1. LRU缓存
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 100000 <= value <= 10^5- 最多调用
2 * 10^5次get和put
解法一:LinkedHashMap
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class LRUCache {
private int capacity;
private LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> cache;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new LinkedHashMap<>(capacity, 0.75f, true) {
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
// 当缓存容量超过capacity时自动移除最近最少使用的元素
return size() > capacity;
}
};
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!cache.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
// 访问key后将其移到最前面
return cache.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/解法二:自定义节点类 + 自定义双端队列
- map中存储node,可以省去在双向链表中查找node的时间,这样让使用最近访问的节点移动到链表头时达到O(1)的需求
class LRUCache {
static class Node {
Node prev;
Node next;
int key;
int value;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
// 双向链表
static class DoubleLinkedList {
Node head;
Node tail;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
head = tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
// 头部添加
public void addFirst(Node newFirst) {
Node oldFirst = head.next;
newFirst.next = oldFirst;
newFirst.prev = head;
head.next = newFirst;
oldFirst.prev = newFirst;
}
// 已知节点删除
public void remove(Node node) {
Node prev = node.prev;
Node next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
// 尾部删除
public Node removeLast() {
Node last = tail.prev;
remove(last);
return last;
}
}
private int capacity;
private final HashMap<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
private final DoubleLinkedList list = new DoubleLinkedList();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!map.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
Node node = map.get(key);
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
// 更新
Node node = map.get(key);
node.value = value;
list.remove(node);
list.addFirst(node);
} else {
// 新增
Node node = new Node(key, value);
map.put(key, node);
list.addFirst(node);
if(map.size() > capacity) {
Node removed = list.removeLast();
map.remove(removed.key);
}
}
}
}2. LFU缓存
请你为 最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
实现 LFUCache 类:
LFUCache(int capacity)- 用数据结构的容量capacity初始化对象int get(int key)- 如果键key存在于缓存中,则获取键的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)- 如果键key已存在,则变更其值;如果键不存在,请插入键值对。当缓存达到其容量capacity时,则应该在插入新项之前,移除最不经常使用的项。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最久未使用 的键。
为了确定最不常使用的键,可以为缓存中的每个键维护一个 使用计数器 。使用计数最小的键是最久未使用的键。
当一个键首次插入到缓存中时,它的使用计数器被设置为 1 (由于 put 操作)。对缓存中的键执行 get 或 put 操作,使用计数器的值将会递增。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入:
["LFUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [3], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, 3, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释:
// cnt(x) = 键 x 的使用计数
// cache=[] 将显示最后一次使用的顺序(最左边的元素是最近的)
LFUCache lfu = new LFUCache(2);
lfu.put(1, 1); // cache=[1,_], cnt(1)=1
lfu.put(2, 2); // cache=[2,1], cnt(2)=1, cnt(1)=1
lfu.get(1); // 返回 1
// cache=[1,2], cnt(2)=1, cnt(1)=2
lfu.put(3, 3); // 去除键 2 ,因为 cnt(2)=1 ,使用计数最小
// cache=[3,1], cnt(3)=1, cnt(1)=2
lfu.get(2); // 返回 -1(未找到)
lfu.get(3); // 返回 3
// cache=[3,1], cnt(3)=2, cnt(1)=2
lfu.put(4, 4); // 去除键 1 ,1 和 3 的 cnt 相同,但 1 最久未使用
// cache=[4,3], cnt(4)=1, cnt(3)=2
lfu.get(1); // 返回 -1(未找到)
lfu.get(3); // 返回 3
// cache=[3,4], cnt(4)=1, cnt(3)=3
lfu.get(4); // 返回 4
// cache=[3,4], cnt(4)=2, cnt(3)=3
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 10^40 <= key <= 10^50 <= value <= 10^9- 最多调用
2 * 10^5次get和put方法
解法一:
class LFUCache {
static class Node {
Node prev;
Node next;
int key;
int value;
int freq;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int key, int value, int freq) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.freq = freq;
}
}
static class DoubleLinkedList {
private final Node head;
private final Node tail;
int size = 0;
public DoubleLinkedList() {
head = tail = new Node();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public void remove(Node node) {
Node prev = node.prev;
Node next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
node.prev = node.next = null;
size--;
}
public void addFirst(Node newFirst) {
Node oldFirst = head.next;
newFirst.prev = head;
newFirst.next = oldFirst;
head.next = newFirst;
oldFirst.prev = newFirst;
size++;
}
public Node removeLast() {
Node last = tail.prev;
remove(last);
return last;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
}
// 频度链表
private final HashMap<Integer, DoubleLinkedList> freqMap = new HashMap<>();
// key和value链表
private final HashMap<Integer, Node> kvMap = new HashMap<>();
private final int capacity;
private int minFreq = 1; // 最小频度
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
/*
key不存在,返回-1
key存在,返回value值,增加节点的使用频度,将其转移到频度+1的链表当中
*/
public int get(int key) {
if(!kvMap.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
// 将节点频度+1,从旧链表转移至新链表
Node node = kvMap.get(key);
// 先删
freqMap.get(node.freq).remove(node);
if(freqMap.get(node.freq).isEmpty() && node.freq == minFreq) {
minFreq++;
}
node.freq++;
/*DoubleLinkedList list = freqMap.get(node.freq);
// 后加
if(list == null) {
list = new DoubleLinkedList();
freqMap.put(node.freq, list);
}
list.addFirst(node);*/
freqMap.computeIfAbsent(node.freq, k -> new DoubleLinkedList()).
addFirst(node);
return node.value;
}
/*
更新:将节点的value更新,增加节点的使用频度,将其转移到频度+1的链表当中
新增:检查是否超过容量,若超过,淘汰minFreq链表的最后节点。创建新节点,放入kvMap,并加入频度为1的双向链表
*/
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(kvMap.containsKey(key)) {
// 更新
Node node = kvMap.get(key);
freqMap.get(node.freq).remove(node);
if(freqMap.get(node.freq).isEmpty() && node.freq == minFreq) {
minFreq++;
}
node.freq++;
freqMap.computeIfAbsent(node.freq, k -> new DoubleLinkedList()).
addFirst(node);
node.value = value;
} else {
// 新增
if(kvMap.size() == capacity) {
Node last = freqMap.get(minFreq).removeLast();
kvMap.remove(last.key);
}
Node node = new Node(key, value, 1);
kvMap.put(key, node);
minFreq = 1;
freqMap.computeIfAbsent(node.freq, k -> new DoubleLinkedList()).addFirst(node);
}
}
}
/**
* Your LFUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LFUCache obj = new LFUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/3. 随机数
3.1 线性同余发生器
- 公式:nextSeed = (seed * a + c) % m
- 32位随机数生成器
- 乘法会超过int范围导致随机性被破坏
package com.itheima.algorithms.leetcode;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/*
线性同余发生器
*/
public class MyRandom {
private final int a;
private final int c;
private final int m;
private int seed;
public MyRandom(int a, int c, int m, int seed) {
this.a = a;
this.c = c;
this.m = m;
this.seed = seed;
}
public int nextInt() {
return seed = (a * seed + c) % m;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRandom r1 = new MyRandom(7, 0, 11, 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(IntStream.generate(r1::nextInt).limit(30).toArray()));
MyRandom r2 = new MyRandom(7, 0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(IntStream.generate(r2::nextInt).limit(30).toArray()));
}
}
3.2 Java版
- 0x5DEECE66DL * 0x5DEECE66DL 不会超过 long 的范围
- m决定只取48位随机数
- 对于nextInt,只取48位随机数的高32位
package com.itheima.algorithms.leetcode;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class MyRandom2 {
private static final long a = 0x5DEECE66DL;
private static final long c = 0xBL;
private static final long m = 1L << 48;
private long seed;
public MyRandom2(long seed) {
this.seed = (seed ^ a) & (m - 1);
}
public int nextInt() {
seed = (a * seed + c) & (m - 1);
return ((int) (seed >>> 16));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random r1 = new Random(1);
MyRandom2 r2 = new MyRandom2(1);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(IntStream.generate(r1::nextInt).limit(10).toArray()));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(IntStream.generate(r2::nextInt).limit(10).toArray()));
}
}
4. 跳表
4.1 randomLevel
设计一个方法调用若干次,每次返回 1~max 的数字,从 1 开始,返回数字的比例减半,例如 max = 4,让大概
-
50% 的几率返回 1
-
25% 的几率返回 2
-
12.5% 的几率返回 3
-
12.5% 的几率返回 4
package com.itheima.algorithms.leetcode;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/*
跳表
*/
public class SkipList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int level = randomLevel(4);
map.compute(level, (k, v) -> v == null ? 1 : v + 1);
}
System.out.println(map.entrySet().stream().collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Map.Entry::getKey,
e -> String.format("%d%%", e.getValue() * 100 / 1000)
)
));
}
/*
设计一个方法,方法会随机返回 1 ~ max的数字
从1开始,数字的几率逐级减半,例如max = 4,让大概
- 50% 的几率返回1
- 25% 的几率返回2
- 12.5% 的几率返回3
- 12.5% 的几率返回4
*/
static Random r = new Random();
static int randomLevel(int max) {
// return r.nextBoolean() ? 1 : r.nextBoolean() ? 2 : r.nextBoolean() ? 3 : 4;
int x = 1;
while(x < max) {
if(r.nextBoolean()) {
return x;
}
x++;
}
return x;
}
}
4.2 跳表

下楼梯规则:
- 若next指针为null,或者next指向的节点值 >= 目标,向下找
- 若next指针不为null,且next指向的节点值 < 目标,向右找
节点的【高度】
- 高度并不需要额外属性来记录,而是由之前节点next == 本节点的个数来决定,或是本节点next数组长度
- 本实现选择了第一种方式来决定高度,本节点的next数组长度统一为MAX
4.3 设计跳表
不使用任何库函数,设计一个 跳表 。
跳表 是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90] ,然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作:
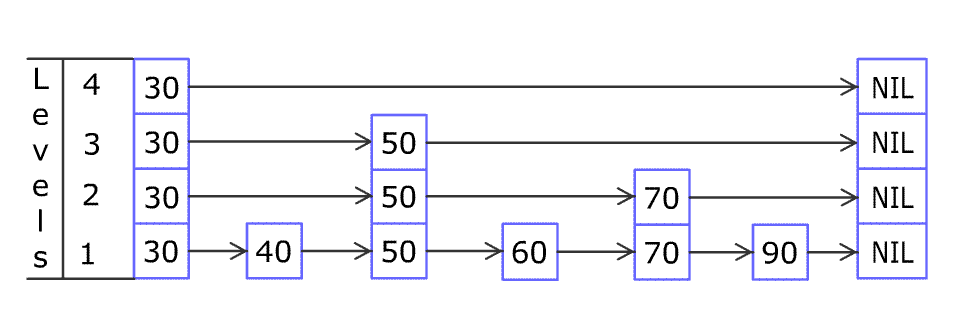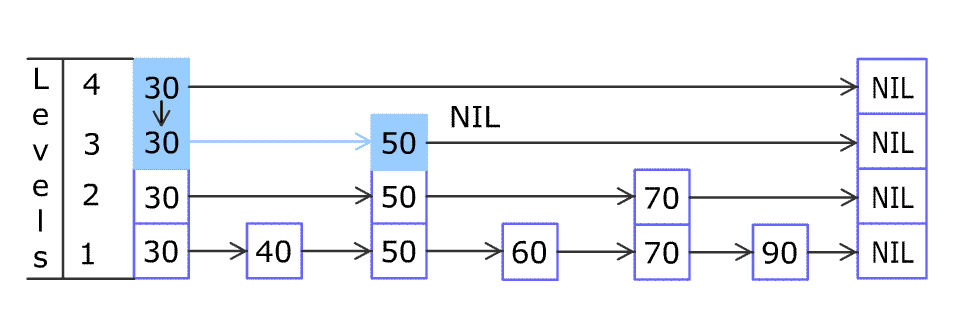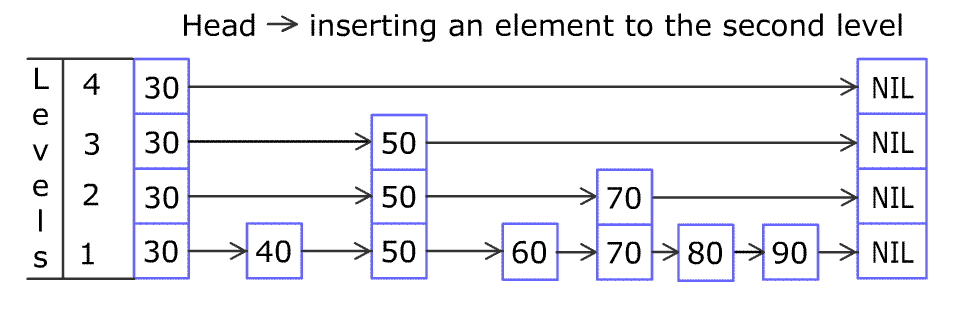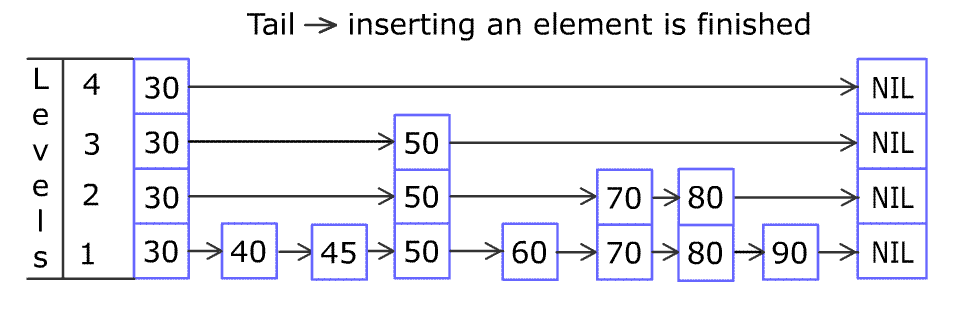
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
了解更多 : 跳表 - OI Wiki
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
bool search(int target): 返回target是否存在于跳表中。void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果num不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个num,删除其中任意一个即可。
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
示例 1:
输入 ["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"] [[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]] 输出 [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false] 解释 Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中 skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
提示:
0 <= num, target <= 2 * 10^4- 调用
search,add,erase操作次数不大于5 * 10^4
class Skiplist {
static Random r = new Random();
static int randomLevel(int max) {
int x = 1;
while (x < max) {
if (r.nextBoolean()) {
return x;
}
x++;
}
return x;
}
private static final int MAX = 16; // redis 32 java 62
private final Node head = new Node(-1);
static class Node {
int val; // 值
Node[] next = new Node[MAX]; // next指针数组
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node(" + val + ")";
}
}
public Skiplist() {
}
public Node[] find(int target) {
Node[] path = new Node[MAX];
Node curr = head;
for (int level = MAX - 1; level >= 0; level--) { // 从下向下找
while (curr.next[level] != null && curr.next[level].val < target) { // 向右找
curr = curr.next[level];
}
path[level] = curr;
}
return path;
}
public boolean search(int target) {
Node[] path = find(target);
Node node = path[0].next[0];
return node != null && node.val == target;
}
public void add(int num) {
// 1. 确定添加位置
Node[] path = find(num);
// 2. 创建新节点随机高度
Node node = new Node(num);
int level = randomLevel(MAX);
// 3. 修改路径节点next指针,以及新结点next指针
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) {
node.next[i] = path[i].next[i];
path[i].next[i] = node;
}
}
public boolean erase(int num) {
// 1. 确定删除位置
Node[] path = find(num);
Node node = path[0].next[0];
if (node == null || node.val != num) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
if (path[i].next[i] != node) {
break;
}
path[i].next[i] = node.next[i];
}
return true;
}
}5. 最小栈
设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack()初始化堆栈对象。void push(int val)将元素val推入堆栈。void pop()删除堆栈顶部的元素。int top()获取堆栈顶部的元素。int getMin()获取堆栈中的最小元素。
示例 1:
输入: ["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"] [[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]] 输出: [null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2] 解释: MinStack minStack = new MinStack(); minStack.push(-2); minStack.push(0); minStack.push(-3); minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -3. minStack.pop(); minStack.top(); --> 返回 0. minStack.getMin(); --> 返回 -2.
提示:
-2^31 <= val <= 2^31 - 1pop、top和getMin操作总是在 非空栈 上调用push,pop,top, andgetMin最多被调用3 * 10^4次
解法一:
class MinStack {
LinkedList<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> min = new LinkedList<>();
public MinStack() {
min.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
min.push(Math.min(val, min.peek()));
}
public void pop() {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
stack.pop();
min.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return min.peek();
}
}6. TinyURL的加密与解密
TinyURL 是一种 URL 简化服务, 比如:当你输入一个 URL https://leetcode.com/problems/design-tinyurl 时,它将返回一个简化的URL http://tinyurl.com/4e9iAk 。请你设计一个类来加密与解密 TinyURL 。
加密和解密算法如何设计和运作是没有限制的,你只需要保证一个 URL 可以被加密成一个 TinyURL ,并且这个 TinyURL 可以用解密方法恢复成原本的 URL 。
实现 Solution 类:
Solution()初始化 TinyURL 系统对象。String encode(String longUrl)返回longUrl对应的 TinyURL 。String decode(String shortUrl)返回shortUrl原本的 URL 。题目数据保证给定的shortUrl是由同一个系统对象加密的。
示例:
输入:url = "https://leetcode.com/problems/design-tinyurl" 输出:"https://leetcode.com/problems/design-tinyurl" 解释: Solution obj = new Solution(); string tiny = obj.encode(url); // 返回加密后得到的 TinyURL 。 string ans = obj.decode(tiny); // 返回解密后得到的原本的 URL 。
提示:
1 <= url.length <= 10^4- 题目数据保证
url是一个有效的 URL
解法一:
要让【长】【短】网址一一对应 1. 用【随机数】作为短网址标识 2. 用【hash码】作为短网址标识 3. 用【递增数】作为短网址标识
public class TinyURLLeetcode535 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*CodecSequence codec = new CodecSequence();
String encoded = codec.encode("https://leetcode.cn/problems/1");
System.out.println(encoded);
encoded = codec.encode("https://leetcode.cn/problems/2");
System.out.println(encoded);*/
// for (int i = 0; i <= 62; i++) {
// System.out.println(i + "\t" + CodecSequence.toBase62(i));
// }
System.out.println(CodecSequence.toBase62(237849728));
}
/*
要让【长】【短】网址一一对应
1. 用【随机数】作为短网址标识
2. 用【hash码】作为短网址标识
3. 用【递增数】作为短网址标识
1) 多线程下可以使用吗?
2) 分布式下可以使用吗?
3) 4e9iAk 是怎么生成的?
a-z 0-9 A-Z 62进制的数字
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
十进制 => 十六进制
31 1f
31 % 16 = 15
31 / 16 = 1
1 % 16 = 1
1 / 16 = 0
长网址: https://leetcode.cn/problems/encode-and-decode-tinyurl/description/
对应的短网址: http://tinyurl.com/4e9iAk
*/
static class CodecSequence {
private static final char[] toBase62 = {
'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M',
'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z',
'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm',
'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'
};
public static String toBase62(int number) {
if (number == 0) {
return String.valueOf(toBase62[0]);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (number > 0) {
int r = number % 62;
sb.append(toBase62[r]);
number = number / 62;
}
return sb.toString();
}
private final Map<String, String> longToShort = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, String> shortToLong = new HashMap<>();
private static final String SHORT_PREFIX = "http://tinyurl.com/";
private static int id = 1;
public String encode(String longUrl) {
String shortUrl = longToShort.get(longUrl);
if (shortUrl != null) {
return shortUrl;
}
// 生成短网址
shortUrl = SHORT_PREFIX + id;
longToShort.put(longUrl, shortUrl);
shortToLong.put(shortUrl, longUrl);
id++;
return shortUrl;
}
public String decode(String shortUrl) {
return shortToLong.get(shortUrl);
}
}
static class CodecHashCode {
private final Map<String, String> longToShort = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, String> shortToLong = new HashMap<>();
private static final String SHORT_PREFIX = "http://tinyurl.com/";
public String encode(String longUrl) {
String shortUrl = longToShort.get(longUrl);
if (shortUrl != null) {
return shortUrl;
}
// 生成短网址
int id = longUrl.hashCode(); // int
while (true) {
shortUrl = SHORT_PREFIX + id;
if (!shortToLong.containsKey(shortUrl)) {
longToShort.put(longUrl, shortUrl);
shortToLong.put(shortUrl, longUrl);
break;
}
id++;
}
return shortUrl;
}
public String decode(String shortUrl) {
return shortToLong.get(shortUrl);
}
}
static class CodecRandom {
private final Map<String, String> longToShort = new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, String> shortToLong = new HashMap<>();
private static final String SHORT_PREFIX = "http://tinyurl.com/";
public String encode(String longUrl) {
String shortUrl = longToShort.get(longUrl);
if (shortUrl != null) {
return shortUrl;
}
// 生成短网址
while (true) {
int id = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt();// 1
shortUrl = SHORT_PREFIX + id;
if (!shortToLong.containsKey(shortUrl)) {
longToShort.put(longUrl, shortUrl);
shortToLong.put(shortUrl, longUrl);
break;
}
}
return shortUrl;
}
public String decode(String shortUrl) {
return shortToLong.get(shortUrl);
}
}
}7. 设计Twitter
设计一个简化版的推特(Twitter),可以让用户实现发送推文,关注/取消关注其他用户,能够看见关注人(包括自己)的最近 10 条推文。
实现 Twitter 类:
Twitter()初始化简易版推特对象void postTweet(int userId, int tweetId)根据给定的tweetId和userId创建一条新推文。每次调用此函数都会使用一个不同的tweetId。List<Integer> getNewsFeed(int userId)检索当前用户新闻推送中最近10条推文的 ID 。新闻推送中的每一项都必须是由用户关注的人或者是用户自己发布的推文。推文必须 按照时间顺序由最近到最远排序 。void follow(int followerId, int followeeId)ID 为followerId的用户开始关注 ID 为followeeId的用户。void unfollow(int followerId, int followeeId)ID 为followerId的用户不再关注 ID 为followeeId的用户。
示例:
输入 ["Twitter", "postTweet", "getNewsFeed", "follow", "postTweet", "getNewsFeed", "unfollow", "getNewsFeed"] [[], [1, 5], [1], [1, 2], [2, 6], [1], [1, 2], [1]] 输出 [null, null, [5], null, null, [6, 5], null, [5]] 解释 Twitter twitter = new Twitter(); twitter.postTweet(1, 5); // 用户 1 发送了一条新推文 (用户 id = 1, 推文 id = 5) twitter.getNewsFeed(1); // 用户 1 的获取推文应当返回一个列表,其中包含一个 id 为 5 的推文 twitter.follow(1, 2); // 用户 1 关注了用户 2 twitter.postTweet(2, 6); // 用户 2 发送了一个新推文 (推文 id = 6) twitter.getNewsFeed(1); // 用户 1 的获取推文应当返回一个列表,其中包含两个推文,id 分别为 -> [6, 5] 。推文 id 6 应当在推文 id 5 之前,因为它是在 5 之后发送的 twitter.unfollow(1, 2); // 用户 1 取消关注了用户 2 twitter.getNewsFeed(1); // 用户 1 获取推文应当返回一个列表,其中包含一个 id 为 5 的推文。因为用户 1 已经不再关注用户 2
提示:
1 <= userId, followerId, followeeId <= 5000 <= tweetId <= 10^4- 所有推特的 ID 都互不相同
postTweet、getNewsFeed、follow和unfollow方法最多调用3 * 10^4次

解法一:
class Twitter {
// 文章类
static class Tweet {
int id;
int time;
Tweet next;
public Tweet(int id, int time, Tweet next) {
this.id = id;
this.time = time;
this.next = next;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getTime() {
return time;
}
}
// 用户类
static class User {
int id;
Set<Integer> followees = new HashSet<>();
Tweet head = new Tweet(-1, -1, null);
public User(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
private final Map<Integer, User> userMap = new HashMap<>();
private static int time;
public Twitter() {
}
// 发布文章
public void postTweet(int userId, int tweetId) {
User user = userMap.computeIfAbsent(userId, User::new);
user.head.next = new Tweet(tweetId, time++, user.head.next);
}
// 获取最新10篇文章(包括自己和关注者)
public List<Integer> getNewsFeed(int userId) {
// 思路:合并k个有序链表
User user = userMap.get(userId);
if(user == null) {
return List.of();
}
PriorityQueue<Tweet> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(Tweet::getTime).reversed());
if(user.head.next != null) {
queue.offer(user.head.next);
}
for (Integer id : user.followees) {
User followee = userMap.get(id);
if(followee.head.next != null) {
queue.offer(followee.head.next);
}
}
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty() && count < 10) {
Tweet max = queue.poll();
res.add(max.id);
if(max.next != null) {
queue.offer(max.next);
}
count++;
}
return res;
}
// 新增关注
public void follow(int followerId, int followeeId) {
User follower = userMap.computeIfAbsent(followerId, User::new);
User followee = userMap.computeIfAbsent(followeeId, User::new);
follower.followees.add(followee.id);
}
// 取消关注
public void unfollow(int followerId, int followeeId) {
User user = userMap.get(followerId);
if(user != null) {
user.followees.remove(followeeId);
}
}
}
/**
* Your Twitter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Twitter obj = new Twitter();
* obj.postTweet(userId,tweetId);
* List<Integer> param_2 = obj.getNewsFeed(userId);
* obj.follow(followerId,followeeId);
* obj.unfollow(followerId,followeeId);
*/