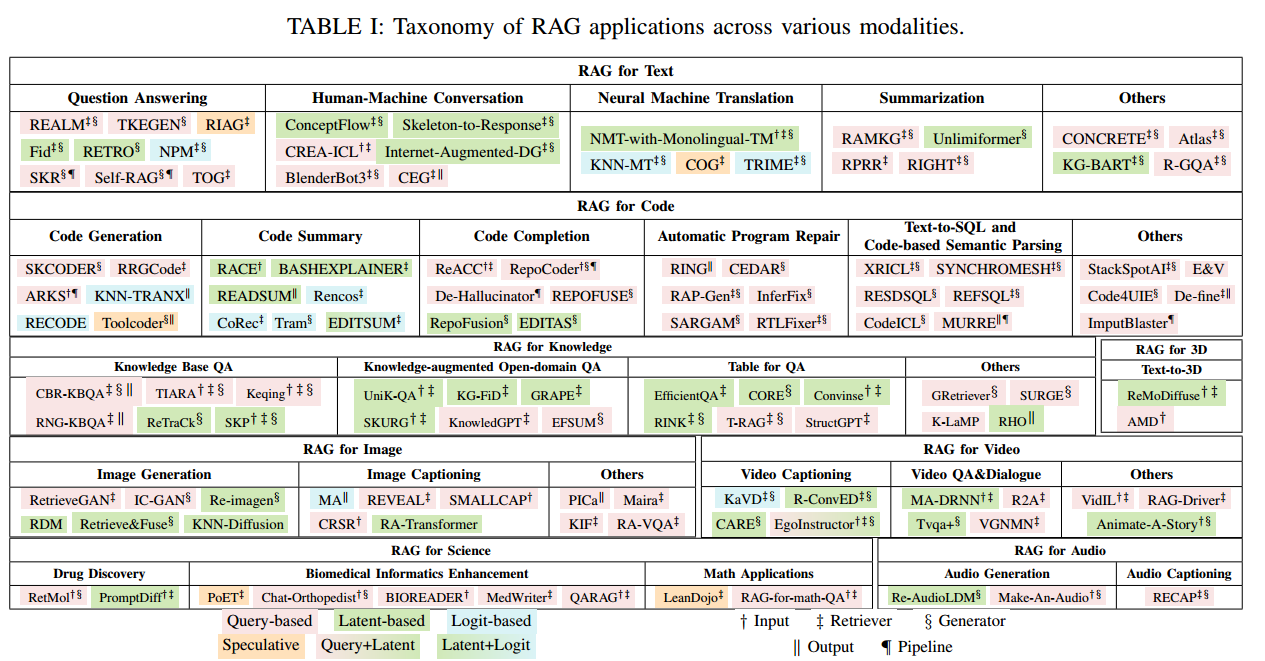
LangChain实战:利用LangChain SQL Agent和GPT进行文档分析和交互

我最近接触到一个非常有趣的挑战,涉及到人工智能数字化大量文件的能力,并使用户可以在这些文件上提出复杂的与数据相关的问题,比如:
- 数据检索问题: 涉及从数据库中获取特定数据点或数据集,例如“电子产品类别中有多少产品?” 或 “2021年第四季度总销售额是多少?”
- 汇总查询: 需要对数据进行总结的问题,如计算平均值、求和、计数等,例如“所有已上架产品的平均价格是多少?”或“每个地区客户的总人数是多少?”
- 数据关系探索: 探究不同数据实体之间关系的问题,比如"哪些客户购买了三种以上不同的产品?" 或 “列出上个月没有交付任何产品的所有供应商。”
- 条件查询: 涉及条件或筛选器,比如“列出2022年发生在超过500美元交易额以上的所有交易” 或 “展示所有缺货商品。”
这些不是你可以仅通过使用RAG来解决的典型问题。相反,我们将利用LangChain的SQLAgent从人类文本中生成复杂的数据库查询。
文档应包含具有大量规格说明的数据,以及更多流畅、自然语言描述等。
我们将执行以下步骤,最终能够提出关于大量文档的复杂问题:
- 阅读所有
PDF文档。 - 使用
GPT分析每个文档的内容,将其解析为JSON对象。 - 将这些对象写入
SQLite获取其他数据库中,分布在多个表中。 - 使用
LangChain SQL代理程序通过自动生成SQL语句来提出问题。
备注:本文涵盖了涉及人工智能和数据处理的概念。为了获得最大价值,您应具备对Python编程能力、GPT模型接入能力、嵌入式技术了解、向量搜索和SQL数据库的基础理解以及使用能力。
使用 Python、LangChain 和 GPT 分析文档
我们将使用Python和LangChain来读取和分析PDF文档。我使用的 Python 为 Python 3.11。
首先,我们安装环境所需要的依赖包:
%pip install pypdf
%pip install langchain
%pip install langchain_openai
%pip install sqlite3
# 导入 pdf 阅读器
from pypdf import PdfReader
# 导入langchain 的消息类型
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
# 导入 openAI
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
现在,让我们来深入研究 PDF 解析。我们的目标是使用 visitor_text 提取有意义的内容,同时忽略不太有用的信息,例如空行、页眉和页脚。
document_content = None
def visitor_body(text, cm, tm, fontDict, fontSize):
y = tm[5]
if text and 35 < y < 770:
page_contents.append(text)
with open(f'./documents/ZMP_55852_XBO_1000_W_HS_OFR.pdf', 'rb') as file:
pdf_reader = PdfReader(file)
page_contents = []
for page in pdf_reader.pages:
# 提取PDF每页文本的内容
page.extract_text(visitor_text=visitor_body)
document_content = "\n".join(page_contents)
print(document_content)
让我们查看解析后的文档:
Product family benefits
_
Short arc with very high luminance for brighter screen illumination
_
Constant color temperature of 6,000 K throughout the entire lamp lifetime
_
Easy to maintain
_
High arc stability
_
Instant light on screen thanks to hot restart function
_
Wide dimming range
Product family features
_
Color temperature: approx. 6,000 K (Daylight)
_
Wattage: 450…10,000 W
_
Very good color rendering index: Ra >
Product datasheet
XBO 1000 W/HS OFR
XBO for cinema projection | Xenon short-arc lamps 450…10,000 W
[..]
Packaging unit
(Pieces/Unit)
Dimensions (length
x width x height)
Volume
Gross weight
4008321082114
XBO 1000 W/HS OFR
Shipping carton box
1
410 mm x 184 mm x
180 mm
13.58 dm³
819.00 g
[..]
在解析的内容中,显而易见地发现它缺乏结构 — 表格不连贯,相关实体分散。
我们使用 GPT 重新帮我们整理文档的内容:
- 我们将指示GPT将解析的数据格式化为一个结构化JSON对象。
- 通过提供一份解析数据的示例,以及在前面加上<<<的提示,我们可以引导
GPT理解并整理文档。 - 利用
OpenAI Chat API,我们将请求GPT从一组新的解析产品数据中生成一个JSON对象。
让我们构建一条深思熟虑的系统消息来启动这个过程。我们将以清晰的指令为GPT开头,接着呈现解析后的数据作为背景,并夹杂目标性提示来完善输出:
认真观察我们如何整合各种提示来塑造我们所需的精确JSON输出。
你会分析产品描述,将其导出为 JSON 格式。我会向您展示一个产品数据表,并用 <<< 描述各个 JSON 对象和属性。然后您可以从另一个产品数据表中创建一个 JSON 对象。
>>> Example product:
Product family benefits <<< benefits (string[])
_
Short arc with very high luminance for brighter screen illumination <<< benefits.[*]
_
Constant color temperature of 6,000 K throughout the entire lamp lifetime <<< benefits.[*]
[..]
_
Wide dimming range <<< benefits.[*]
Product family features <<< product_family (object)
_
Color temperature: approx. 6,000 K (Daylight) <<< product_family.temperature = 6000
_
Wattage: 450…10,000 W <<< product_family.watts_min = 450, product_family.watts_max = 10000
_
Very good color rendering index: Ra >
Product datasheet
XBO 1000 W/HS OFR <<< name
XBO for cinema projection | Xenon short-arc lamps 450…10,000 W <<< description
[..]
Technical data
Electrical data <<< technical_data (object)
Nominal current
50 A <<< technical_data.nominal_current = 50.00
Current control range
30…55 A <<< technical_data.control_range = 30, technical_data.control_range = 55
Nominal wattage
1000.00 W <<< technical_data.nominal_wattage = 1000.00
Nominal voltage
19.0 V <<< technical_data.nominal_voltage = 19.0
Dimensions & weight <<< dimensions (object)
[..]
Safe Use Instruction
The identification of the Candidate List substance is <<< environmental_information.safe_use (beginning of string)
sufficient to allow safe use of the article. <<< environmental_information.safe_use (end of string)
Declaration No. in SCIP database
22b5c075-11fc-41b0-ad60-dec034d8f30c <<< environmental_information.scip_declaration_number (single string!)
Country specific information
[..]
Shipping carton box
1
410 mm x 184 mm x <<< packaging_unity.length = 410, packaging_unit.width = 184
180 mm <<< packaging_unit.height = 180
[..]
"""
我的 prompt 是不同方法的集合:
- <<< benefits(字符串[])— 这里开始了一个字符串列表。
- <<< benefits.[*] — 这行属于字符串列表。
- <<< product_family(对象)— 这里开始了一个对象。
- <<< product_family.temperature = 6000 — 这行是对象的整数属性
- <<< product_family.watts_min = 450,product_family.watts_max = 1000 — 这一行是两个整数属性(例如,当有类似功率:450…10,000 W 的语句时)
在这里你可以完全发挥创意,尝试任何对你有意义的东西。而且需要多次调试 prompt 的内容以适应你的应用场景。
注意: 这里 prompt 最好还是英文的好, 最好不要中文和英文夹着来。
请将以下文本翻译成中文:
要翻译的文字:
- <<< 将其翻译成另一种语言。
- <<< 提供摘要或提供项目符号下的整个句子。
- <<< 将数据拆分为名字和姓名。
测试 prompt
现在我们是时候测试一下 GPT 了,看看它是否能够完美地将我们混乱的 PDF 文本转换成一个整洁的 JSON 对象。
GPT-3.5-Turbo的0125版本在以JSON等请求格式响应时具有更高的准确性,这非常适合我们的情况! 我们已经准备好了system_message,并将其与document_content配对作为输入:
# 初始化 OpenAI Model
chat = ChatOpenAI(model_name='gpt-3.5-turbo-0125', temperature=0)
def convert_to_json(document_content):
messages = [
# 这里是系统的角色设定
SystemMessage(
content=system_message
),
# 这里是我们的输入内容
HumanMessage(
content=document_content
)
]
# 构建 langchain 的链式
answer = chat.invoke(messages)
return answer.content
json = convert_to_json(document_content)
# json 就是 OpenAI Model 返回的内容:
print(json)
一切就绪,我们看一下我们得到的JSON输出了:
{
"name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"description": "XBO for cinema projection | Xenon short-arc lamps 450…10,000 W",
"applications": [
"Classic 35 mm film projection",
"Digital film and video projection",
"Architectural and effect light (“Light Finger”)",
"Sunlight simulation"
],
"technical_data": {
"nominal_current": 50.00,
"control_range_min": 30,
"control_range_max": 55,
"nominal_wattage": 1000.00,
"nominal_voltage": 19.0
},
"dimensions": {
"diameter": 40.0,
"length": 235.0,
"length_base": 205.00,
"light_center_length": 95.0,
"electrode_gap": 3.6,
"weight": 255.00
},
"operating_conditions": {
"max_temp": 230,
"lifespan": 2000,
"service_lifetime": 3000
},
"additional_data": {
"base_anode": "SFa27-11",
"base_cathode": "SFcX27-8",
"product_remark": "OFR = Ozone-free version/H = Suitable for horizontal burning position/S = Short"
},
"capabilities": {
"cooling": "Forced",
"burning_position": "s20/p20"
},
"environmental_information": {
"declaration_date": "10-03-2023",
"primary_product_number": "4008321082114 | 4050300933566",
"candidate_list_substance": "Lead",
"cas_number": "7439-92-1",
"safe_use": "The identification of the Candidate List substance is sufficient to allow safe use of the article.",
"scip_declaration_number": "22b5c075-11fc-41b0-ad60-dec034d8f30c"
},
"logistical_data": {
"product_code": "4008321082114",
"product_name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"packaging_unit": {
"product_code": "4008321082114",
"product_name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"length": 410,
"width": 184,
"height": 180,
"volume": 13.58,
"weight": 819.00
}
}
}
从结果看还是相当不错的。它找到的对象和属性是准确无误。
然而,有一个明显BUG:GPT忽略了一些关键元素,比如利益和产品系列
那么,我们的如何做呢?转向使用 GPT-4 看看效果,它提供增强功能但成本更高且响应时间较慢,还是调整策略以包括函数调用来优化资源同时保持效率?
通过提供一个 JSON Schema 来改善 prompt
在使用 GPT 时,function call 是我最喜欢的功能。它允许我们指定不仅 GPT 可执行的函数本身,还可以指定我们自己的函数所需的 JSON 参数。
下面是一个 function call 的示例:
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather in a given location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The city and state, e.g. beijing",
},
"unit": {"type": "string", "enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"]},
},
"required": ["location"],
},
}
最新的模型gpt-3.5-turbo-0125和gpt-4-turbo-preview经过训练,能够检测何时启动功能调用,并生成与指定函数签名相符的JSON输出.
为了充分利用这一点,我们优化我们的提示,以包含我们期望返回的 JSON 模式。
You analyze product descriptions to export them into a JSON format. I will present you with a product data sheet and describe the individual JSON objects and properties with <<<. You then create a JSON object from another product data sheet.
>>> Example product:
Product family benefits <<< benefits (string[])
[..]
-----
Provide your JSON in the following schema:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"description": {
"type": "string"
},
"applications": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"benefits": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"product_family": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"temperature": {
"type": "number"
},
"watts_min": {
"type": "number"
},
"watts_max": {
"type": "number"
}
}
},
"technical_data": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"nominal_current": {
"type": "number"
},
"control_range_min": {
"type": "number"
},
"control_range_max": {
"type": "number"
},
"nominal_wattage": {
"type": "number"
},
"nominal_voltage": {
"type": "number"
}
}
},
"dimensions": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"diameter": {
"type": "number"
},
"length": {
"type": "number"
},
"length_base": {
"type": "number"
},
"light_center_length": {
"type": "number"
},
"electrode_gap": {
"type": "number"
},
"weight": {
"type": "number"
}
}
},
"operating_conditions": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"max_temp": {
"type": "string"
},
"lifespan": {
"type": "number"
},
"service_lifetime": {
"type": "number"
}
}
},
"logistical_data": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_code": {
"type": "string"
},
"product_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"packaging_unit": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"product_code": {
"type": "string"
},
"product_name": {
"type": "string"
},
"length": {
"type": "number"
},
"width": {
"type": "number"
},
"height": {
"type": "number"
},
"volume": {
"type": "number"
},
"weight": {
"type": "number"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
调整我们的方法后,让我们来看一下新的输出:
{
"name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"description": "XBO for cinema projection | Xenon short-arc lamps 450…10,000 W",
"applications": [
"Classic 35 mm film projection",
"Digital film and video projection",
"Architectural and effect light (“Light Finger”)",
"Sunlight simulation"
],
"benefits": [
"Short arc with very high luminance for brighter screen illumination",
"Constant color temperature of 6,000 K throughout the entire lamp lifetime",
"Easy to maintain",
"High arc stability",
"Instant light on screen thanks to hot restart function",
"Wide dimming range"
],
"product_family": {
"temperature": 6000,
"watts_min": 450,
"watts_max": 10000
},
"technical_data": {
"nominal_current": 50,
"control_range_min": 30,
"control_range_max": 55,
"nominal_wattage": 1000.00,
"nominal_voltage": 19.0
},
"dimensions": {
"diameter": 40.0,
"length": 235.0,
"length_base": 205.00,
"light_center_length": 95.0,
"electrode_gap": 3.6,
"weight": 255.00
},
"operating_conditions": {
"max_temp": "230 °C",
"lifespan": 2000,
"service_lifetime": 3000
},
"logistical_data": {
"product_code": "4008321082114",
"product_name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"packaging_unit": {
"product_code": "4008321082114",
"product_name": "XBO 1000 W/HS OFR",
"length": 410,
"width": 184,
"height": 180,
"volume": 13.58,
"weight": 819.00
}
}
}
这个结果很美丽哦😯。
输出完整地映射了名称和描述,将应用分类为字符串列表,并使用最小值和最大值区分范围 — 所有这些都与我们的 JSON 模式期望完美对齐。
探索 LangChain 的QA能力
虽然幕墙我们主要关注 PDF 分析和 SQL Agent,但如果你已经想继续探索的话,可以尝试使用 LangChain Q&A 和 RAG,尤其是因为它与我们更广泛的目标相契合。
我将提供一些代码和输出,这样我们就能迅速转入真正的内容领域了。
让我们先收集更多产品数据. 下载一些额外随机的PDF文档,并将它们存储在指定的文档文件夹中。接下来,我们需要添加一些代码:
import os
# 导入 langchain 的问答链
from langchain.chains.question_answering import load_qa_chain
# 导入 OpenAI 包
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# 导入向量数据库 FAISS
from langchain.vectorstores import FAISS
下一步涉及阅读和转换所有已下载的PDF文档,然后将它们的JSON输出汇总到一个数组中。
# 从文件夹中获取所有的 pdf 文件
pdf_files = [f for f in os.listdir('./documents') if f.endswith('.pdf')]
json_documents = []
for pdf_file in pdf_files:
with open(f'./documents/{pdf_file}', 'rb') as file:
# 读取文件的内容
pdf_reader = PdfReader(file)
page_contents = []
for page in pdf_reader.pages:
page.extract_text(visitor_text=visitor_body)
json = convert_to_json("\n".join(page_contents))
json_documents.append(json)
此外,我们将整合FAISS相似性搜索库,并将其与我们的文档内容和嵌入模型对齐,以便实现内容向量化。
FAISS是由 Facebook 于2017年开发的,作为 Azure 人工智能搜索服务中 Azure 机器学习的开源替代方案——在比较嵌入向量方面表现相当不错。
# 加载向量化模型
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-3-large")
# 将上面的文本向量化到向量数据库中
docsearch = FAISS.from_texts(documents, embeddings)
提出问题:
chain = load_qa_chain(chat, chain_type="stuff", verbose=True)
# 输入我们的问题
query = "我可以将XBO 1000 W/HS OFR放入长350毫米,宽200毫米的盒子中吗?"
# 向量相似性搜索
docs = docsearch.similarity_search(query)
# 将查到相似的内容做为LLM的内容
chain.run(input_documents=docs, question=query)
观察以最相关的文件内容为基础的回复。
不能,XBO 1000 W/HS OFR 的尺寸为长410毫米,宽184毫米,比盒子的尺寸大,后者为长350毫米,宽200毫米。
目前进展还是不错的。 现在让我们深入研究更高级的应用程序。
SQLight 和 LangChain SQL 代理
RAG 是一个已建立的技术,使用户能够与他们自己的数据进行交流。对于需要一些内部、无结构信息的情况来说,它非常强大。
虽然 RAG 在导航无结构信息方面表现出色,但如何询问与数据相关得多的信息呢? 比如,请给我所有至少有 4000 瓦特的产品。或者提供足够容纳所有产品的运输纸箱尺寸?
当涉及数据中心查询时,SQL 的精准性和结构就会发挥作用。
在SQLite数据库中管理我们的数据
为了管理我们的数据,需要在数据库中对其进行系统化处理。这里直观的步骤包括将数据结构化为SQLite中的关系表,以便执行一些更复杂的查询。
虽然不是强制性要求,但我建议添加以下备用步骤:定义映射我们 JSON 输出结构的类。
通过在数据库插入前集成这些,我们不仅简化了数据验证过程,还确保我们的数据符合预期格式。
如果解析后的 JSON 字典缺少未标记为可选项的必要属性,则可能有错误发生。
import json
from typing import Any, List, Optional
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
@dataclass
class ProductFamily:
watts_min: int
watts_max: int
temperature: Optional[int] = field(default=0)
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'ProductFamily':
_watts_min = int(obj.get("watts_min"))
_watts_max = int(obj.get("watts_max"))
_temperature = obj.get("temperature")
return ProductFamily(_watts_min, _watts_max, _temperature)
@dataclass
class Product:
name: str
description: str
benefits: List[str]
product_family: ProductFamily
@staticmethod
def from_dict(obj: Any) -> 'Product':
_name = str(obj.get("name"))
_description = str(obj.get("description"))
_benefits = obj.get("benefits")
_product_family = ProductFamily.from_dict(obj.get("product_family"))
return Product(_name, _description, _benefits, _product_family)
建立这些类之后,我们重新查看我们的PDF文档。
这一次我们将它们转换为JSON格式,并创建Product对象的实例。此外,我将所有处理过的文档移动到一个processed文件夹中。
import traceback
pdf_files = [f for f in os.listdir('./documents') if f.endswith('.pdf')]
products = []
for pdf_file in pdf_files:
json_content = None
try:
with open(f'./documents/{pdf_file}', 'rb') as file:
pdf_reader = PdfReader(file)
page_contents = []
for page in pdf_reader.pages:
page.extract_text(visitor_text=visitor_body)
document_content = "\n".join(page_contents)
json_content = convert_to_json(document_content)
json_data = json.loads(json_content)
product = Product.from_dict(json_data)
products.append(product)
except Exception as e:
print("{filename} has a problem: {e}".format(filename=pdf_file, e=e))
print(traceback.format_exc())
print(json_content)
else:
os.rename(f'./documents/{pdf_file}', f'./processed/{pdf_file}')
上面的代码太简单了,就不做注释了。
现在我们已经编写了一个强大的产品实例列表,准备插入数据库表中。
对于我们的目前的功能来说,SQLite数据库就足够了。我们会创建三张表来存放我们的数据集:
- 产品 — 产品的基本规格(名称,描述,长度)。
- 产品应用 — 与特定产品相关联的应用程序列表。
- 产品优势 — 与特定产品相关联的优势列表。
我们将执行以下步骤:
- 初始化数据库并创建表格。
- 为每个表格创建包含相关产品数据的元组。
- 执行数据插入过程。
启动数据库并创建表格:
import sqlite3
if(os.path.exists('./db') == False):
os.makedirs('./db')
db_file = './db/products.db'
db_connection = sqlite3.connect(db_file)
db_cursor = db_connection.cursor()
db_cursor.execute('''CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Product
(name TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
description TEXT,
temperature INTEGER,
watts_min INTEGER,
watts_max INTEGER,
dimension_diameter REAL,
dimension_length REAL,
dimension_weight REAL,
packaging_length INTEGER,
packaging_width INTEGER,
packaging_height INTEGER,
packaging_weight REAL) WITHOUT ROWID
''')
db_cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ProductApplication (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
product TEXT,
text TEXT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (product) REFERENCES Product(name)
)
''')
db_cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ProductBenefit (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
product TEXT,
text TEXT NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (product) REFERENCES Product(name)
)
''')
db_connection.commit()
继续创建元组:
products_sql_tuples = [(
p.name,
p.description,
p.product_family.temperature,
p.product_family.watts_min,
p.product_family.watts_max,
p.dimensions.diameter,
p.dimensions.length,
p.dimensions.weight,
p.logistical_data.packaging_unit.length,
p.logistical_data.packaging_unit.width,
p.logistical_data.packaging_unit.height,
p.logistical_data.packaging_unit.weight,) for p in products]
applications_sql_tuples = []
for product in products:
applications_sql_tuples.extend([(product.name, application) for application in product.applications])
benefits_sql_tuples = []
for product in products:
benefits_sql_tuples.extend([(product.name, benefit) for benefit in product.benefits])
最后插入数据:
db_cursor.executemany('''
REPLACE INTO Product (name, description, temperature, watts_min, watts_max, dimension_diameter, dimension_length, dimension_weight, packaging_length, packaging_width, packaging_height, packaging_weight)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
''', products_sql_tuples)
db_cursor.executemany('''
REPLACE INTO ProductApplication (product, text)
VALUES (?, ?)
''', applications_sql_tuples)
db_cursor.executemany('''
REPLACE INTO ProductBenefit (product, text)
VALUES (?, ?)
''', benefits_sql_tuples)
db_connection.commit()
不要忘记关闭光标和连接。
db_cursor.close()
db_connection.close()
让我们来查看一下我们的数据库表格。这里和那里有些字段是NULL,只是因为产品数据表上没有相应的信息。所以没关系。
但所有重要信息都已解析并成功转换。所以我对结果非常满意!

使用 LangChain SQL Agent 查询信息
向 LangChain SQL Agent 提问!
LangChain的SQL代理提供了一种动态与SQL数据库进行交互的方式。它擅长解释表结构并根据用户提示生成SQL查询。
使用SQL代理的主要优势包括:
- 它可以根据数据库模式或内容(如描述特定表)来回答问题。
- 它能通过运行生成的查询、捕获溯源并正确地再生来从错误中恢复。
- 它可以根据需要多次查询数据库以回答用户的问题。
- 只检索相关表的模式,从而节省token。
正如你所期待的那样,LangChain的代码非常清晰,即使在执行复杂操作时也是如此。
对于使用SQL Agent进行查询,这次我想要利用GPT-4。与需要导入大量文档并进行广泛处理相比,数据量较小且可控。
from langchain_community.utilities import SQLDatabase
from langchain.chains import create_sql_query_chain
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_community.agent_toolkits import create_sql_agent
db = SQLDatabase.from_uri("sqlite:///db/products.db")
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4-0125-preview", temperature=0)
agent_executor = create_sql_agent(llm, db=db, agent_type="openai-tools", verbose=True)
一切就绪。我们提出一些比较简单的问题,比如我们目前有多少种产品。
prompt = "How many products do you have?"
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": prompt})
它给出了一个完全正确的答案,包括 SQL 语句:
Invoking:
sql_db_querywithSELECT COUNT(*) AS NumberOfProducts FROM Product[(20,)]There are 20 products in the database .
虽然看起来很简单,SQL代理的能力不仅在于制定SQL查询,还包括识别现有的表格.
现在,让我们增加一些复杂性。我想找到一个适用于所有产品的包装尺寸。
prompt = "I need to find a packaging size that works for all products. What size would that package have?"
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": prompt})
To accommodate all products, the packaging size would need to have the following dimensions:
Length: 605 mm
Width: 420 mm
Height: 900 mm
Weight: 7177.0 grams
This size would work for all products in the database.
这是 SQL 代理设计的查询,用于检索所需信息:
sql_db_query
withSELECT MAX(packaging_length) AS max_length, MAX(packaging_width) AS max_width, MAX(packaging_height) AS max_height, MAX(packaging_weight) AS max_weight FROM Product
现在我们想得到更多信息!让我们询问具有最高可能温度及其用途的产品。
这些信息存储在另一个表中:
prompt = "Provide the product with the highest possible temperature and it's applications."
result = agent_executor.invoke({"input": prompt})
完美,“SharXS 1500W Brilliant” 绝对是拥有最高可能温度的产品:

SQL Agent甚至聪明地找到了ProductApplication表上的引用:

总结:
GPT版本0125 可以完美地提供 JSON 格式的数据。OpenAI 致力于增强函数调用,并确保它符合用于创建可供计算机读取格式的标准用例。
如果设计目标正是针对这种情况,并且仅供企业内部员工使用,那么我会使用 SQL Agent 来处理企业数据库!
但是我觉得允许LLM模型自主执行查询依然风险太大了。

大模型&AI产品经理如何学习
求大家的点赞和收藏,我花2万买的大模型学习资料免费共享给你们,来看看有哪些东西。
1.学习路线图

第一阶段: 从大模型系统设计入手,讲解大模型的主要方法;
第二阶段: 在通过大模型提示词工程从Prompts角度入手更好发挥模型的作用;
第三阶段: 大模型平台应用开发借助阿里云PAI平台构建电商领域虚拟试衣系统;
第四阶段: 大模型知识库应用开发以LangChain框架为例,构建物流行业咨询智能问答系统;
第五阶段: 大模型微调开发借助以大健康、新零售、新媒体领域构建适合当前领域大模型;
第六阶段: 以SD多模态大模型为主,搭建了文生图小程序案例;
第七阶段: 以大模型平台应用与开发为主,通过星火大模型,文心大模型等成熟大模型构建大模型行业应用。
2.视频教程
网上虽然也有很多的学习资源,但基本上都残缺不全的,这是我自己整理的大模型视频教程,上面路线图的每一个知识点,我都有配套的视频讲解。


(都打包成一块的了,不能一一展开,总共300多集)
因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,需要点击下方图片前往获取
3.技术文档和电子书
这里主要整理了大模型相关PDF书籍、行业报告、文档,有几百本,都是目前行业最新的。

4.LLM面试题和面经合集
这里主要整理了行业目前最新的大模型面试题和各种大厂offer面经合集。

👉学会后的收获:👈
• 基于大模型全栈工程实现(前端、后端、产品经理、设计、数据分析等),通过这门课可获得不同能力;
• 能够利用大模型解决相关实际项目需求: 大数据时代,越来越多的企业和机构需要处理海量数据,利用大模型技术可以更好地处理这些数据,提高数据分析和决策的准确性。因此,掌握大模型应用开发技能,可以让程序员更好地应对实际项目需求;
• 基于大模型和企业数据AI应用开发,实现大模型理论、掌握GPU算力、硬件、LangChain开发框架和项目实战技能, 学会Fine-tuning垂直训练大模型(数据准备、数据蒸馏、大模型部署)一站式掌握;
• 能够完成时下热门大模型垂直领域模型训练能力,提高程序员的编码能力: 大模型应用开发需要掌握机器学习算法、深度学习框架等技术,这些技术的掌握可以提高程序员的编码能力和分析能力,让程序员更加熟练地编写高质量的代码。

1.AI大模型学习路线图
2.100套AI大模型商业化落地方案
3.100集大模型视频教程
4.200本大模型PDF书籍
5.LLM面试题合集
6.AI产品经理资源合集
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓