1.引言
在现代Web开发中,IndexedDB作为一种强大的客户端存储技术,越来越受到开发者的青睐。它不仅能够存储大量结构化数据,还提供了高性能的查询和事务支持。在前面的文章中,我们已经详细介绍了IndexedDB的基本概念、使用方法以及在Chrome浏览器中如何调试和管理IndexedDB数据。为了让大家更好地理解和应用这项技术,本篇《浏览器百科:网页存储篇-IndexedDB应用实例(十二)》将通过一些实际的开发实例,展示如何在真实项目中使用IndexedDB进行数据存储和管理,从而帮助开发者更高效地构建功能丰富、性能优异的Web应用。
2.IndexedDB应用实例
首先,我们使用 Vue 3 和 TypeScript 实现了一个简单的网页应用,具体功能如下:
- 用户可以通过表单输入一个 ID 和一个名称,并点击“Add Item”按钮将这个项目添加到 MyObjectStore对象存储中。添加成功后,会弹出提示框通知用户。
- 用户可以点击“Get All Items”按钮,从MyObjectStore 对象存储中获取所有项目,并将其显示在页面上。
- 在每个列表项旁边都有一个“Delete”按钮,用户点击该按钮可以删除相应的项目。删除成功后,会重新获取所有项目并更新显示。
- 用户可以点击“Clear All Items”按钮,清除MyObjectStore对象存储中的所有项目。清除成功后,会弹出提示框通知用户,并更新显示为空。
2.1 主要代码
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
const id = ref<number | null>(null)
const name = ref('')
const items = ref<{ id: number; name: string }[]>([])
let db: IDBDatabase
const openDB = () => {
return new Promise<void>((resolve, reject) => {
const request = indexedDB.open('MyDatabase', 1)
request.onupgradeneeded = (event: IDBVersionChangeEvent) => {
db = (event.target as IDBOpenDBRequest).result
db.createObjectStore('MyObjectStore', { keyPath: 'id' })
}
request.onsuccess = (event: Event) => {
db = (event.target as IDBOpenDBRequest).result
resolve()
}
request.onerror = (event: Event) => {
console.error('Database error:', (event.target as IDBOpenDBRequest).error)
reject((event.target as IDBOpenDBRequest).error)
}
})
}
const addItem = async () => {
if (id.value !== null && name.value) {
const transaction = db.transaction('MyObjectStore', 'readwrite')
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore('MyObjectStore')
const item = { id: id.value, name: name.value }
const request = objectStore.add(item)
request.onsuccess = () => {
alert('Item added successfully')
}
request.onerror = (event: Event) => {
console.error('Add item error:', (event.target as IDBRequest).error)
}
}
}
const getAllItems = () => {
const transaction = db.transaction('MyObjectStore', 'readonly')
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore('MyObjectStore')
const request = objectStore.getAll()
request.onsuccess = (event: Event) => {
items.value = (event.target as IDBRequest).result
}
request.onerror = (event: Event) => {
console.error('Get all items error:', (event.target as IDBRequest).error)
}
}
const deleteItem = (id: number) => {
const transaction = db.transaction('MyObjectStore', 'readwrite')
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore('MyObjectStore')
const request = objectStore.delete(id)
request.onsuccess = () => {
alert('Item deleted successfully')
getAllItems()
}
request.onerror = (event: Event) => {
console.error('Delete item error:', (event.target as IDBRequest).error)
}
}
const clearAllItems = () => {
const transaction = db.transaction('MyObjectStore', 'readwrite')
const objectStore = transaction.objectStore('MyObjectStore')
const request = objectStore.clear()
request.onsuccess = () => {
alert('All items cleared successfully')
items.value = []
}
request.onerror = (event: Event) => {
console.error('Clear all items error:', (event.target as IDBRequest).error)
}
}
onMounted(async () => {
await openDB()
})
</script><template>
<div>
<h1>IndexedDB-test</h1>
<form @submit.prevent="addItem">
<div>
<label for="id">Key:</label>
<input type="number" v-model.number="id" required />
</div>
<div>
<label for="name">Value:</label>
<input type="text" v-model="name" required />
</div>
<button type="submit">Add Item</button>
<button @click="getAllItems">Get All Items</button>
<button @click="clearAllItems">Clear All Items</button>
</form>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">{{ item.id }}: {{ item.name }}
<button @click="deleteItem(item.id)">Delete</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template><style scoped>
label {
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
input {
width: 250px;
height: 30px;
margin-top: 10px;
padding: 5px;
border-radius: 5px;
}
button {
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 10px 15px;
background-color: rgb(97, 152, 255);
color: #ffffff;
border: #ffffff;
margin-left: 20px;
}
button:hover {
background-color: rgb(131, 186, 245);
}
ul {
margin-top: 20px;
}
li {
margin: 5px 0;
}
</style>执行该命令来运行程序:
npm run dev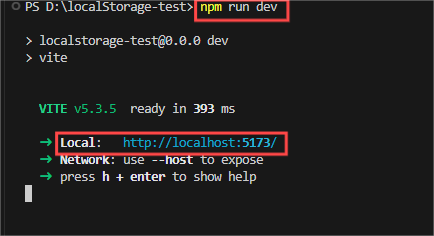
2.2 访问http://localhost:5173/
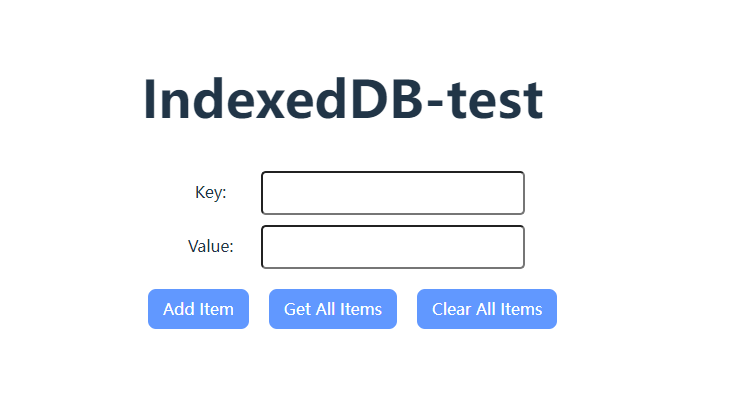
3.进行测试
3.1 添加数据
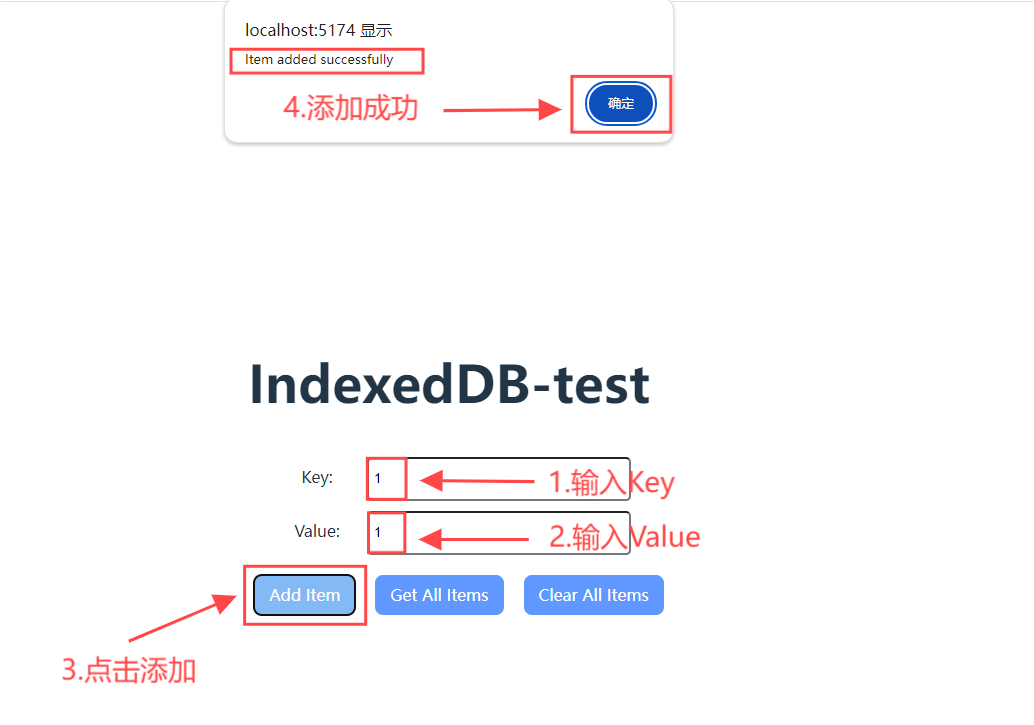
打开窗格查看是否添加成功:

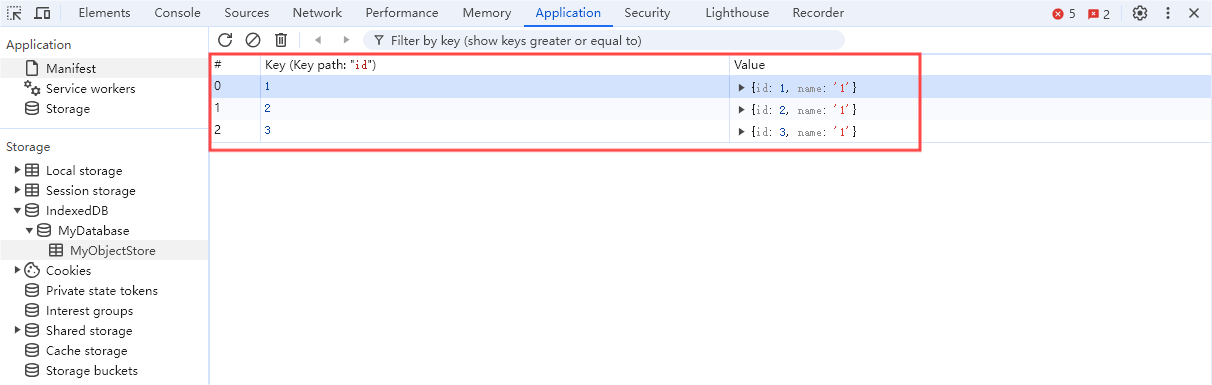
3.2 查看已添加的数据
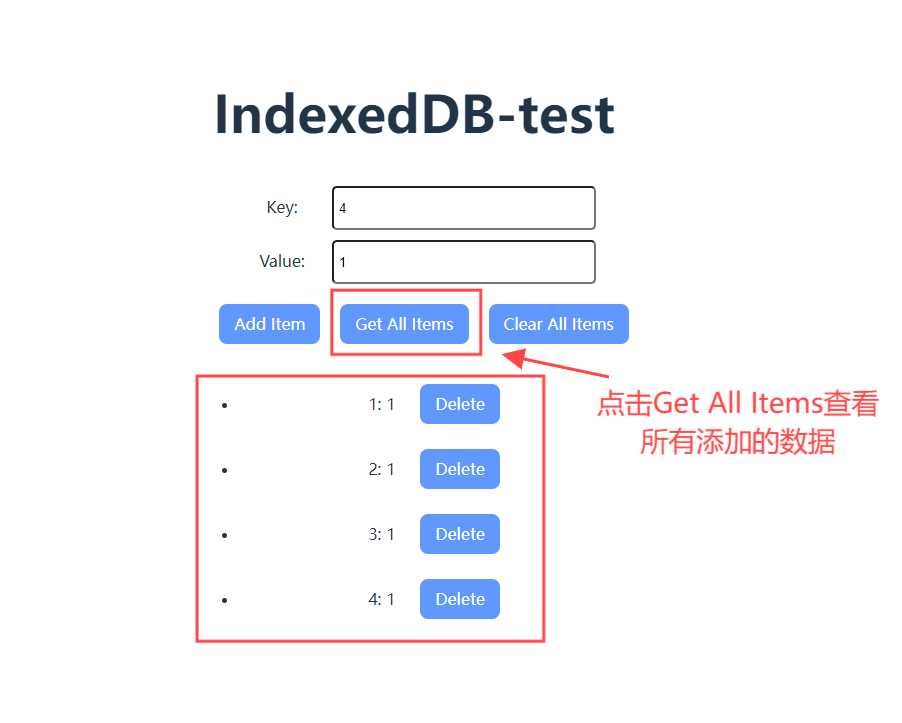
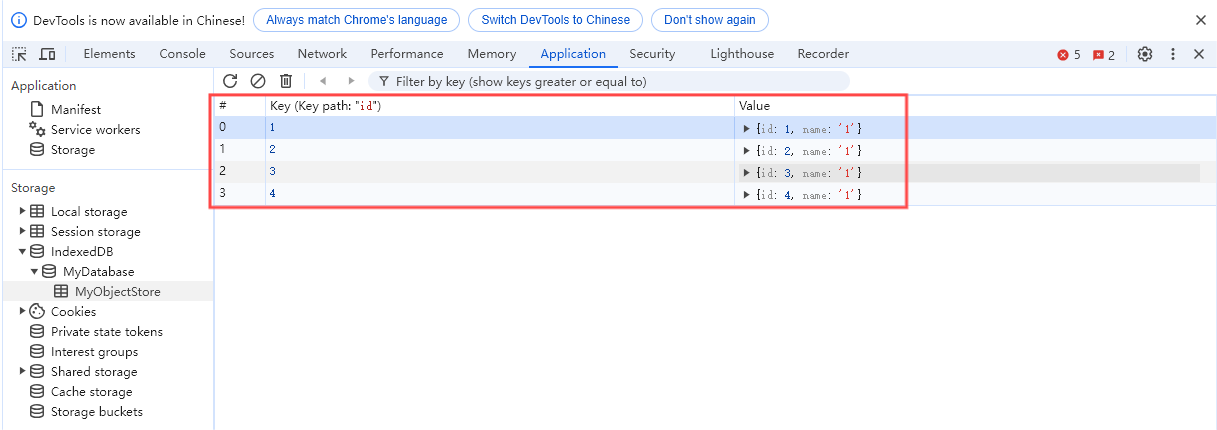
在窗格中验证:
3.3 删除数据
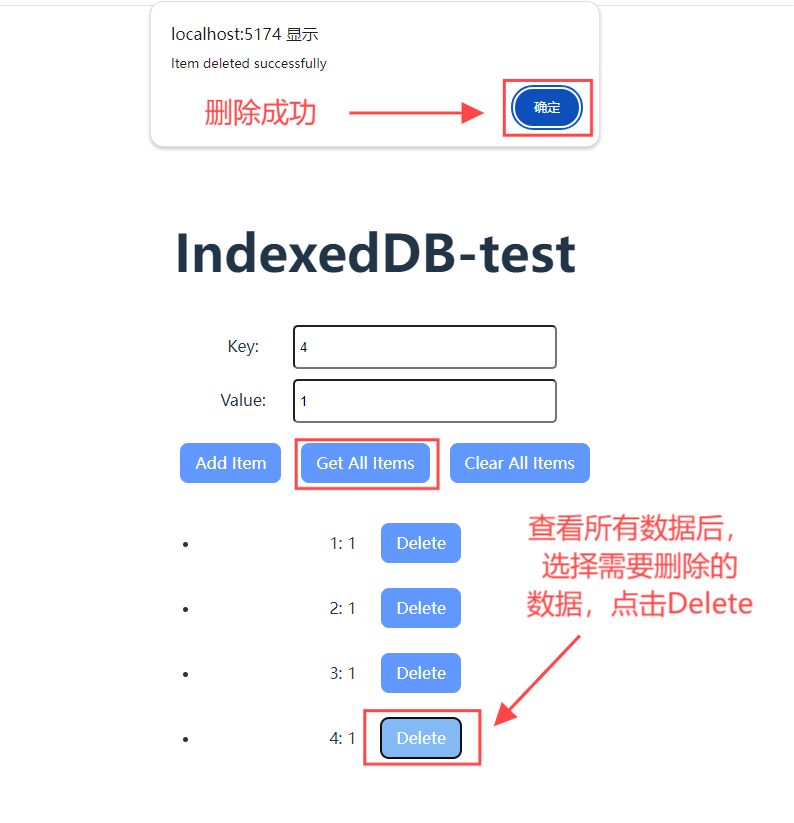
此时,在窗格中查看是否删除成功:
3.4 删除所有数据

此时,在窗格中查看是否删除成功:

4.总结
在本篇《浏览器百科:网页存储篇-IndexedDB应用实例(十二)》中,我们通过一个实际开发实例,详细展示了如何在 Vue 3 和 TypeScript 环境下使用 IndexedDB 进行数据存储和管理。这个实例涵盖了添加、获取、删除单个项目以及清空所有项目的基本操作,帮助开发者在实际项目中更好地应用 IndexedDB。在实际开发中,IndexedDB 提供了强大的本地存储能力和高效的数据查询手段,适用于需要离线支持或需要存储大量结构化数据的 Web 应用。本篇实例为开发者提供了一个良好的入门示例,希望能帮助大家在实际项目中更加高效地应用 IndexedDB,实现功能丰富且性能优异的 Web 应用。
通过实践,可以更好地理解和应用IndexedDB的特性,为开发功能丰富、性能优异的Web应用提供了强大的支持。希望本篇文章能帮助开发者更好地掌握IndexedDB的使用方法,并在实际项目中灵活运用。






![书生浦语三期实战营 [进阶] 茴香豆:企业级知识问答工具实践闯关任务](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f35c088351c946a9867cd5eeaa940daf.png)