一、概述
数据增强是一种通过人工或自动方式对数据进行修改或变换,以增加数据集规模和多样性的技术。在机器学习中,数据增强被广泛应用于解决数据稀缺、数据不平衡、数据噪声等问题,提高模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性。
二、为什么需要数据增强
图像增强在深度学习卷积神经网络 (CNN) 背景下至关重要,因为它有助于满足有效模型训练对大型且多样化数据集的需求。 CNN 需要大量图像才能有效训练,而图像增强提供了一种人为扩展现有数据集的方法。通过缩放、旋转、剪切或裁剪等技术创建图像变化,图像增强有助于生成更全面的可能图像集。这种多样化的数据集使模型能够更好地泛化,减少过度拟合,并在测试或验证过程中对以前未见过的数据进行评估时提高其性能。因此,图像增强对于提高训练数据的质量和数量至关重要,最终导致更强大和更准确的 CNN 模型。
三、什么时候使用数据增强
图像增强可以作为训练模型之前的预处理步骤,也可以在训练过程中实时应用。当用作预处理步骤时,应用增强来增加数据集的大小,特别是在处理需要扩展的小型训练数据集时。这种方法称为离线或预处理增强,涉及生成现有图像的变体以创建更多样化的数据集。应用图像增强时仔细考虑问题领域非常重要,因为某些增强策略可能与特定任务无关或无用。例如,在对不同类型的汽车进行分类时,垂直翻转汽车可能不会为数据集增加价值。因此,图像增强的应用应根据问题领域的具体要求进行定制。
四、数据增强实战
原始图像及标签:
运行数据增强代码:

增强后的数据及标签:
 关键代码:
关键代码:
数据增强:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
def rand(a=0, b=1):
return np.random.rand()*(b-a) + a
def get_random_data(annotation_line, input_shape, jitter=.3, hue=.1, sat=0.7, val=0.4, random=True):
line = annotation_line.split()
#------------------------------#
# 读取图像并转换成RGB图像
#------------------------------#
image = Image.open(line[0])
image = image.convert('RGB')
#------------------------------#
# 获得图像的高宽与目标高宽
#------------------------------#
iw, ih = image.size
h, w = input_shape
#------------------------------#
# 获得预测框
#------------------------------#
box = np.array([np.array(list(map(int,box.split(',')))) for box in line[1:]])
if not random:
scale = min(w/iw, h/ih)
nw = int(iw*scale)
nh = int(ih*scale)
dx = (w-nw)//2
dy = (h-nh)//2
#---------------------------------#
# 将图像多余的部分加上灰条
#---------------------------------#
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image_data = np.array(new_image, np.float32)
#---------------------------------#
# 对真实框进行调整
#---------------------------------#
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)] # discard invalid box
return image_data, box
#------------------------------------------#
# 对图像进行缩放并且进行长和宽的扭曲
#------------------------------------------#
new_ar = iw/ih * rand(1-jitter,1+jitter) / rand(1-jitter,1+jitter)
scale = rand(.25, 2)
if new_ar < 1:
nh = int(scale*h)
nw = int(nh*new_ar)
else:
nw = int(scale*w)
nh = int(nw/new_ar)
image = image.resize((nw,nh), Image.BICUBIC)
#------------------------------------------#
# 将图像多余的部分加上灰条
#------------------------------------------#
dx = int(rand(0, w-nw))
dy = int(rand(0, h-nh))
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w,h), (128,128,128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
image = new_image
#------------------------------------------#
# 翻转图像
#------------------------------------------#
flip = rand()<.5
if flip: image = image.transpose(Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
image_data = np.array(image, np.uint8)
#---------------------------------#
# 对图像进行色域变换
# 计算色域变换的参数
#---------------------------------#
r = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, 3) * [hue, sat, val] + 1
#---------------------------------#
# 将图像转到HSV上
#---------------------------------#
hue, sat, val = cv2.split(cv2.cvtColor(image_data, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV))
dtype = image_data.dtype
#---------------------------------#
# 应用变换
#---------------------------------#
x = np.arange(0, 256, dtype=r.dtype)
lut_hue = ((x * r[0]) % 180).astype(dtype)
lut_sat = np.clip(x * r[1], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
lut_val = np.clip(x * r[2], 0, 255).astype(dtype)
image_data = cv2.merge((cv2.LUT(hue, lut_hue), cv2.LUT(sat, lut_sat), cv2.LUT(val, lut_val)))
image_data = cv2.cvtColor(image_data, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)
#---------------------------------#
# 对真实框进行调整
#---------------------------------#
if len(box)>0:
np.random.shuffle(box)
box[:, [0,2]] = box[:, [0,2]]*nw/iw + dx
box[:, [1,3]] = box[:, [1,3]]*nh/ih + dy
if flip: box[:, [0,2]] = w - box[:, [2,0]]
box[:, 0:2][box[:, 0:2]<0] = 0
box[:, 2][box[:, 2]>w] = w
box[:, 3][box[:, 3]>h] = h
box_w = box[:, 2] - box[:, 0]
box_h = box[:, 3] - box[:, 1]
box = box[np.logical_and(box_w>1, box_h>1)]
return image_data, box
调用代码:
import os
from random import sample
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
from utils.random_data import get_random_data, get_random_data_with_MixUp
from utils.utils import convert_annotation, get_classes
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# Origin_VOCdevkit_path 原始数据集所在的路径
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
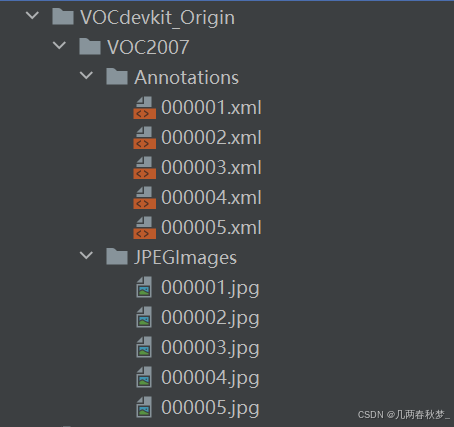
Origin_VOCdevkit_path = "VOCdevkit_Origin"
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
# input_shape 生成的图片大小。
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
input_shape = [640, 640]
if __name__ == "__main__":
Origin_JPEGImages_path = os.path.join(Origin_VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/JPEGImages")
Origin_Annotations_path = os.path.join(Origin_VOCdevkit_path, "VOC2007/Annotations")
#---------------------------#
# 遍历标签并赋值
#---------------------------#
xml_names = os.listdir(Origin_Annotations_path)
#------------------------------#
# 获取一个图像与标签
#------------------------------#
sample_xmls = sample(xml_names, 1)
unique_labels = get_classes(sample_xmls, Origin_Annotations_path)
jpg_name = os.path.join(Origin_JPEGImages_path, os.path.splitext(sample_xmls[0])[0] + '.jpg')
xml_name = os.path.join(Origin_Annotations_path, sample_xmls[0])
line = convert_annotation(jpg_name, xml_name, unique_labels)
#------------------------------#
# 各自数据增强
#------------------------------#
image_data, box_data = get_random_data(line, input_shape)
img = Image.fromarray(image_data.astype(np.uint8))
for j in range(len(box_data)):
thickness = 3
left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle([left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],outline=(255, 255, 255))
img.show()