写这篇博客的起因:
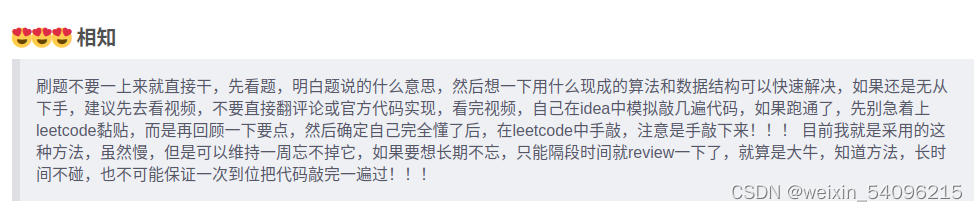
刚开始刷力扣,发现没有一个很好的做题方法,在网络上发现了这个博主的评论,如下。感觉挺适合我,所以开始复习一下数据结构。
c++基础主要是看:
- 1.bilibili上青岛大学王卓第02周03--2.3线性表的类型定义_哔哩哔哩_bilibili的视频(c++)。
刷题主要是看:
- 2.leetcode-代码随想录相关手把手带你撕出正确的二分法 | 二分查找法 | 二分搜索法 | LeetCode:704. 二分查找_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- 3.leetcode-labuladong系列
《labuladong 的算法笔记》纸质书 | labuladong 的算法笔记
一、数组-二分法
问题1:左闭右闭,左闭右开,左开右闭
一般使用左闭右闭和左闭右开比较多
1:左闭右开(left<right)
left=0
right=len(num)-1
m1 = (right - left) // 2 + left
while(left<right):
m1>t,right=m1
m1<t,left=m1+1
m1=t,m1
2:左闭右闭(left<=right)
left=0
right=len(num)-1
m1 = (right - left) // 2 + left
while(left<=right):
m1>t,right=m1-1
m1<t,left=m1+1
m1=t,m1
二、力扣相关例题
704题:二分查找
python语言-左闭右开
from typing import List
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
# self: 这是一个特殊的参数,用来引用类的实例本身。在类方法中,self 是必须的,但在调用方法时通常不需要显式传入,Python会自动处理。
# nums: List[int]: 这是函数的第一个参数,命名为 nums,类型注解指示它应该是一个整数列表。
# target: int: 这是函数的第二个参数,命名为 target,类型注解指示它应该是一个整数。
# -> int: 这部分指定了函数的返回类型,即该函数会返回一个整数。
left, right = 0, len(nums)
while left < right:
middle = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[middle] > target:
right = middle
elif nums[middle] < target:
left = middle + 1
else:
return middle
return -1
def main():
# Example usage:
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
result = solution.search(nums, target)
print(f"Index of {target} in {nums}: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
python语言-左闭右闭
from typing import List
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
# self: 这是一个特殊的参数,用来引用类的实例本身。在类方法中,self 是必须的,但在调用方法时通常不需要显式传入,Python会自动处理。
# nums: List[int]: 这是函数的第一个参数,命名为 nums,类型注解指示它应该是一个整数列表。
# target: int: 这是函数的第二个参数,命名为 target,类型注解指示它应该是一个整数。
# -> int: 这部分指定了函数的返回类型,即该函数会返回一个整数。
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1 # 定义target在左闭右闭的区间里,[left, right]
while left <= right:
middle = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[middle] > target:
right = middle - 1 # target在左区间,所以[left, middle - 1]
elif nums[middle] < target:
left = middle + 1 # target在右区间,所以[middle + 1, right]
else:
return middle # 数组中找到目标值,直接返回下标
return -1 # 未找到目标值
def main():
# Example usage:
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
result = solution.search(nums, target)
print(f"Index of {target} in {nums}: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
c++语言-左闭右开
# include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int search(std::vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size(); // right is the index just beyond the end of the vector
while (left < right) {
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[middle] > target) {
right = middle; // target in left half, [left, middle)
} else if (nums[middle] < target) {
left = middle + 1; // target in right half, [middle + 1, right)
} else {
return middle; // target found at index middle
}
}
return -1; // target not found
}
};
// Example usage
#include <iostream>
int main() {
Solution solution;
std::vector<int> nums = {-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12};
int target = 9;
int result = solution.search(nums, target);
std::cout << "Index of " << target << " in nums: " << result << std::endl;
return 0;
}
c++语言-左闭右闭
# include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int search(std::vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size(); // right is the index just beyond the end of the vector
while (left <= right) {
int middle = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[middle] > target) {
right = middle-1; // target in left half, [left, middle)
} else if (nums[middle] < target) {
left = middle + 1; // target in right half, [middle + 1, right)
} else {
return middle; // target found at index middle
}
}
return -1; // target not found
}
};
// Example usage
#include <iostream>
int main() {
Solution solution;
std::vector<int> nums = {-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12};
int target = 9;
int result = solution.search(nums, target);
std::cout << "Index of " << target << " in nums: " << result << std::endl;
return 0;
}
相关题目:
35题:搜索插入位置
#
# @lc app=leetcode.cn id=35 lang=python
#
# [35] 搜索插入位置
#
# @lc code=start
from typing import List
class Solution():
def searchInsert(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) # 左闭右开区间 [left, right)
while left < right: # 区间不为空
# 循环不变量:
# nums[left-1] < target
# nums[right] >= target
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1 # 范围缩小到 [mid+1, right)
else:
right = mid # 范围缩小到 [left, mid)
return left # 或者 right
def main():
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]
target = 8
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target)
print(f"Index of {target} in {nums}: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
# @lc code=end
34题:在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
#
# @lc app=leetcode.cn id=34 lang=python
#
# [34] 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
#
# @lc code=start
from typing import List
class Solution:
def searchRange(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
result = [-1, -1]
# Edge case: empty list
if not nums:
return result
# Binary search for the left boundary of target
while left <= right:
middle = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[middle] < target:
left = middle + 1
else:
right = middle - 1
# After the loop, `left` is the index of the first occurrence of `target`
if left < len(nums) and nums[left] == target:
result[0] = left
else:
return result
# Binary search for the right boundary of target
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
middle = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[middle] <= target:
left = middle + 1
else:
right = middle - 1
# After the loop, `right` is the index of the last occurrence of `target`
result[1] = right
return result
def main():
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 9, 12]
target = 10
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchRange(nums, target)
print(f"Indices of {target} in {nums}: {result}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
c++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> searchRange(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<int> result = {-1, -1};
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
// First binary search to find the leftmost index of target
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// Found target, adjust right to search left part
result[0] = mid;
right = mid - 1;
}
}
// Second binary search to find the rightmost index of target
left = 0;
right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// Found target, adjust left to search right part
result[1] = mid;
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 9, 9, 12};
int target = 9;
Solution solution;
vector<int> result = solution.searchRange(nums, target);
cout << "Indices of " << target << " in nums: [" << result[0] << ", " << result[1] << "]" << endl;
return 0;
}
367题:有效的完全平方数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool isPerfectSquare(int num) {
if (num == 0 || num == 1) {
return true;
}
long left = 1;
long right = num;
long mid = 0;
while (left <= right) {
mid = (left + right + 1) / 2; // 保证处理到右边界
long long res = mid * mid; // 使用 long long 来存放结果,避免整数溢出
if (res == num) {
return true;
} else if (res > num) {
// [left, mid-1] 区间继续找
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// [mid+1, right] 区间继续找
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
// 测试数据
int nums[] = {16, 14, 25, 0, 1, 100, 99};
int n = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "Number " << nums[i] << (isPerfectSquare(nums[i]) ? " is" : " is not") << " a perfect square." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool isPerfectSquare(int num) {
if (num == 0 || num == 1) {
return true;
}
long left = 1;
long right = num;
long mid = 0;
while (left <= right) {
mid = (left + right + 1) / 2; // 保证处理到右边界
long long res = mid * mid; // 使用 long long 来存放结果,避免整数溢出
if (res == num) {
return true;
} else if (res > num) {
// [left, mid-1] 区间继续找
right = mid - 1;
} else {
// [mid+1, right] 区间继续找
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
// 测试数据
int nums[] = {16, 14, 25, 0, 1, 100, 99};
int n = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "Number " << nums[i] << (isPerfectSquare(nums[i]) ? " is" : " is not") << " a perfect square." << endl;
}
return 0;
}