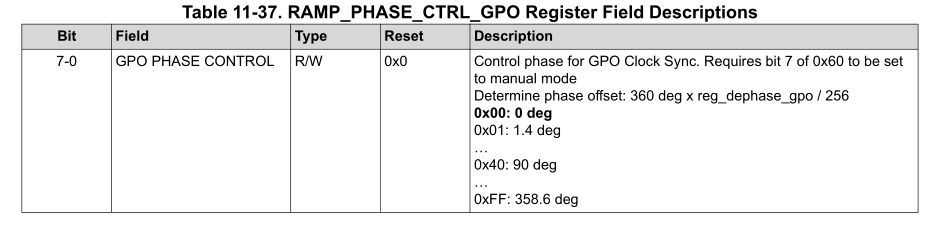
测试可能不是很方便,希望采集一次数据后期还可以使用,这里提供一个案例:
数据写入fosepose.csv
//write.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdint>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
// 定义 FusePose 结构体
typedef struct FusePose_ {
uint64_t time_stamp;
float x;
float y;
float yaw;
} FusePose;
// 函数来写入 FusePose 数据到 CSV 文件
void writeToCSV(const std::string& filename, const FusePose& pose) {
std::ofstream file;
// 打开文件以追加模式
file.open(filename, std::ios::app);
if (!file.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "无法打开文件 " << filename << std::endl;
return;
}
// 将数据写入文件
file << pose.time_stamp << ','
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(6) << pose.x << ','
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(6) << pose.y << ','
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(6) << pose.yaw << '\n';
file.close();
}
int main() {
std::string filename = "fosepose.csv";
// 打开 CSV 文件并写入表头
std::ofstream file;
file.open(filename, std::ios::trunc);
if (file.is_open()) {
file << "time_stamp,x,y,yaw\n";
file.close();
}
// 模拟接收实时数据的循环
while (true) {
// 生成模拟的 FusePose 数据
FusePose pose;
pose.time_stamp = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
pose.x = static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX * 10.0f; // 模拟 x 值
pose.y = static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX * 10.0f; // 模拟 y 值
pose.yaw = static_cast<float>(rand()) / RAND_MAX * 360.0f; // 模拟 yaw 值
// 将数据写入 CSV 文件
writeToCSV(filename, pose);
// 等待 1 秒钟再接收下一条数据
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1));
}
return 0;
}
读数据,并显示
//read.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
// 定义 FusePose 结构体
typedef struct FusePose_ {
uint64_t time_stamp;
float x;
float y;
float yaw;
} FusePose;
// 从 CSV 文件中读取 FusePose 数据
std::vector<FusePose> readFusePosesFromCSV(const std::string& filename) {
std::vector<FusePose> poses;
std::ifstream file(filename);
std::string line;
if (!file.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "无法打开文件 " << filename << std::endl;
return poses;
}
// 跳过表头
std::getline(file, line);
while (std::getline(file, line)) {
std::istringstream iss(line);
std::string token;
FusePose pose;
std::getline(iss, token, ',');
pose.time_stamp = std::stoull(token);
std::getline(iss, token, ',');
pose.x = std::stof(token);
std::getline(iss, token, ',');
pose.y = std::stof(token);
std::getline(iss, token, ',');
pose.yaw = std::stof(token);
poses.push_back(pose);
}
file.close();
return poses;
}
int main() {
std::string filename = "fosepose.csv";
auto poses = readFusePosesFromCSV(filename);
// 使用 OpenCV 创建一个窗口来显示结果
cv::namedWindow("Pose Points", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::Mat image = cv::Mat::zeros(800, 800, CV_8UC3); // 创建一个 800x800 的黑色图像
// 绘制点
for (const auto& pose : poses) {
// 假设 x 和 y 的值在 0 到 10 之间,将它们映射到图像坐标中
int x_pos = static_cast<int>(pose.x * 80); // 映射 x 到图像宽度范围
int y_pos = static_cast<int>(pose.y * 80); // 映射 y 到图像高度范围
// 使用绿色绘制点
cv::circle(image, cv::Point(x_pos, 800 - y_pos), 5, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
// 显示图像
cv::imshow("Pose Points", image);
cv::waitKey(0); // 等待用户按键
return 0;
}
//g++ -o readshow readshow.cpp `pkg-config --cflags --libs opencv4`
效果