Title
题目
Comparison of Multiparametric MRI–targeted and Systematic Biopsies for Detection of Cribriform and Intraductal Carcinoma Prostate Cancer
多参数MRI靶向活检与系统性活检在筛查筛状和导管内癌前列腺癌中的比较
Background
背景
Intraductal carcinoma (IDC) and invasive cribriform (Cr) subtypes of prostate cancer (PCa) are an indication of aggressiveness, but the evidence regarding whether MRI can be used to detect Cr/IDC-pattern PCa is contradictory.
导管内癌(IDC)和侵袭性筛状(Cr)亚型的前列腺癌(PCa)是其侵袭性的标志,但关于MRI是否能检测到Cr/IDC模式的前列腺癌的证据是矛盾的。
Method
方法
This study was a secondary analysis of a prospective randomized controlled trial that recruited participants with a clinical suspicion of PCa between April 2017 and November 2019 at five centers. Participants were randomized 1:1 to either the MRI arm or the systematic biopsy arm. Targeted biopsy was performed in participants with a Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System score of at least 3. MRI features were recorded, and biopsy slides and prostatectomy specimens were reviewed for the presence or absence of Cr/IDC histologic patterns. Comparison of Cr/IDC patterns was performed using generalized linear mixed modeling.
本研究是对一项前瞻性随机对照试验的二次分析,研究对象为2017年4月至2019年11月期间在五个中心招募的临床怀疑患有前列腺癌(PCa)的参与者。参与者被随机分为MRI组和系统性活检组,比例为1:1。在具有前列腺影像报告和数据系统评分(PI-RADS)至少为3的参与者中进行靶向活检。记录MRI特征,并检查活检切片和前列腺切除标本中是否存在Cr/IDC组织学模式。使用广义线性混合模型对Cr/IDC模式进行比较。
Conclusion
结论
MRI-targeted biopsy showed increased detection of Cr/IDC histologic patterns compared with systematic biopsy.
MRI靶向活检相比系统性活检显示出更高的Cr/IDC组织学模式检出率。
Results
结果
A total of 453 participants were enrolled, with 226 in the systematic biopsy arm (median age, 65 years [IQR, 59–70 years]; 196 biopsies available for assessment) and 227 in the mpMRI-targeted biopsy arm (median age, 67 years [IQR, 60–72 years]; 132 biopsies available for assessment). Identification of Cr/IDC PCa was lower in the systematic biopsy arm compared with the mpMRI arm (31 of 196 biopsies [16%] vs 33 of 132 biopsies [25%]; P = .01). No evidence of a difference in mean cancer core length (CCL) (11.3 mm ± 4.4 vs 9.7 mm ± 4.5; P = .09), apparent diffusion coefficient (685 µm2 /sec ± 178 vs 746 µm2 /sec ± 245; P = .52), or dynamic contrast-enhanced positivity (27 [82%] vs 37 [90%]; P = .33) for clinically significant PCa (csPCa) was observed between participants with or without Cr/IDC disease in the MRI arm. Cr/IDC-positive histologic patterns overall had a higher mean CCL compared with Cr/IDC-negative csPCa (11.1 mm ± 4.4 vs 9.2 mm ± 4.1; P = .009).
共招募了453名参与者,系统性活检组226人(中位年龄65岁[IQR, 59–70岁];196份可供评估的活检),mpMRI靶向活检组227人(中位年龄67岁[IQR, 60–72岁];132份可供评估的活检)。在系统性活检组中识别Cr/IDC PCa的比例低于mpMRI组(196份活检中的31份[16%] vs 132份活检中的33份[25%];P = .01)。在MRI组中,具有或不具有Cr/IDC疾病的参与者之间,在平均癌症核心长度(CCL)(11.3 mm ± 4.4 vs 9.7 mm ± 4.5;P = .09)、表观扩散系数(685 µm²/秒 ± 178 vs 746 µm²/秒 ± 245;P = .52)或动态增强阳性率(27 [82%] vs 37 [90%];P = .33)方面没有观察到临床显著性前列腺癌(csPCa)的差异。总体而言,Cr/IDC阳性组织学模式的平均CCL高于Cr/IDC阴性csPCa(11.1 mm ± 4.4 vs 9.2 mm ± 4.1;P = .009)。
Figure
图
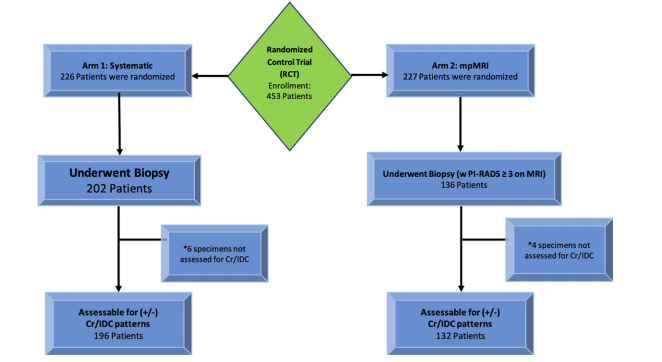
Figure 1: Study flowchart shows patient enrollment and participants analyzed for cribriform (Cr)/intraductal carcinoma (IDC) histologic pattern prostate cancer. mpMRI = multiparametric MRI, PI-RADS = Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System.
图1: 研究流程图显示了患者入组和参与者的分析情况,用于筛查筛状(Cr)/导管内癌(IDC)组织学模式的前列腺癌。mpMRI = 多参数MRI,PI-RADS = 前列腺影像报告和数据系统。
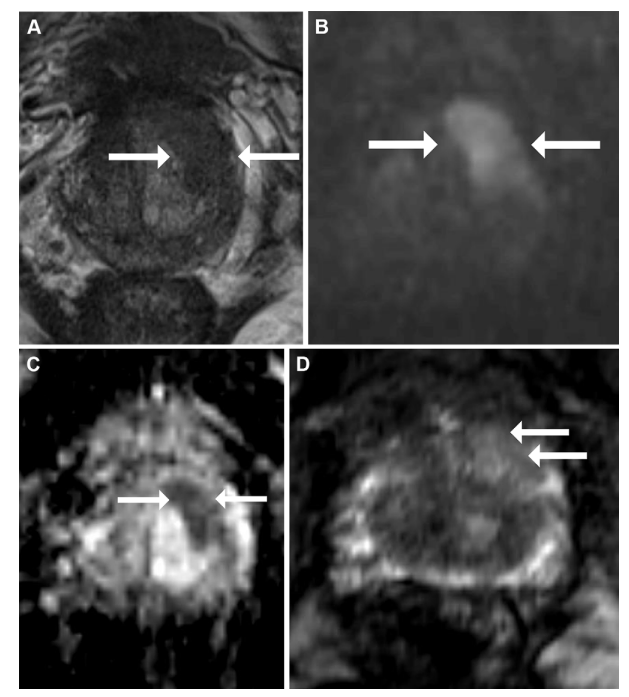
Figure 2: Multiparametric MRI in a 60-year-old male participant with a prostate-specific antigen level of 6.3 ng/mL. (A) Axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo MRI scan (repetition time msec/echo time msec, 3820/97) shows a 19-mm Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System 5 nodule in the left base anterior transition zone (arrows). (B) Diffusionweighted image (b = 1600 sec/mm2 ) and (C) corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map show marked restricted diffusion at the site (arrows), with an ADC of 553 µm2 /sec. (D) Dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows focal and contemporaneous enhancement at the tumor site (arrows) compared with the contralateral transition zone. Targeted biopsy revealed grade group 2 prostate cancer without cribriform (Cr)/intraductal carcinoma (IDC) histologic features. The participant subsequently underwent radical prostatectomy, and evaluation of the prostatectomy specimen also did not reveal a Cr/IDC morphologic pattern.
图2: 一名60岁男性参与者的多参数MRI,其前列腺特异抗原水平为6.3 ng/mL。(A) 轴向T2加权快速自旋回波MRI扫描(重复时间/回波时间,3820/97)显示左基底前移行区的一个19毫米的前列腺影像报告和数据系统5级结节(箭头)。(B) 弥散加权图像(b = 1600 sec/mm²)和(C)相应的表观扩散系数(ADC)图显示该部位有明显的受限扩散(箭头),ADC为553 µm²/秒。(D) 动态对比增强图像显示与对侧移行区相比,肿瘤部位有局灶性和同时增强(箭头)。靶向活检显示2级前列腺癌,无筛状(Cr)/导管内癌(IDC)组织学特征。该参与者随后接受了根治性前列腺切除术,切除标本的评估也未发现Cr/IDC形态模式。
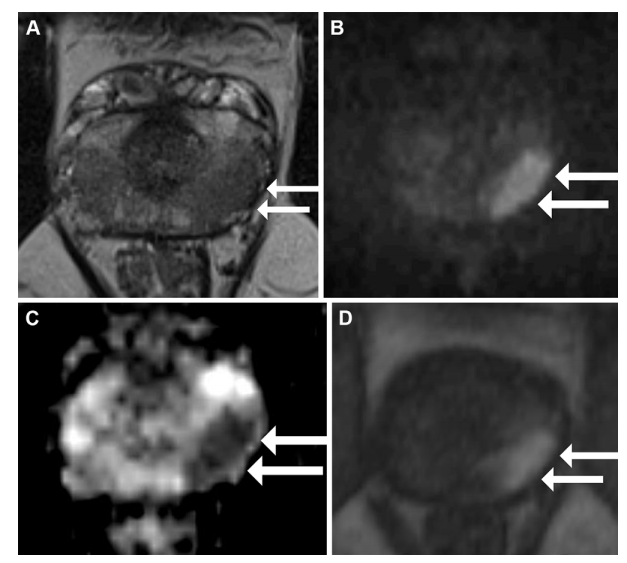
Figure 3: Multiparametric MRI in a 55-year-old male participant with a prostate-specific antigen level of 5.25 ng/mL. (A) Axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo MRI scan (repetition time msec/echo time msec, 3820/97) shows a 17-mm Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System 5 nodule in the left mid gland posterolateral peripheral zone (arrows). (B) Diffusion-weighted image (b = 1600 sec/mm2 ) and (C) corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map show marked restricted diffusion at the site (arrows), with an ADC of 570 µm2 /sec. (D) Dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows focal early enhancement at the tumor site (arrows). Targeted biopsy revealed grade group 3 prostate cancer (PCa) without cribriform (Cr)/intraductal carcinoma (IDC) features. The participant subsequently underwent radical prostatectomy for treatment of PCa, and evaluation of the prostatectomy specimen revealed a Cr/IDC morphologic pattern, which was not detected at initial biopsy
图3: 一名55岁男性参与者的多参数MRI,其前列腺特异抗原水平为5.25 ng/mL。(A) 轴向T2加权快速自旋回波MRI扫描(重复时间/回波时间,3820/97)显示左侧中腺体后外周区的一个17毫米的前列腺影像报告和数据系统5级结节(箭头)。(B) 弥散加权图像(b = 1600 sec/mm²)和(C)相应的表观扩散系数(ADC)图显示该部位有明显的受限扩散(箭头),ADC为570 µm²/秒。(D) 动态对比增强图像显示肿瘤部位的局灶性早期增强(箭头)。靶向活检显示3级前列腺癌(PCa),无筛状(Cr)/导管内癌(IDC)特征。该参与者随后接受了根治性前列腺切除术治疗PCa,切除标本的评估显示了Cr/IDC形态模式,而初次活检未检测到该模式。
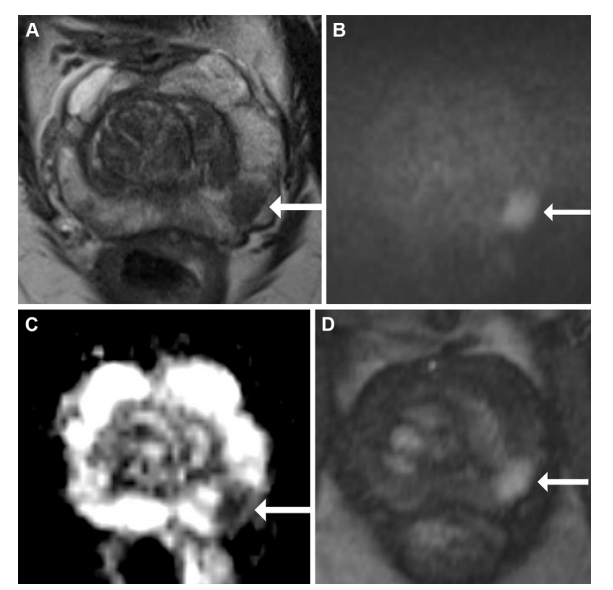
Figure 4: Multiparametric MRI in a 68-year-old male participant with a prostate-specific antigen level of 9.49 ng/mL. (A) Axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo MRI scan (repetition time msec/echo time msec, 3820/97) shows a 13-mm Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System 4 nodule in the left mid gland posterolateral peripheral zone (arrow). (B) Diffusionweighted image (b = 1600 sec/mm2 ) and (C) corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map show marked restricted diffusion at the site (arrows), with an ADC of 515 µm2 /sec. (D) Dynamic contrast-enhanced image shows focal early enhancement at the tumor site (arrow). Targeted biopsy revealed grade group 3 prostate cancer (PCa) with cribriform/intraductal histologic features. The participant underwent radiation therapy for treatment of PCa.
图4: 一名68岁男性参与者的多参数MRI,其前列腺特异抗原水平为9.49 ng/mL。(A) 轴向T2加权快速自旋回波MRI扫描(重复时间/回波时间,3820/97)显示左侧中腺体后外周区的一个13毫米的前列腺影像报告和数据系统4级结节(箭头)。(B) 弥散加权图像(b = 1600 sec/mm²)和(C)相应的表观扩散系数(ADC)图显示该部位有明显的受限扩散(箭头),ADC为515 µm²/秒。(D) 动态对比增强图像显示肿瘤部位的局灶性早期增强(箭头)。靶向活检显示3级前列腺癌(PCa)伴有筛状/导管内组织学特征。该参与者随后接受了前列腺癌的放射治疗。
Table
表

Table 1: Baseline Characteristics of Participants Assessed for Cribriform and Intraductal Histopathologic Patterns at Biopsy
表1:活检时评估筛状和导管内组织病理模式的参与者基线特征
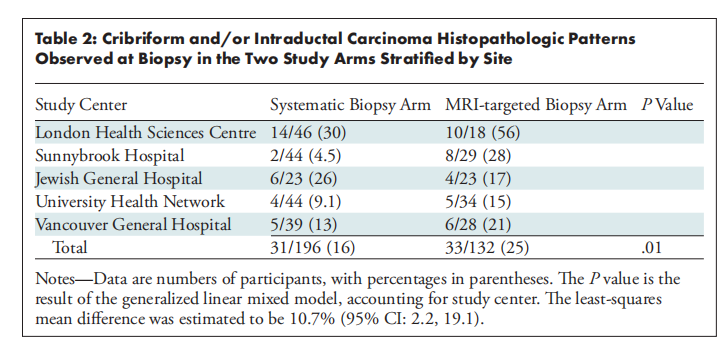
Table 2: Cribriform and/or Intraductal Carcinoma Histopathologic Patterns Observed at Biopsy in the Two Study Arms Stratified by Site
表2:在两组研究中按部位分层观察到的筛状和/或导管内癌组织病理模式
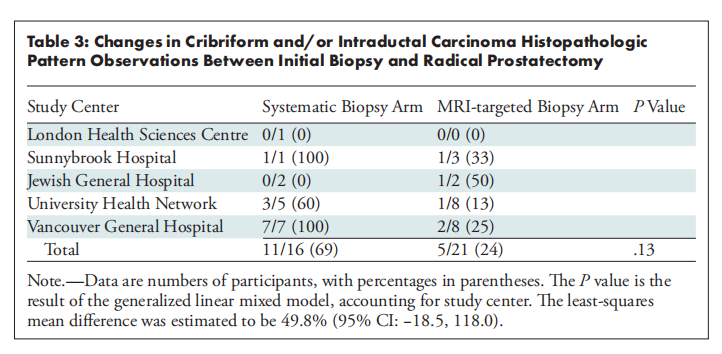
Table 3: Changes in Cribriform and/or Intraductal Carcinoma Histopathologic Pattern Observations Between Initial Biopsy and Radical Prostatectomy
表3:初次活检与根治性前列腺切除术之间筛状和/或导管内癌组织病理模式观察的变化
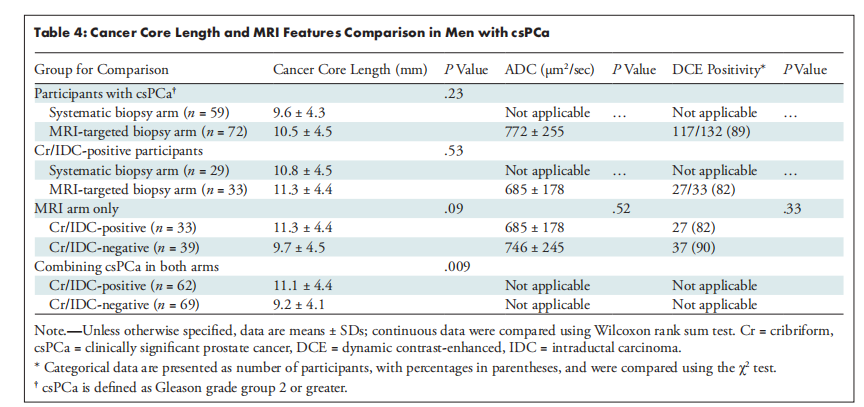
Table 4: Cancer Core Length and MRI Features Comparison in Men with csPCa
表4:具有临床显著性前列腺癌(csPCa)男性的癌症核心长度和MRI特征比较