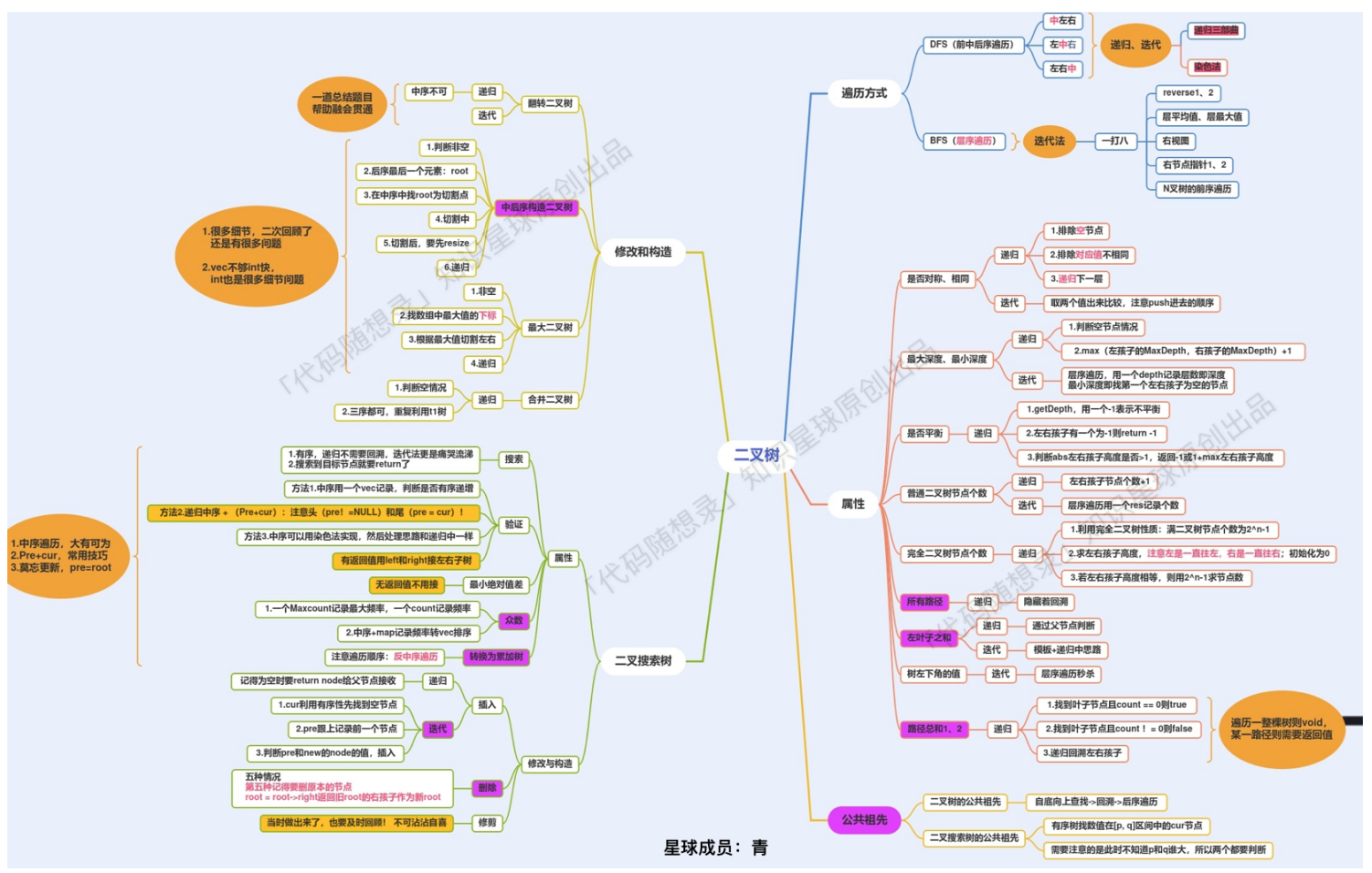
3.7 排序算法
概述
比较排序算法
| 算法 | 最好 | 最坏 | 平均 | 空间 | 稳定 | 思想 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冒泡 | O(n) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O(1) | Y | 比较 | 最好情况需要额外判断 |
| 选择 | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O(1) | N | 比较 | 交换次数一般少于冒泡 |
| 堆 | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O(1) | N | 选择 | 堆排序的辅助性较强,理解前先理解堆的数据结构 |
| 插入 | O(n) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O(1) | Y | 比较 | 插入排序对于近乎有序的数据处理速度比较快,复杂度有所下降,可以提前结束 |
| 希尔 | O(nlogn) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O(1) | N | 插入 | gap序列的构造有多种方式,不同方式处理的数据复杂度可能不同 |
| 归并 | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O(n) | Y | 分治 | 需要额外的O(n)的存储空间 |
| 快速 | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O( n 2 n^2 n2) | O( n l o g n nlogn nlogn) | O(logn) | N | 分治 | 快排可能存在最坏情况,需要把枢轴值选取得尽量随机化来缓解最坏情况下的时间复杂度 |
非比较排序算法
| 非比较排序算法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 稳定性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 计数排序 | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | 稳定 |
| 桶排序 | O(n+k) | O(n+k) | 稳定 |
| 基数排序 | O(d*(n+k)) | O(n+k) | 稳定 |
其中
- n 是数组长度
- k 是桶长度
- d 是基数位数
稳定 vs 不稳定

Java 中的排序
Arrays.sort
JDK 7~13 中的排序实现
| 排序目标 | 条件 | 采用算法 |
|---|---|---|
| int[] long[] float[] double[] | size < 47 | 混合插入排序 (pair) |
| size < 286 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 有序度低 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 有序度高 | 归并排序 | |
| byte[] | size <= 29 | 插入排序 |
| size > 29 | 计数排序 | |
| char[] short[] | size < 47 | 插入排序 |
| size < 286 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 有序度低 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 有序度高 | 归并排序 | |
| size > 3200 | 计数排序 | |
| Object[] | -Djava.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort=true | 传统归并排序 |
| TimSort |
JDK 14~20 中的排序实现
| 排序目标 | 条件 | 采用算法 |
|---|---|---|
| int[] long[] float[] double[] | size < 44 并位于最左侧 | 插入排序 |
| size < 65 并不是最左侧 | 混合插入排序 (pin) | |
| 有序度低 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 递归次数超过 384 | 堆排序 | |
| 对于整个数组或非最左侧 size > 4096,有序度高 | 归并排序 | |
| byte[] | size <= 64 | 插入排序 |
| size > 64 | 计数排序 | |
| char[] short[] | size < 44 | 插入排序 |
| 再大 | 双基准点快排 | |
| 递归次数超过 384 | 计数排序 | |
| size > 1750 | 计数排序 | |
| Object[] | -Djava.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort=true | 传统归并排序 |
| TimSort |
- 其中 TimSort 是用归并+二分插入排序的混合排序算法
- 值得注意的是从 JDK 8 开始支持 Arrays.parallelSort 并行排序
- 根据最新的提交记录来看 JDK 21 可能会引入基数排序等优化
外部排序
1) 冒泡排序
要点
- 每轮冒泡不断地比较相邻的两个元素,如果它们是逆序的,则交换它们的位置
- 下一轮冒泡,可以调整未排序的右边界,减少不必要比较
以数组 3、2、1 的冒泡排序为例,第一轮冒泡

第二轮冒泡

未排序区域内就剩一个元素,结束

优化手段:每次循环时,若能确定更合适的右边界,则可以减少冒泡轮数
以数组 3、2、1、4、5 为例,第一轮结束后记录的 x,即为右边界

非递归版代码
public class BubbleSort {
private static void bubble(int[] a) {
int j = a.length - 1;
while (true) {
int x = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = t;
x = i;
}
}
j = x;
if (j == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
bubble(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
2) 选择排序
要点
- 每一轮选择,找出最大(最小)的元素,并把它交换到合适的位置
以下面的数组选择最大值为例

非递归实现
public class SelectionSort {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
// 1. 选择轮数 a.length - 1
// 2. 交换的索引位置(right) 初始 a.length - 1, 每次递减
for (int right = a.length - 1; right > 0 ; right--) {
int max = right;
for (int i = 0; i < right; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[max]) {
max = i;
}
}
if(max != right) {
swap(a, max, right);
}
}
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
3) 堆排序
要点:
- 建立大顶堆
- 每次将堆顶元素(最大值)交换到末尾,调整堆顶元素,让它重新符合大顶堆特性
建堆

交换,下潜调整





代码
public class HeapSort {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
heapify(a, a.length);
for (int right = a.length - 1; right > 0; right--) {
swap(a, 0, right);
down(a, 0, right);
}
}
// 建堆 O(n)
private static void heapify(int[] array, int size) {
for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
down(array, i, size);
}
}
// 下潜
// leetcode 上数组排序题目用堆排序求解,非递归实现比递归实现大约快 6ms
private static void down(int[] array, int parent, int size) {
while (true) {
int left = parent * 2 + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent;
if (left < size && array[left] > array[max]) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && array[right] > array[max]) {
max = right;
}
if (max == parent) { // 没找到更大的孩子
break;
}
swap(array, max, parent);
parent = max;
}
}
// 交换
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {2, 3, 1, 7, 6, 4, 5};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
4) 插入排序
要点
- 将数组分为两部分 [0 … low-1] [low … a.length-1]
- 左边 [0 … low-1] 是已排序部分
- 右边 [low … a.length-1] 是未排序部分
- 每次从未排序区域取出 low 位置的元素, 插入到已排序区域
例


代码
public class InsertionSort {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int low = 1; low < a.length; low++) {
// 将 low 位置的元素插入至 [0..low-1] 的已排序区域
int t = a[low];
int i = low - 1; // 已排序区域指针
while (i >= 0 && t < a[i]) { // 没有找到插入位置
a[i + 1] = a[i]; // 空出插入位置
i--;
}
// 找到插入位置
if (i != low - 1) {
a[i + 1] = t;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
5) 希尔排序
要点
- 简单的说,就是分组实现插入,每组元素间隙称为 gap
- 每轮排序后 gap 逐渐变小,直至 gap 为 1 完成排序
- 对插入排序的优化,让元素更快速地交换到最终位置
下图演示了 gap = 4,gap = 2,gap = 1 的三轮排序前后比较

代码
public class ShellSort {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
for (int gap = a.length>>1; gap >0 ; gap=gap>>1) {
for (int low = gap; low < a.length; low ++) {
// 将 low 位置的元素插入至 [0..low-1] 的已排序区域
int t = a[low];
int i = low - gap; // 已排序区域指针
while (i >= 0 && t < a[i]) { // 没有找到插入位置
a[i + gap] = a[i]; // 空出插入位置
i -= gap;
}
// 找到插入位置
if (i != low - gap) {
a[i + gap] = t;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 5, 8, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
6) 归并排序
递归实现
要点
- 分 - 每次从中间切一刀,处理的数据少一半
- 治 - 当数据仅剩一个时可以认为有序
- 合 - 两个有序的结果,可以进行合并排序(参见数组练习 E01. 合并有序数组)

代码
public class MergeSortTopDown {
/*
a1 原始数组
i~iEnd 第一个有序范围
j~jEnd 第二个有序范围
a2 临时数组
*/
public static void merge(int[] a1, int i, int iEnd, int j, int jEnd, int[] a2) {
int k = i;
while (i <= iEnd && j <= jEnd) {
if (a1[i] < a1[j]) {
a2[k] = a1[i];
i++;
} else {
a2[k] = a1[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
if (i > iEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, j, a2, k, jEnd - j + 1);
}
if (j > jEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, i, a2, k, iEnd - i + 1);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a1) {
int[] a2 = new int[a1.length];
split(a1, 0, a1.length - 1, a2);
}
private static void split(int[] a1, int left, int right, int[] a2) {
int[] array = Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, left, right + 1);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
// 2. 治
if (left == right) {
return;
}
// 1. 分
int m = (left + right) >>> 1;
split(a1, left, m, a2); // left = 0 m = 0 9
split(a1, m + 1, right, a2); // m+1 = 1 right = 1 3
// 3. 合
merge(a1, left, m, m + 1, right, a2);
System.arraycopy(a2, left, a1, left, right - left + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
时间复杂度
-
两个长度为 m 和 n 的链表合并,时间复杂度是 m + n
-
归并,时间复杂度: f ( n ) = 2 f ( n / 2 ) + n , f ( 1 ) = c f(n) = 2f(n/2) + n, f(1)=c f(n)=2f(n/2)+n,f(1)=c,等价解 f ( n ) = n l o g 2 n + c n f(n) = nlog_2{n} + cn f(n)=nlog2n+cn
8 / \ 4 4 / \ / \ 2 2 2 2 || || || || 11 11 11 11 f(8) = 2f(4) + 8 f(4) = 2f(2) + 4 f(2) = 2f(1) + 2 f(1) = 1 f(8) = 8 + 24 f(4) = 4 + 8 f(2) = 2 + 2 f(1) = 1- 当 n = 16 时,结果 80
- 当 n = 64 时,结果 448
-
若逐一合并,时间复杂度: f ( n ) = ∑ n = 0 n − 1 n + 1 f(n)=\sum\limits_{n=0}^{n-1}n+1 f(n)=n=0∑n−1n+1,等价解 f ( n ) = 1 2 ( n 2 + n ) f(n)=\frac{1}{2}(n^2+n) f(n)=21(n2+n)
1|0 => 1 1|1 => 2 1|2 => 3 1|3 => 4 1|4 => 5 1|5 => 6 1|6 => 7 1|7 => 8 36- 当 n = 16 时,结果 136
- 当 n = 64 时,结果 2080
非递归实现
public class MergeSortBottomUp {
/*
a1 原始数组
i~iEnd 第一个有序范围
j~jEnd 第二个有序范围
a2 临时数组
*/
public static void merge(int[] a1, int i, int iEnd, int j, int jEnd, int[] a2) {
int k = i;
while (i <= iEnd && j <= jEnd) {
if (a1[i] < a1[j]) {
a2[k] = a1[i];
i++;
} else {
a2[k] = a1[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
if (i > iEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, j, a2, k, jEnd - j + 1);
}
if (j > jEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, i, a2, k, iEnd - i + 1);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a1) {
int n = a1.length;
int[] a2 = new int[n];
for (int width = 1; width < n; width *= 2) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2 * width) {
int m = Integer.min(i + width - 1, n - 1);
int j = Integer.min(i + 2 * width - 1, n - 1);
System.out.println(i + " " + m + " " + j);
merge(a1, i, m, m + 1, j, a2);
}
System.arraycopy(a2, 0, a1, 0, n);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
7) 归并+插入
- 小数据量且有序度高时,插入排序效果高
- 大数据量用归并效果好
- 可以结合二者
public class MergeInsertionSort {
public static void insertion(int[] a, int left, int right) {
for (int low = left + 1; low <= right; low++) {
int t = a[low];
int i = low - 1;
while (i >= left && t < a[i]) {
a[i + 1] = a[i];
i--;
}
if (i != low - 1) {
a[i + 1] = t;
}
}
}
/*
a1 原始数组
i~iEnd 第一个有序范围
j~jEnd 第二个有序范围
a2 临时数组
*/
public static void merge(int[] a1, int i, int iEnd, int j, int jEnd, int[] a2) {
int k = i;
while (i <= iEnd && j <= jEnd) {
if (a1[i] < a1[j]) {
a2[k] = a1[i];
i++;
} else {
a2[k] = a1[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
if (i > iEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, j, a2, k, jEnd - j + 1);
}
if (j > jEnd) {
System.arraycopy(a1, i, a2, k, iEnd - i + 1);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a1) {
int[] a2 = new int[a1.length];
split(a1, 0, a1.length - 1, a2);
}
private static void split(int[] a1, int left, int right, int[] a2) {
// int[] array = Arrays.copyOfRange(a1, left, right + 1);
// System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
// 2. 治
if (right == left) {
return;
}
if (right - left <= 32) {
insertion(a1, left, right);
System.out.println("insert..." + left + " " + right +" "+Arrays.toString(a1));
return;
}
// 1. 分
int m = (left + right) >>> 1;
split(a1, left, m, a2); // left = 0 m = 0 9
split(a1, m + 1, right, a2); // m+1 = 1 right = 1 3
System.out.println(left + " " + right + " "+Arrays.toString(a1));
// 3. 合
merge(a1, left, m, m + 1, right, a2);
System.arraycopy(a2, left, a1, left, right - left + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
8) 快速排序
单边循环(lomuto分区)要点
- 选择最右侧元素作为基准点
- j 找比基准点小的,i 找比基准点大的,一旦找到,二者进行交换
- 交换时机:j 找到小的,且与 i 不相等
- i 找到 >= 基准点元素后,不应自增
- 最后基准点与 i 交换,i 即为基准点最终索引
例:
i 和 j 都从左边出发向右查找,i 找到比基准点4大的5,j找到比基准点小的2,停下来交换

i 找到了比基准点大的5,j 找到比基准点小的3,停下来交换

j 到达right 处结束,right 与 i 交换,一轮分区结束

代码
public class QuickSortLomuto {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
int p = partition(a, left, right); // p代表基准点元素索引
quick(a, left, p - 1);
quick(a, p + 1, right);
}
private static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {
int pv = a[right]; // 基准点元素值
int i = left;
int j = left;
while (j < right) {
if (a[j] < pv) { // j 找到比基准点小的了, 没找到大的
if (i != j) {
swap(a, i, j);
}
i++;
}
j++;
}
swap(a, i, right);
return i;
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {5, 3, 7, 2, 9, 8, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
双边循环要点
- 选择最左侧元素作为基准点
- j 找比基准点小的,i 找比基准点大的,一旦找到,二者进行交换
- i 从左向右
- j 从右向左
- 最后基准点与 i 交换,i 即为基准点最终索引
例:
i 找到比基准点大的5停下来,j 找到比基准点小的1停下来(包含等于),二者交换

i 找到8,j 找到3,二者交换,i 找到7,j 找到2,二者交换

i == j,退出循环,基准点与 i 交换

代码
public class QuickSortHoare {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
int p = partition(a, left, right);
quick(a, left, p - 1);
quick(a, p + 1, right);
}
private static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {
int i = left;
int j = right;
int pv = a[left];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && a[j] > pv) {
j--;
}
while (i < j && pv >= a[i]) {
i++;
}
swap(a, i, j);
}
swap(a, left, j);
return j;
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {9, 3, 7, 2, 8, 5, 1, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
随机基准点
使用随机数作为基准点,避免万一最大值或最小值作为基准点导致的分区不均衡
例

改进代码
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(right - left + 1) + left;
swap(a, idx, left);
处理重复值
如果重复值较多,则原来算法中的分区效果也不好,如下图中左侧所示,需要想办法改为右侧的分区效果

改进代码
public class QuickSortHandleDuplicate {
public static void sort(int[] a) {
quick(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
private static void quick(int[] a, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) {
return;
}
int p = partition(a, left, right);
quick(a, left, p - 1);
quick(a, p + 1, right);
}
/*
循环内
i 从 left + 1 开始,从左向右找大的或相等的
j 从 right 开始,从右向左找小的或相等的
交换,i++ j--
循环外 j 和 基准点交换,j 即为分区位置
*/
private static int partition(int[] a, int left, int right) {
int idx = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(right - left + 1) + left;
swap(a, left, idx);
int pv = a[left];
int i = left + 1;
int j = right;
while (i <= j) {
// i 从左向右找大的或者相等的
while (i <= j && a[i] < pv) {
i++;
}
// j 从右向左找小的或者相等的
while (i <= j && a[j] > pv) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
swap(a, i, j);
i++;
j--;
}
}
swap(a, j, left);
return j;
}
private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
int t = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] a = {4, 2, 1, 3, 2, 4}; // 最外层循环 = 要加
// int[] a = {2, 1, 3, 2}; // 内层循环 = 要加
int[] a = {2, 1, 3, 2}; // 内层if要加
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
-
核心思想是
- 改进前,i 只找大于的,j 会找小于等于的。一个不找等于、一个找等于,势必导致等于的值分布不平衡
- 改进后,二者都会找等于的交换,等于的值会平衡分布在基准点两边
-
细节:
- 因为一开始 i 就可能等于 j,因此外层循环需要加等于条件保证至少进入一次,让 j 能减到正确位置
- 内层 while 循环中 i <= j 的 = 也不能去掉,因为 i == j 时也要做一次与基准点的判断,好让 i 及 j 正确
- i == j 时,也要做一次 i++ 和 j-- 使下次循环二者不等才能退出
- 因为最后退出循环时 i 会大于 j,因此最终与基准点交换的是 j
-
内层两个 while 循环的先后顺序不再重要
9) 计数排序
方法1(简化后的计数排序)
public static void sort(int[] a) {
int min = a[0];
int max = a[0];
for (int i : a) {
if (i > max) {
max = i;
} else if (i < min) {
min = i;
}
}
int[] counting = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i : a) {
counting[i - min]++;
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < counting.length; i++) {
while (counting[i] > 0) {
a[k] = i + min;
counting[i]--;
k++;
}
}
}
针对 byte [],因为数据范围已知,省去了求最大、最小值的过程,java 中对 char[]、short[]、byte[] 的排序都可能采用 counting 排序
public static void sort(byte[] a) {
int[] counting = new int[256];
for (int i : a) {
counting[i & 0xFF]++;
}
int k = a.length-1;
for (int i = 128 + 256; k >= 0; ) {
while (counting[--i & 0xFF] ==0);
int v = i & 0xFF;
int c = counting[i & 0xFF];
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
a[k] = (byte) v;
k--;
}
}
}
稳定计数排序
public static void sort2(int[] a) {
int min = a[0];
int max = a[0];
for (int i : a) {
if (i > max) {
max = i;
} else if (i < min) {
min = i;
}
}
int[] counting = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i : a) {
counting[i - min]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < counting.length; i++) {
counting[i] = counting[i] + counting[i - 1];
}
int[] b = new int[a.length];
for (int i = a.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int j = a[i] - min;
counting[j]--;
b[counting[j]] = a[i];
}
System.arraycopy(b, 0, a, 0, a.length);
}
10) 桶排序
初步实现
public class BucketSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ages = {20, 18, 66, 25, 67, 30}; // 假设人类年龄 1~99 那么分为10个桶
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ages));
sort(ages);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ages));
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DynamicArray[] buckets = new DynamicArray[10];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new DynamicArray();
}
for (int v : a) {
DynamicArray bucket = buckets[v / 10];
bucket.addLast(v);
}
for (DynamicArray bucket : buckets) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bucket.array()));
}
int k = 0;
for (DynamicArray bucket : buckets) {
int[] array = bucket.array();
InsertionSort.sort(array);
for (int v : array) {
a[k++] = v;
}
}
}
}
通用
public class BucketSortGeneric {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] ages = {20, 10, 28, 66, 25, 31, 67, 30, 70}; // 假设人类年龄 1~99
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ages));
sort(ages, 20);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ages));
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int range) {
int max = a[0];
int min = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] > max) {
max = a[i];
}
if (a[i] < min) {
min = a[i];
}
}
// 1. 准备桶
DynamicArray[] buckets = new DynamicArray[(max - min) / range + 1];
System.out.println(buckets.length);
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new DynamicArray();
}
// 2. 放入年龄数据
for (int age : a) {
buckets[(age - min) / range].addLast(age);
}
int k = 0;
for (DynamicArray bucket : buckets) {
// 3. 排序桶内元素
int[] array = bucket.array();
InsertionSort.sort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
// 4. 把每个桶排序好的内容,依次放入原始数组
for (int v : array) {
a[k++] = v;
}
}
}
}
11) 基数排序
public class RadixSort {
public static void radixSort(String[] a, int length) {
ArrayList<String>[] buckets = new ArrayList[128];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
for (String s : a) {
buckets[s.charAt(i)].add(s);
}
int k = 0;
for (ArrayList<String> bucket : buckets) {
for (String s : bucket) {
a[k++] = s;
}
bucket.clear();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*String[] phoneNumbers = new String[10];
phoneNumbers[0] = "13812345678";
phoneNumbers[1] = "13912345678";
phoneNumbers[2] = "13612345678";
phoneNumbers[3] = "13712345678";
phoneNumbers[4] = "13512345678";
phoneNumbers[5] = "13412345678";
phoneNumbers[6] = "15012345678";
phoneNumbers[7] = "15112345678";
phoneNumbers[8] = "15212345678";
phoneNumbers[9] = "15712345678";*/
String[] phoneNumbers = new String[10];
phoneNumbers[0] = "138";
phoneNumbers[1] = "139";
phoneNumbers[2] = "136";
phoneNumbers[3] = "137";
phoneNumbers[4] = "135";
phoneNumbers[5] = "134";
phoneNumbers[6] = "150";
phoneNumbers[7] = "151";
phoneNumbers[8] = "152";
phoneNumbers[9] = "157";
RadixSort.radixSort(phoneNumbers, 3);
for (String phoneNumber : phoneNumbers) {
System.out.println(phoneNumber);
}
}
}
基数排序是稳定排序,因此先排个位、再排十位,十位的排序不会打乱个位取值相等的元素顺序
习题
E01. 根据另一个数组次序排序-Leetcode 1122
/*
前提
1. 元素值均 >= 0
2. arr2 内元素唯一,且长度 <= 1000
*/
public class E01Leetcode1122 {
public int[] relativeSortArray(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
int[] count = new int[1001];
for (int i : arr1) {
count[i]++;
}
int[] result = new int[arr1.length];
int k = 0;
for (int i : arr2) {
while (count[i] > 0) {
result[k++] = i;
count[i]--;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) {
while (count[i] > 0) {
result[k++] = i;
count[i]--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
E02. 按出现频率排序-Leetcode 1636
public class E02Leetcode1636 {
public int[] frequencySort(int[] nums) {
int[] count = new int[201];
for (int i : nums) {
count[i + 100]++;
}
return Arrays.stream(nums).boxed().sorted((a, b) -> {
int fa = count[a + 100];
int fb = count[b + 100];
if (fa == fb) {
return Integer.compare(b, a);
} else {
return fa - fb;
}
}).mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
}
E03. 最大间距-Leetcode 164
解法1:桶排序 - 超过内存限制
public class E03Leetcode164_1 {
public int maximumGap(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n < 2) {
return 0;
}
sort(nums, 1);
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ret = Math.max(ret, nums[i] - nums[i - 1]);
}
return ret;
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int range) {
int max = a[0];
int min = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (a[i] > max) {
max = a[i];
}
if (a[i] < min) {
min = a[i];
}
}
// 1. 准备桶
DynamicArray[] buckets = new DynamicArray[(max - min) / range + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new DynamicArray();
}
// 2. 放入数据
for (int age : a) {
buckets[(age - min) / range].addLast(age);
}
int k = 0;
for (DynamicArray bucket : buckets) {
// 3. 排序桶内元素
int[] array = bucket.array();
InsertionSort.sort(array);
// 4. 把每个桶排序好的内容,依次放入原始数组
for (int v : array) {
a[k++] = v;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {13, 26, 16, 11};
int r = new E03Leetcode164_1().maximumGap(nums);
System.out.println(r);
}
}
解法2:基数排序
public class E03Leetcode164 {
public int maximumGap(int[] a) {
if (a.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
// 计算最大值
int max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(a[i], max);
}
// 准备10个桶
ArrayList<Integer>[] buckets = new ArrayList[10];
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.length; i++) {
buckets[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 没超过最大值
long exp = 1;
while (max >= exp) {
for (int j : a) {
buckets[(j / (int) exp) % 10].add(j);
}
int k = 0;
for (ArrayList<Integer> bucket : buckets) {
for (Integer i : bucket) {
a[k++] = i;
}
bucket.clear();
}
exp *= 10;
}
// 求最大间距
int r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
r = Math.max(r, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
}
return r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {3, 6, 16, 1};
int r = new E03Leetcode164().maximumGap(nums);
System.out.println(r);
}
}
解法3:桶排序 - 合理化桶个数
public class E03Leetcode164_3 {
public int maximumGap(int[] nums) {
// 1. 处理特殊情况
if (nums.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
// 2. 桶排序
int max = nums[0];
int min = nums[0];
for (int i1 = 1; i1 < nums.length; i1++) {
if (nums[i1] > max) {
max = nums[i1];
}
if (nums[i1] < min) {
min = nums[i1];
}
}
// 2.1 准备桶
/*
计算桶个数 期望桶个数
(max - min) / range + 1 = nums.length
(max - min) / (nums.length - 1) = range
*/
int range = Math.max((max - min) / (nums.length - 1), 1);
DynamicArray[] buckets = new DynamicArray[(max - min) / range + 1];
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < buckets.length; i1++) {
buckets[i1] = new DynamicArray();
}
// 2.2 放入数据
for (int age : nums) {
buckets[(age - min) / range].addLast(age);
}
int k = 0;
for (DynamicArray bucket : buckets) {
// 2.3 排序桶内元素
int[] array = bucket.array();
InsertionSort.sort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
// 2.4 把每个桶排序好的内容,依次放入原始数组
for (int v : array) {
nums[k++] = v;
}
}
// 3. 寻找最大差值
int r = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
r = Math.max(r, nums[i] - nums[i - 1]);
}
return r;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int[] nums = {1, 10000000};
// int[] nums = {9, 1, 3, 5};
// int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 1};
// int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5};
int[] nums = {15252, 16764, 27963, 7817, 26155, 20757, 3478, 22602, 20404, 6739, 16790, 10588, 16521, 6644, 20880, 15632, 27078, 25463, 20124, 15728, 30042, 16604, 17223, 4388, 23646, 32683, 23688, 12439, 30630, 3895, 7926, 22101, 32406, 21540, 31799, 3768, 26679, 21799, 23740};
int r = new E03Leetcode164_3().maximumGap(nums);
System.out.println(r);
}
}
解法4:在解法3的基础上,只保留桶内最大最小值
public class E03Leetcode164_4 {
public int maximumGap(int[] nums) {
// 1. 处理特殊情况
if (nums.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
// 2. 桶排序
// 桶个数 (max - min) / range + 1 期望桶个数 nums.length + 1
// range = (max - min) / nums.length
int max = nums[0];
int min = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > max) {
max = nums[i];
}
if (nums[i] < min) {
min = nums[i];
}
}
if (max == min) {
return 0;
}
int range = Math.max(1, (max - min) / nums.length);
int size = (max - min) / range + 1;
Pair[] buckets = new Pair[size];
// 2. 放入数据
for (int i : nums) {
int idx = (i - min) / range;
if (buckets[idx] == null) {
buckets[idx] = new Pair();
}
buckets[idx].add(i);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buckets));
// 3. 寻找最大差值
int r = 0;
int lastMax = buckets[0].max;
for (int i = 1; i < buckets.length; i++) {
Pair pair = buckets[i];
if (pair != null) {
r = Math.max(r, pair.min - lastMax);
lastMax = pair.max;
}
}
return r;
}
static class Pair {
int max = 0;
int min = 1000_000_000;
public void add(int v) {
max = Math.max(max, v);
min = Math.min(min, v);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "[" + min + "," + max + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {9, 1, 6, 5};
// int[] nums = {1, 10000000};
// int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 1};
// int[] nums = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5};
// int[] nums = {15252, 16764, 27963, 7817, 26155, 20757, 3478, 22602, 20404, 6739, 16790, 10588, 16521, 6644, 20880, 15632, 27078, 25463, 20124, 15728, 30042, 16604, 17223, 4388, 23646, 32683, 23688, 12439, 30630, 3895, 7926, 22101, 32406, 21540, 31799, 3768, 26679, 21799, 23740};
int r = new E03Leetcode164_4().maximumGap(nums);
System.out.println(r);
}
}
排序数组-Leetcode 912
排序链表-Leetcode 148
其它题目
| 题目编号 | 题目标题 | 排序算法类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 1122 | 数组的相对排序 | 计数排序 |
| 1636 | 按照频率将数组升序排序 | 计数排序 |
| 164 | 最大间距 | 基数排序、桶排序 |
| 315 | 计算右侧小于当前元素的个数 | 基数排序 |
| 347 | 前 K 个高频元素 | 桶排序 |
| 题目编号 | 题目标题 | 排序算法类型 |
|---|---|---|
| 75 | 颜色分类 | 三向切分快速排序 |
| 215 | 数组中的第K个最大元素 | 堆排序 |
| 493 | 翻转对 | 归并排序 |
| 493 | 翻转对 | 树状数组 |
| 524 | 通过删除字母匹配到字典里最长单词 | 循环排序 |
| 977 | 有序数组的平方 | 双指针法 |
本文,已收录于,我的技术网站 pottercoding.cn,有大厂完整面经,工作技术,架构师成长之路,等经验分享!