目录
- 问题引入
- [NOIP2001 提高组] 一元三次方程求解
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- 思路分析
- AC代码
- 思考
- 关于二分和三分
- 例题讲解
- 进击的奶牛
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 思路
- AC代码
- 平均数
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- 数据规模与约定
- AC代码
- Dropping Test
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- 【模板】三分 | 函数
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- AC代码
- Doremy's IQ
- 题面翻译
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例说明
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- AC代码
- Empty Graph
- 题面翻译
- 题目描述
- 输入格式
- 输出格式
- 样例 #1
- 样例输入 #1
- 样例输出 #1
- 提示
- AC代码
问题引入
首先我们来看一下这样一个问题
[NOIP2001 提高组] 一元三次方程求解
题目描述
有形如: a x 3 + b x 2 + c x + d = 0 a x^3 + b x^2 + c x + d = 0 ax3+bx2+cx+d=0 这样的一个一元三次方程。给出该方程中各项的系数( a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d 均为实数),并约定该方程存在三个不同实根(根的范围在 − 100 -100 −100 至 100 100 100 之间),且根与根之差的绝对值 ≥ 1 \ge 1 ≥1。要求由小到大依次在同一行输出这三个实根(根与根之间留有空格),并精确到小数点后 2 2 2 位。
提示:记方程 f ( x ) = 0 f(x) = 0 f(x)=0,若存在 2 2 2 个数 x 1 x_1 x1 和 x 2 x_2 x2,且 x 1 < x 2 x_1 < x_2 x1<x2, f ( x 1 ) × f ( x 2 ) < 0 f(x_1) \times f(x_2) < 0 f(x1)×f(x2)<0,则在 ( x 1 , x 2 ) (x_1, x_2) (x1,x2) 之间一定有一个根。
输入格式
一行, 4 4 4 个实数 a , b , c , d a, b, c, d a,b,c,d。
输出格式
一行, 3 3 3 个实根,从小到大输出,并精确到小数点后 2 2 2 位。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
1 -5 -4 20
样例输出 #1
-2.00 2.00 5.00
提示
【题目来源】
NOIP 2001 提高组第一题
思路分析
这道题的数据范围相当之小,用暴力就能过
AC代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
double a,b,c,d;
inline void check(double i){
double j=i+0.001;
double y1=a*i*i*i+b*i*i+c*i+d;
double y2=a*j*j*j+b*j*j+c*j+d;
if(y1>=0&&y2<=0||y1<=0&&y2>=0)
printf("%.2lf ",(i+j)/2);
}
int main() {
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c,&d);
for(double i=-100;i<=100;i+=0.001)check(i);
return 0;
}
思考
如果这道题的解空间再开打一下,开到1000,10000,那么暴力就一定过不去了
这时候就需要我们的二分法闪亮登场了
关于二分和三分
二分在下之前写过一篇博客讲解
戳这里
二分解决的问题都有一个共同的性质:单调性
而如果某个问题的解空间是单峰的,不管是向外凸还是向内凹,都可以用另一种算法解决,三分
顾名思义,三分就是一种把解空间分成三段的算法,答案一定在某个段内,时间是 l o g 3 ( n ) log_3(n) log3(n)但也是 O ( l o g ( n ) ) O(log(n)) O(log(n))的算法
简单来说,二分解决零点问题,三分解决极值问题
例题讲解
进击的奶牛
题目描述
Farmer John 建造了一个有 N N N( 2 ≤ N ≤ 1 0 5 2 \leq N \leq 10 ^ 5 2≤N≤105) 个隔间的牛棚,这些隔间分布在一条直线上,坐标是 x 1 , x 2 , ⋯ , x N x _ 1, x _ 2, \cdots, x _ N x1,x2,⋯,xN( 0 ≤ x i ≤ 1 0 9 0 \leq x _ i \leq 10 ^ 9 0≤xi≤109)。
他的 C C C( 2 ≤ C ≤ N 2 \leq C \leq N 2≤C≤N)头牛不满于隔间的位置分布,它们为牛棚里其他的牛的存在而愤怒。为了防止牛之间的互相打斗,Farmer John 想把这些牛安置在指定的隔间,所有牛中相邻两头的最近距离越大越好。那么,这个最大的最近距离是多少呢?
输入格式
第 1 1 1 行:两个用空格隔开的数字 N N N 和 C C C。
第 2 ∼ N + 1 2 \sim N+1 2∼N+1 行:每行一个整数,表示每个隔间的坐标。
输出格式
输出只有一行,即相邻两头牛最大的最近距离。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5 3
1
2
8
4
9
样例输出 #1
3
思路
二分每一种可能的间隔长度,检查是否符合条件
AC代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=100005;
int n,m,x[N];
template<typename T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;char c = getchar();int s = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') s = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {x = x*10 + c -'0';c = getchar();}
x*=s;
}
template<typename T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
return;
}
inline bool check(int d){
int cow=1;
int rgt=x[1]+d;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(x[i]<rgt)continue;
++cow;
rgt=x[i]+d;
}
return cow>=m;
}
int main(){
read(n),read(m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)read(x[i]);
sort(x+1,x+n+1);
int l=0,r=x[n]-x[1];
while(l<=r){
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid))l=mid+1;
else r=mid-1;
}
write(r);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
平均数
题目描述
给一个长度为 n n n 的数列,我们需要找出该数列的一个子串,使得子串平均数最大化,并且子串长度 ≥ m \ge m ≥m。
输入格式
第一行两个整数 n n n 和 m m m。
接下来 n n n 行,每行一个整数 a i a_i ai,表示序列第 i i i 个数字。
输出格式
一个整数,表示最大平均数的 1000 1000 1000 倍,如果末尾有小数,直接舍去,不要用四舍五入求整。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
10 6
6
4
2
10
3
8
5
9
4
1
样例输出 #1
6500
提示
数据规模与约定
- 对于 60 % 60\% 60% 的数据,保证 m ≤ n ≤ 1 0 4 m\le n\le 10^4 m≤n≤104;
- 对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据,保证 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 1 \leq m\le n\le 10^5 1≤m≤n≤105, 0 ≤ a i ≤ 2000 0\le a_i\le2000 0≤ai≤2000。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-10;
template<typename T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;char c = getchar();int s = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') s = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {x = x*10 + c -'0';c = getchar();}
x*=s;
}
template<typename T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
return;
}
int n,len,a[100010];
double b[100010],sum[100010];
int main(){
read(n),read(len);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)read(a[i]);
double l=-1e6,r=1e6,mid;
while(r-l>eps){
mid=(l+r)/2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
b[i]=a[i]-mid;
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+b[i];
}
double minn=1e9,tmp=-1e9;
for(int i=len;i<=n;i++){
minn=min(minn,sum[i-len]);
tmp=max(tmp,sum[i]-minn);
}
if(tmp>-eps)l=mid;
else r=mid;
}
cout<<(int)((r+eps)*1000)<<endl;
return 0;
}
Dropping Test
题目描述
在某个课程中,你需要进行 n n n 次测试。
如果你在共计 b i b_i bi 道题的测试 i i i 上的答对题目数量为 a i a_i ai,你的累积平均成绩就被定义为
100 × ∑ i = 1 n a i ∑ i = 1 n b i 100\times \dfrac{\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^n a_i}{\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^n b_i} 100×i=1∑nbii=1∑nai
给定您的考试成绩和一个正整数 k k k,如果您被允许放弃任何 k k k 门考试成绩,您的累积平均成绩的可能最大值是多少。
假设您进行了 3 3 3 次测试,成绩分别为 5 / 5 , 0 / 1 5/5,0/1 5/5,0/1 和 2 / 6 2/6 2/6。
在不放弃任何测试成绩的情况下,您的累积平均成绩是
100 × 5 + 0 + 2 5 + 1 + 6 = 50 100\times \frac{5+0+2}{5+1+6}=50 100×5+1+65+0+2=50
然而,如果你放弃第三门成绩,则您的累积平均成绩就变成了
100 × 5 + 0 5 + 1 ≈ 83.33 ≈ 83 100\times \frac{5+0}{5+1}\approx 83.33\approx 83 100×5+15+0≈83.33≈83
输入格式
输入包含多组测试用例,每个测试用例包含三行。
对于每组测试用例,第一行包含两个整数 n n n 和 k k k。
第二行包含 n n n 个整数,表示所有的 a i a_i ai。
第三行包含 n n n 个整数,表示所有的 b i b_i bi。
当输入用例 n = k = 0 n=k=0 n=k=0 时,表示输入终止,且该用例无需处理。
输出格式
对于每个测试用例,输出一行结果,表示在放弃 k k k 门成绩的情况下,可能的累积平均成绩最大值。
结果应四舍五入到最接近的整数。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3 1
5 0 2
5 1 6
4 2
1 2 7 9
5 6 7 9
0 0
样例输出 #1
83
100
提示
数据范围 1 ≤ n ≤ 1000 1 \le n \le 1000 1≤n≤1000, 0 ≤ k < n 0 \le k < n 0≤k<n, 0 ≤ a i ≤ b i ≤ 1 0 9 0 \le a_i \le b_i \le 10^9 0≤ai≤bi≤109。
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const double eps=1e-8;
int n,k;
double a[1010],b[1010],tmp[1010];
inline bool check(double m){
double cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
tmp[i]=a[i]-b[i]*m;
}
sort(tmp+1,tmp+1+n);
for(int i=n;i>k;i--){
cnt+=tmp[i];
}
return cnt>=0;
}
int main(){
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)){
if(n==0&&k==0)break;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%lf",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%lf",&b[i]);
double st=0,ed=100;
while(fabs(ed-st)>=eps){
double mid=st+(ed-st)/2;
if(check(mid))st=mid;
else ed=mid;
}
st*=100.0;
printf("%.0lf\n",st);
}
return 0;
}
【模板】三分 | 函数
题目描述
给定 n n n 个二次函数 f 1 ( x ) , f 2 ( x ) , … , f n ( x ) f_1(x),f_2(x),\dots,f_n(x) f1(x),f2(x),…,fn(x)(均形如 a x 2 + b x + c ax^2+bx+c ax2+bx+c),设 F ( x ) = max { f 1 ( x ) , f 2 ( x ) , . . . , f n ( x ) } F(x)=\max\{f_1(x),f_2(x),...,f_n(x)\} F(x)=max{f1(x),f2(x),...,fn(x)},求 F ( x ) F(x) F(x) 在区间 [ 0 , 1000 ] [0,1000] [0,1000] 上的最小值。
输入格式
输入第一行为正整数 T T T,表示有 T T T 组数据。
每组数据第一行一个正整数 n n n,接着 n n n 行,每行 3 3 3 个整数 a , b , c a,b,c a,b,c,用来表示每个二次函数的 3 3 3 个系数,注意二次函数有可能退化成一次。
输出格式
每组数据输出一行,表示 F ( x ) F(x) F(x) 的在区间 [ 0 , 1000 ] [0,1000] [0,1000] 上的最小值。答案精确到小数点后四位,四舍五入。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2
1
2 0 0
2
2 0 0
2 -4 2
样例输出 #1
0.0000
0.5000
提示
对于 50 % 50\% 50% 的数据, n ≤ 100 n\le 100 n≤100。
对于 100 % 100\% 100% 的数据, T < 10 T<10 T<10, n ≤ 1 0 4 \ n\le 10^4 n≤104, 0 ≤ a ≤ 100 0\le a\le 100 0≤a≤100, ∣ b ∣ ≤ 5 × 1 0 3 |b| \le 5\times 10^3 ∣b∣≤5×103, ∣ c ∣ ≤ 5 × 1 0 3 |c| \le 5\times 10^3 ∣c∣≤5×103。
AC代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#define eps 1e-10
using namespace std;
int n,t;
struct f{
int a,b,c;
}s[10005];
template<typename T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;char c = getchar();int s = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') s = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {x = x*10 + c -'0';c = getchar();}
x*=s;
}
template<typename T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
return;
}
inline double calc(double num){
double maxn=-1e9;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
maxn=max(maxn,s[i].a*num*num+s[i].b*num+s[i].c);
}
return maxn;
}
int main(){
read(t);
while(t--){
read(n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
read(s[i].a);
read(s[i].b);
read(s[i].c);
}
double l=0,r=1000,midl,midr;
while(r-l>eps){
midl=l+(r-l)/3,midr=r-(r-l)/3;
if(calc(midl)>calc(midr))l=midl;
else r=midr;
}
printf("%.4lf\n",calc(l));
}
return 0;
}
Doremy’s IQ
题面翻译
题目描述
哆来咪·苏伊特参加了 n n n 场比赛。 比赛 i i i 只能在第 i i i 天进行。比赛 i i i 的难度为 a i a_i ai。最初,哆来咪的 IQ 为 q q q 。 在第 i i i 天,哆来咪将选择是否参加比赛 i。只有当她当前的 IQ 大于 0 0 0 时,她才能参加比赛。
如果哆来咪选择在第 i i i 天参加比赛 i i i,则会发生以下情况:
- 如果 a i > q a_i>q ai>q,哆来咪会觉得自己不够聪明,所以 q q q 将会减 1 1 1;
- 否则,什么都不会改变。
如果她选择不参加比赛,一切都不会改变。哆来咪想参加尽可能多的比赛。请给哆来咪一个解决方案。
输入格式
第一行包含一个正整数 t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1\le t\le10^4 1≤t≤104) ,表示测试数据的组数。
第二行包含两个整数 n n n 和 q q q ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 1 0 5 1\le n\le10^5 1≤n≤105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 1 0 9 1\le q\le10^9 1≤q≤109),表示比赛次数和哆来咪最开始时的 IQ。
第三行包含 n n n 个整数 a 1 , a 2 ⋯ a n a_1,a_2⋯a_n a1,a2⋯an( 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1 0 9 1\le a_i≤10^9 1≤ai≤109),表示每场比赛的难度。
数据保证 n n n 之和不超过 1 0 5 10^5 105。
输出格式
对于每组数据,输出一个二进制字符串 s s s,如果哆来咪应该选择参加比赛 i i i,则 s i = 1 s_i=1 si=1,否则 s i = 0 s_i=0 si=0。 字符串中 1 1 1 的数量应该尽可能的多,并且当她的 IQ 为 0 0 0 或更低时,她不应该参加比赛。
如果有多个解决方案,你可以输出任意一个。
样例说明
在第一个测试用例中,哆来咪参加了唯一的比赛。她的 IQ 没有下降。
在第二个测试用例中,哆来咪参加了两个比赛。在参加比赛 2 2 2 后,她的 IQ 下降了 1 1 1。
在第三个测试用例中,哆来咪参加了比赛 1 1 1 和比赛 2 2 2。她的 IQ 在参加比赛 2 2 2 后降至 0 0 0,因此她无法参加比赛 3 3 3。
题目描述
Doremy is asked to test $ n $ contests. Contest $ i $ can only be tested on day $ i $ . The difficulty of contest $ i $ is $ a_i $ . Initially, Doremy’s IQ is $ q $ . On day $ i $ Doremy will choose whether to test contest $ i $ or not. She can only test a contest if her current IQ is strictly greater than $ 0 $ .
If Doremy chooses to test contest $ i $ on day $ i $ , the following happens:
- if $ a_i>q $ , Doremy will feel she is not wise enough, so $ q $ decreases by $ 1 $ ;
- otherwise, nothing changes.
If she chooses not to test a contest, nothing changes.Doremy wants to test as many contests as possible. Please give Doremy a solution.
输入格式
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer $ t $ ( $ 1\le t\le 10^4 $ ) — the number of test cases. The description of the test cases follows.
The first line contains two integers $ n $ and $ q $ ( $ 1 \le n \le 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le q \le 10^9 $ ) — the number of contests and Doremy’s IQ in the beginning.
The second line contains $ n $ integers $ a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_n $ ( $ 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 $ ) — the difficulty of each contest.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case, you need to output a binary string $ s $ , where $ s_i=1 $ if Doremy should choose to test contest $ i $ , and $ s_i=0 $ otherwise. The number of ones in the string should be maximum possible, and she should never test a contest when her IQ is zero or less.
If there are multiple solutions, you may output any.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
5
1 1
1
2 1
1 2
3 1
1 2 1
4 2
1 4 3 1
5 2
5 1 2 4 3
样例输出 #1
1
11
110
1110
01111
提示
In the first test case, Doremy tests the only contest. Her IQ doesn’t decrease.
In the second test case, Doremy tests both contests. Her IQ decreases by $ 1 $ after testing contest $ 2 $ .
In the third test case, Doremy tests contest $ 1 $ and $ 2 $ . Her IQ decreases to $ 0 $ after testing contest $ 2 $ , so she can’t test contest $ 3 $ .
AC代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
#define N 100000
int t,n,q,a[N+2],pos;
bool ans[N+2];
inline bool check(int x){
int w=q;
for(int i=x+1;i<=n;++i){
if(a[i]>w)--w;
}
return w>=0;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)scanf("%d",a+i);
for(int l=0,r=n,mid;l<=r;){
mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(check(mid)){
pos=mid;
r=mid-1;
}
else l=mid+1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=pos;++i){
if(a[i]<=q)ans[i]=true;
else ans[i]=false;
}
for(int i=pos+1;i<=n;++i)ans[i]=true;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)printf("%d",ans[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Empty Graph
题面翻译
给定一个长为 n n n 的序列 a a a。
定义一个 n n n 个点的无向完全图,点 l l l 和点 r r r 之间的距离为 min i ∈ [ l , r ] { a i } \min\limits_{i\in[l,r]}\{a_i\} i∈[l,r]min{ai}。
你可以进行 k k k 次操作,每次操作可以选定 ∀ i ∈ [ 1 , n ] \forall i \in [1,n] ∀i∈[1,n] 并将 a i a_i ai 赋值为一个 [ 1 , 1 0 9 ] [1,10^9] [1,109] 的整数。请最大化这个图的直径。
设 d ( u , v ) d(u,v) d(u,v) 表示 u u u 到 v v v 的最短路径长度,图的直径定义为 max 1 ≤ u < v ≤ n d ( u , v ) \max\limits_{1\leq u < v \leq n} d(u,v) 1≤u<v≤nmaxd(u,v)。
输出最大化的直径长度。
题目描述
— Do you have a wish?
— I want people to stop gifting each other arrays.
O_o and Another Young Boy
An array of $ n $ positive integers $ a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n $ fell down on you from the skies, along with a positive integer $ k \le n $ .
You can apply the following operation at most $ k $ times:
- Choose an index $ 1 \le i \le n $ and an integer $ 1 \le x \le 10^9 $ . Then do $ a_i := x $ (assign $ x $ to $ a_i $ ).
Then build a complete undirected weighted graph with $ n $ vertices numbered with integers from $ 1 $ to $ n $ , where edge $ (l, r) $ ( $ 1 \le l < r \le n $ ) has weight $ \min(a_{l},a_{l+1},\ldots,a_{r}) $ .
You have to find the maximum possible diameter of the resulting graph after performing at most $ k $ operations.
The diameter of a graph is equal to $ \max\limits_{1 \le u < v \le n}{\operatorname{d}(u, v)} $ , where $ \operatorname{d}(u, v) $ is the length of the shortest path between vertex $ u $ and vertex $ v $ .
输入格式
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 10^5 $ , $ 1 \le k \le n $ ).
The second line of each test case contains $ n $ positive integers $ a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n $ ( $ 1 \le a_i \le 10^9 $ ).
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all test cases does not exceed $ 10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case print one integer — the maximum possible diameter of the graph after performing at most $ k $ operations.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
6
3 1
2 4 1
3 2
1 9 84
3 1
10 2 6
3 2
179 17 1000000000
2 1
5 9
2 2
4 2
样例输出 #1
4
168
10
1000000000
9
1000000000
提示
In the first test case, one of the optimal arrays is $ [2,4,5] $ .
The graph built on this array:
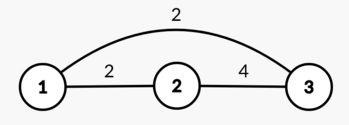 $ \operatorname{d}(1, 2) = \operatorname{d}(1, 3) = 2 $ and $ \operatorname{d}(2, 3) = 4 $ , so the diameter is equal to $ \max(2,2,4) = 4 $ .
$ \operatorname{d}(1, 2) = \operatorname{d}(1, 3) = 2 $ and $ \operatorname{d}(2, 3) = 4 $ , so the diameter is equal to $ \max(2,2,4) = 4 $ .
AC代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
typedef long long ll ;
ll t,n,k,a[N],pre[N],sub[N];
template<typename T>
inline void read(T &x)
{
x=0;char c = getchar();ll s = 1;
while(c < '0' || c > '9') {if(c == '-') s = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') {x = x*10 + c -'0';c = getchar();}
x*=s;
}
template<typename T>
inline void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
putchar('-'),x=-x;
if(x>9)
write(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
return;
}
inline bool check(ll pos){
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
pre[i]=pre[i-1]+(ll)((a[i]<<1)<pos);
for(ll i=n;i;i--)
sub[i]=sub[i+1]+(ll)((a[i]<<1)<pos);
ll minx=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(ll i=1;i<n;i++)
minx=min(minx,pre[i-1]+sub[i+2]+(ll)(a[i] < pos) + (ll)(a[i + 1] < pos));
return minx<=k;
}
int main(){
read(t);
while (t--) {
read(n),read(k);
memset(pre, 0, sizeof(pre));
memset(sub, 0, sizeof(sub));
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) read(a[i]);
ll l = 0, r = 1e9, ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
ll mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
l=mid+1;
ans=mid;
}
else r = mid-1;
}
write(ans);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
这是我的第十二篇文章,如有纰漏也请各位大佬指正
辛苦创作不易,还望看官点赞收藏打赏,后续还会更新新的内容。