本站以分享各种运维经验和运维所需要的技能为主
《python零基础入门》:python零基础入门学习
《python运维脚本》: python运维脚本实践
《shell》:shell学习
《terraform》持续更新中:terraform_Aws学习零基础入门到最佳实战
《k8》从问题中去学习k8s
《docker学习》暂未更新
《ceph学习》ceph日常问题解决分享
《日志收集》ELK+各种中间件
《运维日常》运维日常
《linux》运维面试100问
《DBA》db的介绍使用(mysql、redis、mongodb...)
一. 索引
1.什么是索引
1.索引就好比一本书的目录,它能让你更快的找到自己想要的内容。 2.让获取的数据更有目的性,从而提高数据库检索数据的性能。 # 注意: 在创建表时为字段创建索引,如不指定索引名称,默认会将字段名作为索引名称。 desc select * from 库名 where 判断语句 # 可看出此语句是否走索引。
2.索引的种类
1.BTREE: B+树索引(Btree,B+tree,B*tree)
2.HASH:HASH索引(memery存储引擎支持)
3.FULLTEXT:全文索引(myisam存储引擎支持)
4.RTREE:R树索引
# 总结:
常用为b+树索引,对b+树的分类为Btree B+tree B*tree
三者区别:
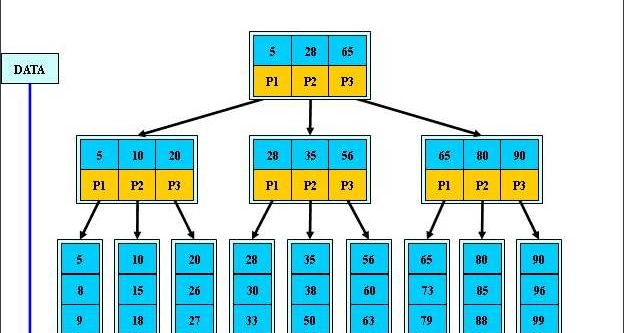
Btree: 走根节点,枝节点,叶子节点,三个节点没有分支
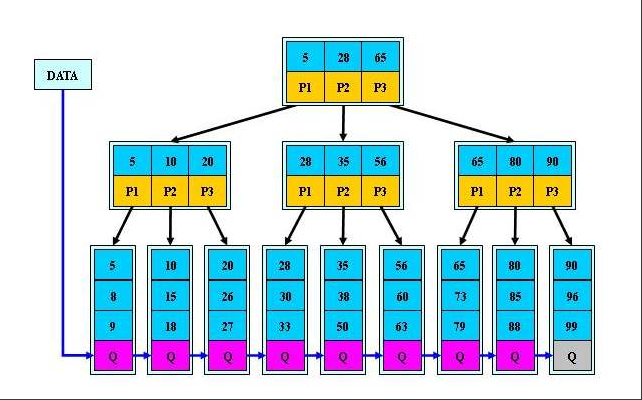
B+tree: 走根节点,枝节点,叶子节点,在叶子节点有做优化,比Btree好
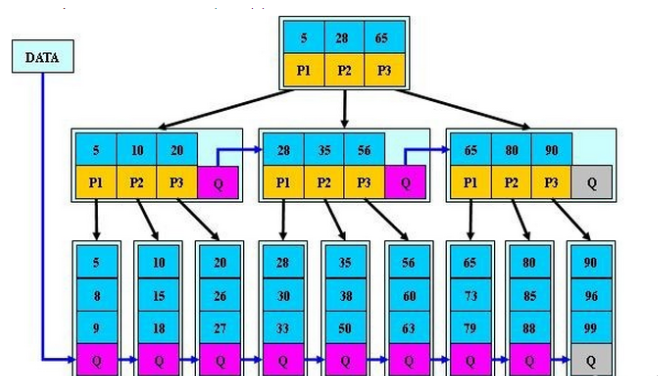
B*tree: 走根节点,枝节点,叶子节点,在枝节点有做优化,比B+tree和Btree好
1)Btree索引
2)B+tree索引
3)B*tree索引
3索引根据算法分类
索引是建立在数据库字段上面的 当where条件后面接的内容有索引的时候,会提高速度
1)主键索引(聚集索引)
#创建表的时候创建主键索引 mysql> create table test(id int not null auto_increment primary key comment '学号'); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) mysql> create table test1(id int not null auto_increment,primary key(id)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) #查看索引命令 mysql> show index from test; #已经有表时添加主键索引 mysql> alter table student add primary key pri_id(id);
2)唯一键索引
#创建表的时候创建唯一键索引 mysql> create table test2(id int not null auto_increment unique key comment '学号'); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) #已经有表时添加唯一键索引 mysql> alter table student add unique key uni_key(name); #注意:创建唯一建索引或主键索引的列不能有重复数据 判断一列能否做唯一建索引 1.查询数据总量 mysql> select count(name) from city; 2.去重查看该列数据总量 mysql> select count(distinct(name)) from city; #以上两个值相等则可以设置唯一建索引
例
#1.查看列的总数据量 mysql> select count(name) from country; +-------------+ | count(name) | +-------------+ | 239 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) #2.查看去重后数据量 mysql> select count(distinct(name)) from country; +-----------------------+ | count(distinct(name)) | +-----------------------+ | 239 | +-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) #3.创建唯一建索引 mysql> alter table country add unique key uni_key(name); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
3)普通索引(辅助索引)
mysql> alter table city add index inx_name(name); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.14 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> create index index_District on city(District); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.06 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
4)全文索引
mysql> create table txt(id int,bookname varchar(12),wenzhang text,fulltext(wenzhang));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.20 sec)
mysql> select * from txt where match(wenzhang) against('查询的内容');
#实例
mysql> create table text(id int,bookname varchar(12) charset utf8,wenzhang text charset utf8,fulltext(wenzhang));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.21 sec)
mysql> insert into text values(1,'红楼梦','上回书说到张飞长坂坡三打白骨精救出宋江');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> select * from text;
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| id | bookname | wenzhang |
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 红楼梦 | 上回书说到张飞长坂坡三打白骨精救出宋江 |
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from text where match(wenzhang) against('上回书说到张飞长坂坡三打白骨精救出宋江');
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| id | bookname | wenzhang |
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
| 1 | 红楼梦 | 上回书说到张飞长坂坡三打白骨精救出宋江 |
+------+-----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
5)查看索引
#方式一: mysql> show index from city; #方式二: mysql> desc city; +-----+ | Key | +-----+ | PRI | #主键索引 | MUL | #普通索引 | UNI | #唯一键索引 | MUL | +-----+
6)删除索引
mysql> alter table city drop index index_District; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
4索引根据配置方法分类
7)联合索引
# 注意:
联合索引在查询时不能用> < 符号,要用等于号,否则联合查询中,多个判断语句,只会将第一个查询走索引,后面直接不走索引。如图一则不走索引,但可将> 查询放到k1=5g后面
# 创建联合索引:
联合索引是在多个列上创建的,多个字段建立一个索引,原则:把最常用来做为条件查询的列放在最前面
#创建people表
create table xiangqin( id, name varchar(10), age int, money bigint, body varchar(10), hight int, weight int, face varchar(10), phone varchar(11), sex enum('f','m'));
#创建联合索引
mysql> alter table xiangqin add index idx_all(sex,money,body,face);
insert into xiangqin values('ly',30,999999999,'perfact',158,90,'nice','133','f'), ('qbl',58,1000000,'bad',150,150,'very bad','000','f'), ('wbq',50,9999999,'suibian',170,120,'suiyi',132,'m');
#查询
走索引
mysql> select * from xiangqin where sex='f' and money>10000000 and body='perfact' and face='nice';
不走索引
mysql> select * from xiangqin where money>10000000 and body='perfact' and face='nice'; mysql> select * from xiangqin where money>10000000 and body='perfact' and face='nice' and sex='f';
# 简单案例:
mysql> create database xiangqing;
mysql> create table xiangqin(id int,name varchar(20),gender enum('m','f'),age tinyint,money int,height int,weight int,looks tinyint);
mysql> insert xiangqin values(1,'qiudao','m',38,-200000,120,130,'10'),(2,'dilireba','f',18,400000,180,100,'60'),(3,'cxk','m',28,100000,170,120,'440'),(4,'fbb','f',18,1000000,165,85,'90');
#创建联合索引
mysql> alter table xiangqin add index lh_key(money,gender,age,looks);
#联合索引使用三种情况
1.部分走索引 money,gender,age
2.全部走索引 money,gender,age,looks
3.不走索引 gender,age
· 图一:
![]()
8)前缀索引
# 概括: 根据字段的前N个字符建立索引 # 注意: 1. 前缀索引只能应用到字符串上的列 2.避免对大列 建索引 3.如果有,就使用前缀索引 # 使用: alter table city add index idx_name(name(5)); #选择name这一列从左到右的前5个字符作为前缀索引
二、explain的使用
1.explain语法
explain + DQL语句
mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode ='CHN' or countrycode ='USA';
#查询中国和美国的数据
mysql> select * from city where countrycode ='CHN' or countrycode ='USA';
mysql> select * from city where countrycode in ('CHN','USA');
mysql> select * from city where countrycode = 'CHN' union all select * from city where countrycode = 'USA';
Extra(扩展)
Using temporary 使用group by大概率出现
Using filesort 使用了order by大概率出现
Using join buffer 使用join on大概率出现
2.扩展group by
#一般与聚合索引一起使用 #建表 mysql> create table jixiao(id int,name varchar(20) charset utf8,jixiao int,product varchar(10) charset utf8); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) #插入数据 mysql> insert jixiao values(1,'qiudao','1000000','房地产'),(2,'niulei','10000','房地产'),(3,'lijianpeng','100000','汽车'),(4,'qiandao','200000',' 汽车'); #查询不同行业绩效最高的人 mysql> select name,sum(jixiao),product from jixiao group by product; +------------+-------------+-----------+ | name | sum(jixiao) | product | +------------+-------------+-----------+ | qiudao | 1010000 | 房地产 | | lijianpeng | 300000 | 汽车 | +------------+-------------+-----------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询房地产行业绩效最高的人 mysql> select name,sum(jixiao),product from jixiao group by product having product='房地产'; +--------+-------------+-----------+ | name | sum(jixiao) | product | +--------+-------------+-----------+ | qiudao | 1010000 | 房地产 | +--------+-------------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
3.查询数据的方式
1)全表扫描
#1.什么是全表扫描 查询数据时type类型为ALL #2.什么情况全表扫描 1)查询数据库所有数据 mysql> explain select * from country 2)没有走索引 没设置索引 索引损坏
2)索引扫描type
# 注意: 此处优先级从上往下对应从低到高,一般企业中需要达到语句查询类型为range 1.index #全索引扫描 mysql> explain select Name from city; 2.range #范围查询 mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode ='CHN' or countrycode ='USA'; #有限制查询到的数据在总数据的20%以内,超过则走全文扫描,所以在查询是可以使用limit限制 mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode != 'CHN' limit 500; 3.ref #精确查询 mysql> explain select * from city where countrycode ='CHN'; 4.eq_ref #使用join on时偶尔会出现 5.const #查询条件是唯一索引或主键索引 mysql> explain select * from city where id=1; 6.system #查询级别与const一样,当数据很少时为该级别 7.null #不需要读取数据,只需要获取最大值或者最小值 mysql> explain select max(population) from city;
三、索引的建立
1.索引的建立原则
1.能创建唯一索引就创建唯一索引
2.为经常需要排序、分组和联合操作的字段建立索引
3.为常作为查询条件的字段建立索引
如果某个字段经常用来做查询条件,那么该字段的查询速度会影响整个表的查询速度。
因此,为这样的字段建立索引,可以提高整个表的查询速度。
4.尽量使用前缀来索引
如果索引字段的值很长,最好使用值的前缀来索引。
例如,TEXT和BLOG类型的字段,进行全文检索,会很浪费时间。如果只检索字段的前面的若干个字符,这样可以提高检索速度。
5.限制索引的数目
索引的数目不是越多越好。每个索引都需要占用磁盘空间,索引越多,需要的磁盘空间就越大。
修改表时,对索引的重构和更新很麻烦。越多的索引,会使更新表变得很浪费时间。
6.删除不再使用或者很少使用的索引
表中的数据被大量更新,或者数据的使用方式被改变后,原有的一些索引可能不再需要。数据库管理员应当定期找出这些索引,将它们删除,从而减少索引对更新操作的影响。
2.总结什么时候不走索引
1)没有查询条件,或者查询条件没有索引
#没有查询条件 mysql> explain select * from city; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | city | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4188 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) #查询条件没有索引 mysql> explain select District from city; +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | city | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 4188 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
2)查询的结果占总数据的20%左右
#占总数据的18%,没走索引 mysql> explain select * from city where population > 400000; #占总数据的15%,走了索引 mysql> explain select * from city where population > 450000; #如果数据量查询就是表中大部分数据,可以用limit做限制 mysql> explain select * from city where population > 400000 limit 100;
3)索引损坏
4)查询条件带了特使符号(+,-)
#在=号左侧有特殊符号,不走索引 mysql> explain select * from city where id-1=1; #在=号右侧有特殊符号,走索引 mysql> explain select * from city where id=3-1;
5)隐式转换
# 什么叫做隐式转换: · 举个例子,当字段类型为字符串(varchar)时,但在插入数据时值为数字,也就是整数。则字段类型和值不匹配,就叫做隐式转换。 #建表 mysql> create table test (id int ,name varchar(20),telnum varchar(10)); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec) #插入数据 mysql> insert into test values(1,'zs','110'),(2,'l4',120),(3,'w5',119),(4,'z4',112); Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec) Records: 4 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 #建立索引 mysql> desc phonenum; +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | name | varchar(10) | YES | | NULL | | | phone | varchar(10) | YES | UNI | NULL | | +-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) #查询语句级别全文扫描(phone字段类型为字符串,需要用引号,如不尊重它的规则,则不给你走索引) mysql> explain select * from phonenum where phone=6666666; +----+-------------+----------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+----------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | phonenum | ALL | uni_key | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | Using where | +----+-------------+----------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) #当给字符加上引号,查询为索引扫描 mysql> explain select * from phonenum where phone='6666666'; +----+-------------+----------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra | +----+-------------+----------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | phonenum | const | uni_key | uni_key | 13 | const | 1 | NULL | +----+-------------+----------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
6)like "%_" 百分号在最前面不走
7)联合索引查询不按照顺序有可能不走索引