Vue2-Vuex基础
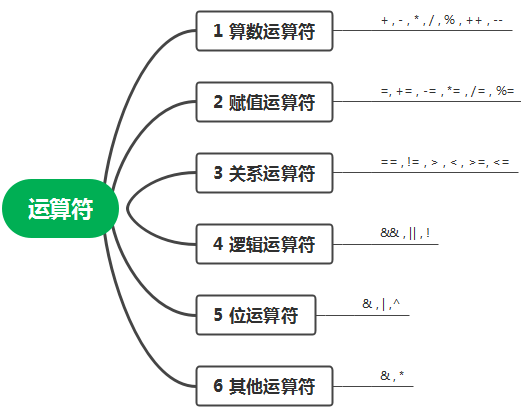
1.Vuex基本概念
在复杂的前端应用程序中,状态管理变得至关重要。Vuex 是 Vue.js 官方提供的状态管理模式和库,它能帮助我们更好地管理应用程序的状态并实现组件间的通信。本文将介绍 Vuex 的基本概念、核心概念和实际应用。
什么是 Vuex?
Vuex 是专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它借鉴了 Flux 和 Redux 的理念,将应用程序的状态抽象出来,集中管理在一个全局的 store 中。这样做的好处是:
- 集中化管理状态:将所有组件的共享状态抽取出来,单独管理,使得状态变化更加可控和可预测。
- 更方便的状态共享:不需要通过 props 或事件来传递状态,任何组件都可以访问状态。
- 易于调试:通过时间旅行工具(Vue Devtools)可以方便地查看状态的变化历史。
Vuex与localStorage,sessionStorage区别?
vuex 可以在多个组件之间共享数据,并且共享的数据是【响应式】的,即数据的变更能及时渲染到模板
与之对比 localStorage 与 sessionStorage 也能共享数据,但缺点是数据并非【响应式】
2.Vuex基本使用方式
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
},
getters: {
},
mutations: {
},
actions: {
},
modules: {
}
})
new Vuex.Store({})创建了一个新的 Vuex Store 实例,并导出这个实例作为默认的导出。- 在
state,getters,mutations,actions, 和modules这些选项中,你可以定义应用程序的状态管理逻辑:- state: 定义应用的状态数据。可以在这里声明需要全局共享的数据。
- getters: 类似于计算属性,用来从 store 中的 state 中派生出一些状态。
- mutations: 定义同步修改 state 的方法。每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的事件类型 (type) 和 一个回调函数 (handler)。
- actions: 类似于 mutations,但是 actions 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。可以用来异步操作。
- modules: 允许将 store 分割成模块。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutations、actions、getters 等。
3.Vuex入门案例
动态显示修改后的用户名称
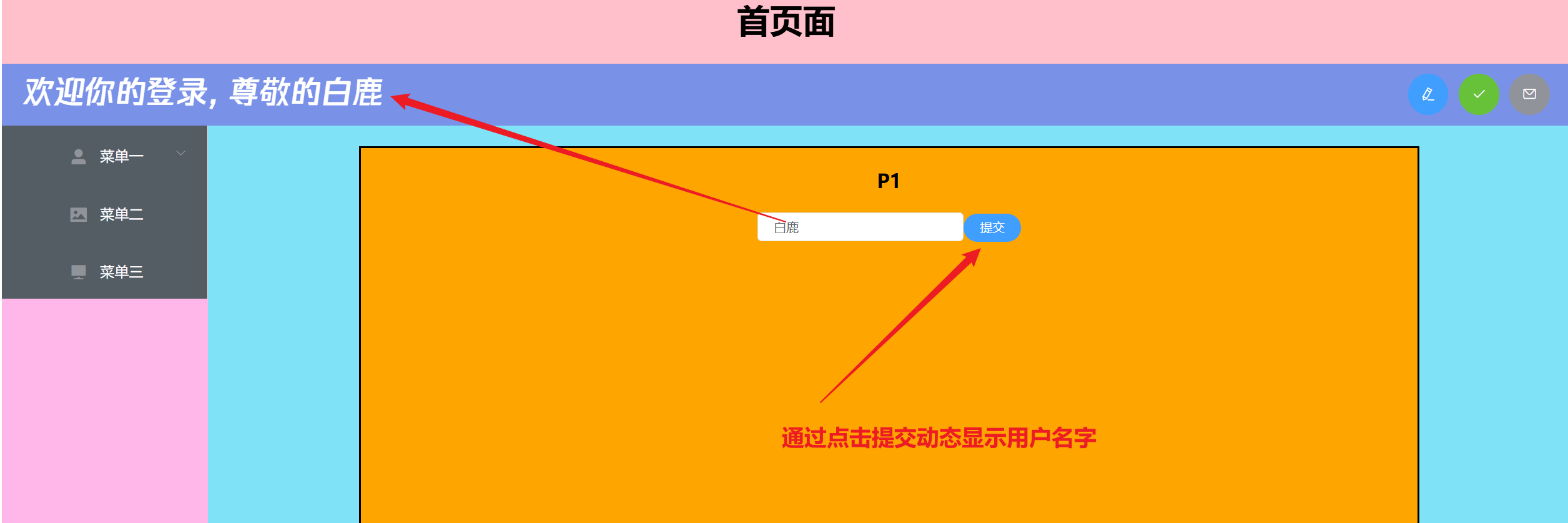
- 首页面基础代码
<template>
<div class="index">
<h1>首页面</h1>
<el-container>
<el-header>
<div class="header1">
欢迎你的登录, 尊敬的
</div>
<div class="header3">
<el-button
type="primary"
icon="el-icon-edit"
circle
@click="jump('/c/p1')"
></el-button>
<el-button
type="success"
icon="el-icon-check"
circle
@click="jump('/c/p2')"
></el-button>
<el-button
type="info"
icon="el-icon-message"
circle
@click="jump('/c/p3')"
></el-button>
</div>
</el-header>
<el-container>
<el-aside width="200px">
<el-menu
router
background-color="#545c64"
text-color="#fff"
active-text-color="#ffd04b"
>
<el-submenu index="">
<span slot="title">
<i class="el-icon-user-solid"></i>
菜单一
</span>
<el-menu-item index="/c/p1">子项1</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="/c/p2">子项2</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item index="/c/p3">子项3</el-menu-item>
</el-submenu>
<el-menu-item>
<span slot="title">
<i class="el-icon-picture"></i>
菜单二
</span>
</el-menu-item>
<el-menu-item>
<span slot="title">
<i class="el-icon-s-platform"></i>
菜单三
</span>
</el-menu-item>
</el-menu>
</el-aside>
<el-main>
<router-view></router-view>
</el-main>
</el-container>
</el-container>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
methods: {
jump(url) {
const currentPath = this.$route.path;
if (currentPath !== url) {
this.$router.push(url);
}
},
},
};
export default options;
</script>
<style scoped>
.index {
background: pink;
text-align: center;
width: auto;
height: 100vh;
}
.el-header {
background: rgb(121, 145, 231);
}
.el-aside {
background: rgb(255, 183, 233);
height: 100vh;
}
.el-main {
background: rgb(128, 226, 246);
height: 100vh;
}
.router-link {
display: inline-block;
padding: 10px 15px;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-top: 5px;
width: 150px;
text-decoration: none;
color: #333; /* 链接文本颜色 */
background-color: #f0f0f0; /* 背景色 */
border: 1px solid #ccc; /* 边框 */
border-radius: 5px; /* 圆角 */
transition: background-color 0.3s, color 0.3s; /* 过渡效果 */
/* 其他样式属性可以根据需要添加 */
}
/* 鼠标悬停时的样式 */
.router-link:hover {
background-color: #e0e0e0;
color: #555;
}
/* 激活状态的样式 */
.router-link.active {
background-color: #007bff; /* 激活时的背景色 */
color: #fff; /* 激活时的文本颜色 */
border-color: #007bff; /* 激活时的边框颜色 */
}
.header1 {
font-size: 30px;
font-family: "腾讯体";
color: white;
float: left;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.header3 {
margin-top: 10px;
float: right;
}
</style>
- P1页面基础代码
<template>
<div class="error">
<h1>P1</h1>
<el-input placeholder="请输入用户名" size="mini" v-model="name"></el-input>
<el-button type="primary" round size="mini" @click="updateName">提交</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
const options = {
data() {
return {
name: "",
};
},
methods: {
updateName() {
},
},
};
export default options;
</script>
<style scoped>
.error {
background: orange;
text-align: center;
border: 2px solid black;
width: 80%;
height: 700px;
margin: 0px auto; /* 左右外边距设置为auto,实现水平居中 */
}
.el-input {
width: 200px;
}
</style>
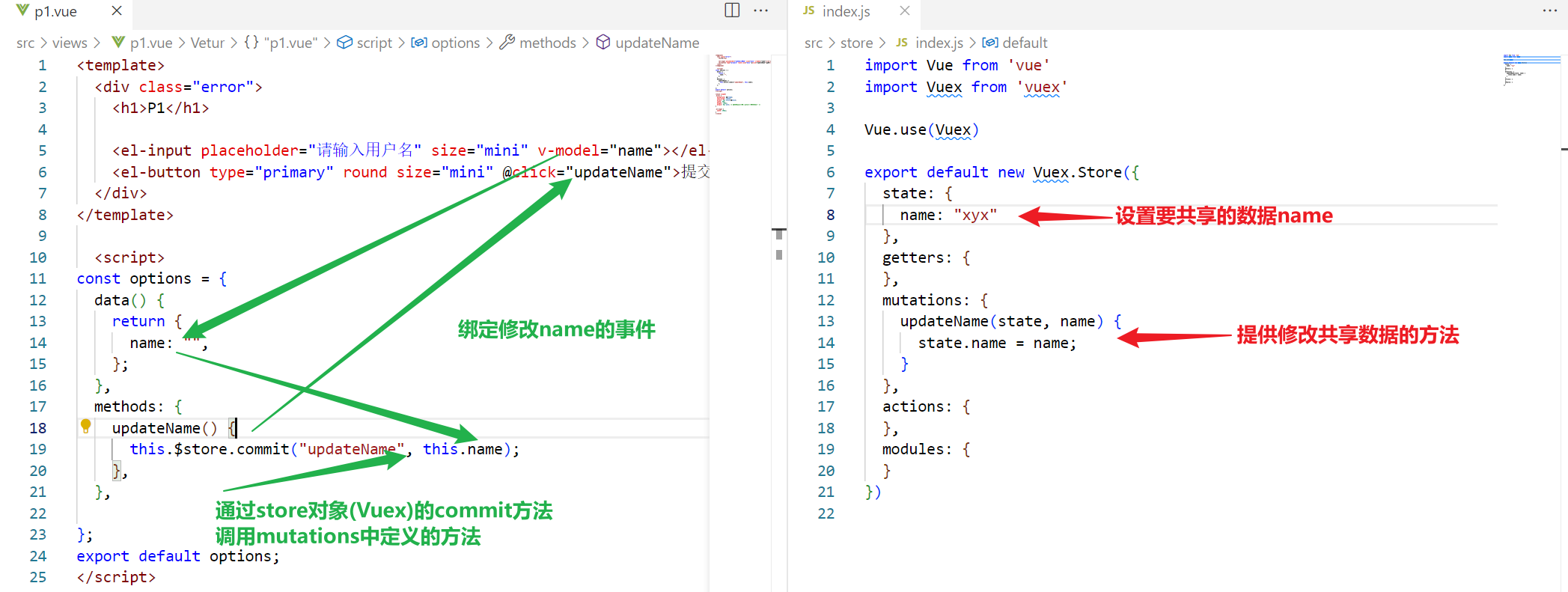
- 编写store内容($store.commit(“方法名”, [方法参数列表]))
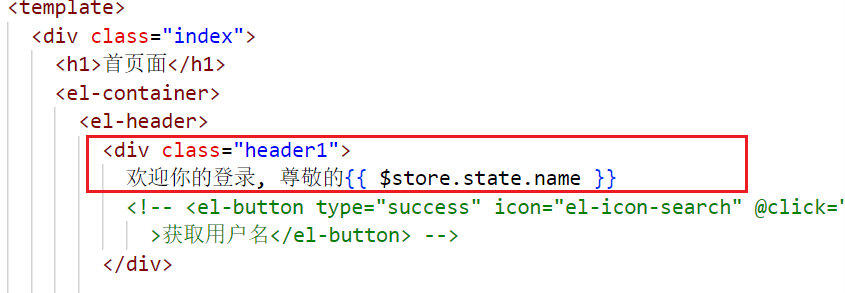
- 显示store的内容($store.state.共享的属性名)
4.mapState-优化共享属性的获取
mapState 是 Vuex 提供的一个辅助函数,用于在组件中获取 Vuex store 中的 state。它的作用是帮助简化从 Vuex store 中获取状态数据的过程,特别是在组件中需要使用多个状态时,可以减少代码的重复性和提高可读性。
//因为被共享的属性常常使用,需要每次从$store中获取,因此可以用计算属性优化这一操作
const options = {
computed : {
name() {
return this.$store.state.name;
}
}
}
//因为每次获取属性均是此代码,因此可以使用Vuex提供的方法获取
const options = {
computed : mapState(["name"])
}
//或者使用展开函数
const options = {
computed : {
...mapState(["name"])
},
}
5.mapMutations-优化修改函数的获取
mapMutations 是 Vuex 提供的一个辅助函数,用于在组件中映射 Vuex store 中的 mutations。它的作用是帮助简化在组件中提交 mutation 的过程,特别是在需要在组件中提交多个 mutation 时,可以减少代码的重复性和提高可读性。
//旧的获取修改函数的方法
const options = {
data() {
return {
name: "",
};
},
methods: {
updateName() {
this.$store.commit("updateName", this.name);
},
},
}
//通过mapMutations解决:通过展开函数将updateName作为methods对象的方法
import { mapMutations } from "vuex";
const options = {
data() {
return {
name: "",
};
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(["updateName"]),
},
};
export default options;
6.Actions方法-处理异步请求的方法
在Vue.js中,特别是与Vuex一起使用时,Actions是Vuex中的一种核心概念。Actions用于处理异步操作,例如调用API、获取数据,然后提交(commit)mutation来修改状态。Actions是通过store.dispatch方法来触发的,而不是直接调用mutation来修改状态。
动态获取名字并展示到页面

- 通过dispatch方法获取actions中的方法
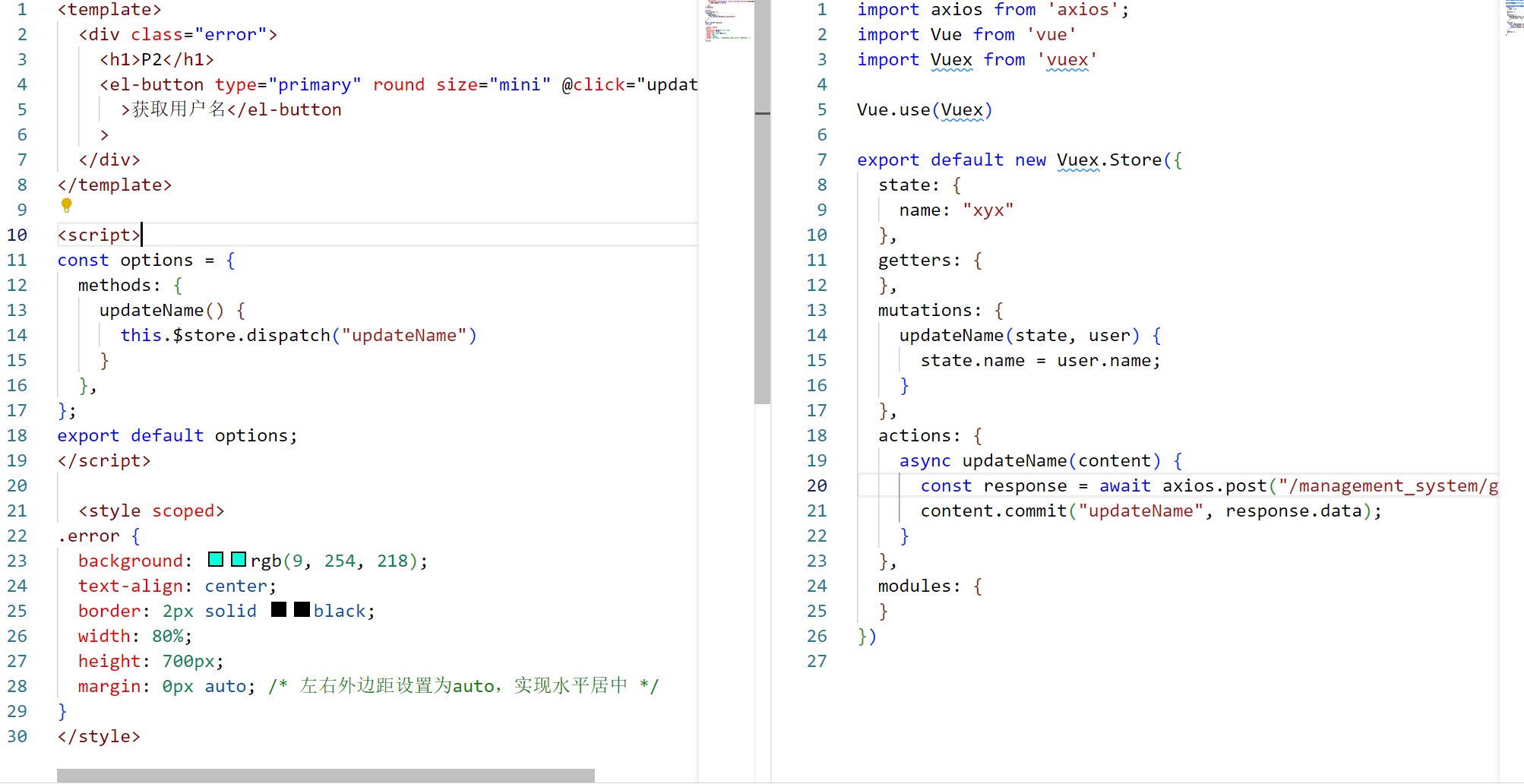
- 优化操作:通过mapActions获取actions中的方法
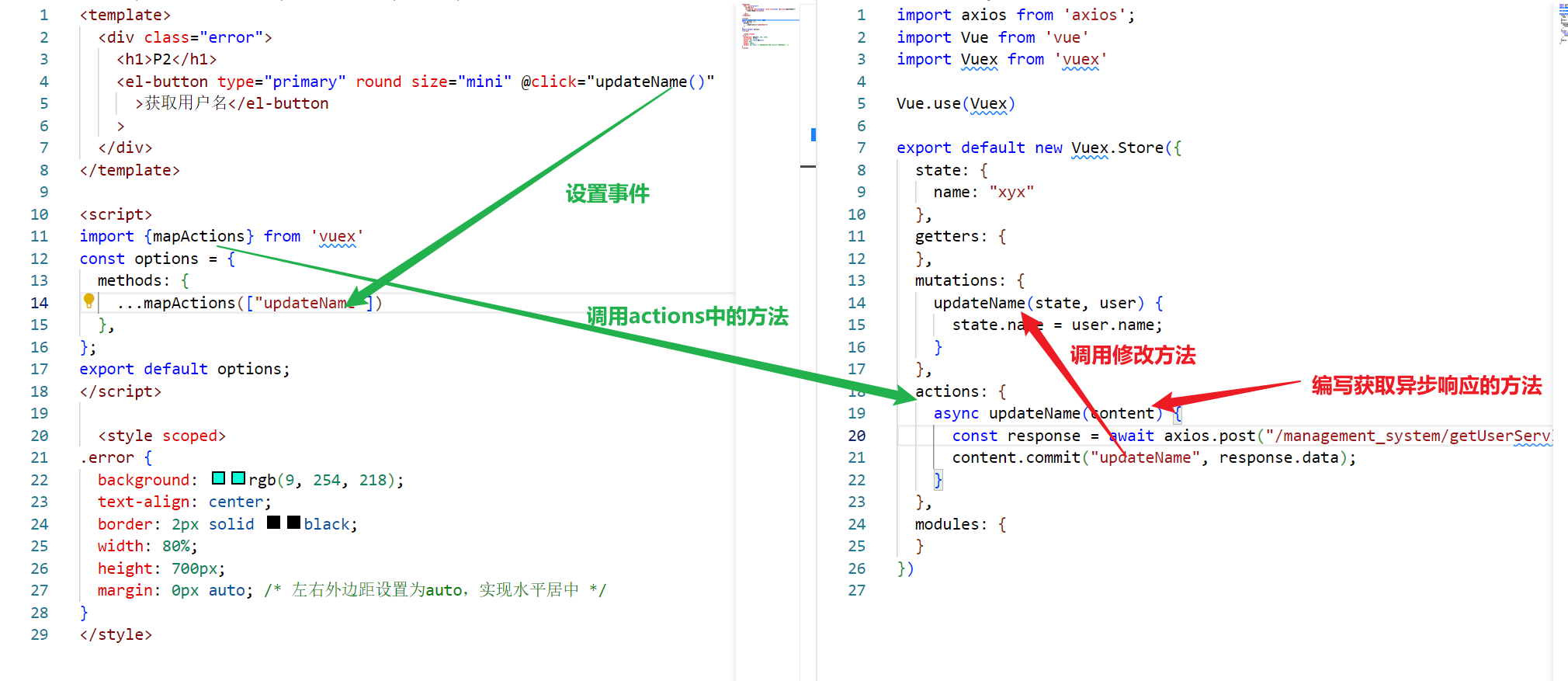
- 案例中服务器代码
package com.tyut.controller;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
@WebServlet("/getUserServlet")
public class GetUserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
response.addHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "http://localhost:7070");
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String[] nameList = {"张三", "李四", "王五", "赵六"};
int index = (int) (Math.random() * 10) % 4;
String name = nameList[index];
String jsonString = "{\"name\":\"" + name + "\"}";
out.write(jsonString);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}