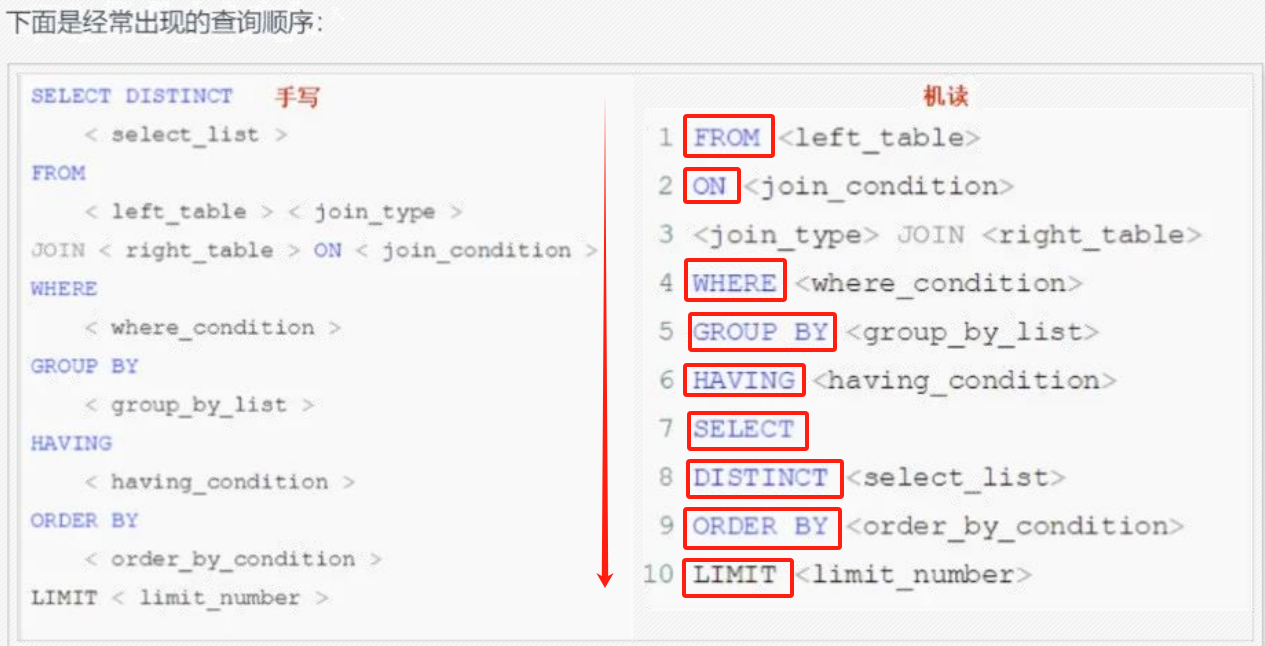
往期文章:
Input系统之IMS的启动流程
input系统之InputReader
1.概述
InputReader和InputDispatcher是Input系统的重要组成部分,InputReader主要负责从设备节点获取原始输入事件,并将封装好的事件交给InputDispatcher;InputDispatcher主要负责将输入事件分发到对应的窗口,本文主要分析InputDispatcher是如何对事件进行分发的,代码基于Android 14。
2.启动InputDispatcher
Input系统之IMS的启动流程中提到过,IMS启动时InputDispatcher会启动一个线程,在这个线程里进行输入事件的分发,先从InputDispatcher创建开始分析。
InputDispatcher是在InputManager.cpp创建的:
2.1 InputManager::InputManager
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = createInputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);//创建InputDispatcher
mProcessor = std::make_unique<InputProcessor>(*mDispatcher);
mBlocker = std::make_unique<UnwantedInteractionBlocker>(*mProcessor);
mReader = createInputReader(readerPolicy, *mBlocker);
}主要通过createInputDispatcher()方法创建InputDispatcher对象,传入了InputDispatcherPolicyInterface对象作为参数。
InputDispatcher负责将输入事件(如触摸事件、键盘事件等)分发到合适的应用程序或View。InputDispatcherPolicyInterface 的作用是定义和提供一些策略,来控制这些事件的分发和处理行为,确保用户的输入得到及时和正确的处理。
2.2 createInputDispatcher
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcherFactory.cpp
std::unique_ptr<InputDispatcherInterface> createInputDispatcher(
InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy) {
return std::make_unique<android::inputdispatcher::InputDispatcher>(policy);
}新建 InputDispatcher对象,继续看InputDispatcher的构造方法
2.3 InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy)
: InputDispatcher(policy, STALE_EVENT_TIMEOUT) {}
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy,
std::chrono::nanoseconds staleEventTimeout)
: mPolicy(policy),//mPolicy用于调用java层方法
mPendingEvent(nullptr),
mLastDropReason(DropReason::NOT_DROPPED),
mIdGenerator(IdGenerator::Source::INPUT_DISPATCHER),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false),
mAppSwitchDueTime(LLONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(nullptr),
mMonitorDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT),
mDispatchEnabled(false),
mDispatchFrozen(false),
mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mMaximumObscuringOpacityForTouch(1.0f),
mFocusedDisplayId(ADISPLAY_ID_DEFAULT),
mWindowTokenWithPointerCapture(nullptr),
mStaleEventTimeout(staleEventTimeout),
mLatencyAggregator(),
mLatencyTracker(&mLatencyAggregator) {
mLooper = sp<Looper>::make(false);//创建mLooper
mReporter = createInputReporter();//创建InputReporter对象
mWindowInfoListener = sp<DispatcherWindowListener>::make(*this);
#if defined(__ANDROID__)
SurfaceComposerClient::getDefault()->addWindowInfosListener(mWindowInfoListener);
#endif
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = nullptr;
}构造方法里主要是创建一些对象、设置一些的变量(定义在InputDispatcher.h里)。
比较重要的就是设置mPolicy,用以调用java层代码,先看下policy这个参数是怎么一步步传递过来的:
1.InputDispatcher的构造方法里传入policy参数
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy)
: InputDispatcher(policy, createInputTracingBackendIfEnabled()) {}
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy,
std::unique_ptr<trace::InputTracingBackendInterface> traceBackend)
: mPolicy(policy),
2.InputManager里创建InputDispatcher
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
InputManager::InputManager(const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& dispatcherPolicy,
PointerChoreographerPolicyInterface& choreographerPolicy,
InputFilterPolicyInterface& inputFilterPolicy) {
mDispatcher = createInputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
3.NativeInputManager里创建InputManager
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
NativeInputManager::NativeInputManager(jobject serviceObj, const sp<Looper>& looper)
: mLooper(looper), mInteractive(true) {
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
mServiceObj = env->NewGlobalRef(serviceObj);
InputManager* im = new InputManager(this, *this, *this, *this);
mInputManager = im;
defaultServiceManager()->addService(String16("inputflinger"), im);
}可以看出mPolicy就是NativeInputManager对象,内部通过jni调用java层代码。
2.4 InputDispatcher::start
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcher->start();//调用InputDispatcher的start方法
......
result = mReader->start();//调用InputReader的start方法
......
return OK;
}
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;//防止重复创建InputDispatcher线程
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake(); });//创建一个名为InputDispatcher的线程,并调用dispatchOnce()方法
return OK;
}IMS启动时会调用InputDispatcher的start()方法来启动线程,首先判断线程是否创建,如果已经创建则直接返回,否则创建InputThread对象,将"InputDispatcher"作为线程名称传入。InputDispatcher对应的线程就是在InputThread里启动的,先来看下InputThread。
2.5 InputThread::InputThread
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputThread.cpp
InputThread::InputThread(std::string name, std::function<void()> loop, std::function<void()> wake)
: mName(name), mThreadWake(wake) {// : mName(name), mThreadWake(wake)初始化mName和mThreadWake
mThread = sp<InputThreadImpl>::make(loop);//创建线程
mThread->run(mName.c_str(), ANDROID_PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//线程启动
}InputDispatcher的start方法里创建InputThread对象时传递了三个参数:"InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake();
从InputThread的构造方法里可以看出,这三个参数分别表示:
name:std::string 类型,表示线程名称。
loop: std::function<void()> 类型的函数对象,表示线程的主要循环逻辑。
wake:std::function<void()> 类型的函数对象,用于唤醒线程。
继续看下InputThread的构造方法里做了什么,首先是初始化mName和mThreadWake变量,mName 表示线程的名称,mThreadWake 表示唤醒函数。
接着创建mThread线程,通过InputThreadImpl创建对应的线程,并定义了线程的执行方法。
最后,run方法启动线程,并设置线程的优先级。
可以看出InputDispatcher启动的线程实际上是在InputThreadImpl里启动的(InputReader也是)。
2.6 InputThread::InputThreadImpl
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputThread.cpp
class InputThreadImpl : public Thread {//InputThreadImpl继承自Thread,是一个线程实现类
public:
explicit InputThreadImpl(std::function<void()> loop)//构造函数接受一个 std::function<void()> 类型的参数 loop,该函数对象将作为线程的主要循环逻辑
: Thread(/* canCallJava */ true), mThreadLoop(loop) {} 调用基类Thread的构造函数,并将参数 true 传递给它
~InputThreadImpl() {}
private:
std::function<void()> mThreadLoop;//用于存储线程的循环逻辑
bool threadLoop() override {//重写Thread里的函数,它定义了线程的主循环逻辑。
mThreadLoop();
return true;//返回 true表示线程继续运行。返回 false,则表示线程应终止
}
};
InputThreadImpl是一个继承自Thread的线程实现类,内部重写了threadLoop()方法,当线程启动后,将会在内部不断循环调用threadLoop()方法,直至返回false。从上述代码可以看出threadLoop()返回值为true,所以函数会一直保持循环。
每循环一次threadLoop()方法都会调用一次mThreadLoop()方法,在InputThreadImpl的构造方法里将loop参数赋值给mThreadLoop(),loop是一个类型为std::function<void()> 的函数对象,从上面的代码可以看出,InputDispatcher线程启动传递的loop参数为dispatchOnce()方法,所以启动名为InputDispatcher的线程后,会循环调用dispatchOnce()方法。
3.分发事件
3.1 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce
InputDispatcher的线程启动后,会循环调用dispatchOnce()方法来进行事件的分发,下面分析一次循环的分发流程。
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LLONG_MAX;//初始化下次唤醒时间为最大值
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);//申请锁,确保线程安全
mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// 通知所有等待的线程调度器仍然活跃
// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.
// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {//如果mCommandQueue里没有待处理的commands
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);//进行调度循环,调度循环会将commands排入mCommandQueue队列以便随后运行
}
// Run all pending commands if there are any.
// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {//如果mCommandQueue里有待处理的commands,执行所有的commands
nextWakeupTime = LLONG_MIN;//如果有命令运行,则设置下一个唤醒时间为最小值,确保下一次轮询会立即唤醒
}
// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,
// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.
//如果还在等待事件的确认,需要提前唤醒以检查是否出现了ANR
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();//检查是否发生anr,并获取下次监测anr的时间
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);//nextAnrCheck为下次监测anr的时间,区两者间小的值设置为下次唤醒时间
// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or
// pending or queued events
if (nextWakeupTime == LLONG_MAX) {//如果下一个唤醒时间仍然是最大值,说明没有命令,也没有待处理或排队的事件,将进入无限长的睡眠
mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();// 通知所有等待的线程调度器已进入空闲状态
}
} // release lock
// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);// 计算超时时间(毫秒)
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);//轮询事件,等待回调或超时或唤醒
}InputDispatcher在一次线程循环中,dispatchOnce()函数的大致流程为:
(1)如果mCommandQueue里没有待处理的commands, 执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime)方法进行调度循环,调度循环会产生新的commands并排入mCommandQueue队列以便随后运行。
(2)如果mCommandQueue里有待处理的commands,runCommandsLockedInterruptable()方法执行所有的commands,并设置下一个唤醒时间为最小值。
(3)处理anr:processAnrsLocked()检查是否需要提前唤醒以处理应用无响应(ANR)问题。
(4)进入空闲状态:如果 nextWakeupTime 仍然是最大值,表示没有命令和事件需要处理,通知所有线程调度器已进入空闲状态,将进入无限长的睡眠。
(5)pollOnce(timeoutMillis)轮询:计算超时时间,等待回调或超时或唤醒事件发生。
下面分别对这些流程进行分析。
在分析这些流程之前先看下mCommandQueue是什么。
3.1.1 mCommandQueue
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.h
using Command = std::function<void()>;
std::deque<Command> mCommandQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command&& command) {
mCommandQueue.push_back(command);
}可以看出mCommandQueue是一个用以保存Command的序列容器,将需要执行的Command命令排队到mCommandQueue里,以便在合适的时机处理。
Command是在postCommandLocked()方法里添加到mCommandQueue里的,有以下场景会添加Command:

Command实际指向一个函数,通过调用java层代码来告知java层某些策略、配置已更改,比如dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked配置更改、onAnrLocked发生anr等(后面流程具体分析)。
继续分析dispatchOnce()流程。
3.1.2 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked
(1)如果mCommandQueue里没有待处理的commands, 执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime)方法进行调度轮询,调度循环会产生新的commands,将commands插入mCommandQueue队列以便随后运行。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t& nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间
// Reset the key repeat timer whenever normal dispatch is suspended while the
// device is in a non-interactive state. This is to ensure that we abort a key
// repeat if the device is just coming out of sleep.
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {//设备处于非交互状态时、
resetKeyRepeatLocked();//重置按键重复计时器,确保了在设备从睡眠模式恢复时能够中止任何正在进行的键重复。
}
// If dispatching is frozen, do not process timeouts or try to deliver any new events.
if (mDispatchFrozen) {//如果调度被冻结,则不处理超时或尝试传递任何新事件
if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {
ALOGD("Dispatch frozen. Waiting some more.");
}
return;
}
// Ready to start a new event.
// If we don't already have a pending event, go grab one.
//准备处理新的事件
if (!mPendingEvent) {//如果没有待处理的事件
if (mInboundQueue.empty()) {//mInboundQueue为空,表示没有输入事件
// Synthesize a key repeat if appropriate.
if (mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry) {//合成一个键重复事件
if (currentTime >= mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime) {
mPendingEvent = synthesizeKeyRepeatLocked(currentTime);
} else {
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime);//等待下一次唤醒时间
}
}
// Nothing to do if there is no pending event.
if (!mPendingEvent) {//如果没有待处理的事件,直接返回
return;
}
} else {//mInboundQueue不为空,表示有输入事件
// Inbound queue has at least one entry.
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();//从mInboundQueue队列中获取一个事件
mInboundQueue.pop_front();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();// 记录入队列长度
}
// Poke user activity for this event.
if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
pokeUserActivityLocked(*mPendingEvent);// 对于这个事件,触发用户活动
}
}
// Now we have an event to dispatch.
// All events are eventually dequeued and processed this way, even if we intend to drop them.
//现在有一个事件需要调度
//所有事件最终都会以这种方式出队和处理,即使我们打算丢弃它们
ALOG_ASSERT(mPendingEvent != nullptr);//确保mPendingEvent不为null
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED;//丢弃原因
//根据事件的策略标志和调度状态决定是否丢弃事件
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {
dropReason = DropReason::POLICY;
} else if (!mDispatchEnabled) {
dropReason = DropReason::DISABLED;
}
if (mNextUnblockedEvent == mPendingEvent) {
mNextUnblockedEvent = nullptr;
}
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {//根据待处理事件的类型进行处理
case EventEntry::Type::CONFIGURATION_CHANGED: {//配置改变
const ConfigurationChangedEntry& typedEntry =
static_cast<const ConfigurationChangedEntry&>(*mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchConfigurationChangedLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);//处理配置更改事件
dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED; // configuration changes are never dropped 配置更改事件不会被丢弃
break;
}
//下同,根据待处理事件的类型,调用不同的方法去处理事件
case EventEntry::Type::DEVICE_RESET: {
const DeviceResetEntry& typedEntry =
static_cast<const DeviceResetEntry&>(*mPendingEvent);
done = dispatchDeviceResetLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);
dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED; // device resets are never dropped
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::FOCUS: {
std::shared_ptr<const FocusEntry> typedEntry =
std::static_pointer_cast<const FocusEntry>(mPendingEvent);
dispatchFocusLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);
done = true;
dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED; // focus events are never dropped
break;
}
......
}
if (done) {//事件已经处理完成
if (dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
dropInboundEventLocked(*mPendingEvent, dropReason);//处理丢弃的事件
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
releasePendingEventLocked();//释放对当前事件的持有,并允许下一个事件处理。
nextWakeupTime = LLONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately 立刻处理下一次事件
}
}在 dispatchOnceInnerLocked()方法中进行事件的分发,如果mPendingEvent(mPendingEvent是从mInboundQueue中取出的事件)待处理的事件为空,检查mInboundQueue队列是否为空,在input系统之InputReader-CSDN博客里提到过,InputReader最终会把读取的事件处理好的放入mInboundQueue队列,如果mInboundQueue不为空,表示有新的输入事件产生。
如果mInboundQueue为空,可能合成一个键重复事件,也可能派发线程陷入休眠,等待下一次唤醒;如果mInboundQueue中有事件,取出队列中的第一个事件并根据待处理事件的类型进行处理;
3.1.3 InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptable
(2)如果mCommandQueue里有待处理的commands,runCommandsLockedInterruptable()方法执行所有的commands,并设置下一个唤醒时间为最小值,确保下一次轮询会立即唤醒.
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptable() {
if (mCommandQueue.empty()) {//如果mCommandQueue为空,返回false
return false;
}
do {//循环执行mCommandQueue里的command,直到mCommandQueue为空
auto command = std::move(mCommandQueue.front());//取出mCommandQueue里的command并执行
mCommandQueue.pop_front();
// Commands are run with the lock held, but may release and re-acquire the lock from within.
command();
} while (!mCommandQueue.empty());
return true;
}循环执行mCommandQueue里的command,直到mCommandQueue为空。
3.1.4 InputDispatcher::processAnrsLocked
(3)处理anr:processAnrsLocked()检查是否需要提前唤醒以处理应用无响应(ANR)问题。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
nsecs_t InputDispatcher::processAnrsLocked() {
const nsecs_t currentTime = now();//获取当前时间
nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = LLONG_MAX;//初始化nextAnrCheck为最大,这个变量用以跟踪下次触发anr检查的时间
// Check if we are waiting for a focused window to appear. Raise ANR if waited too long
//检查是否有等待焦点窗口超时
if (mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value() && mAwaitedFocusedApplication != nullptr) {//如果当前焦点窗口超时,并且正在等待的焦点应用不为空
if (currentTime >= *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime) {//anr超时,mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime默认值为5s
processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked();//处理没有焦点窗口的anr超时
mAwaitedFocusedApplication.reset();//重置mAwaitedFocusedApplication
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = std::nullopt;//设置mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime超时时间
return LLONG_MIN;
} else {//未发生anr超时
// Keep waiting. We will drop the event when mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime comes.
nextAnrCheck = *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime;
}
}
// Check if any connection ANRs are due
nextAnrCheck = std::min(nextAnrCheck, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());//更新 nextAnrCheck 为当前 nextAnrCheck 和 mAnrTracker 中第一个超时值的最小值
if (currentTime < nextAnrCheck) { // most likely scenario 如果当前时间早于nextAnrCheck,则表示未发生异常,返回下次anr检查时间
return nextAnrCheck; // everything is normal. Let's check again at nextAnrCheck
}
// If we reached here, we have an unresponsive connection.
std::shared_ptr<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked(mAnrTracker.firstToken());
if (connection == nullptr) {
ALOGE("Could not find connection for entry %" PRId64, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());
return nextAnrCheck;
}
connection->responsive = false;
// Stop waking up for this unresponsive connection
mAnrTracker.eraseToken(connection->getToken());
onAnrLocked(connection);//处理ANR
return LLONG_MIN;
}processAnrsLocked()方法用以根据不同的条件判断是否需要触发ANR:
(1)如果有等待焦点的应用,但是没有等待焦点的窗口,调用processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked()方法处理anr事件;
(2)如果有应用的窗口获取到了焦点,但是等待超时(5s)没有响应,则调用onAnrLocked()方法处理。
processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked()方法最终也是调用的onAnrLocked()方法。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::onAnrLocked(std::shared_ptr<InputApplicationHandle> application) {
std::string reason =
StringPrintf("%s does not have a focused window", application->getName().c_str());//anr原因,没有焦点窗口
updateLastAnrStateLocked(*application, reason);//更新anr状态
auto command = [this, app = std::move(application)]() REQUIRES(mLock) {
scoped_unlock unlock(mLock);
mPolicy.notifyNoFocusedWindowAnr(app);//生成一个command,用于调用mPolicy.notifyNoFocusedWindowAnr方法
};
postCommandLocked(std::move(command));//将command插入到mCommandQueue任务队列中,以便在适当的时候执行。
}onAnrLocked()方法用于处理应用程序没有焦点窗口的anr情况,创建一个command,主要是用来执行mPolicy.notifyNoFocusedWindowAnr方法来通知发生了anr事件,将command通过postCommandLocked(std::move(command))方法插入到mCommandQueue任务队列中,以便在适当的时候执行。
4.KEY类型事件处理
在上文提到过dispatchOnceInnerLocked()方法会取出mInboundQueue队列中的第一个事件并根据待处理事件的类型进行处理,有CONFIGURATION_CHANGED配置变化类型、DEVICE_RESET设备重置类型、KEY按键类型、MOTION类型等事件,下面分析下KEY按键类型的事件处理:
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {
std::shared_ptr<const KeyEntry> keyEntry =
std::static_pointer_cast<const KeyEntry>(mPendingEvent);//KeyEntry类型,包含当前键事件的详细信息
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && isStaleEvent(currentTime, *keyEntry)) {
dropReason = DropReason::STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DropReason::BLOCKED;
}
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, keyEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);//分发按键事件
if (done && mTracer) {
ensureEventTraced(*keyEntry);
mTracer->eventProcessingComplete(*keyEntry->traceTracker);
}
break;调用dispatchKeyLocked()方法处理KEY类型事件
4.1 dispatchKeyLocked
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<const KeyEntry> entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t& nextWakeupTime) {
// Preprocessing.
if (!entry->dispatchInProgress) {//如果事件还没有被处理
if (entry->repeatCount == 0 && entry->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN &&
(entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED) &&
(!(entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_DISABLE_KEY_REPEAT))) {//依次为:是否是第一次按下、是否是按下事件、是否是受信任的按键事件、没有被禁用重复事件
if (mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry &&
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->keyCode == entry->keyCode &&
// We have seen two identical key downs in a row which indicates that the device
// driver is automatically generating key repeats itself. We take note of the
// repeat here, but we disable our own next key repeat timer since it is clear that
// we will not need to synthesize key repeats ourselves.
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->deviceId == entry->deviceId) {//上一个按键事件是否与当前按键事件相同,并且来自相同的设备
// Make sure we don't get key down from a different device. If a different
// device Id has same key pressed down, the new device Id will replace the
// current one to hold the key repeat with repeat count reset.
// In the future when got a KEY_UP on the device id, drop it and do not
// stop the key repeat on current device.
//增加重复计数,并且重置按键重复状态。设置nextRepeatTime为最大值,表明不需要自己生成重复事件
entry->repeatCount = mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->repeatCount + 1;
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime = LLONG_MAX; // don't generate repeats ourselves
} else {//如果不是重复按键,重置按键重复状态,并设置下一次重复的时间
// Not a repeat. Save key down state in case we do see a repeat later.
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
mKeyRepeatState.nextRepeatTime = entry->eventTime + mConfig.keyRepeatTimeout;
}
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = entry;//更新lastKeyEntry为当前的按键事件
} else if (entry->action == AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP && mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry &&
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry->deviceId != entry->deviceId) {//如果按键事件是up抬起事件,并且 lastKeyEntry 的设备ID与当前设备ID不同
// The key on device 'deviceId' is still down, do not stop key repeat
if (debugInboundEventDetails()) {
ALOGD("deviceId=%d got KEY_UP as stale", entry->deviceId);
}
} else if (!entry->syntheticRepeat) {//如果按键事件不是合成重复事件,则重置按键重复状态
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
}
if (entry->repeatCount == 1) {//按键事件的重复次数为1
entry->flags |= AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_LONG_PRESS;//标识为长按事件
} else {
entry->flags &= ~AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_LONG_PRESS;//清除长按事件
}
entry->dispatchInProgress = true;//标记为处理中的按键事件
logOutboundKeyDetails("dispatchKey - ", *entry);
}
// Handle case where the policy asked us to try again later last time.
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::TRY_AGAIN_LATER) {//是否要求稍后再试(TRY_AGAIN_LATER)
if (currentTime < entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime) {//如果当前时间小于计划的唤醒时间
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime);//设置下次唤醒时间
return false; // wait until next wakeup 需要等待唤醒
}
//重置interceptKeyResult和interceptKeyWakeupTime
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::UNKNOWN;
entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime = 0;
}
// Give the policy a chance to intercept the key.
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::UNKNOWN) {//如果 interceptKeyResult 为 UNKNOWN
if (entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {//是否需要将事件传递给用户
sp<IBinder> focusedWindowToken =
mFocusResolver.getFocusedWindowToken(getTargetDisplayId(*entry));//获取当前焦点窗口的令牌
auto command = [this, focusedWindowToken, entry]() REQUIRES(mLock) {
doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingCommand(focusedWindowToken, *entry);//生成command以在事件分发前拦截按键,这里就是我们熟知的调用interceptKeyBeforeDispatching()方法的地方
};
postCommandLocked(std::move(command));//将command插入队列,后面进行处理
// Poke user activity for keys not passed to user
pokeUserActivityLocked(*entry);//记录用户活动
return false; // wait for the command to run
} else {//如果不需要传递给用户,设置interceptKeyResult为CONTINUE
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::CONTINUE;
}
} else if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::InterceptKeyResult::SKIP) {//如果需要跳过(SKIP)当前事件,更新丢弃原因为 POLICY
if (*dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
*dropReason = DropReason::POLICY;
}
}
// Clean up if dropping the event.
if (*dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {//如果丢弃该事件
setInjectionResult(*entry,
*dropReason == DropReason::POLICY ? InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED
: InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED);
mReporter->reportDroppedKey(entry->id);//报告丢弃的按键事件
// Poke user activity for undispatched keys
pokeUserActivityLocked(*entry);//记录用户活动
return true;
}
// Identify targets.
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult;
sp<WindowInfoHandle> focusedWindow =
findFocusedWindowTargetLocked(currentTime, *entry, nextWakeupTime,
/*byref*/ injectionResult);//查找焦点窗口作为事件分发的目标window
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING) {//注入结果。如果结果是 PENDING,返回 false,表示需要等待。
return false;
}
setInjectionResult(*entry, injectionResult);//设置注入结果
if (injectionResult != InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED) {//如果注入结果设置失败,直接返回true
return true;
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(focusedWindow == nullptr);//如果焦点窗口为 nullptr,记录信息
//创建事件的目标列表,将焦点窗口添加到目标列表中,并设置相应的调度模式和标志
std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
addWindowTargetLocked(focusedWindow, InputTarget::DispatchMode::AS_IS,
InputTarget::Flags::FOREGROUND, getDownTime(*entry), inputTargets);
// Add monitor channels from event's or focused display.
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));//添加监视通道到事件的目标列表中
if (mTracer) {
ensureEventTraced(*entry);
for (const auto& target : inputTargets) {
mTracer->dispatchToTargetHint(*entry->traceTracker, target);
}
}
// Dispatch the key.
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);//最后,分发按键事件
return true;
}dispatchKeyLocked()方法里首先处理按键事件的重复逻辑,它检测按键是否需要重复生成,根据按键的状态和设备ID管理按键重复,并设置相应的标志;
接着判断按键事件在分发之前是否需要进行拦截,doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingCommand()方法调用mPolicy.interceptKeyBeforeDispatching()方法进行按键分发拦截,我们熟知的interceptKeyBeforeDispatching()方法就是在这里调用的;
然后,通过findFocusedWindowTargetLocked()方法找到所有可以接收当前事件的窗口,构建InputTarget队列存放这些找到的窗口。
最后调用dispatchEventLocked()方法将事件派发到获取到的窗口。
这里重点有两个:findFocusedWindowTargetLocked()找到目标窗口、dispatchEventLocked()方法分发按键事件,分别分析这两个方法。
4.2 findFocusedWindowTargetLocked
这个方法用于寻找当前焦点窗口以处理输入事件。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
sp<WindowInfoHandle> InputDispatcher::findFocusedWindowTargetLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const EventEntry& entry, nsecs_t& nextWakeupTime,
InputEventInjectionResult& outInjectionResult) {
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED;//初始化结果 // Default result
int32_t displayId = getTargetDisplayId(entry);//根据输入事件获取display id
sp<WindowInfoHandle> focusedWindowHandle = getFocusedWindowHandleLocked(displayId);//获取焦点窗口对象
std::shared_ptr<InputApplicationHandle> focusedApplicationHandle =
getValueByKey(mFocusedApplicationHandlesByDisplay, displayId);//获取焦点应用
// If there is no currently focused window and no focused application
// then drop the event.
if (focusedWindowHandle == nullptr && focusedApplicationHandle == nullptr) {//如果焦点窗口和焦点应用都为null
ALOGI("Dropping %s event because there is no focused window or focused application in "
"display %" PRId32 ".",
ftl::enum_string(entry.type).c_str(), displayId);
return nullptr;//直接返回
}
// Drop key events if requested by input feature
if (focusedWindowHandle != nullptr && shouldDropInput(entry, focusedWindowHandle)) {//如果焦点窗口不为空,但是需要丢弃当前事件
return nullptr;//直接返回
}
// Compatibility behavior: raise ANR if there is a focused application, but no focused window.
// Only start counting when we have a focused event to dispatch. The ANR is canceled if we
// start interacting with another application via touch (app switch). This code can be removed
// if the "no focused window ANR" is moved to the policy. Input doesn't know whether
// an app is expected to have a focused window.
if (focusedWindowHandle == nullptr && focusedApplicationHandle != nullptr) {//如果焦点窗口为null,但是焦点应用不为null
if (!mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value()) {
// We just discovered that there's no focused window. Start the ANR timer
std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = focusedApplicationHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(
DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);//获取分发输入事件的超时时间(anr超时时间),默认为5s
mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();//设置mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime为发生anr的事件
mAwaitedFocusedApplication = focusedApplicationHandle;//赋值mAwaitedFocusedApplication为焦点应用
mAwaitedApplicationDisplayId = displayId;//事件分发的目标displayId赋值给mAwaitedApplicationDisplayId
ALOGW("Waiting because no window has focus but %s may eventually add a "
"window when it finishes starting up. Will wait for %" PRId64 "ms",
mAwaitedFocusedApplication->getName().c_str(), millis(timeout));
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime);//下次唤醒时间,把anr发生的时间赋值给nextWakeupTime,即先休眠,在anr发生的时间时再check一次
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;//结果设置PENDING暂停
return nullptr;
} else if (currentTime > *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime) {//如果当前时间大于anr发生的时间,表示anr发生时又check了一遍,还是只有焦点应用没有焦点窗口
// Already raised ANR. Drop the event
ALOGE("Dropping %s event because there is no focused window",
ftl::enum_string(entry.type).c_str());
return nullptr;//丢弃此事件
} else {//当前时间还没有到达anr发生的时间
// Still waiting for the focused window
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;//继续pending暂停
return nullptr;
}
}
// we have a valid, non-null focused window
//到这里表示已经获取到一个可用的、非空的焦点窗口
resetNoFocusedWindowTimeoutLocked();//重置anr超时时间
// Verify targeted injection.
//验证输入事件是否可以正确地注入到指定的窗口。它会检查事件的目标UID和窗口的UID是否匹配,并根据验证结果返回适当的信息
if (const auto err = verifyTargetedInjection(focusedWindowHandle, entry); err) {
ALOGW("Dropping injected event: %s", (*err).c_str());
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::TARGET_MISMATCH;
return nullptr;
}
if (focusedWindowHandle->getInfo()->inputConfig.test(
WindowInfo::InputConfig::PAUSE_DISPATCHING)) {//如果当前窗口处于pause状态,继续对事件进行pending
ALOGI("Waiting because %s is paused", focusedWindowHandle->getName().c_str());
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;
return nullptr;
}
// If the event is a key event, then we must wait for all previous events to
// complete before delivering it because previous events may have the
// side-effect of transferring focus to a different window and we want to
// ensure that the following keys are sent to the new window.
//
// Suppose the user touches a button in a window then immediately presses "A".
// If the button causes a pop-up window to appear then we want to ensure that
// the "A" key is delivered to the new pop-up window. This is because users
// often anticipate pending UI changes when typing on a keyboard.
// To obtain this behavior, we must serialize key events with respect to all
// prior input events.
//如果事件是按键事件,那么必须等待所有先前的事件完成后才能传递该事件,因为先前的事件可能会产生将焦点转移到其他窗口的副作用,确保后续按键可以被发送到新窗口。
if (entry.type == EventEntry::Type::KEY) {//如果当前事件是KEY按键类型事件
if (shouldWaitToSendKeyLocked(currentTime, focusedWindowHandle->getName().c_str())) {//是否需要等待
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, *mKeyIsWaitingForEventsTimeout);//设置下次唤醒时间,以便时间到时间后继续处理
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;
return nullptr;
}
}
outInjectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED;//到这里,获取焦点窗口成功
return focusedWindowHandle;//返回焦点窗口
}首先根据输入事件的显示id获取当前焦点窗口(通过getFocusedWindowHandleLocked()方法)和焦点应用程序;
接着分别处理无焦点窗口和焦点应用程序、无焦点窗口但有焦点应用程序的情况,启动anr计时器。
如果有焦点窗口,resetNoFocusedWindowTimeoutLocked()重置无焦点窗口的超时时间,检查焦点窗口是否暂停事件分发,处理按键事件的特殊情况。
最后通过所有检查,设置注入结果为 SUCCEEDED,返回焦点窗口句柄。
4.3 dispatchEventLocked
这个方法用于分发按键事件到目标窗口。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
std::shared_ptr<const EventEntry> eventEntry,
const std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
ATRACE_CALL();
if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {
ALOGD("dispatchEventToCurrentInputTargets");
}
processInteractionsLocked(*eventEntry, inputTargets);
ALOG_ASSERT(eventEntry->dispatchInProgress); // should already have been set to true
pokeUserActivityLocked(*eventEntry);//记录用户活动
for (const InputTarget& inputTarget : inputTargets) {//遍历目标窗口
std::shared_ptr<Connection> connection = inputTarget.connection;//获取窗口的connection
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);//事件派发
}
}
dispatchEventLocked()方法负责将输入事件分发到指定的目标窗口,遍历目标窗口,然后通过prepareDispatchCycleLocked()方法进行派发事件。
4.4 prepareDispatchCycleLocked
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const std::shared_ptr<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<const EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
ATRACE_NAME_IF(ATRACE_ENABLED(),
StringPrintf("prepareDispatchCycleLocked(inputChannel=%s, id=0x%" PRIx32 ")",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), eventEntry->id));
if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ prepareDispatchCycle - flags=%s, "
"globalScaleFactor=%f, pointerIds=%s %s",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), inputTarget.flags.string().c_str(),
inputTarget.globalScaleFactor, bitsetToString(inputTarget.getPointerIds()).c_str(),
inputTarget.getPointerInfoString().c_str());
}
// Skip this event if the connection status is not normal.
// We don't want to enqueue additional outbound events if the connection is broken.
if (connection->status != Connection::Status::NORMAL) {//窗口连接状态不为NORMAL时,直接返回
if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dropping event because the channel status is %s",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(),
ftl::enum_string(connection->status).c_str());
}
return;
}
// Split a motion event if needed.
if (inputTarget.flags.test(InputTarget::Flags::SPLIT)) {//InputTarget的flag为SPLIT,这里主要处理MOTION触摸事件
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(eventEntry->type != EventEntry::Type::MOTION,
"Entry type %s should not have Flags::SPLIT",
ftl::enum_string(eventEntry->type).c_str());//只有MOTION类型事件才有SPLIT flag
const MotionEntry& originalMotionEntry = static_cast<const MotionEntry&>(*eventEntry);
if (inputTarget.getPointerIds().count() != originalMotionEntry.getPointerCount()) {
if (!inputTarget.firstDownTimeInTarget.has_value()) {
logDispatchStateLocked();
LOG(FATAL) << "Splitting motion events requires a down time to be set for the "
"target on connection "
<< connection->getInputChannelName() << " for "
<< originalMotionEntry.getDescription();
}
std::unique_ptr<MotionEntry> splitMotionEntry =
splitMotionEvent(originalMotionEntry, inputTarget.getPointerIds(),
inputTarget.firstDownTimeInTarget.value());
if (!splitMotionEntry) {
return; // split event was dropped
}
if (splitMotionEntry->action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_CANCEL) {
std::string reason = std::string("reason=pointer cancel on split window");
android_log_event_list(LOGTAG_INPUT_CANCEL)
<< connection->getInputChannelName().c_str() << reason << LOG_ID_EVENTS;
}
if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Split motion event.",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());
logOutboundMotionDetails(" ", *splitMotionEntry);
}
enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection,
std::move(splitMotionEntry),
inputTarget);
return;
}
}
// Not splitting. Enqueue dispatch entries for the event as is.
enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry,
inputTarget);//将事件添加到派发队列
}主要是调用enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked()方法将事件添加到派发队列。
4.5 enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const std::shared_ptr<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<const EventEntry> eventEntry, const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
ATRACE_NAME_IF(ATRACE_ENABLED(),
StringPrintf("enqueueDispatchEntryAndStartDispatchCycleLocked(inputChannel=%s, "
"id=0x%" PRIx32 ")",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), eventEntry->id));
const bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.empty();//outboundQueue队列是否为空
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);//将eventEntry事件添加到outboundQueue队列中
// If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {//如果outboundQueue队列不为空
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);//启动派发循环
}
}
startDispatchCycleLocked()方法开始派发循环。
4.6 startDispatchCycleLocked
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const std::shared_ptr<Connection>& connection) {
ATRACE_NAME_IF(ATRACE_ENABLED(),
StringPrintf("startDispatchCycleLocked(inputChannel=%s)",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str()));
if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ startDispatchCycle", connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
while (connection->status == Connection::Status::NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {//循环处理outboundQueue中的事件,直到队列为空或连接状态不再正常
std::unique_ptr<DispatchEntry>& dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front();//取出头部数据
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;//deliveryTime 设置为当前时间
const std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(connection);//计算超时时间,默认5s
dispatchEntry->timeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();
// Publish the event.
status_t status;
const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
switch (eventEntry.type) {//待分发的事件类型
case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {//按键类型
const KeyEntry& keyEntry = static_cast<const KeyEntry&>(eventEntry);
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac = getSignature(keyEntry, *dispatchEntry);
if (DEBUG_OUTBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS) {
LOG(INFO) << "Publishing " << *dispatchEntry << " to "
<< connection->getInputChannelName();
}
// Publish the key event.
status = connection->inputPublisher
.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq, keyEntry.id,
keyEntry.deviceId, keyEntry.source,
keyEntry.displayId, std::move(hmac),
keyEntry.action, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry.keyCode, keyEntry.scanCode,
keyEntry.metaState, keyEntry.repeatCount,
keyEntry.downTime, keyEntry.eventTime);//KEY类型事件派发
if (mTracer) {
mTracer->traceEventDispatch(*dispatchEntry, keyEntry.traceTracker.get());
}
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
if (DEBUG_OUTBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS) {
LOG(INFO) << "Publishing " << *dispatchEntry << " to "
<< connection->getInputChannelName();
}
const MotionEntry& motionEntry = static_cast<const MotionEntry&>(eventEntry);
status = publishMotionEvent(*connection, *dispatchEntry);
if (mTracer) {
mTracer->traceEventDispatch(*dispatchEntry, motionEntry.traceTracker.get());
}
break;
}
......
}
// Check the result.
if (status) {//派发结果
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {//派发结果为WOULD_BLOCK
if (connection->waitQueue.empty()) {
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event because the pipe is full. "
"This is unexpected because the wait queue is empty, so the pipe "
"should be empty and we shouldn't have any problems writing an "
"event to it, status=%s(%d)",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), statusToString(status).c_str(),
status);
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, /*notify=*/true);
} else {
// Pipe is full and we are waiting for the app to finish process some events
// before sending more events to it.
if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event because the pipe is full, "
"waiting for the application to catch up",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
}
} else {
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not publish event due to an unexpected error, "
"status=%s(%d)",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), statusToString(status).c_str(),
status);
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, /*notify=*/true);
}
return;
}
// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.
const nsecs_t timeoutTime = dispatchEntry->timeoutTime;
connection->waitQueue.emplace_back(std::move(dispatchEntry));//将事件排入waitQueue
connection->outboundQueue.erase(connection->outboundQueue.begin());//将已完成派发的事件从outboundQueue中移除
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
if (connection->responsive) {
mAnrTracker.insert(timeoutTime, connection->getToken());
}
traceWaitQueueLength(*connection);
}
}取出outboundQueue里的所有事件进行派发,根据EventEntry事件类型,通过Connection调用InputPublisher里对应的函数将事件发布到应用程序,这里主要分析InputPublisher.publishKeyEvent()方法处理按键事件类型的流程。
4.7 InputPublisher.publishKeyEvent
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId,
int32_t source, int32_t displayId,
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac, int32_t action,
int32_t flags, int32_t keyCode, int32_t scanCode,
int32_t metaState, int32_t repeatCount, nsecs_t downTime,
nsecs_t eventTime) {
ATRACE_NAME_IF(ATRACE_ENABLED(),
StringPrintf("publishKeyEvent(inputChannel=%s, action=%s, keyCode=%s)",
mChannel->getName().c_str(), KeyEvent::actionToString(action),
KeyEvent::getLabel(keyCode)));
ALOGD_IF(debugTransportPublisher(),
"channel '%s' publisher ~ %s: seq=%u, id=%d, deviceId=%d, source=%s, "
"action=%s, flags=0x%x, keyCode=%s, scanCode=%d, metaState=0x%x, repeatCount=%d,"
"downTime=%" PRId64 ", eventTime=%" PRId64,
mChannel->getName().c_str(), __func__, seq, eventId, deviceId,
inputEventSourceToString(source).c_str(), KeyEvent::actionToString(action), flags,
KeyEvent::getLabel(keyCode), scanCode, metaState, repeatCount, downTime, eventTime);
if (!seq) {
ALOGE("Attempted to publish a key event with sequence number 0.");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
//将事件信息封装成InputMessage类型
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::KEY;
msg.header.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.eventId = eventId;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.displayId = displayId;
msg.body.key.hmac = std::move(hmac);
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);//通过调用InputChannel的sendMessage()方法将封装好的InputMessage发送给client
}将KeyEntry类型输入事件信息封装成InputMessage类型,然后调用InputChannel的sendMessage()方法将封装好的InputMessage发送给client。
4.8 InputChannel::sendMessage
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
ATRACE_NAME_IF(ATRACE_ENABLED(),
StringPrintf("sendMessage(inputChannel=%s, seq=0x%" PRIx32 ", type=0x%" PRIx32
")",
name.c_str(), msg->header.seq, msg->header.type));
const size_t msgLength = msg->size();
InputMessage cleanMsg;
msg->getSanitizedCopy(&cleanMsg);
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(getFd(), &cleanMsg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);//通过socket的send方法发送事件
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
......
return OK;
}至此,输入事件通过socket的send()方法被发送给应用程序。
5. InputChannel
输入事件最终会通过InputChannel发送到应用程序层,它作为应用程序和系统之间的桥梁,不但负责发送输入事件,同时也负责接收事件的处理结果。
5.1 创建InputChannel
InputChannel是在ViewRootImpl.setView()设置View的时候创建的
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView,
int userId) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
......
InputChannel inputChannel = null;
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
inputChannel = new InputChannel();//1.创建InputChannel对象
}
try {
mOrigWindowType = mWindowAttributes.type;
......
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId,
mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibleTypes(), inputChannel, mTempInsets,
mTempControls, attachedFrame, compatScale);//2.将InputChannel添加到mWindowSession的引用
......
if (inputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(inputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());//3.通过InputChannel创建WindowInputEventReceiver,用于接收和处理输入事件
......
}
}
setView()方法里对于InputChannel主要做了以下操作:
(1)创建InputChannel对象
(2)将InputChannel添加到mWindowSession的引用
(3)通过InputChannel创建WindowInputEventReceiver,用于接收和处理输入事件
InputChannel的构造函数为空,实际并没有做什么操作,所以我们从第二步开始分析。
5.2 WMS.addWindow()
将InputChannel添加到mWindowSession的引用之后被一步步传递给WMS.addWindow():
WindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser()->Session.addToDisplayAsUser()->WMS.addWindow()
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility,
int displayId, int requestUserId, @InsetsType int requestedVisibleTypes,
InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState,
InsetsSourceControl.Array outActiveControls, Rect outAttachedFrame,
float[] outSizeCompatScale) {
......
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow,
appOp[0], attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId,
session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
......
final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null
&& (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0);
if (openInputChannels) {
win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel);//调用WindowState的openInputChannel()方法
}
......
return res;
}
调用WindowState的openInputChannel()方法
5.3 WindowState.openInputChannel
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java
void openInputChannel(@NonNull InputChannel outInputChannel) {
if (mInputChannel != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Window already has an input channel.");
}
String name = getName();//获取当前窗口的名称
mInputChannel = mWmService.mInputManager.createInputChannel(name);//这里才是真正创建InputChannel的地方
mInputChannelToken = mInputChannel.getToken();
mInputWindowHandle.setToken(mInputChannelToken);
mWmService.mInputToWindowMap.put(mInputChannelToken, this);
mInputChannel.copyTo(outInputChannel);
}
调用IMS.createInputChannel()方法创建InputChannel,传入当前窗口的名称做为参数。然后依次调用NativeInputManagerService.createInputChannel()->com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.createInputChannel(),最终调用InputDispatcher的createInputChannel()
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
base::Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> NativeInputManager::createInputChannel(
const std::string& name) {
ATRACE_CALL();
return mInputManager->getDispatcher().createInputChannel(name);
}5.4 InputDispatcher.createInputChannel
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
Result<std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>> InputDispatcher::createInputChannel(const std::string& name) {
if (DEBUG_CHANNEL_CREATION) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ createInputChannel", name.c_str());
}
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> serverChannel;//服务端InputChannel
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel> clientChannel;//客户端InputChannel
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);//1.通过InputChannel的openInputChannelPair创建一对服务端serverChannel和客户端clientChannel
if (result) {
return base::Error(result) << "Failed to open input channel pair with name " << name;
}
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
const sp<IBinder>& token = serverChannel->getConnectionToken();//获取服务端token
const int fd = serverChannel->getFd();//2.得到serverChannel的文件描述符
std::shared_ptr<Connection> connection =
std::make_shared<Connection>(std::move(serverChannel), /*monitor=*/false,
mIdGenerator);//3.创建connection对象
auto [_, inserted] = mConnectionsByToken.try_emplace(token, connection);
if (!inserted) {
ALOGE("Created a new connection, but the token %p is already known", token.get());
}
std::function<int(int events)> callback = std::bind(&InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback,
this, std::placeholders::_1, token);// 创建一个回调函数,用于处理接收事件
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, sp<LooperEventCallback>::make(callback),
nullptr); // 4.将文件描述符fd添加到looper中,事件类型为 ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT,回调函数为handleReceiveCallback,用于监听serverChannel的文件描述符
} // release lock
// Wake the looper because some connections have changed.
mLooper->wake();
return clientChannel;//5.返回客户端的inputchannel给java层
}InputDispatcher.cpp里的createInputChannel()方法才是真正创建InputChannel的地方。里面定义了一对服务端serverChannel和客户端clientChannel,通过InputChannel::openInputChannelPair()方法创建serverChannel和clientChannel。
接着获取serverChannel的文件描述符并设置监听,当有ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT(即input事件)类型事件发生时,会回调InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback方法。
Looper::addfd()方法可以将对应的文件描述符注册到epoll中,Looper.cpp会监听文件描述符,有数据产生时,会执行对应的回调。
最后,返回客户端的clientChannel给java层的WindowState.openInputChannel(),用来接收InputDispatcher传来的输入事件数据。
5.5 InputChannel::openInputChannelPair
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const std::string& name,
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>& outServerChannel,
std::unique_ptr<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {//用于创建一对UNIX域的流式套接字(SOCK_SEQPACKET),它们可以进行双向通信
status_t result = -errno;
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not create socket pair. errno=%s(%d)", name.c_str(),
strerror(errno), errno);
outServerChannel.reset();
outClientChannel.reset();
return result;
}
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
//设置套接字的发送和接收缓冲区大小,sockets[0]和sockets[1]分别代表这对套接字的两个端点。
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
sp<IBinder> token = sp<BBinder>::make();
//创建服务器端InputChannel
std::string serverChannelName = name + " (server)";
android::base::unique_fd serverFd(sockets[0]);
outServerChannel = InputChannel::create(serverChannelName, std::move(serverFd), token);
//创建客户端InputChannel
std::string clientChannelName = name + " (client)";
android::base::unique_fd clientFd(sockets[1]);
outClientChannel = InputChannel::create(clientChannelName, std::move(clientFd), token);
return OK;
}openInputChannelPair()方法用于创建一对InputChannel(客户端和服务端),内部使用socket来实现双向通信。
6.接收处理输入事件
在4.8 InputChannel::sendMessage中提到输入事件通过socket的send()方法发送出去,那么应用程序是如何接收输入事件呢?
上文提到InputDispatcher::createInputChannel()方法创建的clientChannel就是用来接收输入事件的。InputDispatcher::createInputChannel()方法最终会返回到客户端clientChannel给ViewRootImpl。
在5.1创建InputChannel中提到,会通过返回的InputChannel创建WindowInputEventReceiver,用于接收和处理输入事件。
6.1 WindowInputEventReceiver
WindowInputEventReceiver是ViewRootImpl的内部类,它从InputChannel中接收到输入事件,然后将其传递给相应的窗口。看下它是如何接收输入事件的。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper);
}
......
}WindowInputEventReceiver的构造函数里调用父类InputEventReceiver的构造函数
6.2 InputEventReceiver
frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
if (inputChannel == null) {//检查传入的 inputChannel 是否为空
throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null");
}
if (looper == null) {// 检查传入的 looper 是否为空
throw new IllegalArgumentException("looper must not be null");
}
// 初始化成员变量
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),
mInputChannel, mMessageQueue);// 调用nativeInit方法对mReceiverPtr进行本地初始化,并传入当前对象的弱引用、inputChanne 和消息队列
mCloseGuard.open("InputEventReceiver.dispose");
}
InputEventReceiver构造函数的主要作用是初始化输入事件接收器,通过调用nativeInit方法对mReceiverPtr进行本地初始化,确保InputEventReceiver能够正确地接收和处理输入事件。
6.3 android_view_InputEventReceiver::nativeInit
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel =
android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);
if (inputChannel == nullptr) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "InputChannel is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
if (messageQueue == nullptr) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");
return 0;
}
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue); // 创建 NativeInputEventReceiver 实例
status_t status = receiver->initialize(); // 初始化 NativeInputEventReceiver 实例
if (status) {
std::string message = android::base::
StringPrintf("Failed to initialize input event receiver. status=%s(%d)",
statusToString(status).c_str(), status);
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, message.c_str());
return 0;
}
receiver->incStrong(gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.clazz); // retain a reference for the object
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get()); // 返回指向 NativeInputEventReceiver 对象的指针
}
NativeInputEventReceiver::NativeInputEventReceiver(
JNIEnv* env, jobject receiverWeak, const std::shared_ptr<InputChannel>& inputChannel,
const sp<MessageQueue>& messageQueue)
: mReceiverWeakGlobal(env->NewGlobalRef(receiverWeak)),
mInputConsumer(inputChannel),
mMessageQueue(messageQueue),
mBatchedInputEventPending(false),
mFdEvents(0) {
traceBoolVariable("mBatchedInputEventPending", mBatchedInputEventPending);
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Initializing input event receiver.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
}
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);
return OK;
}主要是创建并初始化NativeInputEventReceiver,关联java层传过来的 mInputChannel和mMessageQueue,重点是setFdEvents()方法
6.4 setFdEvents
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {
mFdEvents = events;
const int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();// 获取与InputChannel关联的文件描述符
if (events) {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, nullptr);// 监听InputChannel的文件描述符
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);// 从Looper中移除文件描述符
}
}
}NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents方法调用Looper::addFd()方法来监听客户端InputChannel的文件描述。
上文提到过Looper::addfd()方法可以将对应的文件描述符注册到epoll中,Looper.cpp会监听文件描述符,有数据产生时,会执行对应的回调。
这里的回调方法是this,即NativeInputEventReceiver,NativeInputEventReceiver继承自LooperCallback并实现了handleEvent()方法,所以最后执行的是NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent()。
一但向服务端InputChannel保存的socket写入数据,则会触发NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent()回调。
6.4 NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
int NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent(int receiveFd, int events, void* data) {
// Allowed return values of this function as documented in LooperCallback::handleEvent
......
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, /*consumeBatches=*/false, -1, nullptr);
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "handleReceiveCallback");
return status == OK || status == NO_MEMORY ? KEEP_CALLBACK : REMOVE_CALLBACK;
}
......
}调用consumeEvents()处理事件。
6.5 NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents
frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
......
for (;;) {//启动死循环
uint32_t seq;
InputEvent* inputEvent;
status_t status = mInputConsumer.consume(&mInputEventFactory,
consumeBatches, frameTime, &seq, &inputEvent);//1.从InputConsumer中读取socket中的输入数据
......
switch (inputEvent->getType()) {//2.对获取到的事件类型进行封装
case InputEventType::KEY:
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Received key event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
inputEventObj =
android_view_KeyEvent_obtainAsCopy(env,
static_cast<KeyEvent&>(*inputEvent));
break;
case InputEventType::MOTION: {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Received motion event.",
getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
const MotionEvent& motionEvent = static_cast<const MotionEvent&>(*inputEvent);
if ((motionEvent.getAction() & AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE) && outConsumedBatch) {
*outConsumedBatch = true;
}
inputEventObj = android_view_MotionEvent_obtainAsCopy(env, motionEvent);
break;
}
......
if (inputEventObj.get()) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq,
inputEventObj.get());//3.通过jni回调java层的InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent()函数
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
ALOGE("Exception dispatching input event.");
skipCallbacks = true;
}
} else {
ALOGW("channel '%s' ~ Failed to obtain event object.",
getInputChannelName().c_str());
skipCallbacks = true;
}
}
}
}consumeEvents()方法启动一个死循环:
(1)InputConsumer读取socket中的输入数据。
(2)对获取到的事件类型进行封装
(3)回调java层的InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent()函数。
先看下是如何从InputConsumer读取socket中的输入数据的。
6.6 InputConsumer::consume
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::consume(InputEventFactoryInterface* factory, bool consumeBatches,
nsecs_t frameTime, uint32_t* outSeq, InputEvent** outEvent) {
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_TRANSPORT_CONSUMER,
"channel '%s' consumer ~ consume: consumeBatches=%s, frameTime=%" PRId64,
mChannel->getName().c_str(), toString(consumeBatches), frameTime);
*outSeq = 0;
*outEvent = nullptr;
// Fetch the next input message.
// Loop until an event can be returned or no additional events are received.
while (!*outEvent) {
if (mMsgDeferred) {
// mMsg contains a valid input message from the previous call to consume
// that has not yet been processed.
mMsgDeferred = false;
} else {
// Receive a fresh message.
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);//通过InputChannel的receiveMessage读取socket中的输入数据
......
switch (mMsg.header.type) {//对不同类型事件进行封装
case InputMessage::Type::KEY: {
KeyEvent* keyEvent = factory->createKeyEvent();
if (!keyEvent) return NO_MEMORY;
initializeKeyEvent(keyEvent, &mMsg);
*outSeq = mMsg.header.seq;
*outEvent = keyEvent;
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_TRANSPORT_CONSUMER,
"channel '%s' consumer ~ consumed key event, seq=%u",
mChannel->getName().c_str(), *outSeq);
break;
}
case InputMessage::Type::MOTION: {
ssize_t batchIndex = findBatch(mMsg.body.motion.deviceId, mMsg.body.motion.source);
if (batchIndex >= 0) {
Batch& batch = mBatches[batchIndex];
if (canAddSample(batch, &mMsg)) {
batch.samples.push_back(mMsg);
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_TRANSPORT_CONSUMER,
"channel '%s' consumer ~ appended to batch event",
mChannel->getName().c_str());
break;
} else if (isPointerEvent(mMsg.body.motion.source) &&
mMsg.body.motion.action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_CANCEL) {
// No need to process events that we are going to cancel anyways
const size_t count = batch.samples.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
const InputMessage& msg = batch.samples[i];
sendFinishedSignal(msg.header.seq, false);
}
batch.samples.erase(batch.samples.begin(), batch.samples.begin() + count);
mBatches.erase(mBatches.begin() + batchIndex);
} else {
// We cannot append to the batch in progress, so we need to consume
// the previous batch right now and defer the new message until later.
mMsgDeferred = true;
status_t result = consumeSamples(factory, batch, batch.samples.size(),
outSeq, outEvent);
mBatches.erase(mBatches.begin() + batchIndex);
if (result) {
return result;
}
ALOGD_IF(DEBUG_TRANSPORT_CONSUMER,
"channel '%s' consumer ~ consumed batch event and "
"deferred current event, seq=%u",
mChannel->getName().c_str(), *outSeq);
break;
}
}
......
}
return OK;
}调用InputChannel的receiveMessage读取socket中的输入数据,mChannel是客户端的InputChannel
frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg) {
ssize_t nRead;
do {
nRead = ::recv(getFd(), msg, sizeof(InputMessage), MSG_DONTWAIT);
} while (nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR);
......
return OK;
}通过socket的recv()方法读取事件,在4.8 InputChannel::sendMessage中提到过输入事件通过socket的send()方法被发送,在这里客户端就可以读取发送的输入事件。
consumeEvents()方法会对InputConsumer读取数据进行封装,最后通过jni调用java层的InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent()函数处理事件。
至此,上层就可以处理输入事件。