A. Square
题目链接:
Problem - A - Codeforces
思路:
题目比较简单:就是给你一个矩形的四个顶点的坐标,然后让你求矩形的面积,我们知道矩形的面积等于长乘宽,那么,如何就矩形的长和宽,长等于四个坐标中纵坐标的最大值-纵坐标的最小值, 宽等于四个坐标中横坐标的最大值-横坐标的最小值
代码实现:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int Maxx=-1000;
int Minx=1000;
int Maxy=-1000;
int Miny=1000;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
Maxx=max(Maxx,x);
Minx=min(Minx,x);
Maxy=max(Maxy,y);
Miny=min(Miny,y);
}
cout<<(Maxx-Minx)*(Maxy-Miny)<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B. Arranging Cats
原题链接:
Problem - B - Codeforces
题意翻译
给定一个只由 0/1 组成的字符串 b。你可以对这个字符串做以下操作,使得它最终变为另一个只有 0/1 组成的字符串 f(保证 b 和 f 长度相等):
- 如果 bi=0,将 bi 修改为 1;
- 如果 bi=1,将 bi 修改为 0;
- 如果 bi=1 且 bj=0,交换 bi 和 bj。
请你求出最少的修改次数。
思路:
贪心求解,我们有两个字符串b和f ,b串表示现在每个箱子的状态,f串是目标箱子的状态,我们用两个数字x和y, x表示需要移走的猫的数量,y表示需要添加的猫的数量,对于需要移走的数量不为0的情况下,优先让其去满足添加猫的数量,这样只用一次操作就可以满足两个位置,所以先内部满足,内部满足之后,如果还需要移走猫或者添加猫的话,直接加上需要移走猫的数目或者需要添加猫的数目
代码实现:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
string b,f;
cin>>b;
cin>>f;
int x=0; //需要移走的猫的数目
int y=0; //需要添加的猫的数目
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]=='1' && f[i]=='0') x++;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]=='0' && f[i]=='1') y++;
}
int ans=0;
while(x && y)
{
x--;
y--;
ans++;
}
ans+=x;
ans+=y;
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Sending Messages
题目描述
Stepan是一个busy的人。今天,他需要在 m1,m2,…mn 时刻发送 n 条信息。很惨的是,到 0 时刻,他的手机只剩 f 个单位电量。此时手机已开机。
手机每开机一时刻就会损失 a 个单位电量。此外,Stepan可以随时关闭手机,稍后再开机,每次共消耗 b 个单位的能量。开关机不花费任何时间,这样就可以在 x 时刻打开它,同时发送信息,反之,在 x 时刻发送信息同时关闭手机也是可以的。
如果在任何时候电量降至 0 以下,则手机自动关机,无法发送消息。Stepan想知道是否可以在不给手机充电的情况下发送所有信息。
思路:
我们只需要这n条消息都发送,然后看看发送完n条消息之后手机剩余的电量时候是大于0即可,若是小于等于0则说明无法完成发送n条消息,至于发送消息的间隔是否需要关机则看两次发送消息的间隔是否足够长即两次间隔的时间与每分钟耗电量的乘积 与 一次开关机耗电量进行比较,因为(m[i]- m[i-1])*a 可能会爆int 所以这道题 我们需要开 long long
代码实现:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int n,a,b;
long long f;
cin>>n>>f>>a>>b;
vector<long long> m(n+1);
m[0]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>m[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
f-=min(b*1LL,(m[i]-m[i-1])*a*1LL);
}
if(f<=0) cout<<"NO"<<endl;
else cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. Very Different Array
题目描述
Stepan is a very busy person. Today he needs to send nn messages at moments m1,m2,…mn ( mi<mi+1 ). Unfortunately, by the moment 00 , his phone only has f units of charge left. At the moment 0 , the phone is turned on.
The phone loses aa units of charge for each unit of time it is on. Also, at any moment, Stepan can turn off the phone and turn it on later. This action consumes bb units of energy each time. Consider turning on and off to be instantaneous, so you can turn it on at moment xx and send a message at the same moment, and vice versa, send a message at moment xx and turn off the phone at the same moment.
If at any point the charge level drops to 0 (becomes ≤0 ), it is impossible to send a message at that moment.
Since all messages are very important to Stepan, he wants to know if he can send all the messages without the possibility of charging the phone.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains a single integer tt ( 1≤t≤104 ) — the number of test cases. This is followed by the descriptions of the test cases.
The first line of each test case contains four integers n , f , a , and b ( 1≤n≤2⋅105 , 1≤f,a,b≤109 ) — the number of messages, the initial phone's charge, the charge consumption per unit of time, and the consumption when turned off and on sequentially.
The second line of each test case contains nn integers m1,m2,…,mn ( 1≤mi≤109 , mi<mi+1 ) — the moments at which messages need to be sent.
It is guaranteed that in a test the sum of nn over all test cases does not exceed 2⋅105.
输出格式
For each test case, output "YES" if Stepan can send all the messages, and "NO" otherwise.
You can output each letter in any case (lowercase or uppercase). For example, the strings "yEs", "yes", "Yes", and "YES" will be accepted as a positive answer.
题意翻译
给你一个长度为 n 的序列 a,和一个长度为 m 的序列 b,其中 m≥n。
你的任务是在 b 中选出 n 个数以任意顺序组成序列 c,使得 D=∑i=1n∣ai−ci∣ 最大。输出 D 即可。
多组测试数据,t≤100。
1≤n≤m≤2×105。
1≤ai,bi≤109。
思路:
排序加双指针来实现这道题,我们要从数组b的m个元素中选出n个构成数组c,使得数组c与数组a对应元素的差的绝对值的和最大,首先,先将a和b都按照从小到大进行排序,一定是最小和元素和最大的元素的差值是最大的,我们令一对指针分别指向a的左端和右端,另一对指针指向b的左端和右端,然后判断即可,具体实现看代码
代码实现:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<int> a(n);
vector<int> b(m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>b[i];
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
sort(b.begin(),b.end());
long long ans=0;
int i=0;
int j=n-1;
int l=0;
int r=m-1;
while(i<=j)
{
if(abs(a[i]-b[r])>abs(a[j]-b[l]))
{
ans+=abs(a[i]-b[r]);
i++;
r--;
}
else
{
ans+=abs(a[j]-b[l]);
l++;
j--;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. Eat the Chip:
原题链接:
Problem - E - Codeforces
题目描述
Alice and Bob are playing a game on a checkered board. The board has hh rows, numbered from top to bottom, and ww columns, numbered from left to right. Both players have a chip each. Initially, Alice's chip is located at the cell with coordinates (xa,ya) (row xa , column ya ), and Bob's chip is located at (xb,yb). It is guaranteed that the initial positions of the chips do not coincide. Players take turns making moves, with Alice starting.
On her turn, Alice can move her chip one cell down or one cell down-right or down-left (diagonally). Bob, on the other hand, moves his chip one cell up, up-right, or up-left. It is not allowed to make moves that go beyond the board boundaries.
More formally, if at the beginning of Alice's turn she is in the cell with coordinates (xa,ya)(xa,ya) , then she can move her chip to one of the cells (xa+1,ya) , (xa+1,ya−1) , or (xa+1,ya+1) . Bob, on his turn, from the cell (xb,yb) can move to (xb−1,yb) , (xb−1,yb−1)(xb−1,yb−1) , or (xb−1,yb+1) . The new chip coordinates (x′,y′) must satisfy the conditions 1≤x′≤h1≤x′≤h and 1≤y′≤w1≤y′≤w .
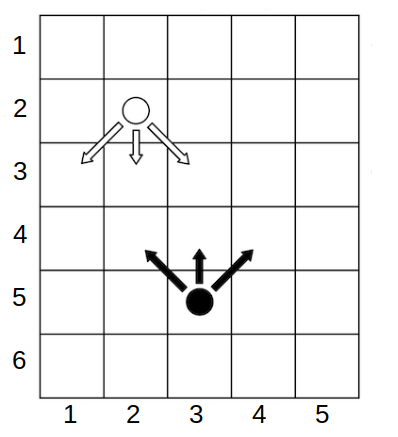
Example game state. Alice plays with the white chip, Bob with the black one. Arrows indicate possible moves. A player immediately wins if they place their chip in a cell occupied by the other player's chip. If either player cannot make a move (Alice—if she is in the last row, i.e. xa=h, Bob—if he is in the first row, i.e. xb=1 ), the game immediately ends in a draw.
What will be the outcome of the game if both opponents play optimally?
输入格式
Each test consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer t ( 1≤t≤104 ) — the number of test cases. This is followed by the description of the test cases.
Each test case consists of a single line containing six integers h , w , xa , ya , xb , yb ( 1≤xa,xb≤h≤106, 1≤ya,yb≤w≤109 ) — the dimensions of the board and the initial positions of Alice's and Bob's chips. It is guaranteed that either xa≠xb or ya≠yb .
It is guaranteed that the sum of hh over all test cases does not exceed 106106 .
输出格式
For each test case, output "Alice" if Alice wins, "Bob" if Bob wins, and "Draw" if neither player can secure a victory. You can output each letter in any case (lowercase or uppercase). For example, the strings "bOb", "bob", "Bob", and "BOB" will be accepted as Bob's victory.
题意翻译
有一个棋盘,上面有两个棋子,一个称作 a,一个称作 b,a 可以向下,左下,右下走,b 可以向上,左上,右上走。
如果一个棋子不能再走,即 aa 碰到了下边界或 bb 碰到了上边界则平局,输出 Draw。
如果一个棋子进入了对方当前所在格子,这一方直接胜利,a 胜利输出 Alice,b 胜利输出 Bob,保证双方初始所在位置不同。
棋盘大小 h×w,初始 a 的坐标为 (xa,ya),初始 b 的坐标为(xb,yb),a 先移动。多组数据。
数据范围 1≤xa,xb≤h≤106,1≤ya,yb≤w≤109,1≤T≤1041≤xa。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
12 6 5 2 2 5 3 4 1 2 1 4 1 1 4 1 3 1 1 5 5 1 4 5 2 4 4 1 1 4 4 10 10 1 6 10 8 10 10 2 6 10 7 10 10 9 1 8 1 10 10 8 1 10 2 10 10 1 1 2 1 10 10 1 3 4 1 10 10 3 1 1 1
输出 #1复制
Alice Bob Draw Draw Draw Alice Draw Draw Bob Alice Alice Draw
思路:
这道题是一道博弈论加贪心的题目,那么如何解决这道题目呢,首先我们由于Alice 只能往下走,Bob只能往上走,若是开始的时候 xb<=xa 的话,两个人最终的结果就是平局,Alice 在向 x=h 靠近走,Bob 在向 x=1 靠近走,开始时二人的差为 xb-xa , 然后得两个人彼此靠近,如果为偶数的话,xb-xa 为偶数的话,两个人各走 一半 的步伐, 若为奇数的话,Alice比Bob多走一步,因为Alice先手, 因此就是走了 (xb-xa+1)/ 2 呗,记 la 为Alice 向左走的最左端点的x的坐标,记ra 为Alice向右走的最右端的x的坐标 ,lb,rb同理为Bob 的, 如果是 xb-xa 为奇数的话,那么是Alice 追击 Bob ,如果Alice左右能到达的范围都比Bob 大的话,那么就是Alice赢,否则平局,奇数同理
代码实现:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int h,w,xa,ya,xb,yb;
cin>>h>>w>>xa>>ya>>xb>>yb;
if(xb<=xa)
{
cout<<"Draw"<<endl;
return;
}
else
{
int la=max(1,ya-(xb-xa+1)/2);
int ra=min(w,ya+(xb-xa+1)/2);
int lb=max(1,yb-(xb-xa)/2);
int rb=min(w,yb+(xb-xa)/2);
if((xb-xa)%2==1)
{
if(la<=lb && ra>=rb)
{
cout<<"Alice"<<endl;
return;
}
}
else
{
if(lb<=la && rb>=ra)
{
cout<<"Bob"<<endl;
return;
}
}
cout<<"Draw"<<endl;
return;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}