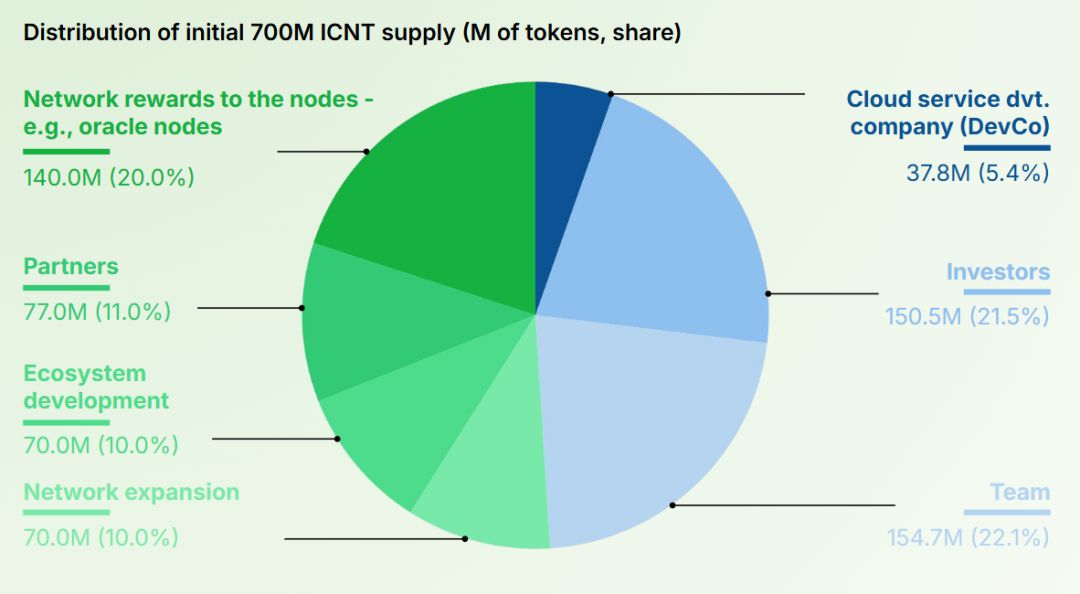
七种工作模式介绍
1.Simple(简单模式)

P:生产者,也就是要发送信息的程序
C:消费者,消息的接收者
Queue:消息队列。图中黄色背景部分,类似一个邮箱,可以缓存发送信息;生产者向其中投递信息,消费者从其中取出消息
特点:一个生产者P,一个消费者C,消息只能被消费一次,就被称为点对点模式
2.Work Queue(工作队列)
一个生产者P,多个消费者C1,C2.在多个消息的情况下,Work Queue会将消息分配给不同的消费者,每个消费者都会接收到不同的消息.
特点:消息不会重复,分配给不同的消费者.
适用场景:集群环境种做异步处理
比如12306的短信通知服务,订票成功后,订单消息会发送到RabbitMQ,短信服务从RabbitMQ获取订单信息,并发送不同的通知信息给消费者.
生产者代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1.建立连接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
//设置参数
factory.setHost(Constants.HOST);//ip
factory.setPort(Constants.PORT);
factory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST);//虚拟机名称
factory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//用户名
factory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD);//密码
//创建连接Connection
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//2.创建channel通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE,true,false,false,null);
//4.发送消息
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
String msg = "hello,work queue~"+i;
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.WORK_QUEUE,null,msg.getBytes());
}
//5.资源释放
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}消费者代码,不过是两个消费者
package rabbitmq.work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3. 声明队列 使用内置的交换机
//如果队列不存在, 则创建, 如果队列存在, 则不创建
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
//4. 消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息, 就会执行的方法
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+ new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.WORK_QUEUE, true, consumer);
//6. 资源释放
// channel.close();
// connection.close();
}
}
启动两个消费者跟生产者可以观察到



此时队列里就有两个消费者。
3.Publish/Subscribe(发布/订阅)
在这个模式种出现了一个Exchange的角色
作⽤: ⽣产者将消息发送到Exchange, 由交换机将消息按⼀定规则路由到⼀个或多个队列中(上图中⽣产
者将消息投递到队列中, 实际上这个在RabbitMQ中不会发⽣. )
RabbitMQ交换机有四种类型: fanout,direct, topic, headers, 不同类型有着不同的路由策略. AMQP协议⾥还有另外两种类型, System和⾃定义, 此处不再描述.
1.
Fanout:⼴播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列(
Publish/Subscribe模式)
2.
Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key的队列(
Routing模式
)
3.
Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列(
Topics模式
)
4.
headers类型的交换器不依赖于路由键的匹配规则来路由消息, ⽽是根据发送的消息内容中的
headers属性进⾏匹配. headers类型的交换器性能会很差,⽽且也不实⽤,基本上不会看到它的存在.
Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息, 不具备存储消息的能⼒, 因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息就会丢失
生产者代码
package rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,true);
//4.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,true,false,false,null);
//5.绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"");
channel.queueBind(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE2,Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"");
//6.发布消息
String msg = "hello fanout....";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.FANOUT_EXCHANGE,"", null, msg.getBytes());
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
//7.释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者代码(有两个消费者)
package rabbitmq.fanout;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4.消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息, 就会执行的方法
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+ new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.FANOUT_QUEUE1,true,consumer);
}
}运行生产者代码可以看到

两个队列分别有一条信息,同时Exchange跟多个队列绑定关系

此时运行消费者

两个消费者都收到信息
4.路由模式
队列和交换机的绑定, 不能是任意的绑定了, ⽽是要指定⼀个BindingKey(RoutingKey的⼀种)
消息的发送⽅在向Exchange发送消息时, 也需要指定消息的RoutingKey
Exchange也不再把消息交给每⼀个绑定的key, ⽽是根据消息的RoutingKey进⾏判断, 只有队列绑定时的BindingKey和发送消息的RoutingKey 完全⼀致, 才会接收到消息
生产者代码
package rabbitmq.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Producer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3. 声明交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT, true);
//4. 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
//5. 绑定交换机和队列
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "a");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "a");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "b");
channel.queueBind(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE2, Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, "c");
//6. 发送消息
String msg = "hello direct, my routingkey is a....";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"a", null, msg.getBytes());
String msg_b = "hello direct, my routingkey is b....";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"b", null, msg_b.getBytes());
String msg_c = "hello direct, my routingkey is c....";
channel.basicPublish(Constants.DIRECT_EXCHANGE,"c", null, msg_c.getBytes());
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
//7. 释放资源
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}消费者代码
package rabbitmq.direct;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class Consumer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3. 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4. 消费消息
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
//从队列中收到消息, 就会执行的方法
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:"+ new String(body));
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.DIRECT_QUEUE1, true, consumer);
}
}
运行代码可以看到队列2有三条消息,队列1有一条消息

5.Topics(通配符模式)
在topic类型的交换机在匹配规则上, 有些要求:
1.
RoutingKey 是⼀系列由点(
.
)分隔的单词, ⽐如 "
stock.usd.nyse
", "
nyse.vmw
",
"
quick.orange.rabbit
"
2.
BindingKey 和RoutingKey⼀样, 也是点(
.
)分割的字符串.
3.
Binding Key中可以存在两种特殊字符串, ⽤于模糊匹配
◦
* 表⽰⼀个单词
◦
# 表⽰多个单词(0-N个
6.RPC通信
RPC(Remote Procedure Call), 即远程过程调⽤. 它是⼀种通过⽹络从远程计算机上请求服务, ⽽不需要
了解底层⽹络的技术. 类似于Http远程调⽤.
RabbitMQ实现RPC通信的过程, ⼤概是通过两个队列实现⼀个可回调的过程.
⼤概流程如下:
1.
客⼾端发送消息到⼀个指定的队列, 并在消息属性中设置replyTo字段, 这个字段指定了⼀个回调队列, 服务端处理后, 会把响应结果发送到这个队列.
2.
服务端接收到请求后, 处理请求并发送响应消息到replyTo指定的回调队列
3.
客⼾端在回调队列上等待响应消息. ⼀旦收到响应,客⼾端会检查消息的correlationId属性,以确保它是所期望的响应.
编写客户端代码
1.
声明两个队列, 包含回调队列replyQueueName, 声明本次请求的唯⼀标志corrId
2.
将replyQueueName和corrId配置到要发送的消息队列中
3.
使⽤阻塞队列来阻塞当前进程, 监听回调队列中的消息, 把请求放到阻塞队列中
4.
阻塞队列有消息后, 主线程被唤醒,打印返回内容
package rabbitmq.rpc;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE, true, false, false, null);
//3. 发送请求
String msg = "hello rpc...";
//设置请求的唯一标识
String correlationID = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
//设置请求的相关属性
AMQP.BasicProperties props = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(correlationID)
.replyTo(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE)
.build();
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, props, msg.getBytes());
//4. 接收响应
//使用阻塞队列, 来存储响应信息
final BlockingQueue<String> response = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1);
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String respMsg = new String(body);
System.out.println("接收到回调消息: "+ respMsg);
if (correlationID.equals(properties.getCorrelationId())){
//如果correlationID校验一致
response.offer(respMsg);
}
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE, true, consumer);
String result = response.take();
System.out.println("[RPC Client 响应结果]:"+ result);
}
}服务端代码
package rabbitmq.rpc;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//1. 建立连接
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//2. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//3. 接收请求
channel.basicQos(1);
DefaultConsumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String request = new String(body,"UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收到请求:"+ request);
String response = "针对request:"+ request +", 响应成功";
AMQP.BasicProperties basicProperties = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(properties.getCorrelationId())
.build();
channel.basicPublish("", Constants.RPC_RESPONSE_QUEUE, basicProperties, response.getBytes());
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
};
channel.basicConsume(Constants.RPC_REQUEST_QUEUE, false, consumer);
}
}
7.Publisher Confirms(发布确认)
作为消息中间件, 都会⾯临消息丢失的问题.
消息丢失⼤概分为三种情况:
1.
⽣产者问题. 因为应⽤程序故障, ⽹络抖动等各种原因, ⽣产者没有成功向broker发送消息.
2.
消息中间件⾃⾝问题. ⽣产者成功发送给了Broker, 但是Broker没有把消息保存好, 导致消息丢失.
3.
消费者问题. Broker 发送消息到消费者, 消费者在消费消息时, 因为没有处理好, 导致broker将消费失败的消息从队列中删除
针对问题1, 可以采⽤发布确认(Publisher Confirms)机制实现.
发布确认 属于RabbitMQ的七⼤⼯作模式之⼀.
⽣产者将信道设置成confirm(确认)模式, ⼀旦信道进⼊confirm模式, 所有在该信道上⾯发布的消息都会被指派⼀个唯⼀的ID(从1开始), ⼀旦消息被投递到所有匹配的队列之后, RabbitMQ就会发送⼀个确认给⽣产者(包含消息的唯⼀ID), 这就使得⽣产者知道消息已经正确到达⽬的队列了, 如果消息和队列是可持久化的, 那么确认消息会在将消息写⼊磁盘之后发出. broker回传给⽣产者的确认消息中 deliveryTag 包含了确认消息的序号, 此外 broker 也可以设置channel.basicAck⽅法中的multiple参数, 表⽰到这个序号之前的所有消息都已经得到了处理.
发布确认有三种策略
package rabbitmq.publisher.confirms;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConfirmListener;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import rabbitmq.constant.Constants;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.SortedSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class PublisherConfirms {
private static final Integer MESSAGE_COUNT = 200;
static Connection createConnection() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost(Constants.HOST);
connectionFactory.setPort(Constants.PORT); //需要提前开放端口号
connectionFactory.setUsername(Constants.USER_NAME);//账号
connectionFactory.setPassword(Constants.PASSWORD); //密码
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost(Constants.VIRTUAL_HOST); //虚拟主机
return connectionFactory.newConnection();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//单独确认
publishingMessagesIndividually();
//批量确认
publishingMessagesInBatches();
//异步确认
handlingPublisherConfirmsAsynchronously();
}
private static void handlingPublisherConfirmsAsynchronously() throws Exception{
try (Connection connection = createConnection()) {
//1. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//2. 设置信道为confirm模式
channel.confirmSelect();
//3. 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE3, true, false, false, null);
//4. 监听confirm
//集合中存储的是未确认的消息ID
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
SortedSet<Long> confirmSeqNo = Collections.synchronizedSortedSet(new TreeSet<>());
channel.addConfirmListener(new ConfirmListener() {
@Override
public void handleAck(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
if(multiple){
confirmSeqNo.headSet(deliveryTag+1).clear();
}else{
confirmSeqNo.remove(deliveryTag);
}
}
@Override
public void handleNack(long deliveryTag, boolean multiple) throws IOException {
if (multiple){
confirmSeqNo.headSet(deliveryTag+1).clear();
}else {
confirmSeqNo.remove(deliveryTag);
}
//业务需要根据实际场景进行处理, 比如重发, 此处代码省略
}
});
//5. 发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < MESSAGE_COUNT; i++) {
String msg = "hello publisher confirms"+i;
long seqNo = channel.getNextPublishSeqNo();
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE3, null, msg.getBytes());
confirmSeqNo.add(seqNo);
}
while (!confirmSeqNo.isEmpty()){
Thread.sleep(10);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("异步确认策略, 消息条数: %d, 耗时: %d ms \n",MESSAGE_COUNT, end-start);
}
}
//批量确认
private static void publishingMessagesInBatches() throws Exception{
try(Connection connection = createConnection()) {
//1. 开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//2. 设置信道为confirm模式
channel.confirmSelect();
//3. 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE2, true, false, false, null);
//4. 发送消息, 并进行确认
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int batchSize = 100;
int outstandingMessageCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MESSAGE_COUNT; i++) {
String msg = "hello publisher confirms"+i;
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE2, null, msg.getBytes());
outstandingMessageCount++;
if (outstandingMessageCount==batchSize){
channel.waitForConfirmsOrDie(5000);
outstandingMessageCount = 0;
}
}
if (outstandingMessageCount>0){
channel.waitForConfirmsOrDie(5000);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("批量确认策略, 消息条数: %d, 耗时: %d ms \n",MESSAGE_COUNT, end-start);
}
}
//单独确认
private static void publishingMessagesIndividually() throws Exception{
try(Connection connection = createConnection()){
//1.开启信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//2.设置信道为confirm模式
channel.confirmSelect();
//3.声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE1,true,false,false,null);
//4.发送消息吗,并等待确认
long start =System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i< MESSAGE_COUNT;i++){
String msg = "hello publisher confirms"+i;
channel.basicPublish("",Constants.PUBLISHER_CONFIRMS_QUEUE1,null,msg.getBytes());
//等待确认
channel.waitForConfirmsOrDie(5000);
}
long end =System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.printf("单独确认策略, 消息条数: %d, 耗时: %d ms \n",MESSAGE_COUNT, end-start);
}
}
}



![[Python学习日记-63] 继承与派生](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/dc4f30b642844d749b26aac5381591ea.png)