作者前言
🎂 ✨✨✨✨✨✨🍧🍧🍧🍧🍧🍧🍧🎂
🎂 作者介绍: 🎂🎂
🎂 🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉🎉 🎂
🎂作者id:老秦包你会, 🎂
简单介绍:🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂
喜欢学习C语言、C++和python等编程语言,是一位爱分享的博主,有兴趣的小可爱可以来互讨 🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂
🎂个人主页::小小页面🎂
🎂gitee页面:秦大大🎂
🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂🎂
🎂 一个爱分享的小博主 欢迎小可爱们前来借鉴🎂
list
- **作者前言**
- list的介绍
- list的简单使用
- reverse
- merge
- unique
- splice
- list的模拟实现
- 迭代器的模拟
- **普通的迭代器**
- const迭代器
- 反向迭代器
- 重载->
list的介绍
list页面
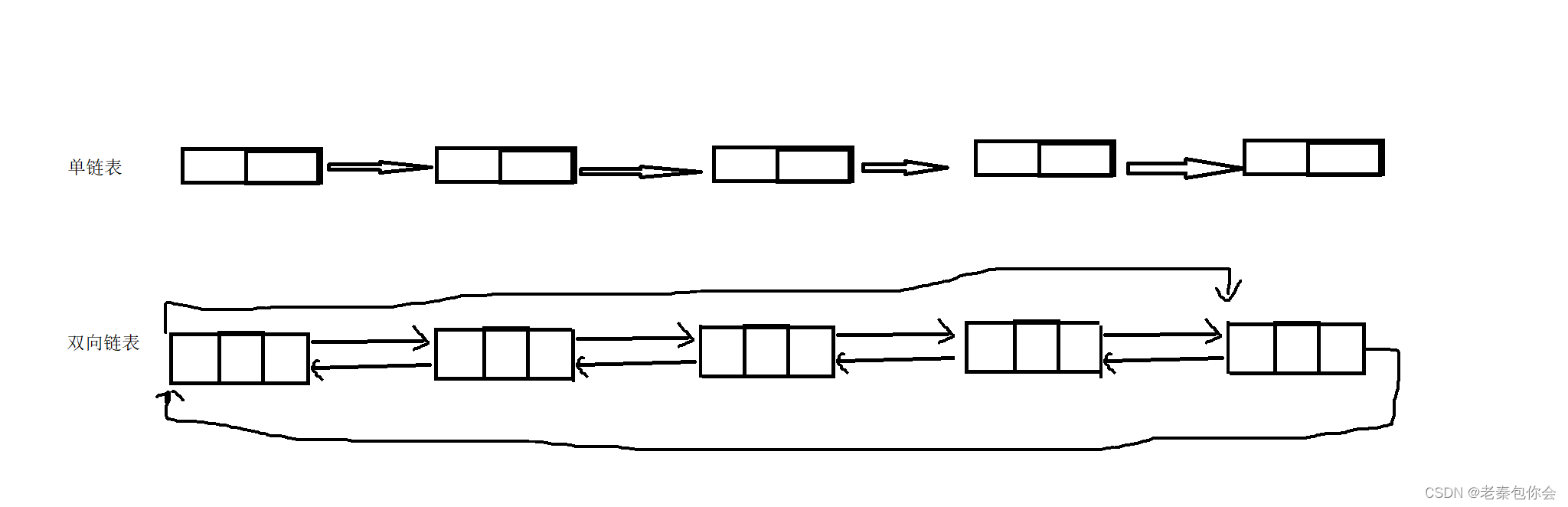
list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
2. list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向
其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3. list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高
效。
4. 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率
更好。
5. 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list
的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间
开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这
可能是一个重要的因素)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(11);
lt.push_back(12);
lt.push_back(13);
lt.push_back(14);
lt.push_back(15);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& e:lt)
{
cout << e;
}
return 0;
}
前面我们知道,string和vector的遍历方式有迭代器,下标和 地址
但是在list中没有下标,通过地址去访问困难,只能通过迭代器去访问,这个时候就会很方便,不用再和之前的C语言那样,获取到对应的地址进行方位,我们只需获取到对应的迭代器就可以快速,迭代器的优势也慢慢的体现出来了
list的简单使用
经过前面的string和vector我们可以使用一些简单 的成员函数,begin、end等相关的成员函数,我这里不详细的去介绍了,下面我简单的介绍一些不经常讲过的,
reverse
需要注意的是这个名称,在string和vector中是reserve()成员函数,是一个进行空间扩大的函数,这两者是不一样的,而reverse是list中特有的成员函数
进行翻转,把元素从头到尾进行翻转
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(11);
lt.push_back(12);
lt.push_back(13);
lt.push_back(14);
lt.push_back(15);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
lt.reverse();
for (auto& e:lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}

merge
合并列表
该算法将一个有序list容器加入另一个有序list容器中,且两个list容器必须都为逆序或顺序
unique
去重
前提条件就是: 相同的元素要站在一堆,最好的方式就是有序
splice
连接
把一个list容器的一些内容或者整个连接到另外一个list容器上面去,右边的list容器就变空了

list的模拟实现
前面我们实现过单链表和双向链表,这次我们模拟实现list和前面的类似
节点的类以及list的类,有两个
我们可以写一个命名空间里面进行
下面我们以这个图为例子

所以我们要创建一个节点类, list里面是一个链表,
节点类:
//节点类
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
public:
ListNode<T>* left;
ListNode<T>* rigth;
T val;
ListNode(const T& num = T())
:left(nullptr)
,rigth(nullptr)
,val(num)
{
}
bool operator==(const ListNode<T> n)
{
return this == &n;
}
};
跟我们刚开始 的C语言的节点写法一样,
迭代器的模拟
普通的迭代器
//迭代器
template<class T>
class _list_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* node;
_list_iterator(ListNode<T>* n)//需要注意的是这里尽量不要用引用
:node(n)
{
}
_list_iterator(const Self& n)
:node(n.node)
{
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
T& operator*()
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n)
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n)
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
在迭代器类的那里,我们不能使用地址来typedef,因为地址不连续,所以需要写一个迭代器类,迭代器类里面要进行运算符重载,必须重载* 、 != 、前后置++和–, 这里的迭代器只是一个普通的迭代器,如果要实现一个const迭代器就需要另外写法
const迭代器
我们明白const迭代器防止的是指向的内容不能修改,不是迭代器本身不能修改,所以不能在普通迭代器使用const关键字修饰
// const 迭代器
template<typename T>
class _list_const_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_const_iterator const_self;
typedef const_self Self;
Node const* node;//这里可以不添加const修饰
_list_const_iterator( const Node* n)
:node(n)
{
}
Self& operator++() //前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) //后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
const T& operator*() const
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n) const
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n) const
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
这是和普通类相似很多的写法,唯一不同的就是operator那里返回值不同,但是这种写法冗余了,图中的很多函数都加了const修饰this,让起不能修改this的成员,需要注意的就是使用const修饰this, 要知道this的成员是否要修改,根据情况来定,
我们要清楚: const迭代器有两个作用一个是迭代器本身可以修改,一个是其指向的内容不能被修改,如果简单理解为 const iterator就是const迭代器,是错误的,因为这样写只能说明 该值不能被修改,违背了const迭代器的第一个作用.
方法2:
在普通迭代器上再增加一个类型,用来控制operator的返回值
template<class T, class Ref>
class _list_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T,Ref> Self;
Node* node;
_list_iterator(ListNode<T>* n)
:node(n)
{
}
_list_iterator(const Self& n)
:node(n.node)
{
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
Ref& operator*()
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n)
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n)
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
反向迭代器
这里我使用的方法是适配器的方法,套一个外壳,只要传入不同的迭代器就可以实现对应的++、–等功能
// 反向迭代器, 使用适配器的方法
template<class T, class Ref,class Compart = _list_iterator<T, Ref>>
class _list_reverse__iterator
{
public:
typedef _list_reverse__iterator<T,Ref> Self;
_list_reverse__iterator(Compart cp)
:it(cp)
{
}
Self& operator++()
{
it--;
return *this;
}
/* Self& operator++()const
{
it--;
return *this;
}*/
Self operator++(int)
{
Compart ne = it;
it--;
return ne;
}
/* Self operator++(int)const
{
Compart ne = it;
it--;
return ne;
}*/
Self& operator--()
{
it++;
return it;
}
/* Self& operator--()const
{
it++;
return it;
}*/
Self operator--(int)
{
Compart ne = *this;
it++;
return ne;
}
/*Self operator--(int)const
{
Compart ne = *this;
it++;
return ne;
}*/
bool operator!=(const Self& iter)
{
return it != iter.it;
}
/*bool operator!=(const Self& iter)const
{
return it != iter.it;
}*/
bool operator==(const Self& iter)
{
return it == iter.it;
}
/* bool operator==(const Self& iter)const
{
return it == iter.it;
}*/
Ref& operator*()
{
return *it;
}
/*Ref& operator*()const
{
return *it;
}*/
private:
Compart it;
};
这里重载了const修饰的this指针的运算符,可以不看,这里的原理就是, 只要传入不同的迭代器,然后进行对应的操作, 所以说,反向迭代器的实现,就可以解决const反向迭代器的实现了,可以说一举多得
重载->
这里有一个好玩的点
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
class AA
{
public:
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
};
template<class T>
class BB
{
public:
T* operator->()
{
return &(this->t);
}
private:
T t;
};
}
int main()
{
bit::BB<bit::AA> t;
cout << t->a << endl;// t.operator->()->a
cout << t->b << endl;//t.operator->()->b
return 0;
}
需要注意的是这里这里c++会省略一个**->**,增加了可读性,这里本来有两个->,省略了一个,由此可见,我们如果要重载一个->就要注意了
list类:
//迭代器
template<class T>
class _list_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T> Self;
Node* node;
_list_iterator(ListNode<T>*& n)
:node(n)
{
}
_list_iterator(const Self& n)
:node(n.node)
{
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
T& operator*()
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n)
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n)
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
//记得我们模拟实现的list要有哨兵位
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T> iterator;
list()//初始化,创建哨兵位
{
_head = new Node();
_head->left = _head;
_head->rigth = _head;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete this->_head;
cout << "析构完毕" << endl;
}
list(list<T>& n)
{
//浅拷贝(容易野指针)
//this->_head = n._head;
_head = new Node();
_head->left = _head;
_head->rigth = _head;
for ( const auto& e : n)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& n)
{
Node* swapelem = this->_head;
this->_head = n._head;
n._head = swapelem;
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> n)
{
////方法1
//if (this != &n)
//{
// clear();
// for (const auto& e : n)
// {
// push_back(e);
// }
//}
//方法2
swap(n);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
pop_front();
it = begin();
}
}
void push_back(const T& num)
{
//方法1
/*Node* nextnode = new Node(num);
_head->left->rigth = nextnode;
_head->left = nextnode;
nextnode->rigth = _head;*/
//方法二
inset(end(), num);
}
iterator begin()
{
iterator it(_head->rigth);
return it;
// return _head->rigth 隐式类型转换
}
iterator end()
{
//隐式类型转换
return _head;
}
iterator inset(iterator pos, const T& num)
{
Node* cur = pos.node;//记得当前位置
Node* prev = cur->left;//上一个
Node* newnode = new Node(num);
newnode->rigth = cur;
cur->left = newnode;
newnode->left = prev;
prev->rigth = newnode;
return newnode;
}
void push_front(const T& num)
{
inset(begin(), num);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* prev = (pos.node)->left;
Node* next = (pos.node)->rigth;
prev->rigth = next;
next->left = prev;
delete pos.node;
return next;
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
我们需要注意的就是迭代器和list 的初始化,
总代码代码如下:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<istream>
#include<list>
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
//节点类
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
public:
ListNode<T>* left;
ListNode<T>* rigth;
T val;
ListNode(const T& num = T())
:left(nullptr)
, rigth(nullptr)
, val(num)
{
}
bool operator==(const ListNode<T> n)
{
return this == &n;
}
};
//迭代器
template<class T, class Ref>
class _list_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T, Ref> Self;
Node* node;
_list_iterator(ListNode<T>* n)
:node(n)
{
}
_list_iterator(const Self& n)
:node(n.node)
{
}
Self& operator++()//前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
Ref& operator*()
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n)
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n)
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
// 反向迭代器, 使用适配器的方法
template<class T, class Ref,class Compart = _list_iterator<T, Ref>>
class _list_reverse__iterator
{
public:
typedef _list_reverse__iterator<T,Ref> Self;
_list_reverse__iterator(Compart cp)
:it(cp)
{
}
Self& operator++()
{
it--;
return *this;
}
/* Self& operator++()const
{
it--;
return *this;
}*/
Self operator++(int)
{
Compart ne = it;
it--;
return ne;
}
/* Self operator++(int)const
{
Compart ne = it;
it--;
return ne;
}*/
Self& operator--()
{
it++;
return it;
}
/* Self& operator--()const
{
it++;
return it;
}*/
Self operator--(int)
{
Compart ne = *this;
it++;
return ne;
}
/*Self operator--(int)const
{
Compart ne = *this;
it++;
return ne;
}*/
bool operator!=(const Self& iter)
{
return it != iter.it;
}
/*bool operator!=(const Self& iter)const
{
return it != iter.it;
}*/
bool operator==(const Self& iter)
{
return it == iter.it;
}
/* bool operator==(const Self& iter)const
{
return it == iter.it;
}*/
Ref& operator*()
{
return *it;
}
/*Ref& operator*()const
{
return *it;
}*/
private:
Compart it;
};
// const 迭代器
template<typename T>
class _list_const_iterator
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_const_iterator const_self;
typedef const_self Self;
Node const* node;
_list_const_iterator(const Node*& n)
:node(n)
{
}
Self& operator++() //前置++
{
node = node->rigth;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int) //后置++
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->rigth;
return newnode;
}
Self& operator--()//前置--
{
node = node->left;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)//后置--
{
Self newnode(*this);
node = node->left;
return newnode;
}
const T& operator*() const
{
return this->node->val;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& n) const
{
return !(*this == n);
}
bool operator==(const Self& n) const
{
return node == n.node;
}
};
//记得我们模拟实现的list要有哨兵位
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef _list_iterator<T, T> iterator;
typedef _list_iterator<T, const T> const_iterator;
typedef _list_reverse__iterator<T, T,iterator> reverse_iterator;
typedef _list_reverse__iterator<T, const T,const_iterator> const_reverse_iterator;
list()//初始化,创建哨兵位
{
_head = new Node();
_head->left = _head;
_head->rigth = _head;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete this->_head;
cout << "析构完毕" << endl;
}
list(const list<T>& n)
{
//浅拷贝(容易野指针)
//this->_head = n._head;
_head = new Node();
_head->left = _head;
_head->rigth = _head;
for (const auto& e : n)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& n)
{
Node* swapelem = this->_head;
this->_head = n._head;
n._head = swapelem;
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> n)
{
////方法1
//if (this != &n)
//{
// clear();
// for (const auto& e : n)
// {
// push_back(e);
// }
//}
//方法2
swap(n);
return *this;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
pop_front();
it = begin();
}
}
void push_back(const T& num)
{
//方法1
/*Node* nextnode = new Node(num);
_head->left->rigth = nextnode;
_head->left = nextnode;
nextnode->rigth = _head;*/
//方法二
inset(end(), num);
}
iterator begin()
{
iterator it(_head->rigth);
return it;
// return _head->rigth 隐式类型转换
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
const_iterator it(_head->rigth);
return it;
}
reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return --end();
}
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const
{
return --end();
}
iterator end()
{
//隐式类型转换
return _head;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
const_iterator it(_head);
return it;
}
reverse_iterator rend()
{
//隐式类型转换
return end();
}
const_reverse_iterator rend()const
{
//隐式类型转换
return end();
}
iterator inset(iterator pos, const T& num)
{
Node* cur = pos.node;//记得当前位置
Node* prev = cur->left;//上一个
Node* newnode = new Node(num);
newnode->rigth = cur;
cur->left = newnode;
newnode->left = prev;
prev->rigth = newnode;
return newnode;
}
void push_front(const T& num)
{
inset(begin(), num);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* prev = (pos.node)->left;
Node* next = (pos.node)->rigth;
prev->rigth = next;
next->left = prev;
delete pos.node;
return next;
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
}
int main()
{
bit::list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(222);
bit::list<int> lt;
lt = lt1;
lt.push_front(10);
lt.push_front(12);
lt.push_front(13);
lt.push_front(14);
lt.push_front(15);
lt.push_front(16);
lt.pop_back();
lt.pop_front();
//bit::list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
//lt.erase(it);
//lt.clear();
//it = lt.begin();
//while (it != lt.end())
//{
// cout << *it << endl;
// it++;
//}
//it--;
//cout << *it-- << endl;
const bit::list<int> lt2(lt);
bit::list<int>::const_reverse_iterator const_it = lt2.rbegin();
while (const_it != lt2.rend())
{
cout << *const_it << endl;
const_it++;
}
//for (auto& e : lt2)
//{
// cout << e << endl;
//}
//for (const auto& e : lt)
//{
// cout << e << endl;
//}
return 0;
}