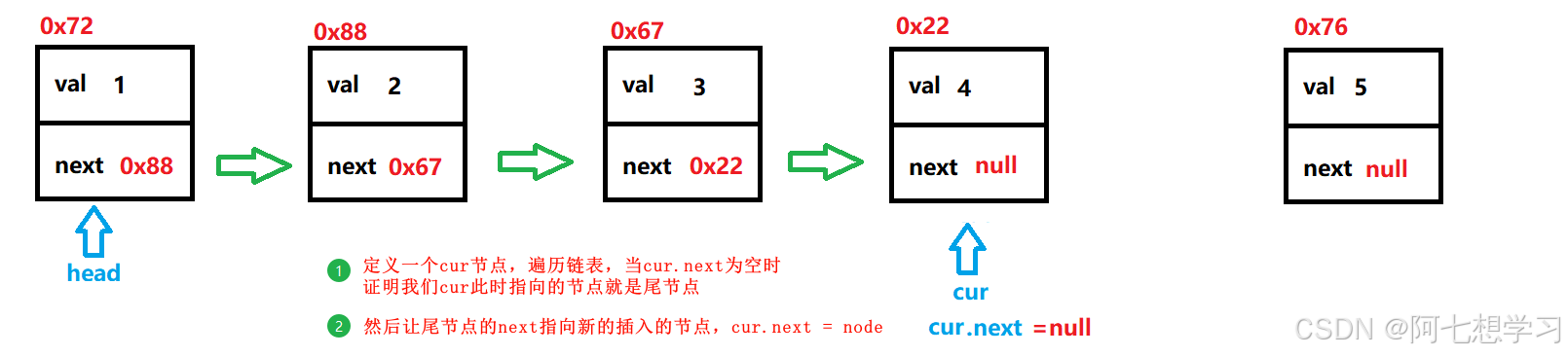
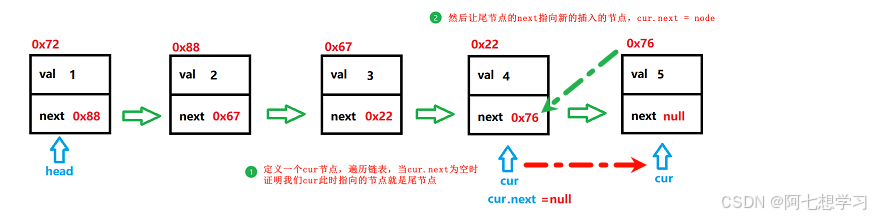
addLast(int data) — 尾插法
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (isEmpty(this)){
head = node;
return; //要记得加
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur.next){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
contains() — 查找是否包含关键字key
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if(key == cur.val){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
同样是遍历链表,查找到就返回true,找不到就返回false
addIndex() — 任意位置插入
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
int len = size();
if(index < 0 || index > len){
System.out.println("输入错误");
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(0 == index){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (len - 1 == index){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (0 != index - 1){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
这里分了三种情况,当插入位置是0,既是头插,当插入位置为节点的长度-1时,则是尾插,其余部分是中间插入,头插和尾插直接调用上面的方法即可,这里介绍中间插入。


remove() — 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if(isEmpty(this)){
System.out.println("空链表无法使用");
}
if(key == head.val){
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur.next){
if(key != cur.next.val){
cur = cur.next;
}else {
ListNode del = cur.next;
if (null != del.next) {
cur.next = del.next;
}else {
cur.next = null;
}
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有要删除的选项");
}
删除也分为三个可能,头删,中间删,尾删,因为我们val里放的是一个基本变量,不用担心空间的释放,因为没有引用变量来引用这个对象,比如如果我们放的是一个自己定义的学生对象,我们就需要将val置为空,而这里我们只需要让被删除的节点不被前后节点指向就是删除了。
头删很简单,直接让头节点指向头节点的下一个节点即可。
接下来我们主要考虑,中间的删除和尾删。
中间删除


尾删除
这个很简单,在中间删除进行判断中,如果del的next为空,说明我们要删除最后一个节点,直接将cur.next置为空即可

removeAllKey() — 删除所有值为key的节点
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(head == null){
return;
}
while (head !=null && key == head.val){
head = head.next;
}
ListNode del = cur;
while (null != cur.next){
if(key == cur.next.val){
del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
这里和上面的删除第一个值为key的节点很相似,只是把原来在遇到后删除直接返回,变成了遍历整个链表,反复执行删除操作,上面的代码理解了,可以很容易看懂,这里不多赘述了。
clear() — 清空链表
//清空链表
public void clear() {
ListNode cur;
while (null != head.next){
cur = head;
head = head.next;
cur.next = null;
}
head = null;
}
这个就简单了,这里也可以将value置为空,因为我们是整数类型,不用担心内存浪费的问题,直接将head一直往后置空就好,就相当于在删除了。
最后是整个自定义单向无头链表的实现代码整合
public class MySingleLinkedList implements ILinkedList{
static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int size = 0;
while (cur != null){
size++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return size;
}
@Override
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if(key == cur.val){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
private boolean isEmpty(MySingleLinkedList mySingleLinkedList){
return 0 == mySingleLinkedList.size();
}
@Override
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
@Override
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (isEmpty(this)){
head = node;
return; //要记得加
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur.next){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
@Override
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
int len = size();
if(index < 0 || index > len){
System.out.println("输入错误");
return;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(0 == index){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (len - 1 == index){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (0 != index - 1){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
@Override
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if(isEmpty(this)){
System.out.println("空链表无法使用");
}
if(key == head.val){
head = head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur.next){
if(key != cur.next.val){
cur = cur.next;
}else {
ListNode del = cur.next;
if (null != del.next) {
cur.next = del.next;
}else {
cur.next = null;
}
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有要删除的选项");
}
@Override
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(head == null){
return;
}
while (head !=null && key == head.val){
head = head.next;
}
ListNode del = cur;
while (null != cur.next){
if(key == cur.next.val){
del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode cur;
while (null != head.next){
cur = head;
head = head.next;
cur.next = null;
}
head = null;
}
}
2.2 单向链表的例题
例题1.反转链表

public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
ListNode newNode = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = newNode;
}
return pre;
}
例题2. 链表的中间节点
快慢指针
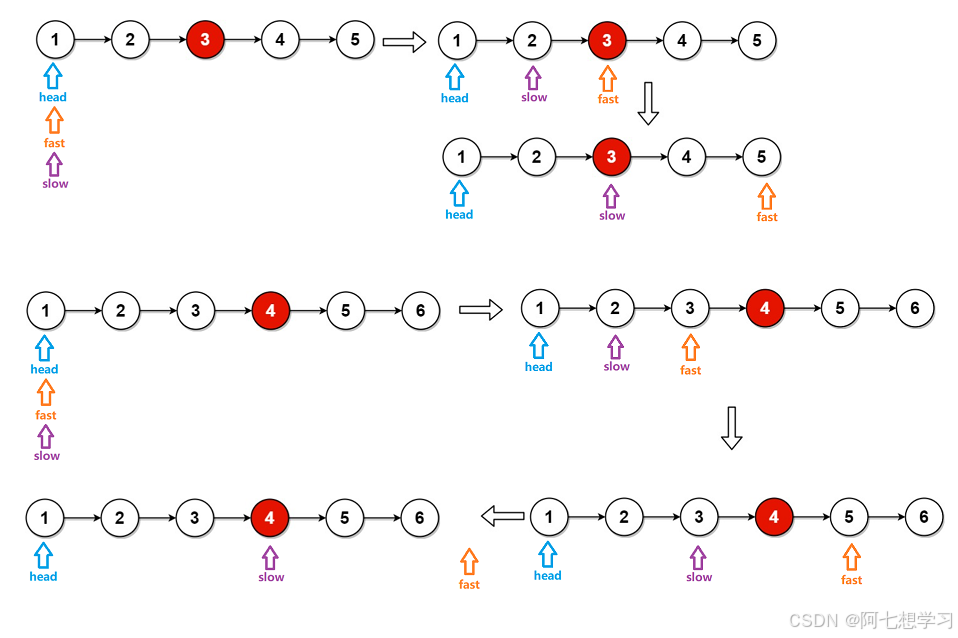
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
例题3. 合并两个有序链表
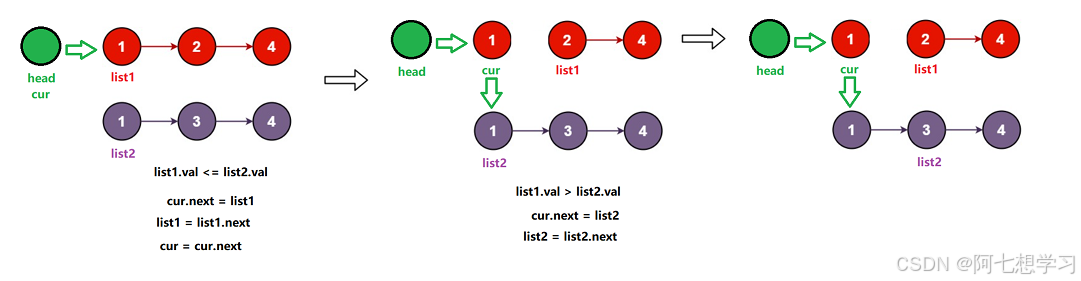
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = head;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
cur.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
cur.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(list1 != null){
cur.next = list1;
}
if(list2 != null){
cur.next = list2;
}
return head.next;
}
例题4. 链表分割

public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {
// write code here
ListNode lb = null;
ListNode le = null;
ListNode bb = null;
ListNode be = null;
ListNode cur = pHead;
if(cur == null){
return pHead;
}
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val < x){
if(lb == null){
lb = cur;
le = cur;
}else{
le.next = cur;
le = cur;
}
}else{
if(bb == null){
bb = cur;
be = cur;
}else{
be.next = cur;
be = cur;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(lb != null){
le.next = bb;
}else{
return bb;
}
if(bb != null){
be.next = null;
}
return lb;
}
例题5. 链表的回文结构
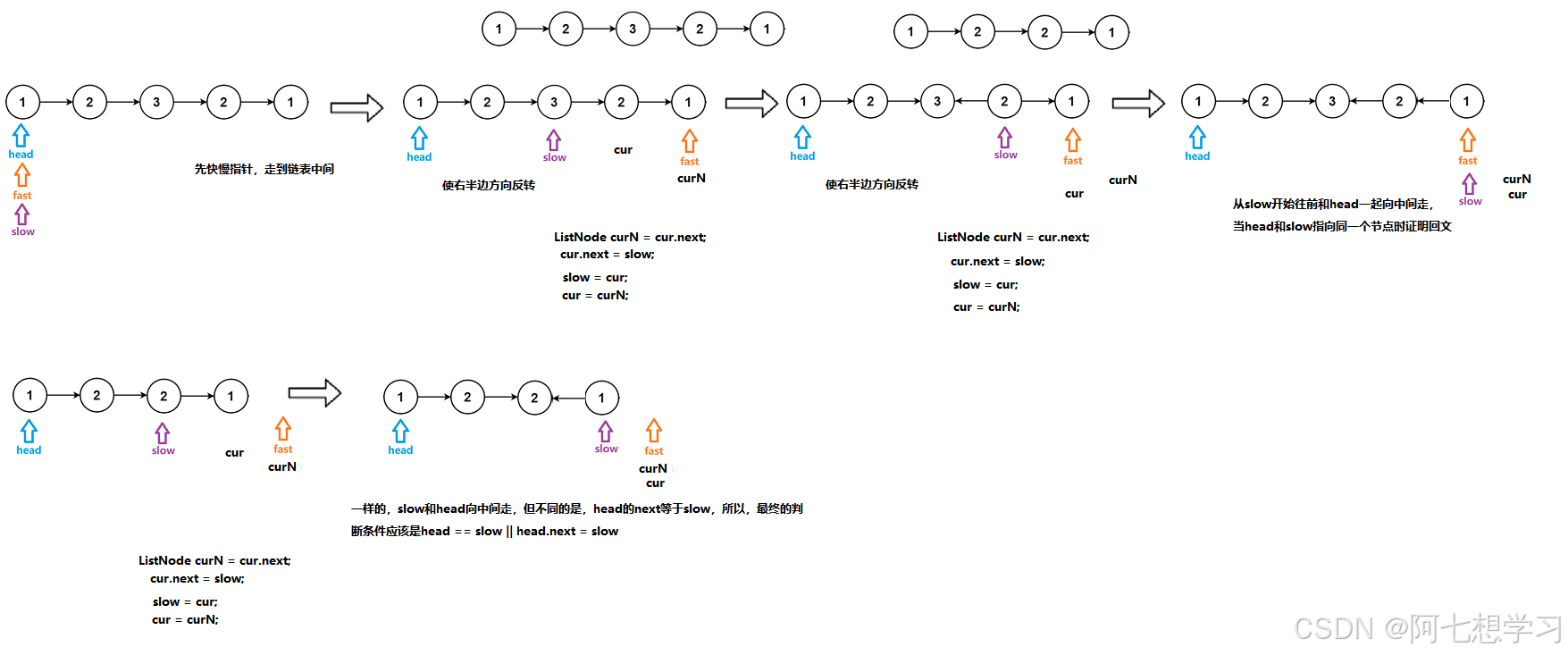
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
// write code here
if (A == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode head = A;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curN = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curN;
}
while (head != slow) {
if (head.next == slow) {
return head.val == slow.val;
}
if (head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
} else {
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
}
while (head != slow) {
if (head.next == slow) {
return head.val == slow.val;
}
if (head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
} else {
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
}
return true;
}
例题6. 相交链表

public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode cur1 = headA;
ListNode cur2 = headB;
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
while(cur1 != null){
count1++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while(cur2 != null){
count2++;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1 = headA;
cur2 = headB;
if(count1 < count2){
int m = count2 - count1;
while(m != 0){
cur2 = cur2.next;
m--;
}
}else{
int m = count1 - count2;
while(m != 0){
cur1 = cur1.next;
m--;
}
}
while(cur1 != null){
if(cur1 == cur2){
return cur1;
}else{
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
return null;
}
例题7. 环形链表

public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while(fast != slow){
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
三、双向链表
一个双向链表有三个整数值: 数值、向后的节点链接、向前的节点链接。
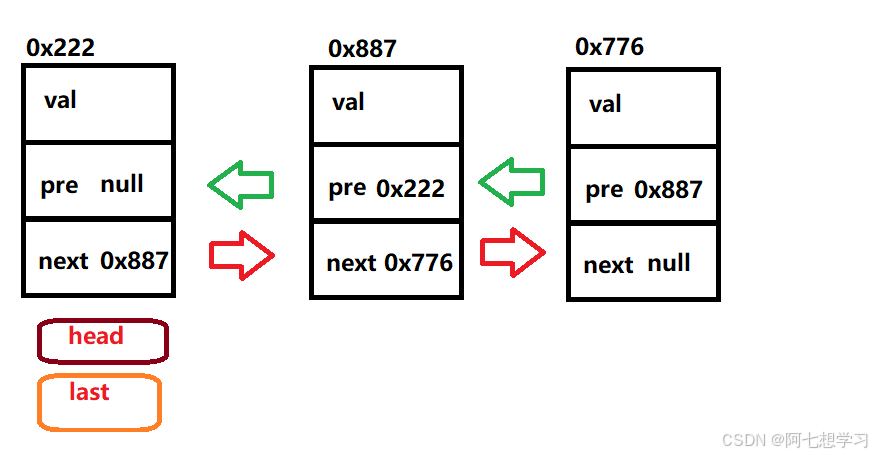
与单向链表不同的是,我们需要两个域来分别记录前一个节点的位置和后一个节点的位置。
3.1 双向链表的个人实现
双向链表的实现和单向链表的实现其实并不会差很多,只是我们要考虑一个节点的关于前后节点的引用。所以解析会相对简单。
同样的,通过接口来规范化我们定义的双向链表
public interface ILinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data);
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data);
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data);
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key);
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key);
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key);
//得到单链表的长度
public int size();
public void display();
public void clear();
}
display() — 展示链表内容
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
size() — 链表长度
public int size() {
int size = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
size++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return size;
}
addFirst() — 头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode first = new ListNode(data);
if(null == this.head){
this.head = first;
this.last = first;
}else {
first.next = this.head;
this.head.pre = first;
this.head = first;
}
}
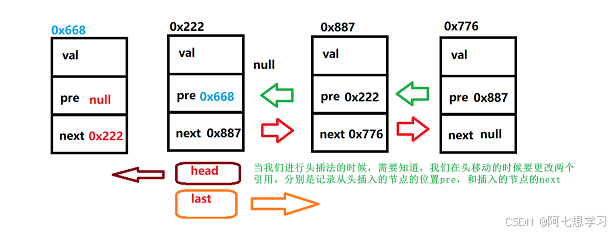
addLast() — 尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode nlast = new ListNode(data);
if(null == this.head){
this.head = nlast;
this.last = nlast;
}else {
this.last.next = nlast;
nlast.pre = this.last;
this.last = nlast;
}
}
因为我们有一个last引用专门用来指向尾节点,所以,我们直接可以用last来插入即可。
addIndex() — 按位置插入
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try {
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new ErrorIndexException("错误的位置!!");//这是自定义的异常
}
if(0 == index){
addFirst(data);
return;
}//头插法
if (size() == index){
addLast(data);
return;
}//尾插法
ListNode cur = head;
while (index - 1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
node.pre = cur.next.pre;
cur.next.pre = node;
cur.next = node;
}catch (ErrorIndexException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
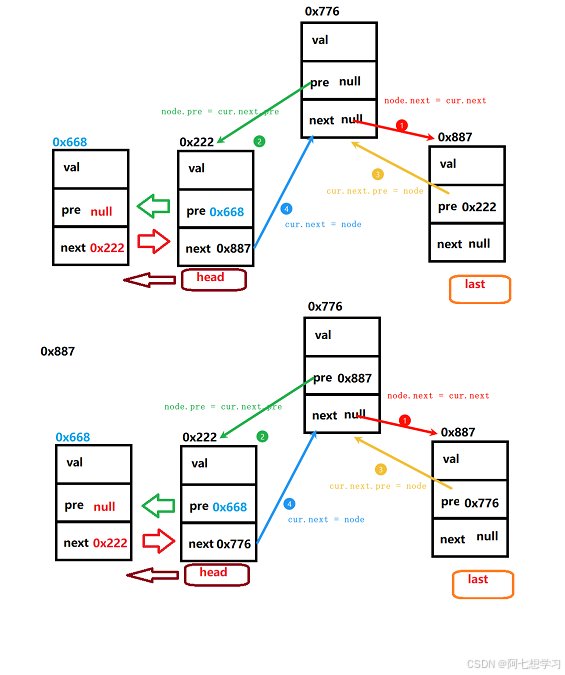
contains() — 是否包含某个数
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if (key == cur.val){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
remove() — 删除某数
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if(key == cur.val){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
head.pre = null;
return;
}
if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
return;
}
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("没有所要删除的数字");
}
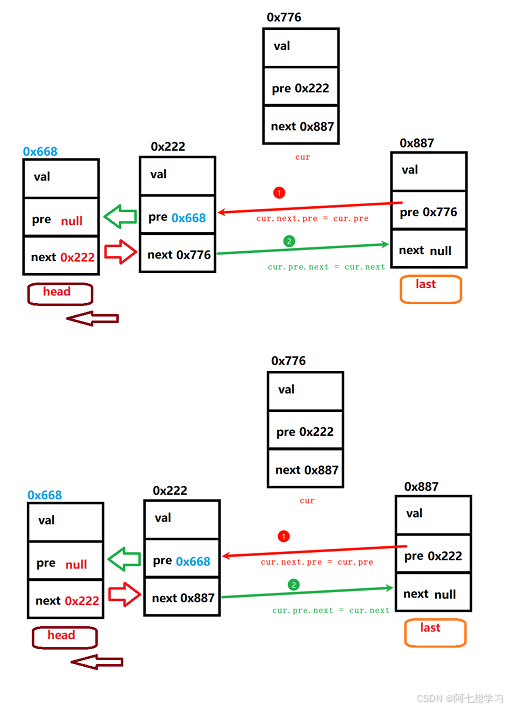
我们分为三种情况,删除的为头节点,尾节点,和中间的。
removeAllKey() — 删除所有的数为目标数的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if(key == cur.val){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
cur = head;
continue;
}
if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
cur = last;
continue;
}
if(cur.next != null && cur.pre != null){
ListNode curN = cur;
curN.next.pre = curN.pre;
curN.pre.next = curN.next;
cur = curN.next;
continue;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
与上面的删除某个节点不同的是我们需要记录被删除的点(用curN记录),便于我们可以继续遍历链表。
clear() — 清空链表
public void clear() {
while (null != head){
ListNode headN = head;
head = head.next;
headN = null;
}
head = null;
}
最后是整个个人实现链表的代码整合
public class MyLinkedList implements ILinkedList{
static class ListNode{
private final int val;
private ListNode pre;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
private ListNode head;
private ListNode last;
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode first = new ListNode(data);
if(null == this.head){
this.head = first;
this.last = first;
}else {
first.next = this.head;
this.head.pre = first;
this.head = first;
}
}
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode nlast = new ListNode(data);
if(null == this.head){
this.head = nlast;
this.last = nlast;
}else {
this.last.next = nlast;
nlast.pre = this.last;
this.last = nlast;
}
}
@Override
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
try {
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new ErrorIndexException("错误的位置!!");
}
if(0 == index){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (size() == index){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (index - 1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
node.pre = cur.next.pre;
cur.next.pre = node;
cur.next = node;
}catch (ErrorIndexException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if (key == cur.val){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void remove(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if(key == cur.val){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
head.pre = null;
return;
}
if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
return;
}
cur.next.pre = cur.pre;
cur.pre.next = cur.next;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("没有所要删除的数字");
}
@Override
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
if(key == cur.val){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
cur = head;
continue;
}
if(cur == last){
last = last.pre;
last.next = null;
cur = last;
continue;
}
if(cur.next != null && cur.pre != null){
ListNode curN = cur;
curN.next.pre = curN.pre;
curN.pre.next = curN.next;
cur = curN.next;
continue;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
int size = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
size++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return size;
}
@Override
public void display() {
ListNode cur = head;
while (null != cur){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
while (null != head){
ListNode headN = head;
head = head.next;
headN = null;
}
head = null;
}
}
3.2 关于真正的java中提供的链表的使用
// 引入 LinkedList 类
import java.util.LinkedList;
LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<E>(); // 普通创建方法
或者
LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c); // 使用集合创建链表
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();//链表的实例化
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
linkedList.add(4);
linkedList.add(5);
linkedList.add(6);
linkedList.add(7);
//foreach遍历
for (int e:
linkedList) {
System.out.println(e);
}
//迭代器正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> iterator = linkedList.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next() + " ");
}
//反向迭代器反向遍历
while (iterator.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(iterator.previous() + " ");
}
关于双向链表的例题很多都要涉及后面诸如栈队列的内容,所以先不提供了,同时我们也可以发现,同样的题,双向链表要比单向链表要容易解决,因为它可以记录前后两个节点。
总结
本篇文章介绍了有关数据结构中链表的相关内容,如单向链表,双向链表,如果有什么不正确的、不严谨的地方,还望指正,谢谢大家!

![[Codesys]常用功能块应用分享-BMOV功能块功能介绍及其使用实例说明](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/42e93b825ee24940b6a7601b90554c97.png)