背景
一般来说SpringCloud Gateway到后面服务的路由属于内网交互,因此路由方式是否是Https就显得不是那么重要了。事实上也确实如此,大多数的应用开发时基本都是直接Http就过去了,不会一开始就是直接上Https。然而随着时间的推移,项目规模的不断扩大,当被要求一定要走Https时,就会面临一种困惑:将所有服务用一刀切的方式改为Https方式监听,同时还要将网关服务所有的路由方式也全部切为Https方式,一旦生产环境上线出问题将要面临全量服务的归滚,这时运维很可能跳出来说:生产环境几十个服务,每个服务最少2个节点,全量部署和回滚不可能在短时间完成。另外测试同学也可能会说,现在没有全量接口自动化回归测试工具,做一个次人工的全量接口回归测试也不现实。因此在这种情况下最稳妥的方式是实现:SpringCloud Gateway & SpringBoot RestController Http/Https双支持,这样可以做到分批分次进行切换,那么上面的困惑自然也就不存在了。
1. SpringBoot Http/Https监听双支持
1.1 代码实现
为了不对原来的Http监听产生任何影响,因此需要保障以下两点:
1、原主端口(server.port)监听什么都不变,监听方式仍为http,附加端口监听方式为https。(需要绕开的问题是:如果一个服务有多个监听端口,主端口会优先选择https方式)
2、附加端口不进行nacos服务注册(主要的考虑点还是不对原来的http监听和路由产生任何影响,这里我的方案是https监听端口号为http端口+10000)。
这样就能实现SpringBoot服务主端口Http监听,附加端口Https监听。
实现代码如下:
import org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector;
import org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* HttpsConnectorAddInConfiguration
*
* @author chenx
*/
@Configuration
public class HttpsConnectorAddInConfiguration {
private static final int HTTPS_PORT_OFFSET = 10000;
@Value("${server.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${additional-https-connector.ssl.key-store:XXX.p12}")
private String keyStore;
@Value("${additional-https-connector.ssl.key-store-password:XXX}")
private String keyStorePassword;
@Value("${additional-https-connector.ssl.key-store-type:PKCS12}")
private String keyStoreType;
@Value("${additional-https-connector.ssl.enabled:false}")
private boolean enabled;
@Bean
public WebServerFactoryCustomizer<TomcatServletWebServerFactory> servletContainer() {
return server -> {
if (!this.enabled) {
return;
}
Connector httpsConnector = this.createHttpsConnector();
server.addAdditionalTomcatConnectors(httpsConnector);
};
}
/**
* createHttpsConnector
*
* @return
*/
private Connector createHttpsConnector() {
Connector connector = new Connector(TomcatServletWebServerFactory.DEFAULT_PROTOCOL);
connector.setScheme("https");
connector.setPort(this.port + HTTPS_PORT_OFFSET);
connector.setSecure(true);
Http11NioProtocol protocol = (Http11NioProtocol) connector.getProtocolHandler();
protocol.setSSLEnabled(true);
protocol.setKeystoreFile(this.keyStore);
protocol.setKeystorePass(this.keyStorePassword);
protocol.setKeystoreType(this.keyStoreType);
protocol.setSslProtocol("TLS");
return connector;
}
}
备注:
1、上述代码中的配置默认值大家自行修改(key-store:XXX.p12,key-store-password:XXX),如果觉得配置additional-https-connector相关配置命名不合适也可自行修改。当配置好additional-https-connector相关配置(additional-https-connector.ssl.enabled是一个https附加端口监听的开关),启动服务就可以看到类似如下的日志,同时查看nacos中的服务实例也会发现并没有进行https端口的服务注册;
2、这里我用的是p12自签证书,证书需要放到项目的resouces目录下(可以用keytool -genkey命令去生成一个)。

1.2 配置
配置示例如下,keyStore、keyStorePassword、keyStoreType使用代码中的默认值,需要更换证书的时候再进行配置。
server:
port: 9021
tomcat:
min-spare-threads: 400
max-threads: 800
additional-https-connector:
ssl:
enabled: true
2. SpringCloud Gateway Http/Https路由双支持
思路:在网关服务增加自定义配置(HttpsServiceConfig)来定义需要切换为https路由的服务列表,然后使用过滤器(HttpsLoadBalancerFilter)进行转发uri的https重写;
这样就能实现在配置列表中的服务进行Https路由,否则保持原有Https路由。
2.1 代码实现
- HttpsServiceConfig
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.cloud.endpoint.event.RefreshEvent;
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* HttpsServiceConfig
*
* @author chenx
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
@RefreshScope
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "bw.gateway")
public class HttpsServiceConfig {
private List<String> httpsServices;
private Set<String> httpsServiceSet = new HashSet<>();
public List<String> getHttpsServices() {
return this.httpsServices;
}
public void setHttpsServices(List<String> httpsServices) {
this.httpsServices = httpsServices;
this.updateHttpsServices();
}
public Set<String> getHttpsServiceSet() {
return this.httpsServiceSet;
}
/**
* handleRefreshEvent
*/
@EventListener(RefreshEvent.class)
public void handleRefreshEvent() {
this.updateHttpsServices();
}
/**
* updateHttpsServices
*/
private void updateHttpsServices() {
this.httpsServiceSet = CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(this.httpsServices) ? new HashSet<>(this.httpsServices) : new HashSet<>();
log.info("httpsServiceSet updated, httpsServiceSet.size() = {}", this.httpsServiceSet.size());
}
}
- HttpsLoadBalancerFilter
import com.beam.work.gateway.common.FilterEnum;
import com.beam.work.gateway.config.HttpsServiceConfig;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.ServiceInstance;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.Route;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.ServerWebExchangeUtils;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* HttpsLoadBalancerFilter
*
* @author chenx
*/
@Slf4j
@RefreshScope
@Component
public class HttpsLoadBalancerFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private static final int HTTPS_PORT_OFFSET = 10000;
private final LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
@Autowired
private HttpsServiceConfig httpsServiceConfig;
public HttpsLoadBalancerFilter(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) {
this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return FilterEnum.HTTPS_LOAD_BALANCER_FILTER.getCode();
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
Route route = exchange.getAttribute(ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_ROUTE_ATTR);
boolean isRewriteToHttps = Objects.nonNull(route) && this.httpsServiceConfig.getHttpsServiceSet().contains(route.getId());
if (isRewriteToHttps) {
ServiceInstance instance = this.loadBalancer.choose(route.getUri().getHost());
if (Objects.nonNull(instance)) {
URI originalUri = exchange.getRequest().getURI();
URI httpsUri = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUri(originalUri)
.scheme("https")
.host(instance.getHost())
.port(instance.getPort() + HTTPS_PORT_OFFSET)
.build(true)
.toUri();
log.info("HttpsLoadBalancerFilter RewriteToHttps: {}", httpsUri.toString());
exchange.getAttributes().put(ServerWebExchangeUtils.GATEWAY_REQUEST_URL_ATTR, httpsUri);
}
}
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
}
备注:
1、这里实现了配置的刷新,因此需要进行服务的https路由切换时只需修改配置即可,而网关服务不需要重启;
2、过滤器使用Set进行判断,效率上肯定优于对List的遍历查找;
3、过滤器的Order建议放到最后,因此可以直接使用Integer.MAX_VALUE(我们的项目中有多个过滤器,并且通过FilterEnum枚举去统一管理);
2.2 配置
配置示例:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
enabled: true
httpclient:
ssl:
use-insecure-trust-manager: true
connect-timeout: 10000
response-timeout: 120000
pool:
max-idle-time: 15000
max-life-time: 45000
evictionInterval: 5000
routes:
- id: bw-star-favorite
uri: lb://bw-star-favorite
order: -1
predicates:
- Path=/star-favoritear/v1/**
bw:
gateway:
xssRequestFilterEnable: false
xssResponseFilterEnable: false
httpsServices:
- bw-star-favorite
备注:
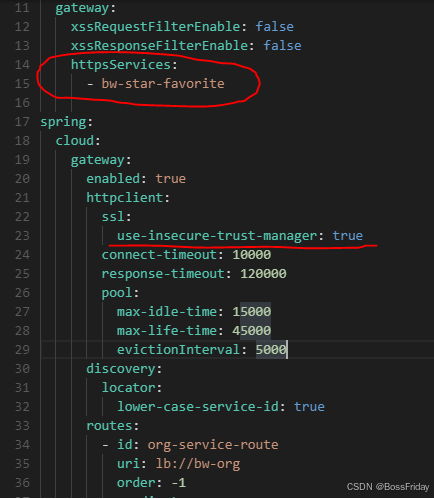
1、需要变更的配置为:
- 开启ssl信任(spring.cloud.gateway.httpclient.ssl):
- 设置https路由服务列表(bw.gateway.httpsServices)
结束语
通过上述两步就能实现SpringCloud Gateway & SpringBoot RestController Http/Https双支持,严谨的做法是还需要将FeignClient的调用进行Https化,上面的实现方式中之所以不对https端口进行注册的原因就是避免Http方式的FeignClient去调用Https目标端口从而引发问题。关于FeignClient的Https切换实际上也可以借鉴网关的思路将请求uri重写为端口号+10000的https请求即可。
那么通过这个思路就可以实现:服务的分批、FeignClient分步Https路由切换,从而保障整个割接风险可控和平滑。