构建研究代理可能很复杂,但使用 LangChain 和 Ollama,它会变得更加简单和模块化。
在本教程中,我们将向你展示如何基于Llama 3.2创建一个研究代理,该代理可以路由查询、执行网络搜索并使用工作流和 LLM 的组合生成详细响应。最后,你将拥有一个功能齐全的代理,可以处理各种信息检索任务!

NSDT工具推荐: Three.js AI纹理开发包 - YOLO合成数据生成器 - GLTF/GLB在线编辑 - 3D模型格式在线转换 - 可编程3D场景编辑器 - REVIT导出3D模型插件 - 3D模型语义搜索引擎 - AI模型在线查看 - Three.js虚拟轴心开发包 - 3D模型在线减面 - STL模型在线切割
1、环境搭建
为了构建我们的研究代理,我们将使用 Ollama 进行 LLM 交互,使用 LangChain 进行工作流管理,使用 LangGraph 定义工作流节点,使用 LangChain 社区库进行扩展功能。对于网络搜索,我们还将使用 duckduckgo-search。
首先安装和配置这些工具。
Ollama 安装步骤
要在你的系统中使用 Ollama,需要安装 Ollama 应用程序,然后在系统中下载 LLama 3.2 模型。
- 从 Ollama 官方网站下载安装程序。
- 运行安装程序并按照屏幕上的说明完成设置。 Ollama 支持 MacO 和 Windows。
- 安装后,可以使用终端运行模型:
- 打开终端。
- 导航到安装 Ollama 的目录。
- 运行以下命令列出可用模型:
ollama list。 - 要下载并运行模型,请使用:
ollama pull <model_name>和ollama run <model_name>
你可以使用 Python 中的以下 pip 命令安装其他库:
!pip install langchain==0.2.12
!pip install langgraph==0.2.2
!pip install langchain-ollama==0.1.1
!pip install langsmith== 0.1.98
!pip install langchain_community==0.2.11
!pip install duckduckgo-search==6.2.13导入所需的库
# Displaying final output format
from IPython.display import display, Markdown, Latex
# LangChain Dependencies
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import JsonOutputParser, StrOutputParser
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOllama
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
from langchain_community.utilities import DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph
# For State Graph
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
import os2、代码实现
定义要使用的LLM
# Defining LLM
local_llm = 'llama3.2'
llama3 = ChatOllama(model=local_llm, temperature=0)定义web搜索工具:
# Web Search Tool
wrapper = DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper(max_results=25)
web_search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchRun(api_wrapper=wrapper)可以使用如下命令测试工具:
# Test Run
resp = web_search_tool.invoke("current Weather in New York")
print(resp)
Example output:
"East wind around 8 mph. Partly sunny, with a high near 69. Northeast wind around 8 mph. Mostly cloudy, with a low around 59. East wind 3 to 6 mph. Mostly sunny, with a high near 73. Light and variable wind becoming south 5 to 7 mph in the afternoon. Mostly clear, with a low around 60定义提示词:
# Generation Prompt
generate_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an AI assistant for Research Question Tasks, that synthesizes web search results.
Strictly use the following pieces of web search context to answer the question. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
keep the answer concise, but provide all of the details you can in the form of a research report.
Only make direct references to material if provided in the context.
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
Question: {question}
Web Search Context: {context}
Answer:
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>""",
input_variables=["question", "context"],
)
# Chain
generate_chain = generate_prompt | llama3 | StrOutputParser()
# Test Run
question = "who is Yan Lecun?"
context = ""
generation = generate_chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
print(generation)生成提示模板 ( generate_prompt):
- 此提示用于代理的生成阶段。
- 它创建一个模板,其中动态插入来自网络搜索的问题 (
{question}) 和上下文 ({context})。 - 该模板指示 AI 助手:
- 从给定的网络搜索上下文中合成信息。
- 保持答案简洁而详细,类似于研究报告。
- 如果提供的上下文中不存在所需信息,只需说“我不知道”。
链配置 ( generate_chain):
generate_chain通过将generate_prompt与模型(例如 llama3)和字符串输出解析器 (StrOutputParser) 链接在一起而形成。- 字符串输出解析器确保以纯文本格式返回最终响应。
代码定义了研究代理的生成阶段,其中它使用网络搜索上下文回答用户查询,或者在上下文为空时以“我不知道”响应。这种结构确保以简洁的报告格式提供准确且基于上下文的响应
定义路由提示:
# Router
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an expert at routing a user question to either the generation stage or web search.
Use the web search for questions that require more context for a better answer, or recent events.
Otherwise, you can skip and go straight to the generation phase to respond.
You do not need to be stringent with the keywords in the question related to these topics.
Give a binary choice 'web_search' or 'generate' based on the question.
Return the JSON with a single key 'choice' with no premable or explanation.
Question to route: {question}
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
""",
input_variables=["question"],
)
# Chain
question_router = router_prompt | llama3_json | JsonOutputParser()
# Test Run
question = "What's up?"
print(question_router.invoke({"question": question}))路由器提示模板 ( router_prompt):
- 本节使用
PromptTemplate类创建提示模板。 - 模板是格式化的文本,将动态填充特定问题。
- 它指示助手何时使用网络搜索(针对最近事件或上下文密集型问题)以及何时生成响应(针对一般或上下文无关的查询)。
- 它强调以 JSON 格式返回 web_search 或 generate 的二元选择。
链配置 ( question_router):
question_router使用router_prompt作为输入,并将其与llama3_json模型和JsonOutputParser链接起来。- 管道接受问题,使用指定的 LLM(例如 LLaMA)对其进行处理,并使用单个键将结果解析为 JSON 输出:“choice”,其中 web_search 或 generate 作为值。
定义网络搜索查询转换器提示:
# Query Transformation
query_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an expert at crafting web search queries for research questions.
More often than not, a user will ask a basic question that they wish to learn more about, however it might not be in the best format.
Reword their query to be the most effective web search string possible.
Return the JSON with a single key 'query' with no premable or explanation.
Question to transform: {question}
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
""",
input_variables=["question"],
)
# Chain
query_chain = query_prompt | llama3_json | JsonOutputParser()
# Test Run
question = "What's happened recently with Gaza?"
print(query_chain.invoke({"question": question}))查询转换提示 ( query_prompt):
- 此提示专为优化网络搜索查询而设计。
- 它将用户的随意或基本问题转换为有效的网络搜索字符串,可以检索更多相关信息。
- 指示 LLM 将问题重新表述为更适合搜索引擎的格式。
- 响应以 JSON 形式返回,其中包含单个键:查询,不包含任何其他文本。
链配置 ( query_chain):
query_chain将query_prompt与语言模型 (llama3_json) 和JsonOutputParser相结合。- 此设置允许提示转换查询并以 JSON 格式返回输出。
使用图形状态定义模块化研究代理工作流程:
# Graph State
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""
Represents the state of our graph.
Attributes:
question: question
generation: LLM generation
search_query: revised question for web search
context: web_search result
"""
question : str
generation : str
search_query : str
context : str
# Node - Generate
def generate(state):
"""
Generate answer
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): New key added to state, generation, that contains LLM generation
"""
print("Step: Generating Final Response")
question = state["question"]
context = state["context"]
# Answer Generation
generation = generate_chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
return {"generation": generation}
# Node - Query Transformation
def transform_query(state):
"""
Transform user question to web search
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Appended search query
"""
print("Step: Optimizing Query for Web Search")
question = state['question']
gen_query = query_chain.invoke({"question": question})
search_query = gen_query["query"]
return {"search_query": search_query}
# Node - Web Search
def web_search(state):
"""
Web search based on the question
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Appended web results to context
"""
search_query = state['search_query']
print(f'Step: Searching the Web for: "{search_query}"')
# Web search tool call
search_result = web_search_tool.invoke(search_query)
return {"context": search_result}
# Conditional Edge, Routing
def route_question(state):
"""
route question to web search or generation.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
str: Next node to call
"""
print("Step: Routing Query")
question = state['question']
output = question_router.invoke({"question": question})
if output['choice'] == "web_search":
print("Step: Routing Query to Web Search")
return "websearch"
elif output['choice'] == 'generate':
print("Step: Routing Query to Generation")
return "generate"GraphState 类:
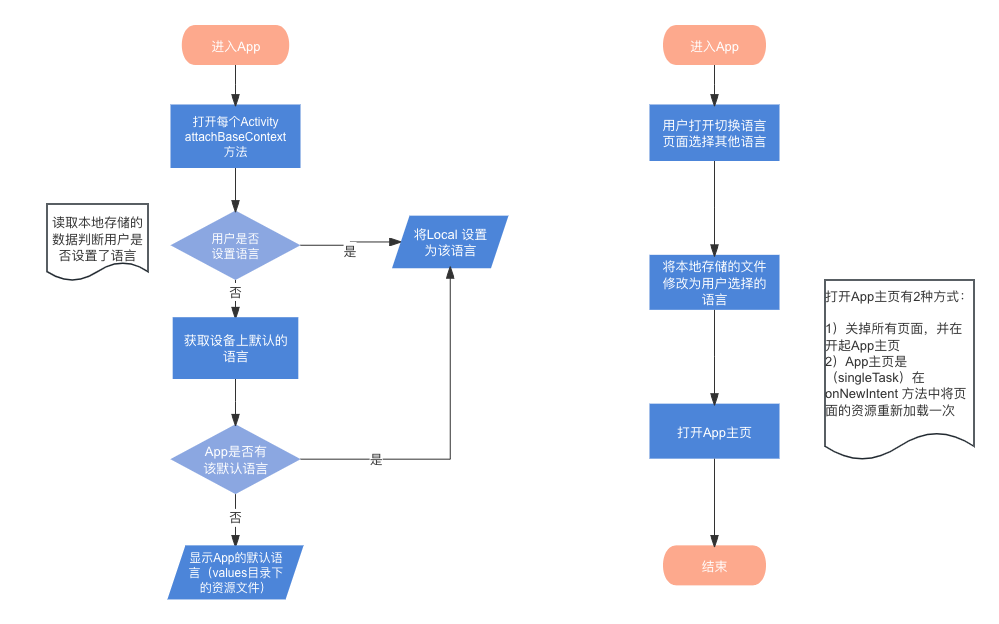
- GraphState 是一个 TypedDict,它定义了图形工作流中使用的状态字典的结构。
- 它包括四个键:
- question:原始用户问题。
- generation:LLM 生成的最终答案。
- search_query:针对网络搜索优化的问题。
- context:用于生成响应的网络搜索结果。
生成节点 (generate):
- 此函数根据问题和上下文使用 LLM 生成最终响应。
- 它在图形状态中输出生成键。
- 打印消息:步骤:生成最终响应以指示其操作。
查询转换节点 (transform_query):
- 此节点优化用户针对网络搜索的问题。
- 调用 query_chain 并在状态中输出 search_query 键。
- 打印消息:步骤:优化网络搜索查询。
网络搜索节点 (web_search):
- 此节点使用优化查询 (search_query) 执行网络搜索。
- 使用 Web 搜索工具 (web_search_tool.invoke) 并输出状态中的上下文键。
- 打印搜索查询和消息:步骤:在 Web 上搜索:“<search_query>”。
条件路由 (route_question):
- 此函数根据 question_router 做出的决定将问题路由到 web_search 或 generate。
- 打印消息:步骤:路由查询。
- 如果选择是 web_search,它将路由到 web_search 节点并打印将查询路由到 Web 搜索。
- 如果选择是 generate,它将路由到 generate 节点并打印将查询路由到 Generation。
代码片段使用图形状态定义模块化研究代理工作流的核心节点和决策逻辑。每个函数代表工作流中的一个不同步骤,根据要求修改共享状态并通过适当的节点路由问题。最终输出是使用上下文(如果可用)或直接通过 LLM 生成生成的结构良好的响应。
使用 StateGraph 构建基于状态的工作流:
# Build the nodes
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
workflow.add_node("websearch", web_search)
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate)
# Build the edges
workflow.set_conditional_entry_point(
route_question,
{
"websearch": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "websearch")
workflow.add_edge("websearch", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
# Compile the workflow
local_agent = workflow.compile()创建 StateGraph 实例(工作流):
- StateGraph 用于表示研究代理的工作流。
- 工作流使用 GraphState 类型初始化,确保所有节点都遵循定义的状态结构。
将节点添加到图表:
- 以下节点已添加到工作流:
- “websearch”:执行 web_search 函数以执行网络搜索。
- “transform_query”:执行 transform_query 函数以优化用户问题以进行网络搜索。
- “generate”:执行 generate 函数以使用 LLM 创建最终响应。
设置条件入口点 (workflow.set_conditional_entry_point):
- 使用 route_question 函数定义工作流的入口点。
- 它根据其决定将问题路由到两个节点之一:
- “websearch”:如果查询需要更多上下文。
- “generate”:如果不需要网络搜索。
定义工作流边缘:
- 边缘定义节点之间的流程:
- “transform_query”->“websearch”:转换查询后,转到网络搜索。
- “websearch”->“generate”:完成网络搜索后,将结果传递给生成节点。
- “generate”->END:生成最终响应后,工作流结束。
编译工作流:
- workflow.compile() 步骤创建一个编译代理 (local_agent),可以调用该代理根据定义的工作流来处理查询。
- local_agent 将根据定义的逻辑自动执行节点并路由查询。
代码使用 StateGraph 构建基于状态的工作流,其中包含用于查询转换、网络搜索和响应生成的节点。工作流根据预定义的条件自动路由这些节点,确保以最有效的方式处理每个查询以产生高质量的答案。
定义运行Agent的函数:
def run_agent(query):
output = local_agent.invoke({"question": query})
print("=======")
display(Markdown(output["generation"]))3、测试Agent
示例1:
run_agent("What is Latest news About Open AI?")输出:

示例2:
run_agent("what is Transformer in AI?")输出:

4、构建Streamlit应用程序来运行代理

在运行 Streamlit 应用之前,请确保已安装所有必需的库。
打开终端并安装 streamlit
!pip install streamlit 如果有 requirements.txt 文件,你也可以使用以下命令安装依赖项:
pip install -r requirements.txt接下来创建一个名为 streamlit_app.py 的新文件(或使用你喜欢的任何其他名称),并将之前提供的完整 Streamlit 代码粘贴到其中。
使用以下代码:
# Displaying final output format
from IPython.display import display, Markdown, Latex
# LangChain Dependencies
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import JsonOutputParser, StrOutputParser
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOllama
from langchain_community.tools import DuckDuckGoSearchRun
from langchain_community.utilities import DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph
# For State Graph
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
import streamlit as st
import os
# Defining LLM
def configure_llm():
st.sidebar.header("Configure LLM")
# Model Selection
model_options = ["llama3.2"]
selected_model = st.sidebar.selectbox("Choose the LLM Model", options=model_options, index=0)
# Temperature Setting
temperature = st.sidebar.slider("Set the Temperature", min_value=0.0, max_value=1.0, value=0.5, step=0.1)
# Create LLM Instances based on user selection
llama_model = ChatOllama(model=selected_model, temperature=temperature)
llama_model_json = ChatOllama(model=selected_model, format='json', temperature=temperature)
return llama_model, llama_model_json
# Streamlit Application Interface
st.title("Personal Research Assistant powered By Llama3.2")
llama3, llama3_json=configure_llm()
wrapper = DuckDuckGoSearchAPIWrapper(max_results=25)
web_search_tool = DuckDuckGoSearchRun(api_wrapper=wrapper)
generate_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an AI assistant for Research Question Tasks, that synthesizes web search results.
Strictly use the following pieces of web search context to answer the question. If you don't know the answer, just say that you don't know.
keep the answer concise, but provide all of the details you can in the form of a research report.
Only make direct references to material if provided in the context.
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
Question: {question}
Web Search Context: {context}
Answer:
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>""",
input_variables=["question", "context"],
)
# Chain
generate_chain = generate_prompt | llama3 | StrOutputParser()
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an expert at routing a user question to either the generation stage or web search.
Use the web search for questions that require more context for a better answer, or recent events.
Otherwise, you can skip and go straight to the generation phase to respond.
You do not need to be stringent with the keywords in the question related to these topics.
Give a binary choice 'web_search' or 'generate' based on the question.
Return the JSON with a single key 'choice' with no premable or explanation.
Question to route: {question}
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
""",
input_variables=["question"],
)
# Chain
question_router = router_prompt | llama3_json | JsonOutputParser()
query_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="""
<|begin_of_text|>
<|start_header_id|>system<|end_header_id|>
You are an expert at crafting web search queries for research questions.
More often than not, a user will ask a basic question that they wish to learn more about, however it might not be in the best format.
Reword their query to be the most effective web search string possible.
Return the JSON with a single key 'query' with no premable or explanation.
Question to transform: {question}
<|eot_id|>
<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
""",
input_variables=["question"],
)
# Chain
query_chain = query_prompt | llama3_json | JsonOutputParser()
# Graph State
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""
Represents the state of our graph.
Attributes:
question: question
generation: LLM generation
search_query: revised question for web search
context: web_search result
"""
question : str
generation : str
search_query : str
context : str
# Node - Generate
def generate(state):
"""
Generate answer
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): New key added to state, generation, that contains LLM generation
"""
print("Step: Generating Final Response")
question = state["question"]
context = state["context"]
# Answer Generation
generation = generate_chain.invoke({"context": context, "question": question})
return {"generation": generation}
# Node - Query Transformation
def transform_query(state):
"""
Transform user question to web search
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Appended search query
"""
print("Step: Optimizing Query for Web Search")
question = state['question']
gen_query = query_chain.invoke({"question": question})
search_query = gen_query["query"]
return {"search_query": search_query}
# Node - Web Search
def web_search(state):
"""
Web search based on the question
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Appended web results to context
"""
search_query = state['search_query']
print(f'Step: Searching the Web for: "{search_query}"')
# Web search tool call
search_result = web_search_tool.invoke(search_query)
return {"context": search_result}
# Conditional Edge, Routing
def route_question(state):
"""
route question to web search or generation.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
str: Next node to call
"""
print("Step: Routing Query")
question = state['question']
output = question_router.invoke({"question": question})
if output['choice'] == "web_search":
print("Step: Routing Query to Web Search")
return "websearch"
elif output['choice'] == 'generate':
print("Step: Routing Query to Generation")
return "generate"
# Build the nodes
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
workflow.add_node("websearch", web_search)
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate)
# Build the edges
workflow.set_conditional_entry_point(
route_question,
{
"websearch": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "websearch")
workflow.add_edge("websearch", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
# Compile the workflow
local_agent = workflow.compile()
def run_agent(query):
output = local_agent.invoke({"question": query})
print("=======")
return output["generation"]
user_query = st.text_input("Enter your research question:", "")
if st.button("Run Query"):
if user_query:
st.write(run_agent(user_query))将脚本文件保存在你的工作目录中。确保其命名正确,例如: streamlit_app.py。
在保存 streamlit_app.py 的同一目录中打开你的终端。
使用以下命令运行 Streamlit 应用程序:
streamlit run streamlit_app.py一旦应用程序开始运行,默认网络浏览器中将打开一个新选项卡,显示 Streamlit 界面。
或者,你可以手动打开浏览器并转到终端中显示的地址,通常如下所示:
http://localhost:8501/配置 LLM 模型:
- 使用侧边栏选项配置 LLM 模型:
- 选择模型(请记住,必须先从 ollama 网站下载到您的系统中)
- 使用滑块设置温度。
输入你的查询:
- 在主界面中,你将看到一个标有“输入您的研究问题:”的文本输入框。
- 在框中输入您的问题。
运行查询:
- 单击“运行查询”按钮。
- 该应用程序将使用配置的工作流程处理您的查询并显示结果。
查看输出:
- 最终答案将自动显示。
5、结束语
使用 LangChain 和 Streamlit 创建研究代理展示了将模块化工作流与交互式应用程序相结合的强大功能。通过利用基于状态的决策节点和动态 LLM 配置,我们构建了一个能够路由查询、执行 Web 搜索和生成简明研究报告的工具。此设置不仅简化了复杂代理的开发,还为未来的增强提供了灵活性。
随着人工智能的不断发展,集成此类框架对于构建更直观和上下文感知的应用程序至关重要。所以,尝试一下,尝试不同的模型,看看你的研究代理如何针对各种用例进行定制!
原文链接:Llama 3.2 构建智能代理 - BimAnt