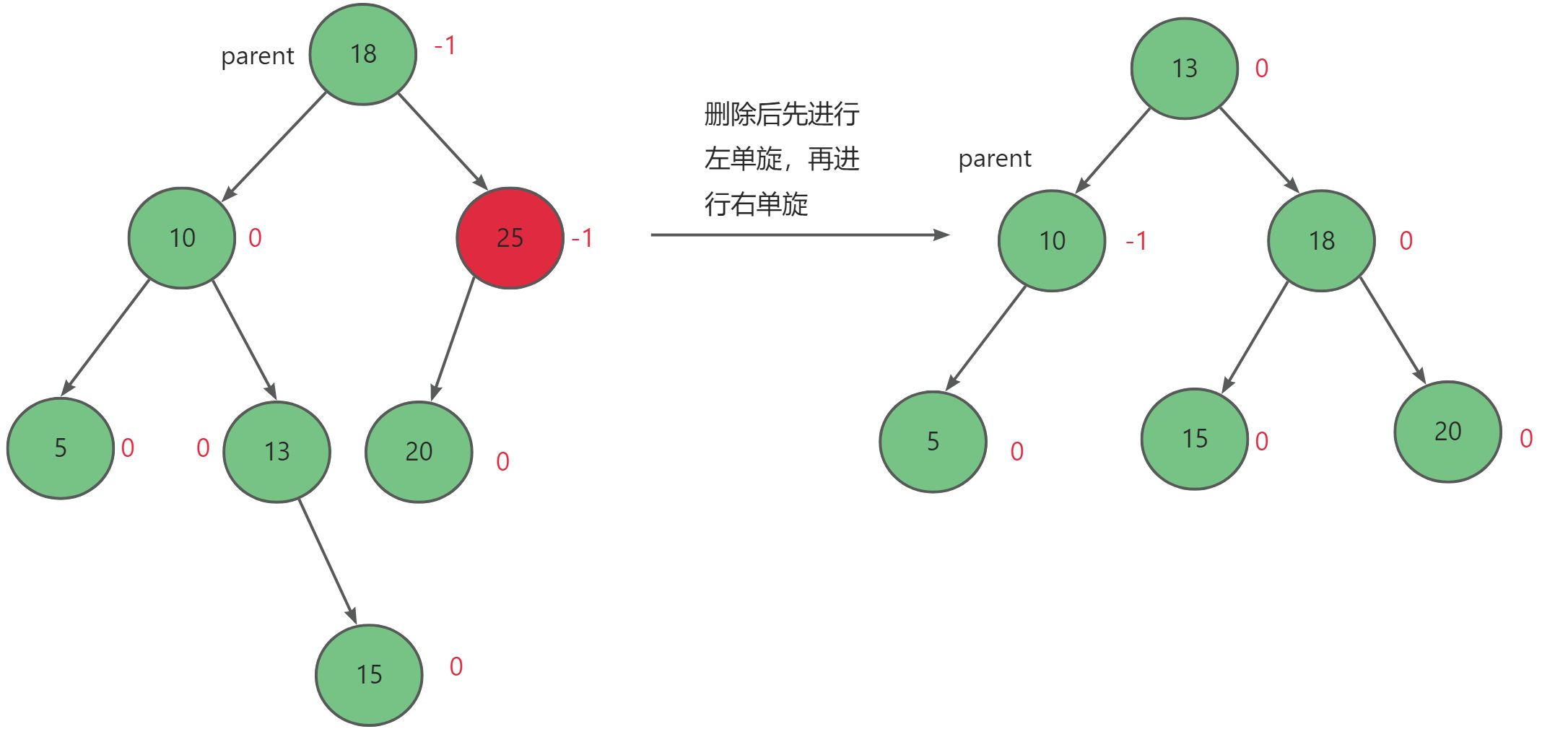
一、工具类展示
提供对集合的过滤、拼接、排序、MAP转化、分组、转为SET集合等方法
/**
* stream 流工具类
*
*/
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
public class StreamUtils {
/**
* 将collection过滤
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param function 过滤方法
* @return 过滤后的list
*/
public static <E> List<E> filter(Collection<E> collection, Predicate<E> function) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return CollUtil.newArrayList();
}
return collection.stream().filter(function).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 将collection拼接
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param function 拼接方法
* @return 拼接后的list
*/
public static <E> String join(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, String> function) {
return join(collection, function, StringUtils.SEPARATOR);
}
/**
* 将collection拼接
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param function 拼接方法
* @param delimiter 拼接符
* @return 拼接后的list
*/
public static <E> String join(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, String> function, CharSequence delimiter) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return StringUtils.EMPTY;
}
return collection.stream().map(function).filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.joining(delimiter));
}
/**
* 将collection排序
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param comparing 排序方法
* @return 排序后的list
*/
public static <E> List<E> sorted(Collection<E> collection, Comparator<E> comparing) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return CollUtil.newArrayList();
}
return collection.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).sorted(comparing).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 将collection转化为类型不变的map<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<V> ----> Map<K,V>}</B>
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param key V类型转化为K类型的lambda方法
* @param <V> collection中的泛型
* @param <K> map中的key类型
* @return 转化后的map
*/
public static <V, K> Map<K, V> toIdentityMap(Collection<V> collection, Function<V, K> key) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
return collection.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.toMap(key, Function.identity(), (l, r) -> l));
}
/**
* 将Collection转化为map(value类型与collection的泛型不同)<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> -----> Map<K,V> }</B>
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param key E类型转化为K类型的lambda方法
* @param value E类型转化为V类型的lambda方法
* @param <E> collection中的泛型
* @param <K> map中的key类型
* @param <V> map中的value类型
* @return 转化后的map
*/
public static <E, K, V> Map<K, V> toMap(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, K> key, Function<E, V> value) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
return collection.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.toMap(key, value, (l, r) -> l));
}
/**
* 将collection按照规则(比如有相同的班级id)分类成map<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> -------> Map<K,List<E>> } </B>
*
* @param collection 需要分类的集合
* @param key 分类的规则
* @param <E> collection中的泛型
* @param <K> map中的key类型
* @return 分类后的map
*/
public static <E, K> Map<K, List<E>> groupByKey(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, K> key) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
return collection
.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(key, LinkedHashMap::new, Collectors.toList()));
}
/**
* 将collection按照两个规则(比如有相同的年级id,班级id)分类成双层map<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> ---> Map<T,Map<U,List<E>>> } </B>
*
* @param collection 需要分类的集合
* @param key1 第一个分类的规则
* @param key2 第二个分类的规则
* @param <E> 集合元素类型
* @param <K> 第一个map中的key类型
* @param <U> 第二个map中的key类型
* @return 分类后的map
*/
public static <E, K, U> Map<K, Map<U, List<E>>> groupBy2Key(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, K> key1, Function<E, U> key2) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
return collection
.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(key1, LinkedHashMap::new, Collectors.groupingBy(key2, LinkedHashMap::new, Collectors.toList())));
}
/**
* 将collection按照两个规则(比如有相同的年级id,班级id)分类成双层map<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> ---> Map<T,Map<U,E>> } </B>
*
* @param collection 需要分类的集合
* @param key1 第一个分类的规则
* @param key2 第二个分类的规则
* @param <T> 第一个map中的key类型
* @param <U> 第二个map中的key类型
* @param <E> collection中的泛型
* @return 分类后的map
*/
public static <E, T, U> Map<T, Map<U, E>> group2Map(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, T> key1, Function<E, U> key2) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection) || key1 == null || key2 == null) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
return collection
.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(key1, LinkedHashMap::new, Collectors.toMap(key2, Function.identity(), (l, r) -> l)));
}
/**
* 将collection转化为List集合,但是两者的泛型不同<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> ------> List<T> } </B>
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param function collection中的泛型转化为list泛型的lambda表达式
* @param <E> collection中的泛型
* @param <T> List中的泛型
* @return 转化后的list
*/
public static <E, T> List<T> toList(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, T> function) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection)) {
return CollUtil.newArrayList();
}
return collection
.stream()
.map(function)
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 将collection转化为Set集合,但是两者的泛型不同<br>
* <B>{@code Collection<E> ------> Set<T> } </B>
*
* @param collection 需要转化的集合
* @param function collection中的泛型转化为set泛型的lambda表达式
* @param <E> collection中的泛型
* @param <T> Set中的泛型
* @return 转化后的Set
*/
public static <E, T> Set<T> toSet(Collection<E> collection, Function<E, T> function) {
if (CollUtil.isEmpty(collection) || function == null) {
return CollUtil.newHashSet();
}
return collection
.stream()
.map(function)
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
/**
* 合并两个相同key类型的map
*
* @param map1 第一个需要合并的 map
* @param map2 第二个需要合并的 map
* @param merge 合并的lambda,将key value1 value2合并成最终的类型,注意value可能为空的情况
* @param <K> map中的key类型
* @param <X> 第一个 map的value类型
* @param <Y> 第二个 map的value类型
* @param <V> 最终map的value类型
* @return 合并后的map
*/
public static <K, X, Y, V> Map<K, V> merge(Map<K, X> map1, Map<K, Y> map2, BiFunction<X, Y, V> merge) {
if (MapUtil.isEmpty(map1) && MapUtil.isEmpty(map2)) {
return MapUtil.newHashMap();
} else if (MapUtil.isEmpty(map1)) {
map1 = MapUtil.newHashMap();
} else if (MapUtil.isEmpty(map2)) {
map2 = MapUtil.newHashMap();
}
Set<K> key = new HashSet<>();
key.addAll(map1.keySet());
key.addAll(map2.keySet());
Map<K, V> map = new HashMap<>();
for (K t : key) {
X x = map1.get(t);
Y y = map2.get(t);
V z = merge.apply(x, y);
if (z != null) {
map.put(t, z);
}
}
return map;
}
}
准备数据如下:
public static List<TestDemo> getList() {
List<TestDemo> list = new ArrayList<>();
TestDemo demo1 = new TestDemo();
demo1.setTestKey("1");
demo1.setOrderNum(1);
list.add(demo1);
TestDemo demo2 = new TestDemo();
demo2.setTestKey("2");
demo2.setOrderNum(2);
list.add(demo2);
TestDemo demo3 = new TestDemo();
demo3.setTestKey("3");
demo3.setOrderNum(5);
TestDemo demo4 = new TestDemo();
demo4.setTestKey("1");
demo4.setOrderNum(4);
list.add(demo1);
list.add(demo2);
list.add(demo3);
list.add(demo4);
return list;
}
二、过滤
过滤:testKey 等于1的数据
static void testFilter() {
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
List<TestDemo> filter = StreamUtils.filter(list, demo -> "1".equals(demo.getTestKey()));
for (TestDemo demo : filter){
Console.log("demo->{}", demo);
}
}过滤结果:testKey 等于1的数据
demo->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null) demo->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null) demo->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
二、拼接
逗号拼接; 不传入连接符默认是逗号拼接
static void testJoin() {
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
String join = StreamUtils.join(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey(), "--");
Console.log("join->{}", join);
}
拼接结果:
join->1--2--1--2--3--1
三、 排序
传入Comparator ,对比 return o1.getOrderNum() - o2.getOrderNum() :
- o1 = 02 : 返回等于0
- o1 > 02 : 返回大于0
- o1 < 02 : 返回小于0
static void testSort() {
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
List<TestDemo> sorted = StreamUtils.sorted(list, new Comparator<TestDemo>() {
@Override
public int compare(TestDemo o1, TestDemo o2) {
return o1.getOrderNum() - o2.getOrderNum();
}
});
for (TestDemo demo : sorted) {
Console.log("sorted->{}", demo);
}
}上面简写:
static void testSort() {
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
List<TestDemo> sorted = StreamUtils.sorted(list, (o1, o2) -> o1.getOrderNum() - o2.getOrderNum());
for (TestDemo demo : sorted) {
Console.log("sorted->{}", demo);
}
}如图看orderNum 的排序:
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
sorted->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
四、转换MAP
testKey作为MAP集合的key
static void testToIdentityMap(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
Map<String, TestDemo> map = StreamUtils.toIdentityMap(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey());
//Map<String, TestDemo> map1 = StreamUtils.toIdentityMap(list, demo -> demo.getOrderNum().toString());
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
Console.log("testToIdentityMap->{}->{}", key, map.get(key));
}
}打印结果:
testToIdentityMap->1->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
testToIdentityMap->2->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)
testToIdentityMap->3->TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)五、转换MAP,重新定义返回Value
- String作为key
- 并将 value值,由 TestDemo转换为了TestDemoVo对象
static void toMap(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
Map<String, Object> map = StreamUtils.toMap(list, new Function<TestDemo, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(TestDemo testDemo) {
return testDemo.getOrderNum().toString();
}
},
new Function<TestDemo, Object>() {
@Override
public Object apply(TestDemo testDemo) {
TestDemoVo copy = BeanCopyUtils.copy(testDemo, TestDemoVo.class);
return copy;
}
}
);
for (Object key : map.keySet()) {
Console.log("toMap->{}->{}", key, map.get(key));
}
}打印结果:
value由 TestDemo转换为了TestDemoVo.class
toMap->1->TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null)
toMap->2->TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null)
toMap->4->TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null)
toMap->5->TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null)六、分组
1-根据testKey分组
static void testGroup(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
Map<String, List<TestDemo>> map = StreamUtils.groupByKey(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey());
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
Console.log("testGroup->{}->{}", key, map.get(key));
}
}返回结果:
testGroup->1->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]
testGroup->2->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]
testGroup->3->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]2- 根据2个条件分组:外层根据testKey ,内层根据:orderNum
static void testGroup2(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
Map<String, Map<Integer, List<TestDemo>>> stringMapMap = StreamUtils.groupBy2Key(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey(), demo -> demo.getOrderNum());
for (String keyout : stringMapMap.keySet()) {
Map<Integer, List<TestDemo>> integerListMap = stringMapMap.get(keyout);
Console.log("外层->{}->{}", keyout, stringMapMap.get(keyout));
for (Integer keyin : integerListMap.keySet()) {
Console.log("内层->{}->{}", keyin, integerListMap.get(keyin));
}
}
}
结果:
外层->1->{1=[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)], 4=[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]}
内层->1->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]
内层->4->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]
外层->2->{2=[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]}
内层->2->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null), TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]
外层->3->{5=[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]}
内层->5->[TestDemo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, version=null, delFlag=null)]七、将collection转化为List集合,但是两者的泛型不同
static void testToList(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
//返回单个属性集合
List<String> strings = StreamUtils.toList(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey());
Console.log("testToList->{}", strings);
//转换为vo类
List<TestDemoVo> testDemoVos = StreamUtils.toList(list, demo -> {
TestDemoVo copy = BeanCopyUtils.copy(demo, TestDemoVo.class);
return copy;
});
Console.log("testToList->{}", testDemoVos);
}返回结果:
testToList->[1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1]
testToList->[TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null), TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null), TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=1, testKey=1, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null), TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=2, testKey=2, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null), TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=5, testKey=3, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null), TestDemoVo(id=null, deptId=null, userId=null, orderNum=4, testKey=1, value=null, createTime=null, createBy=null, updateTime=null, updateBy=null)]八、转换set集合去掉重复
//转换为set (去掉重复数据)
static void testToSet(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
Set<String> strings = StreamUtils.toSet(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey());
Console.log("testToSet->{}", strings);
}结果:
testToSet->[1, 2, 3]九、合并
合并两个相同key类型的map
static void testMerge(){
List<TestDemo> list = getList();
//先得到2个,key同类型,value 类型不一样的 map
Map<String, String> map1 = StreamUtils.toMap(list, demo -> demo.getTestKey(), demo -> demo.getTestKey());
Map<String, Integer> map2 = StreamUtils.toMap(list, demo -> demo.getOrderNum()+"",demo->demo.getOrderNum());
//合并
Map<String, String> merge = StreamUtils.merge(map1, map2, (value1, value2) -> value1 + "--" + value2);
Console.log("testMerge->{}", merge);
}结果:
相同的key合并,value 用符号--拼接
testMerge->{1=1--1, 2=2--2, 3=3--null, 4=null--4, 5=null--5}