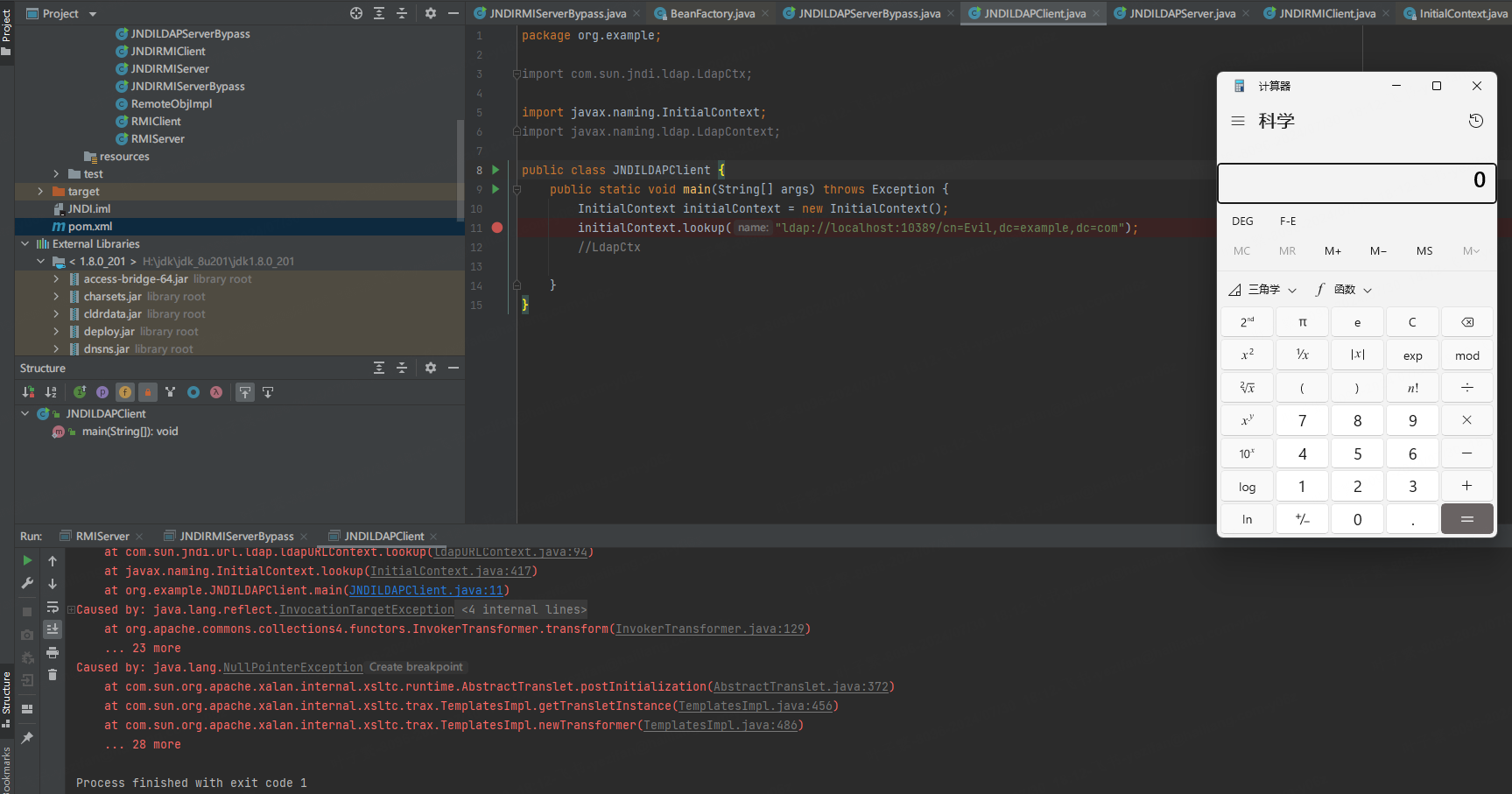
八月拍了拍你,并对你说:“好运就要开始了”!
目录
- 编程语言 | C | 代码整理 | 4月
- 2019/4/1
- 2019/4/2
- 2019/4/2
- 2019/4/3
- 2019/4/4
- 2019/4/5
- 2019/4/6
- 2019/4/7
- 2019/4/8
- 2019/4/9
- 2019/4/10
- 2019/4/11
- 2019/4/12
- 2019/4/13
- 2019/4/14
- 2019/4/15
- 2019/4/16
- 2019/4/20
- 2019/4/21
- 2019/4/23
- 2019/4/25
- 2019/4/27
- 2019/4/30
编程语言 | C | 代码整理 | 4月

2019/4/1
1.递归和非递归分别实现求第n个斐波那契数。
法一
#include <stdio.h>
int Fib(int n){
if (n <= 2){
return 1;
}
return Fib(n - 1) + Fib(n - 2);
}
int main(){
int ret = 0;
printf("ret = %d\n", Fib(10));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//法二
#include <stdio.h>
int Fib(int n){
//if(n == 1 || n == 2)
if (n <= 2){
return 1;
}
int last2 = 1; //第i-2项
int last1 = 1; //第i-1项
int cur = 0; //第i项
for (int i = 3; i <= n; ++i){
cur = last1 + last2;
last2 = last1;
last1 = cur;
}
return cur;
}
int main(){
printf("cur = %d\n", Fib(6));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//法三 0
#include <stdio.h>
int Fib(int n,int last2,int last1){
//if (n == 1 || n == 2)
if (n <= 2){
return 1;
}
return Fib(n - 1,last1,last1+last2);
}
int main(){
int ret = 0;
printf("ret = %d\n", Fib(20,1,1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.编写一个函数实现n^k,使用递归实现 0
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int myPow(int n, int k)
{
if (k == 1)
{
return k;
}
return n * myPow(n, k - 1);
}
int main(){
int ret = 0;
printf("ret=%d\n", myPow(6, 2));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3. 写一个递归函数DigitSum(n),输入一个非负整数,返回组成它的数字之和,
例如,调用DigitSum(1729),则应该返回1 + 7 + 2 + 9,它的和是19 0000
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int DigitNum(int n){
if (n == 0)
{
return 0;
}
return n % 10 + DigitNum(n / 10);
}
int main(){
printDigitNum(1729);
printf("\n%d\n", DigitNum(1729));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4. 编写一个函数 reverse_string(char * string)(递归实现)
实现:将参数字符串中的字符反向排列。
//要求:不能使用C函数库中的字符串操作函数。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
void reverse_string(char* string) {
char p; //定义一个字符来存储第一个地址自增后第一个字符
p = *string;
if (*(string++) == '\0')
return; //如果是结束符号,那么返回
else
reverse_string(string++);
printf("%c", p); //顺序执行输出p存储的字符,再返回上一层
}
int main() {
char string[20];
gets(string);
reverse_string(string);
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.递归和非递归分别实现strlen
void reverse_string(char * str)
{
int len = strlen(str) - 1;
char tmp;
if (str[0] == '\0')
{
return;
}
tmp = str[0];
str[0] = str[len];
str[len] = '\0'; //保证下一次能找到尾部
reverse_string(str + 1);
str[len] = tmp;
}
int main()
{
printDigitNum(1729, 16);
printf("\n%d\n", DigitNum(1729));
printf("%d\n", myStrlenN("bitekeji"));
printf("%d\n", myStrlen("bitekeji"));
char test[] = "bitekeji";
reverse_string(test);
puts(test);
return 0;
}
6.递归和非递归分别实现求n的阶乘
#include <stdio.h>
int Factor(int n){
if (n == 1){
return 1;
}
return n*Factor(n - 1);
}
int main(){
int ret = 0;
printf("ret=%d\n",Factor(5));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7.递归方式实现打印一个整数的每一位
#include <stdio.h>
int fun(int number) {
if(number>9)
{
fun(number/10);
}
printf("%d ",number%10);
}
int main() {
int number;
printf("输入一个数字:\n");
scanf("%d",&number);
fun(number);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
2019/4/2
//创建一个字符型二维数组(3*3)表示棋盘(x表
//x示玩家落子,o表示电脑落子,' '表示未落子)
//1.游戏开始是, 进行初始化棋盘, 把所有元素都设为''
//2.提示玩家落子(输入一个坐标)
//3.判定胜负
//4.电脑落子(基于随机数的方式生成一个坐标)
//5.判定胜负
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Menu(){
printf("==================\n");
printf("1.开始游戏\n");
printf("0.结束游戏\n");
printf("==================\n");
printf("请输入您的选择: ");
int choice = 0;
scanf("%d",&choice);
return choice;
}
#define MAX_ROW 3
#define MAX_COL 3
char chess_board[MAX_ROW][MAX_COL];
void Init(){
for (int row = 0; row < MAX_ROW; ++row){
for (int col = 0; col < MAX_COL; ++col){
chess_board[row][col] = ' ';
}
}
//设置随机种子
srand((unsigned int)time(0));
}
void print(){
for (int row = 0; row < MAX_ROW; ++row){
printf("| %c | %c | %c |\n", chess_board[row][0],
chess_board[row][1], chess_board[row][2]);
if (row != MAX_ROW - 1){
printf("|---|---|---|\n");
}
}
//为了调试程序临时加的代码,最好给他加上一个统一风格的注释
//TODO
//system("pause");
}
void PlayerMove(){
printf("玩家落子!\n");
while (1){
printf("请输入落子位置的坐标(row col): ");
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &row, &col);
//检查用户输入的坐标是否合法
if (row < 0 || row >= MAX_ROW ||
col < 0 || col >= MAX_COL){
printf("您输入的坐标非法!请重新输入!\n");
continue;
}
if (chess_board[row][col] != ' '){
printf("您要落子的位置已经被占了!\n");
continue;
}
chess_board[row][col] = 'x';
break;
}
printf("玩家落子完毕!\n");
}
void ComputerMove(){
printf("电脑落子\n");
while (1){
int row = rand() % 3;
int col = rand() % 3;
if (chess_board[row][col] != ' '){
continue;
}
chess_board[row][col] = 'o';
break;
}
printf("电脑落子完毕\n");
}
//返回值表示胜利者是谁
//x表示玩家胜
//o表示电脑胜利
//' '表示未分出胜负
//如果棋盘满了返回1;否则返回0;
int IsFull(){
for (int row = 0; row < MAX_ROW; ++row){
for (int col = 0; col < MAX_COL; ++col){
//未满
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
//返回值表示胜利者是谁
//x表示玩家胜
//q表示和棋
//' '表示胜负未分
char CheckWinner(){
//检查所有行是否连成一条线
for (int row = 0; row < MAX_ROW; ++row){
if (chess_board[row][0] == chess_board[row][1]
&& chess_board[row][0] == chess_board[row][2]){
return chess_board[row][0];
}
}
//检查所有列是否连成一条线
for (int col = 0; col < MAX_COL; ++col){
if (chess_board[0][col] == chess_board[1][col]
&& chess_board[0][col] == chess_board[0][2]){
return chess_board[0][col];
}
}
//检查所有对角线是否连成一条线
if (chess_board[0][0] == chess_board[1][1]
&& chess_board[0][0] == chess_board[2][2]){
return chess_board[0][0];
}
if (chess_board[0][2] == chess_board[1][1]
&& chess_board[0][0] == chess_board[2][0]){
return chess_board[0][2];
}
//棋盘满并且未分出胜负
if (IsFull()){
return 'q';
}
return ' ';
}
//自顶向下式的程序开发方法
void Game(){
//1.初始化棋盘
Init();
char winner = ' ';
while (1){
//2.打印棋盘
print();
//3.玩家落子
PlayerMove();
//4.检测胜负
winner = CheckWinner();
if (winner != ' '){
//胜负已分
break;
}
//5.电脑落子
ComputerMove();
//6.检测胜负
winner = CheckWinner();
if (winner != ' '){
break;
}
}
print();
if (winner == 'x'){9+-
printf("您赢了!\n");
}
else if (winner == 'o'){
printf("您真菜!\n");
}
else if (winner == 'q'){
printf("您和电脑五五开!\n");
}
else{
printf("代码好像出bug了!\n");
}
}
int main(){
while (1){
int choice = Menu();
if (choice == 1){
Game();
}
else if (choice == 0){
printf("goodbye!\n");
break;
}
else{
printf("您的输入有误!\n");
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/2
//1.先搞两个二维数组地图
//(a)show_map玩家看到的地图,已经翻开和未翻开两种状态
//(b)mine_map地雷布局图,每个位置标记是否是地雷(0/1)
//2.初始化,初始化刚才两个地图
//(a)show_map初始化就是把每个元素都设为*
//(b)mine_map初始化随机生成10个地雷
//3.打印地图
//4.提示用户输入一个坐标,表示要翻开某个位置(进行必要的合法性判定)
//5.该位置是否是地雷.如果是地雷,游戏结束!
//6.如果不是地雷,先判定是否是游戏胜利(把所有不是地雷的格子翻开)
//7.给当前位置的格子生成一个数字表示周围有几个雷(先不实现翻开一片的功能)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int Menu(){
printf("================\n");
printf(" 1.开始游戏\n");
printf(" 0.退出游戏\n");
printf("================\n");
printf("请输入您的选择: \n");
int choice = 0;
scanf("%d",&choice);
return choice;
}
#define Max_Row 9
#define Max_Col 9
#define Mine_Count 10
void Init(char show_map[Max_Row][Max_Col],
char mine_map[Max_Row][Max_Col]){
//1.对于show_map,都需要设为*
for (int row = 0; row < Max_Row; ++row){
for (int col = 0; col < Max_Col; ++col){
show_map[row][col] = '*';
}
}
//2.对于mine_map,需要随机生成若干个地雷
//使用0表示不是地雷,使用1表示是地雷
for (int row = 0; row < Max_Row; ++row){
for (int col = 0; col < Max_Col; ++col){
mine_map[row][col] = '0';
}
}
int n = Mine_Count;
while (n>0){
//生辰一组随机坐标
int row = rand() % Max_Row;
int col = rand() % Max_Col;
if (mine_map[row][col] == '1'){
//该位置已经设置是地雷了,需要重新生成
continue;
}
mine_map[row][col] = '1';
--n;
}
}
void PrintMap(char show_map[Max_Row][Max_Col]){
//不光能打印出地图.还能带坐标
//先打印第一行
printf(" ");
for (int col = 0; col < Max_Col; ++col){
printf("%d ",col);
}
printf("\n");
//打印一个分割线
for (int col = 0; col < Max_Col-2; ++col){
printf("---");
}
printf("\n");
//再打印其他行
for (int row = 0; row < Max_Row; ++row){
printf("%d| ",row);
//打印本行每一列
for (int col = 0; col < Max_Col; ++col){
printf("%c ",show_map[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void UpdateShowMap(int row, int col,
char show_map[Max_Row][Max_Col],
char mine_map[Max_Row][Max_Col]){
//根据当前位置来判定这个位置周围8个格子有几个地雷,
//并且将这个数字更新到Show_Map中
int count = 0;
if (row-1 >= 0 && col-1 >= 0 &&
row-1 < Max_Row && col-1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row - 1][col - 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row - 1 >= 0 && col >= 0 &&
row - 1 < Max_Row && col < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row - 1][col] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row - 1 >= 0 && col + 1 >= 0 &&
row - 1 < Max_Row && col + 1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row - 1][col + 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row >= 0 && col - 1 >= 0 &&
row < Max_Row && col - 1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row][col - 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row >= 0 && col + 1 >= 0 &&
row < Max_Row && col + 1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row][col + 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row + 1 >= 0 && col - 1 >= 0 &&
row + 1 < Max_Row && col - 1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row + 1][col - 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row +1 >= 0 && col >= 0 &&
row + 1 < Max_Row && col < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row + 1][col] == '1'){
++count;
}
if (row + 1 >= 0 && col + 1 >= 0 &&
row +1 < Max_Row && col + 1 < Max_Col &&
mine_map[row + 1][col + 1] == '1'){
++count;
}
//得到了周围8个人格子中的地雷个数
//假设count为2,实际想看到的内容是字符2 '2',也就是ascii中的50
//
show_map[row][col] ='0'+ count;
}
void Game(){
//1.先创建地图,并初始化
char show_map[Max_Row][Max_Col];
char mine_map[Max_Row][Max_Col];
//已经翻开的空格的个数(非地雷)
int blank_count_already_show = 0;
Init(show_map, mine_map);
while (1){
//2.打印地图
PrintMap(show_map);
//TODO 这个打印是为了调临时加的
PrintMap(mine_map);
//3.让用户输入坐标并且进行合法性检测
printf("请输入一组坐标(row col):");
int row = 0;
int col = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &row, &col);
//清掉之前打印的内容
system("cls");
if (row < 0 || row >= Max_Row || col < 0 ||
col >= Max_Col){
printf("您的输入非法!请重新输入!\n");
continue;
}
if (show_map[row][col] != '*'){
printf("您输入的位置已经翻开了!\n");
continue;
}
//4.判定是否是地雷
if (mine_map[row][col] == '1'){
printf("游戏结束!\n");
PrintMap(mine_map);
break;
}
//5.判定游戏是否胜利
//判定所有的非地雷位置都被翻开了
++blank_count_already_show;
if (blank_count_already_show == Max_Row*Max_Col
- Mine_Count){
printf("游戏胜利!\n");
PrintMap(mine_map);
break;
}
//6.统计当前位置周围的累的个数
UpdateShowMap(row,col,show_map,mine_map);
}
}
int main(){
while (1){
int choice = Menu();
if (choice == 1){
Game();
}
else if (choice == 0){
printf("goodbye!\n");
break;
}
else{
printf("您的输入有误!\n");
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/3
1. 5位运动员参加了10米台跳水比赛,有人让他们预测比赛结果
A选手说:B第二,我第三;
B选手说:我第二,E第四;
C选手说:我第一,D第二;
D选手说:C最后,我第三;
E选手说:我第四,A第一;
比赛结束后,每位选手都说对了一半,请编程确定比赛的名次。
#include <stdio.h>
int checkRank(int * player, int n){
int i, res = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
res |= 1 << player[i];
}
return res == 0x3e;
}
int main(){
int player[5] = { 0 };
for (player[0] = 1; player[0] <= 5; player[0]++){
for (player[1] = 1; player[1] <= 5; player[1]++){
for (player[2] = 1; player[2] <= 5; player[2]++){
for (player[3] = 1; player[3] <= 5; player[3]++){
for (player[4] = 1; player[4] <= 5; player[4]++){
A选手说:B第二,我第三;
B选手说:我第二,E第四;
C选手说:我第一,D第二;
D选手说:C最后,我第三;
E选手说:我第四,A第一;
if ((player[0] == 3) + (player[1] == 2) == 1 &&
(player[1] == 2) + (player[4] == 4) == 1 &&
(player[2] == 1) + (player[3] == 2) == 1 &&
(player[2] == 5) + (player[3] == 3) == 1 &&
(player[4] == 4) + (player[0] == 1) == 1 &&
checkRank(player, 5)){
printf("a是第%d\n" \
"b是第%d\n" \
"c是第%d\n" \
"d是第%d\n" \
"e是第%d\n",
player[0], player[1], player[2], player[3], player[4]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.日本某地发生了一件谋杀案,警察通过排查确定杀人凶手必为4个
嫌疑犯的一个。以下为4个嫌疑犯的供词。
A说:不是我。
B说:是C。
C说:是D。
D说:C在胡说
已知3个人说了真话,1个人说的是假话。
现在请根据这些信息,写一个程序来确定到底谁是凶手。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int murder = 0;
for (murder = 'A'; murder < 'E'; ++murder){
A说:不是我。
B说:是C。
C说:是D。
D说:C在胡说
if ((murder != 'A') + (murder == 'C') + (murder == 'D')
+ (murder != 'D') == 3){
printf("%c是凶手\n", murder);
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.在屏幕上打印杨辉三角。
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
#include <stdio.h>
void printArray(int * arr, int n){
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main(){
int n = 10;
int i, j;
#if 0
int data[20][20] = { 0 };
printf("%d\n", data[0][0] = 1);
for (i = 1; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", data[i][0] = 1);
for (j = 1; j < i; j++){
printf("%d ", data[i][j] = data[i - 1][j - 1] + data[i - 1][j]);
}
printf("%d\n", data[i][j] = 1);
}
#else
int data[20] = { 1, 1 };
puts("1");
puts("1 1");
for (i = 2; i < n; i++){
data[i] = 1;
for (j = i - 1; j > 0; j--){
data[j] += data[j - 1];
}
printArray(data, i + 1);
}
#endif
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/4
1.编写函数:unsigned int reverse_bit(unsigned int value);
这个函数的返回值value的二进制位模式从左到右翻转后的值。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
unsigned int reverse(unsigned int data){
int tmp1, tmp2;
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = 31; i < j; i++, j--){
tmp1 = !!(data & 1 << i);
tmp2 = !!(data & 1 << j);
data &= ~(1 << i);
data &= ~(1 << j);
data |= tmp1 << j;
data |= tmp2 << i;
}
return data;
}
int main(){
unsigned int n, sn = 2;
scanf("%u", &n);
int i;
unsigned int tmp, sum = 0;
printf("%u\n", reverse(n));
return 0;
for (i = 0; i < 32; n /= sn, i++){
tmp = n % sn;
sum = sum * sn + tmp;
}
printf("%u\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.编程实现:一组数据中只有一个数字出现了一次。其他所有数字都是成对
出现的。请找出这个数字。(使用位运算)
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int arr[9] = { 1, 3, 5, 2, 1, 2, 4, 3, 4 };
int res = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 9; i++){
res ^= arr[i];
}
printf("%d\n", res);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.有一个字符数组的内容为:"student a am i",
请你将数组的内容改为"i am a student".
要求:不能使用库函数。
只能开辟有限个空间(空间个数和字符串的长度无关)。
student a am i
i ma a tneduts
i am a student
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void reversestr(char * str, int start, int end){
char tmp;
int i, j;
for (i = start, j = end - 1; i < j; i++, j--){
tmp = str[i];
str[i] = str[j];
str[j] = tmp;
}
}
char * reverseWordN(char * str){
int i;
int start = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i]; i++){
if (str[i] == ' '){
reversestr(str, start, i);
start = i + 1;
}
}
reversestr(str, start, i);
reversestr(str, 0, i);
return str;
}
char * reverseWordY(char * str){
char * ptmp;
char tmp[100] = { 0 };
while (ptmp = strrchr(str, ' ')){
strcat(tmp, ptmp + 1);
strcat(tmp, " ");
*ptmp = '\0';
}
strcat(tmp, str);
strcpy(str, tmp);
return str;
}
int main(){
char str[] = "I don't like study";
puts(reverseWordY(str));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.实现一组数字,第二个数是第一个的二倍,第三个数是第一个数的三倍
#include <stdio.h>
int checkNum(int a, int b, int c){
int res = 0;
res |= 1 << a % 10;
res |= 1 << a / 10 % 10;
res |= 1 << a / 100;
res |= 1 << b % 10;
res |= 1 << b / 10 % 10;
res |= 1 << b / 100;
res |= 1 << c % 10;
res |= 1 << c / 10 % 10;
res |= 1 << c / 100;
return res == 0x3fe;
}
int main(){
int a, b, c;
for (a = 123; a <= 329; a++){
for (b = 246; b <= 658; b++){
for (c = 369; c <= 987; c++) {
if (b == a * 2 && c == a * 3 && checkNum(a, b, c)){
printf("%d %d %d\n", a, b, c);
}
}
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/5
//1.用函数求两个数中的最大值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Max(int x, int y){
if (x > y){
return x;
}
return y;
}
int main(){
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
//函数的调用,实际参数
int ret = Max(a, b);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.两个数相除
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int Divide(int x, int y, int* ok){
if (y==0){
*ok = 0;
}
*ok = 1;
return x / y;
}
int main(){
int ok = 0;
int ret = Divide(10, 3, &ok);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.两个数的交换
#include <stdio.h>
void Swap(int* x,int* y){
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
int main(){
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
Swap(&a, &b); // 等价 int* x=&a;
printf("%d %d\n",a, b); // int* y=&b;
system("pause"); // int tmp=*x;
return 0; // *x = *y;
} // *y = tmp; */
//4.判断一个数是否为素数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
//如果是素数返回1,否则返回0
int IsPrime(int x){
if (x <= 0){
return 0;
}
if (x == 1){
return 0;
}
for (int i = 2; i < x; ++i){
if (x%i == 0){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n",IsPrime(108));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//5.编写一个函数,实现一个整形有序数组的二分查找
int Binarysearch(int* arr[],int size,int to_find){
//[left,right]
int left = 0;
int right = size - 1;
while (left<right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (to_find < arr[mid]){
right = mid - 1;
}
else if (to_find > arr[mid]){
left = mid + 1;
}
else{
return 1;
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr[4] = { 1,2,3,4 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int ret = Binarysearch(arr, size, 2);
printf("%d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//6.编写一个函数,判断是不是闰年
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int IsLeapYear(int year){
if (year % 100 == 0){
//判断是不是世纪闰年
if (year % 400 == 0){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
else{
//判断是不是普通闰年
if (year % 4 == 0){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n", IsLeapYear(2008));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//7.编写一个函数,每调用一次函数,就会将num的值增加1
//方法一
void Func(int* x){
*x += 1;
}
int main(){
int x = 0;
Func(&x);
printf("%d\n",x);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//方法二
int Strlen(char str[]){
if (str[0]=='\0 '){
return 0;
}
return 1 + Strlen(str + 1);
}
int main(){
char str[] = "abcd";
int ret = Strlen(str);
printf("ret = %d\n",ret);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/6
//实现一个通讯录,完成联系人信息的存储.
//1.新增
//2.删除
//3.修改
//4.查找记录
//5.打印全部记录
//6.排序记录
//7.清空全部记录
//管理
//1.把基本信息抽象并描述出来(结构体)
//2.需要管理很多数据,就需要组织起来(数据结构)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <windows.h>
//通讯录每个条目的抽象
typedef struct PersonInfo{
char name[1024];
char phone[1024]; //电话号码用字符串表示
}PersonInfo;
//通讯录的最大容量
#define MAX_PERSON_INFO_SIZE 1000
//通信录本体的抽象
typedef struct AddressBook{
PersonInfo persons[MAX_PERSON_INFO_SIZE];
//[0,size)
int size; //控制通讯录的有效和无效
}AddressBook;
AddressBook g_address_book; //全局变量
void Init(){
g_address_book.size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_PERSON_INFO_SIZE; ++i){
g_address_book.persons[i].name[0] = '\0';
g_address_book.persons[i].phone[0] = '\0';
}
}
int Menu(){
printf("===================\n");
printf(" 1.新增联系人\n");
printf(" 2.删除联系人\n");
printf(" 3.查找联系人\n");
printf(" 4.修改联系人\n");
printf(" 5.打印全部联系人\n");
printf(" 6.排序联系人\n");
printf(" 7.清空联系人\n");
printf(" 0.退出\n");
printf("===================\n");
printf(" 请输入您的选择: ");
int choice = 0;
scanf("%d",&choice);
return choice;
}
void Empty(){
//这个函数就是用来凑数
}
void AddPersonInfo(){
printf("新增联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size >= MAX_PERSON_INFO_SIZE){
printf("您的通讯录已满,请重试!\n");
return;
}
PersonInfo* person_info = &g_address_book.persons[g_address_book.size];
printf("请输入联系人姓名: ");
//必须获取到一个指针修改的内容是一个预期的内容
scanf("%s",person_info -> name);
printf("请输入联系人电话: ");
scanf("%s",person_info -> phone);
++g_address_book.size;
printf("新增联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void DelPersonInfo(){
printf("删除联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size <= 0){
printf("删除失败!通讯录为空!\n");
}
printf("请输入要删除的序号: ");
int id = 0;
scanf("%d",&id);
if (id < 0 || id >= g_address_book.size){
printf("删除失败!输入的序号有误!\n");
return;
}
g_address_book.persons[id] = g_address_book.
persons[g_address_book.size - 1];
--g_address_book.size;
printf("删除联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void FindPersonInfo(){
printf("查找联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size <= 0){
printf("查找失败,通信录为空!\n");
return;
}
//根据姓名查找电话
printf("请输入要查找的姓名: ");
char name[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s",name);
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.size;++size){
//元素地址取出来
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[i];
if (strcmp(info ->name,name) == 0){
//序号i
printf("[%d] %s\t%s\n", i, info->name, info->phone);
}
}
printf("查找联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void UpdatePersonInfo(){
printf("更新联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size<=0){
printf("修改失败,通信录为空!\n");
return;
}
printf("请输入要修改的序号: ");
int id = 0;
scanf("%d",&id);
if (id < 0||id>=g_address_book.size){
printf("修改失败,输入的序号有误!\n");
return;
}
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[id];
printf("请输入新的姓名: (%s)\n",info -> name);
char name[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", name);
if (strcmp(name, "*") != 0){
strcmp(info->name, name);
}
char phone[1024] = { 0 };
printf("请输入新的电话: (%s)\n", info-> phone);
scanf("%s", phone);
if (strcmp(phone, "*") != 0){
strcmp(info->phone,phone);
}
printf("更新联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void PrintAllPersonInfo(){
printf("打印全部联系人\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.size; ++i){
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[i];
printf("[%d] %s\t%s\n", i, info->name, info->phone);
}
printf("共打印了 %d 条数据!\n", g_address_book.size);
printf("打印全部联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void SortPersonInfo(){
//按照字节序排序,取结构体中的姓名字段
char name[1024] = { '\0' };
char phone[1024] = { '\0' };
int bound;
int i;
int size;
for (i = 0; i < g_address_book.size; i++) {
for (bound = 0; bound < g_address_book.size; bound++) {
for (size = bound; size<g_address_book.size - 1; size++) {
if (strcmp(g_address_book.persons[size].name,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name)>0) {
strcpy(name, g_address_book.persons[size].name);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size].name,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name,name);
//copy 电话号码
strcpy(phone, g_address_book.persons[size].phone);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size].phone,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].phone);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size + 1].phone, phone);
}
}
}
}
printf("排序所有联系人:\n");
printf("排序成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void ClearAllPersonInfo(){
printf("清空全部数据\n");
printf("您真的要清空全部数据吗?Y/N\n");
char choice[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s",choice);
if (strcmp(choice,"Y")==0){
g_address_book.size = 0;
printf("清空全部数据成功!\n");
}
else{
printf("清空操作取消!\n");
}
}
typedef void(*Func)(); //函数指针的类型
// Vim操作风格
int main(){
Func arr[] = {
Empty,
AddPersonInfo,
DelPersonInfo,
FindPersonInfo,
UpdatePersonInfo,
PrintAllPersonInfo,
SortPersonInfo,
ClearAllPersonInfo
};
Init();
while (1){
int choice = Menu();
if (choice < 0 || choice >= sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0])){
printf("您的输入有误!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
continue;
}
else if (choice==0){
printf("goodbye!\n");
break;
}
else {
Sleep(200);
system("cls");
arr[choice]();
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/7
//1.打印数组中的元素以及各自的地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int arr[10] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10;++i){
printf("%d\n",arr[i]);
printf("%p\n",&arr[i]); //%p打印指针变量的值,打印地址
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.打印出二维数组中的元素以及各自的地址
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int arr[3][4] = { (1,2),(3,4),5 };
int row;
int col;
for (row = 0; row < 3; ++row){
for (col = 0; col < 4; ++col){
printf("%d ", arr[row][col]);
printf("%p\n",&arr[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int arr[3][4] = { 0 };
int row;
int col;
for (row = 0; row < 3; ++row){
for (col = 0; col < 4; ++col){
printf("&arr[%d][%d]=%p\n",row,col, &arr[row][col]);
}
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.操作符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
//按位与&两个数据都为1,结果为1,否则都为0;
//按位或|两个数据都为0,结果为0,否则都为1;
//按位异或^,相同位0,相异为1;
//按位取反~,0变1,1变0;
//16进制的数字就是4个2进制位
//%x打印一个无符号的十六进制的整数
int x = 0x1;
int y = 0x2;
int n = 10;
n = n | (1 << 4);
printf("%x\n", x & y);
printf("%x\n", x | y);
printf("%x\n", x ^ y);
printf("%x\n", ~x);
printf("%x\n", ~ y);
printf("%x\n",n);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//4.编写代码实现,求一个整数存储中的二进制中1的个数
//解法一 0
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int num = -1;
int i = 0;
int count = 0;
while (num){
++count;
num = num &(num - 1);
}
printf("%d\n", count);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//解法二
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//打印1的个数
int CountBit(int num){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32;++i){
if (num&(1<<i)){
++count;
}
}
return count;
}
int main(){
int x = -10;
// +10 1010
// 1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1010 原码(-10)
// 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0101 反码
// 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0110 补码(反码+1)
printf("%d\n",CountBit(x));
printf("%p",&x);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//5.不创建临时变量,实现两个数的交换
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
x = x^y;
y = x^y;
x = x^y;
printf("%d %d",x,y);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//6.360笔试题
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int i = 0, a = 0, b = 2, c = 3, d = 4;
//对于逻辑与&&操作符来说,如果左侧的表达式值为0,那么右侧不再计算
//对于逻辑或||操作符来说,如果左侧的表达式值为1,那么右侧不再计算
//i = a++ && ++b && d++ && c++;
i = a++ || ++b || c++ || d++;
//printf(" a=%d b=%d c=%d d=%d",a, b, c,d); //1 2 3 4
printf("\n");
printf(" a=%d b=%d c=%d d=%d", a, b, c, d); //1 3 3 4
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//7.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char a = 0xff;
a = (a << 1) >> 1;
printf("%x",a); //ffffffff
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//8.操作符的属性
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 30;
int ret = ++a + ++b + ++c;
printf("%d",ret); //63
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/8
//冒泡排序基本原理:
//1.比较相邻的元素,如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个;
//2.对每一对相邻元素做同样的工作,从开始第一对到结尾的最后一对;
//3.在这一点,最后的元素应该会是最大的数。
//4.针对所有的元素重复以上的步骤,除了最后一个。
//5.持续每次对越来越少的元素重复上面的步骤,直到没有任何一对数字需要比较。
//普通解法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Swap(int* x,int* y){
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
//数组作为函数参数,就会隐式转换成指针
void BubbleSort(int arr[],int size){
printf("size=%d\n",size);
//每次找最小值,[0,bound)已排序区间,[bound,size)未排序
//初始情况下,所有元素都是待排序的,已排序区间为空,
//待排序区间为整个数组
//每次找出一个最小值,放在数组开头位置
//当已排序区间扩充和整个数组一样,数组就排好序了
//一种找size次就完成整个排序,每次找到一个元素,已排序区间就扩充
//一个元素,待排序区间就减少一个元素
int bound = 0;
for (bound = 0; bound < size; ++bound){
//具体完成找最小元素和交换的过程
for (int cur = size - 1; cur < size;--cur){
if (arr[cur-1]>arr[cur]){
//如果两个元素不满足升序要求就交换
Swap(&arr[cur - 1], &arr[cur]);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int arr[4] = { 9, 5, 2, 7 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
BubbleSort(arr, size);
for (int i = 0; i < 4;++i){
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//优化 函数调用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Swap(int* x, int* y){
int tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
typedef int(*Cmp)(int x, int y);
//数组作为函数参数,就会隐式转换成指针
void BubbleSort(int*arr[], int size,Cmp cmp){
printf("size=%d\n", size);
//每次找最小值,[0,bound)已排序区间,[bound,size)未排序
//初始情况下,所有元素都是待排序的,已排序区间为空,
//待排序区间为整个数组
//每次找出一个最小值,放在数组开头位置
//当已排序区间扩充和整个数组一样,数组就排好序了
//一种找size次就完成整个排序,每次找到一个元素,已排序区间就扩充
//一个元素,待排序区间就减少一个元素
int bound = 0;
for (bound = 0; bound < size; ++bound){
//具体完成找最小元素和交换的过程
for (int cur = size - 1; cur > bound; --cur){
if (!cmp(arr[cur - 1],arr[cur])){
//如果两个元素不满足升序要求就交换
Swap(&arr[cur - 1], &arr[cur]);
}
}
}
}
int Less(int x, int y){
if (x < y){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int Greater(int x, int y){
if (x > y){
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int arr[4] = { 9, 5, 2, 7 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
BubbleSort(arr, size,Greater);
//BubbleSort(arr, size, Less);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/9
//1.指针
//定义:是编程语言中的一个对象,利用地址,它的值直接指向存在电脑存储器中
// 另一个地方的值.由于通过地址能找到所需的变量单元,可以说,地址指向该
//变量单元, 因此, 将地址形象化成为"指针",通过找到地址的内存单元.
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int x = 10;
int* p = &x;
double y = 10.0;
double* p2 = &y;
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p));
printf("%d\n",*p);
printf("%p\n",p);
printf("%p\n",p);
printf("%f\n",*p2);
printf("%d\n",sizeof(p2));
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char*p1 = 0x100;
char*p2 = 0x200;
printf("%x\n",p2-p1);
//指针相减,通常情况下是没有意义的,变量在哪个地址取决于操作系统,
//再去做差,可能得到的值就会发生变化
//指针相减其实就是求两个指针之间隔了多少个元素
short*p3 = 0x100;
short*p4 = 0x200;
printf("%x\n", p4 - p3);
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//指针比较(指针中存的地址是否相同,或者是否指向同一块内存空间)
/*int main(){
int n1 = 10;
int*p1 = &n1;
int n2 = 10;
int*p2 = &n2;
if (p1==p2){
printf("呵呵\n");
}
else{
printf("哈哈\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//2.指针和数组
/*int main(){
int arr[] = { 0 };
printf("%d\n",sizeof(arr));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr+0));
printf("%d\n", sizeof(arr[0]));
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//3.二级指针
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int arr[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
//arr是一个指向首元素的指针
//&arr是一个指向整个数组的指针(数组指针)
printf("%p\n", &arr[0]); //打印://0073FA7C
printf("%p\n", arr); //0073FA7C
printf("%p\n", arr + 1); //0073FA80
printf("%p\n", &arr); //0073FA7C
printf("%p\n", &arr + 1); //0073FA8C
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//4.结构体
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
struct Student{
long int num;
char name[20]; //member/成员/属性/字段
char sex;
char addr[20];
}a = { 10101, "Li Lin",'M',"123 Beijing Road" };
printf("NO.:%ld\nname:%s\nsex:%c\naddress:%s\n", a.num, a.name,
a.sex, a.addr);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/10
//1.设计一个程序来判断当前机器的字节序.
//解法一
/*#include <stdio.h>
//如果是小端就返回1,否则返回0
int IsLittleEnd(){
int num = 10;
char*p = (char*)#
if (*p==0){
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main(){
printf("%d\n",IsLittleEnd()); // 1
int num = 10;
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//解法二
/*#include <stdio.h>
int check_sys(){
int i = 10;
return(*(char*)&i);
}
int main(){
int ret = check_sys();
if (ret==1){
printf("小端\n");
}
else{
printf("大端\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//2.
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char a = -1;
signed char b = -1;
unsigned char c = -1;
printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d",a,b,c); // a=-1 b=-1 c=255
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//3.
//%u无符号整形
//解题思路 char->int->unsigned int
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char a = -128;
printf("%u\n", a); //4294967168(溢出)
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//4.
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
char a = 128;
printf("%u\n", a); //4294967168(溢出)
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//5.
//解题思路 i+j-->unsigned-->int
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i = -20;
unsigned int j = 10;
printf("%d\n", i+j); //-10
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//6.
//解题思路:-1-i如果当成int来理解,不可能是0,如果当成char来理解,就有机会;
//转成char的过程中高位就截断,高位是什么都不重要,重要的是得让低位8位为0
//即可,构造一个Ascii值为0的字符,0-254这样的下标,对应的元素就是字符串的
//有效数字
/*#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char a[1000];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 1000;++i){
a[i] = -1 - i;
}
printf("%d",strlen(a)); //255
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//7.溢出,死循环
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
unsigned char i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= 255;++i){ //255 无符号
printf("hello word\n"); //1111 1111
} //0000 0001
system("pause"); //10000 0000
return 0;
}*/
//8.浮点型在内存中的存储
/*int main(){
int n = 9;
float*pf = (float*)&n;
printf("n的值为:%d\n",n);
printf("*pf的值为:%f\n",*pf);
*pf = 9.0;
printf("num的值为:%d\n",n);
printf("*pf的值为:%f\n",*pf);
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
//程序运行结果
//n的值为:9
//* pf的值为 : 0.000000
//num的值为 : 1091567616
//* pf的值为 : 9.000000
//9.误差区间
/*#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
float i = 19.0;
float j = i / 7.0;
if (j * 7.0 - i < 0.0001 && j * 7.0 - i > -0.0001){
printf("呵呵\n");
}
else{
printf("哈哈\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}*/
2019/4/11
//指针的进阶
//1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
char w = 'w';
char* p = &w;
char* p2 = "hehehehe";
char str[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c' };
char *p3 = str;
printf("%c\n",*p2);
printf("%s\n", p2);
printf("%s\n", p3);
printf("%s\n", p2+1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//程序运行结果:
h
hehehehe
abc烫烫烫烫汤X ?
ehehehe
//2.
//解析:虽然指针和数组在C语言中经常混用,但是两者之间也是有本质差别
//数组是自带内存空间的,往往是把原来的数据又复制一份放到当前新的内
//存空间中;指针是不自带内存空间的,自身内存空间就是4个字节,不管指向
//的是什么内容,这4个字节只是保存对应内存空间的地址,不涉及数据拷贝的
//过程.
int main(){
char str1[] = "hehe";
char str2[] = "hehe";
if (str1==str2){
printf("hehe\n");
}
char* str3 = "hehe";
char* str4 = "hehe";
if (str3==str4){
printf("haha");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.
int main(){
int arr[4] = { 0 };
int* p = arr;
printf("%p\n",&arr[0]);
//普通指针
printf("%p\n",arr);
printf("%p\n", arr+1);
//数组指针
printf("%p\n",&arr);
printf("%p\n", &arr+1);
//二级指针
printf("%p\n",&p);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//程序运行结果:
00B7FB30
00B7FB30
00B7FB34
00B7FB30
00B7FB40
00B7FB24
//4.一级指针传参
#include <stdio.h>
void Func(){
printf("hehe\n");
}
int main(){
printf("%p\n",Func);
printf("%p\n", &Func);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//5.函数指针的用途:转移表
//exp:计算器
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int Add(int x, int y){
return x + y;
}
int Sub(int x, int y){
return x - y;
}
int Mul(int x, int y){
return x * y;
}
int Div(int x, int y){
return x / y;
}
typedef int(*Func)(int x, int y);
int main(){
Func arr[] = { Add, Sub, Mul, Div };
while (1){
printf("1.相加\n");
printf("2.相减\n");
printf("3.相乘\n");
printf("4.相除\n");
printf("请输入您要进行的运算: ");
int choice = 0;
scanf("%d",&choice);
//转移表,表驱动的方式
arr[choice - 1](10, 20);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//6.//对一个数组进行逆序
void Reverse(char arr[],int size){
int left = 0;
int right = size - 1;
while (left<=right){
swap(&arr[left],&arr[right]);
++left;
--right;
}
}
void Reverse(char arr[],int size){
std::reverse(arr,arr+size)
}
2019/4/12
//指针和数组笔试题
//一维数组
//1.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a)); //16 整个数组占有字节的内存
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 0)); //4 隐式转换为指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a)); //4 指向首元素
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1)); //4 指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[1])); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&a)); //16 整个数组
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0])); //4 首元素指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1)); //4 第二个元素指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&*a)); //4 首元素地址
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结:
1.只要是指针,sizeof()就是4个字节
2.&a数组指针,数组指针解引用到了整个数组
//字符数组
//2.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
char a[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a)); //6 不包括'\0'
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 0)); //4 指向首元素地址
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a)); //1 指向首元素'a'
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[1])); //1 指向元素'b'
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&a)); //6
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0])); //4 首元素指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1)); //4 第二个元素指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&*a)); //4 首元素地址
//未定义行为
printf("%d\n",strlen(a));
printf("%d\n", strlen(a+0));
printf("%d\n", strlen(*a));
printf("%d\n", strlen(a[1]));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a + 1));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a[0]+1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
char a[] = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a)); //7 包括'\0'
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 0)); //4 指向首元素的指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a)); //1 sizeof("a")
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a + 1)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[1])); //1 sizeof("b")
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&a)); //6
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&*a)); //4 首元素地址
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0])); //4 首元素指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0] + 1)); //4 第二个元素地址
printf("%d\n", strlen(a)); //6
printf("%d\n", strlen(a + 0)); //6
printf("%d\n", strlen(*a)); //未定义行为 首元素'a'=97
printf("%d\n", strlen(a[1])); //未定义行为
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a)); //6
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a + 1)); //未定义行为 越界
printf("%d\n", strlen(&a[0] + 1)); //5
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//4.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char *p = "abcdef";
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p)); //4 指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p + 0)); //4 指向首元素的指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*p)); //1 sizeof("a")
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p + 1)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(p[1])); //1 sizeof("b")
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p)); //4 二级指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*&p)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&*p)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p + 1)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p[0])); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&p[0] + 1)); //4 第二个元素指针
printf("%d\n", strlen(p)); //6
printf("%d\n", strlen(p + 0)); //5 从b开始,遇到'\0'结束
printf("%d\n", strlen(*p)); //未定义行为 首元素'a'=97
printf("%d\n", strlen(p[0])); //未定义行为 a
//未定义行为 &p二级指针,对应的内存中计提有多少字节还不确定
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p));
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p + 1)); //未定义行为 越界
printf("%d\n", strlen(&p[0] + 1)); //5 从下一个元素地址开始
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//二维数组
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
int a[3][4] = { 0 };
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a)); //48 4*12
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0][0])); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0])); //16 4*4 a[0]=>int[4]
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[0]+ 1)); //4 指向第二个元素的指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a[0]+1)); //4 =>sizeof(a[0][1])
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a+1)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(a + 1))); //16 *(a + 1)=>a[1]
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a[0]+1)); //4 数组指针
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&*a)); //4
printf("%d\n", sizeof(&a + 1)); //4
//a[0]长度为4个元素的数组,&a[0]得到了一个数组指针,&a[0]+1还是
//数组指针,*(&a[0]+1)便得到了一各数组
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*(&a[0]+1))); //16
printf("%d\n", sizeof(*a)); //16
printf("%d\n", sizeof(a[3])); //16
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/13
1..调整数组使奇数全部都位于偶数前面。
//例如:
//输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数,来调整该数组中数字的顺序使得数组中
//所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有偶数位于数组的后半部分。
//解法一:
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]))
void divide(int * a, int n){
int s[128] = { 0 };
int d[128] = { 0 };
int i, counts = 0, countd = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (a[i] % 2){
s[counts++] = a[i];
}
else{
d[countd++] = a[i];
}
}
for (i = 0; i < counts; i++){
a[i] = s[i];
}
for (; i < n; i++){
a[i] = d[i - counts];
}
}
void printArray(int * a, int n){
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main(){
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
divide(a, SIZE(a));
printArray(a, SIZE(a));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//解法二:
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]))
void divide(int * a, int n){
int start = 0;
int end = n - 1;
int tmp;
while (a[start++] % 2);
while (a[end--] % 2 == 0);
while (start < end){
tmp = a[end + 1];
a[end + 1] = a[start - 1];
a[start - 1] = tmp;
while (a[start++] % 2);
while (a[end--] % 2 == 0);
}
}
void printArray(int * a, int n){
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
int main(){
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
divide(a, SIZE(a));
printArray(a, SIZE(a));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.2.
//杨氏矩阵
//有一个二维数组.数组的每行从左到右是递增的,每列从上到下是递增的.
//在这样的数组中查找一个数字是否存在。时间复杂度小于O(N);
//数组:1 2 3
// 4 5 6
// 7 8 9
#include <stdio.h>
int findnum(int a[][3], int x, int y, int f){
int i = 0, j = x - 1;
while (j >= 0 && i < y){
if (a[i][j] < f){
++i;
}
else if (a[i][j] > f){
--j;
}
else{
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int a[][3] = { { 1, 3, 5 },
{ 3, 6, 7 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
if (findnum(a, 3, 3, 2)){
printf("It has been found!\n");
}
else{
printf("It hasn't been found!\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/14
//1.实现一个函数,可以左旋字符串中的k个字符。
//ABCD左旋一个字符得到BCDA; ABCD左旋两个字符得到CDAB
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int round(char s[], int k){
int len = strlen(s);
char * tmp = (char *)calloc(len + 1, sizeof(char));
if (tmp == NULL){
return 1;
}
int i;
k %= len;
for (i = 0; i < len - k; i++){
tmp[i] = s[i + k];
}
for (; i < len; i++){
tmp[i] = s[i + k - len];
}
for (i = 0; i < len; i++){
s[i] = tmp[i];
}
free(tmp);
return 0;
}
int main(){
char s[] = "ABCDE";
round(s, 2);
puts(s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.2.判断一个字符串是否为另外一个字符串旋转之后的字符串。
//例如:给定s1 =AABCD和s2 = BCDAA,返回1,
//给定s1 = abcd和s2 = ACBD,返回0.
//AABCD左旋一个字符得到ABCDA
//AABCD左旋两个字符得到BCDAA
//AABCD右旋一个字符得到DAABC
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int find(char * a, char * b){
char * tmp = (char *)calloc(strlen(a) * 2 + 1, sizeof(char));
if (tmp == NULL){
return 0;
}
strcpy(tmp, a);
strcat(tmp, a);
if (strstr(tmp, b)){
free(tmp);
return 1;
}
free(tmp);
return 0;
}
int main(){
char a[] = "AABCD";
char b[] = "BCDAA";
if (find(a, b)){
printf("找到了\n");
}
else{
printf("没找到\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/15
//1.一个数组中只有两个数字是出现一次,
//其他所有数字都出现了两次,找出这两个数字,编程实现。
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]))
int main(){
int a[] = { 8, 10, 8, 2, 11, 9, 12, 11, 9, 2 };
int i, sum = 0;
int pos;
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SIZE(a); i++){
sum ^= a[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++){
if (sum & 1 << i){
pos = i;
break;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < SIZE(a); i++){
if (a[i] & 1 << pos){
num1 ^= a[i];
}
else{
num2 ^= a[i];
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", num1, num2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.喝汽水,1瓶汽水1元,2个空瓶可以换一瓶汽水, 给20元,可以多少汽水。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int i;
int sum = 0;
for (i = 20; i > 1; i /= 2){
sum += i - i % 2;
i += i % 2;
}
printf("%d", sum + 1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.模拟实现strcpy
//char * strcpy(char * destination, const char * source);
//Return Value : destination is returned.
//destination=dest;source=src;
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
char* Strcpy(char* dest, const char* src) {
int i;
assert(src != NULL);
assert(dest != NULL);
for (i = 0; src[i] != '\0'; ++i) {
dest[i] = src[i];
}
dest[i] = '\0';
return dest;
}
int main() {
char* p = "abcdef";
char string[1024] = {0};
Strcpy(string, p);
printf("%s\n",string);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//运行结果
//abcdef
//4.模拟实现strcat
//char * strcat(char * destination, const char * source);
//Return Value : destination is returned.
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
char* Strcat(char* dest, const char* src) {
int i;
int j;
assert(src != NULL);
assert(dest != NULL);
for(i = 0;dest[i]!='\0';++i);
for (j = 0; src[j] != '\0'; ++i, ++j) {
dest[i] = src[j];
}
dest[i] = '\0';
return dest;
}
int main() {
char string1[1024]="aaa";
char string2[1024]="bbb";
Strcat(string2, string1);
printf("%s\n",string1);
printf("%s\n", string2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/16
//1.模拟实现strcpy
//char * strcpy(char * destination, const char * source);
//Return Value : destination is returned.
//destination=dest;source=src;
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
char* Strcpy(char* dest, const char* src) {
int i;
assert(src != NULL);
assert(dest != NULL);
for (i = 0; src[i] != '\0'; ++i) {
dest[i] = src[i];
}
dest[i] = '\0';
return dest;
}
int main() {
char* p = "abcdef";
char string[1024] = { 0 };
Strcpy(string, p);
printf("%s\n", string);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//运行结果
//abcdef
//2.模拟实现strcat
//char * strcat(char * destination, const char * source);
//Return Value : destination is returned.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
char* Strcat(char* dest, const char* src) {
int i;
int j;
assert(src != NULL);
assert(dest != NULL);
for (i = 0; dest[i] != '\0'; ++i);
for (j = 0; src[j] != '\0'; ++i, ++j) {
dest[i] = dest[j];
}
dest[i] = '\0';
return dest;
}
int main() {
char string1[1024] = "aaa";
char string2[1024] = "bbb";
Strcat(string2, string1);
printf("%s\n", string1);
printf("%s\n", string2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//3.实现strstr
//char * strstr(const char *, const char *);
//Return Value:
//A pointer to the first occurrence in str1 of the entire sequence of
//characters specified in str2, or a null pointer if the sequence is
//not present in str1.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
char* Strstr(const char * str1,const char * str2){
assert(str1 != NULL);
assert(str2 != NULL);
if (*str2 == '\0'){
return NULL;
}
//黑指针功能是记录从哪个位置找字符串
const char* black_ptr = str1;
while (*black_ptr !='0'){
//红指针帮我们完成具体的字符串比较
const char* red_ptr = black_ptr;
const char* sub_ptr = str2;
while (*red_ptr == *sub_ptr && *red_ptr != '\0'
&& *sub_ptr != '\0') {
++red_ptr;
++sub_ptr;
}
if (*sub_ptr == '\0') {
return black_ptr;
}
++black_ptr;
}
return NULL;
}
//4.实现strchr
char * strchr(const char *, int);
Returns a pointer to the first occurrence of character in the
C string str.
The terminating null - character is considered part of the C string.
Therefore, it can also be located in order to retrieve a pointer to
the end of a string.
#include <string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
const char* Strchr(const char* str,int character) {
assert(str != NULL);
while (*str++) {
if (character == *str) {
return str;
}
}
return NULL;
}
int main () {
const char* search_char;
char str[1024];
char character;
gets(str);
character = getchar();
search_char = Strchr(str, character);
puts(search_char);
return 0;
}
//5.实现strcmp
int strcmp(const char * str1, const char * str2);
#include <string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
int Strcmp(const char* str1, const char* str2) {
assert(str1 != NULL);
assert(str2 != NULL);
int i;
for (i = 0; str1[i] != '\0'&&str2[i] != '\0'; ++i){
if (str1[i] < str2[i]){
return -1;
}
else{
//什么都不做,直接比较下一个字符
}
}
if (str1[i] < str2[i]){
return -1;
}
else if (str1[i] > str2[i]){
return 1;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
int main(){
char str1[1024] = "aaa";
char str2[1024] = "bbb";
//strcmp o(n)=n
int ret = Strcmp(str1,str2);
if (ret>0){
printf("str1 > str2\n");
}
else if (ret<0){
printf("str1 < str2\n");
}
else{
printf("str1==str2\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//6.实现memcpy
//void * memcpy(void * destination, const void * source, size_t num);
//Return Value:
//destination is returned
#include <string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void* Memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t num) {
assert(dest != NULL);
assert(src != NULL);
const char* psrc = (const char*)src;
const char* pdest = (const char*)dest;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num; ++i){
pdest[i] = psrc[i];
}
return dest;
}
int main() {
int arr1[4] = { 0 };
int arr2[4] = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
Memcpy(arr1,arr2,16);
for (int i = 0; i < 4;++i){
printf("%d\n",arr1[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//7.实现memmove
//void * memmove(void * destination, const void * source, size_t num);
#include <string.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
void *Memmove(void* dest, const void* src, size_t num) {
char* pdest = (char*)dest;
const char* psrc = (char*)src;
if (dest == NULL || src == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//地址不重叠时候,从前面开始复制
if (pdest <= psrc || pdest >= psrc + num) {
while (num--) {
*pdest++ = *psrc++;
}
}
//地址重叠时候,从尾部开始复制
else {
//减1 就是获取下标,到了尾指针
pdest = pdest + num - 1;
psrc = psrc + num - 1;
while (num--) {
*pdest-- = *psrc--;
}
}
return dest;
}
int main() {
const char string1[1024] = "we are the best!";
char string2[1024];
Memmove(string1 + 3, string1, strlen(string1) + 1);
printf("%s\n", string1 + 3);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/20
//num1
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int* ptr = (int*)(&a+1);
printf("%d,%d",*(a+1),*(ptr-1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
2,5
//num2
#include <stdio.h>
//结构体大小为20个字节
struct test{
int num;
char* pcname;
char cha[2];
short sba[4];
}*p; //结构体指针(未初始化,其实默认为0)
int main(){
//%p十六进制打印
printf("%d\n", p + 0x1);
printf("%d\n", (unsigned long)p + 0x1);
printf("%d\n", (unsigned int*)p + 0x1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
0x14 0x1 0x4
//num3
int main(){
int a[4] = {1,2,3,4}; 总结://1.(int)a+1,其实地址+1
int* ptr1 = (int*)(&a+1); //2.对int*解引用的含义
int* ptr2 = (int*)((int)a+1); //3.整数在内存中如何存储
printf("%x,%x",ptr1[-1],*ptr2);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4, 2000000
//num4
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
int a[3][2] = {(0,1),(2,3),(4,5)};
int*p;
p = a[0];
printf("%d\n", p[0]); //a[0][0]=1
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//num5
int main(){
//指针相减=>相间隔元素
int a[5][5];
int(*p)[4];
p = a;
printf("%p,%d\n",&p[4][2]-&a[4][2],&p[4][2]-&a[4][2]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
FFFFFFFC, -4
//num6.
int main(){
int a[2][5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
6, 7, 8, .9, 10};
int *ptr1 = (int*)(&a + 1); //&a+1会跳出整个二维数组
int *ptr2 = (int *)(*(a + 1)); //*(a+1)=>a[1]
printf("%d,%d",*(ptr1-1),*(ptr2-1));
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
10,5
//num7
int main(){
char* a[] = {"work","at","alibaba"};
char** pa = a; //pa二级指针
pa++;
printf("%s\n",*pa);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
at
//num8.
int main(){
char* c[] = {"ENTER","NEW","POINT","FIRST"};
char** cp[] = {c+3,c+2,c+1};
char*** cpp = cp;
printf("%s\n",**++cpp);
printf("%s\n",*--*++cpp+3);
printf("%s\n", *cpp[-2]+3);
printf("%s\n", cpp[-1][-1]+1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
POINT
ER
ST
EW
2019/4/21
//实现一个通讯录,完成联系人信息的存储.
//1.新增
//2.删除
//3.修改
//4.查找记录
//5.打印全部记录
//6.排序记录
//7.清空全部记录
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <windows.h>
//通讯录每个条目的抽象
typedef struct PersonInfo{
char name[1024];
char phone[1024]; //电话号码用字符串表示
}PersonInfo;
typedef struct AddressBook{
PersonInfo* persons;
//[0,size)
int size; //控制通讯录的有效和无效
int capacity;
}AddressBook;
AddressBook g_address_book; //全局变量
void Init(){
g_address_book.size = 0;
//申请100个内存空间
g_address_book.capacity = 100;
g_address_book.persons = (PersonInfo*)malloc(100*sizeof(PersonInfo));
g_address_book.capacity * sizeof(PersonInfo);
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.capacity; ++i){
g_address_book.persons[i].name[0] = '\0';
g_address_book.persons[i].phone[0] = '\0';
}
}
int Menu(){
printf("===================\n");
printf(" 1.新增联系人\n");
printf(" 2.删除联系人\n");
printf(" 3.查找联系人\n");
printf(" 4.修改联系人\n");
printf(" 5.打印全部联系人\n");
printf(" 6.排序联系人\n");
printf(" 7.清空联系人\n");
printf(" 0.退出\n");
printf("===================\n");
printf(" 请输入您的选择: ");
int choice = 0;
scanf("%d", &choice);
return choice;
}
void Empty(){
//这个函数就是用来凑数
}
void AddPersonInfo(){
printf("新增联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size >= g_address_book.capacity){
printf("当前空间不足,进行扩容!\n");
g_address_book.capacity += 100;
/*g_address_book.persons = (PersonInfo*)realloc(
g_address_book.persons, g_address_book.capacity*
sizeof(PersonInfo));*/
PersonInfo* p = (PersonInfo*)malloc(g_address_book.capacity*
sizeof(PersonInfo));
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.size;++i){
p[i] = g_address_book.persons[i];
}
free(g_address_book.persons);
g_address_book.persons = p;
return;
}
PersonInfo* person_info = &g_address_book.persons[g_address_book.size];
printf("请输入联系人姓名: ");
//必须获取到一个指针修改的内容是一个预期的内容
scanf("%s", person_info->name);
printf("请输入联系人电话: ");
scanf("%s", person_info->phone);
++g_address_book.size;
printf("新增联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void DelPersonInfo(){
printf("删除联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size <= 0){
printf("删除失败!通讯录为空!\n");
}
printf("请输入要删除的序号: ");
int id = 0;
scanf("%d", &id);
if (id < 0 || id >= g_address_book.size){
printf("删除失败!输入的序号有误!\n");
return;
}
g_address_book.persons[id] = g_address_book.
persons[g_address_book.size - 1];
--g_address_book.size;
printf("删除联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void FindPersonInfo(){
printf("查找联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size <= 0){
printf("查找失败,通信录为空!\n");
return;
}
//根据姓名查找电话
printf("请输入要查找的姓名: ");
char name[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", name);
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.size; ++size){
//元素地址取出来
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[i];
if (strcmp(info->name, name) == 0){
//序号i
printf("[%d] %s\t%s\n", i, info->name, info->phone);
}
}
printf("查找联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void UpdatePersonInfo(){
printf("更新联系人\n");
if (g_address_book.size <= 0){
printf("修改失败,通信录为空!\n");
return;
}
printf("请输入要修改的序号: ");
int id = 0;
scanf("%d", &id);
if (id < 0 || id >= g_address_book.size){
printf("修改失败,输入的序号有误!\n");
return;
}
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[id];
printf("请输入新的姓名: (%s)\n", info->name);
char name[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", name);
if (strcmp(name, "*") != 0){
strcmp(info->name, name);
}
char phone[1024] = { 0 };
printf("请输入新的电话: (%s)\n", info->phone);
scanf("%s", phone);
if (strcmp(phone, "*") != 0){
strcmp(info->phone, phone);
}
printf("更新联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void PrintAllPersonInfo(){
printf("打印全部联系人\n");
for (int i = 0; i < g_address_book.size; ++i){
PersonInfo* info = &g_address_book.persons[i];
printf("[%d] %s\t%s\n", i, info->name, info->phone);
}
printf("共打印了 %d 条数据!\n", g_address_book.size);
printf("打印全部联系人成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void SortPersonInfo(){
//按照字节序排序,取结构体中的姓名字段
char name[1024] = { '\0' };
char phone[1024] = { '\0' };
int bound;
int i;
int size;
for (i = 0; i < g_address_book.size; i++) {
for (bound = 0; bound < g_address_book.size; bound++) {
for (size = bound; size<g_address_book.size - 1; size++) {
if (strcmp(g_address_book.persons[size].name,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name)>0) {
strcpy(name, g_address_book.persons[size].name);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size].name,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size + 1].name, name);
//copy 电话号码
strcpy(phone, g_address_book.persons[size].phone);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size].phone,
g_address_book.persons[size + 1].phone);
strcpy(g_address_book.persons[size + 1].phone, phone);
}
}
}
}
printf("排序所有联系人:\n");
printf("排序成功!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
}
void ClearAllPersonInfo(){
printf("清空全部数据\n");
printf("您真的要清空全部数据吗?Y/N\n");
char choice[1024] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", choice);
if (strcmp(choice, "Y") == 0){
g_address_book.size = 0;
printf("清空全部数据成功!\n");
}
else{
printf("清空操作取消!\n");
}
}
typedef void(*Func)(); //函数指针的类型
// Vim操作风格
int main(){
Func arr[] = {
Empty,
AddPersonInfo,
DelPersonInfo,
FindPersonInfo,
UpdatePersonInfo,
PrintAllPersonInfo,
SortPersonInfo,
ClearAllPersonInfo
};
Init();
while (1){
int choice = Menu();
if (choice < 0 || choice >= sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0])){
printf("您的输入有误!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
continue;
}
else if (choice == 0){
printf("goodbye!\n");
break;
}
else {
Sleep(200);
system("cls");
arr[choice]();
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2019/4/23
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#pragma once
//1.将温度计测量的度数华式法(64F)转换为摄氏度(17.8度)
int main(){
float f, c;
f = 64.0;
c = (5.0 / 9)*(f - 32);
printf("f=%f,c=%f\n",f,c);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.计算存款利息.有1000元,想存一年,有三种方法可选:(1)活期,年利率为r1.
//(2)一年期为定期,,年利率为r2.(3)存两次半年期,年利率为r3,,分别计算一
//年后按三种方法的本息和.
//解题思路:
//一年活期存款 : 一年后本息和为p1 = p0*(1 + r1);
//一年定期存款:一年后本息和为p2 = p0*(1 + r2);
//两次半年定期存款, 一年后本息和为p3 = p0*(1 + r3 / 2)*(1 + r3 / 2);
int main(){
//定义变量
float p0 = 1000, r1 = 0.0036, r2 = 0.0225, r3 = 0.0198, p1, p2, p3;
p1 = p0*(1 + r1);
p2= p0*(1 + r2);
p3 = p0*(1 + r3 / 2)*(1 + r3 / 2);
printf("p1=%f\np2=%f\np3=%f\n",p1,p2,p3);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
p1 = 1003.599976
p2 = 1022.500061
p3 = 1019.897949
请按任意键继续. . .
//3.给定一个大写字母,要求用小写字母输出.
int main(){
char c1, c2;
c1 = 'A'; //将字符'A'的ASCII代码放到c1变量中
c2 = c1 + 32; //得到字符'a'的ASCII代码放在c2变量中
printf("%c\n",c2); //输出c2的值,是一个字符
printf("%d\n",c2); //输出c2的值,是字符'a'的ASCII代码
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
a
97
//4.先后输出BOY三个字符.
法一:
int main(){
char a = 'B', b = 'O', c = 'Y'; //定义三个字符变量并且初始化
putchar(a); //像显示器输出字符B
putchar(b); //像显示器输出字符O
putchar(c); //像显示器输出字符Y
putchar('\n'); //像显示器输出一个换行符
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法二:
int main(){
int a = 66, b = 79, c = 89;
putchar(a);
putchar(b);
putchar(c);
putchar('\n');
system("pause");
return 0;
}
法三:
int main(){
putchar(getchar()); //将接受的字符输出B
putchar(getchar()); //像显示器输出字符O
putchar(getchar()); //像显示器输出字符Y
putchar('\n');
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//5.求解ax^2+bx+c=0方程的解.
解题思路:
(1)a = 0, 不是二次方程.
(2)b ^ 2 - 4ac = 0, 方程有两个相等实根.
(3)b ^ 2 - 4ac > 0, 方程有两个不等实根.
(4)b ^ 2 - 4ac < 0, 方程有两个共轭复根, 应当以p + qi和p - qi的形式输出复根,
其中p = -b / 2a, q = sqrt(b ^ 2 - 4ac) / 2a.
int main(){
double a, b, c, disc, x1, x2, realpart, imagpart;
scanf("%lf,%lf,%lf",&a,&b,&c);
printf("The equation");
if (fabs(a)<=1e-6){
printf("is not a quadratic\n");
}
else{
disc = b*b - 4 * a * c;
if (fabs(disc) <= 1e-6){
printf(" has two equal roots:%8.4f\n",-b/(2 * a));
}
else{
if (disc>1e-6){
x1 = (-b + sqrt(disc) / (2 * a));
x2 = (-b - sqrt(disc) / (2 * a));
printf(" has distinct real roots:%8.4f and %8.4f\n",x1,x2);
}
else{
realpart = -b / (2 * a); //复根的实部
imagpart = sqrt(-disc) / (2 * a); //复根的虚部
printf(" has complex roots:\n");
printf("%8.4f + %8.4fi\n", realpart,imagpart);
printf("%8.4f - %8.4fi\n", realpart, imagpart);
}
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
程序分析:
(1)程序中用disc代表b^2-4ac,先计算disc的值.
(2)由于disc(即b ^ 2 - 4ac)是实数,而实数在计算和存储时会有一些小的误差,
因此采取判别disc的绝对值(fabs(disc))是否小于一个很小的数(例如10^-6).
(3)realpart代表实部,imagpart代表虚部.
2019/4/25
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#pragma once
//1.求1+2+3+4+...+100的值
//解法一:
int main(){
int i = 1, sum = 0;
while (i<=100){
sum += i;
++i;
}
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//解法二:
int main(){
int i = 1, sum = 0;
do{
sum += i;
++i;
} while (i <= 100);
printf("sum = %d\n", sum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.在全系1000名学生中举行慈善募捐,当总数达到10万元时就结束,
//统计此时捐款的人数以及平均捐款的数目.
解析:
(1)用循环来处理,实际循环的次数不知道,可以设为最大值,即最多会有1000人捐款
(2)用if语句检查是否达到10万元,如果达到就不再执行.
(3)定义变量存放捐款数(amount), 总捐款数(total), 人均存款数(aver).
#define SUM 100000 //指定符号常量SUM代表100000
int main(){
float amount, aver, total;
int i;
for (i = 1, total = 0; i < 1000;++i){
printf("please enter amount:");
scanf("%f",&amount);
total += amount;
if (total>SUM) break;
}
aver = total / i;
printf("num=%d\naver=%10.2f\n",i,aver);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
please enter amount : 10000
please enter amount : 20000
please enter amount : 30000
please enter amount : 25000
please enter amount : 15000
please enter amount : 20000
num = 6
aver = 20000.00
//3.输出以下4 * 5的矩阵.
1 2 3 4 5
2 4 6 8 10
3 6 9 12 15
4 8 12 16 20
int main(){
int i, j, n = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 4;++i){
for (j = 1; j <= 5;++j,++n){ //n用来累计输出数据的个数
if (n % 5 == 0){ //控制输出在5个数据后换行
printf("\n");
}
printf("%d\t",i*j);
}
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int main(){
int i, j, n = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 4; ++i){
for (j = 1; j <= 5; ++j, ++n){
if (n % 5 == 0){
printf("\n");
}
if (i==3&&j==1){
break;
}
printf("%d\t", i*j);
}
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
2 4 6 8 10
4 8 12 16 20
int main(){
int i, j, n = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 4; ++i){
for (j = 1; j <= 5; ++j, ++n){
if (n % 5 == 0){
printf("\n");
}
if (i == 3 && j == 1){
continue;
}
printf("%d\t", i*j);
}
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
2 4 6 8 10
6 9 12 15
4 8 12 16 20
//4.用公式π/4=1-(1/3)+(1/5)-(1/7)+...求pi的近似值,直到大西安某一项的
//绝对值小于10^(-6).
//解析:
//(1)每项的分子都是1
//(2)后一项的分母是前一项的分母加2
//(3)第一项的符号为正,从第二项起,每一项的符号与前一项的符号相反.
int main(){
int flag = 1; //用来表示数值的符号
//pi代表多项式的值,最后代表π,n代表分母
double pi = 0.0, n = 1.0, term = 1.0;
while (fabs(term)>1e-6){ //检查绝对值
pi += term;
n += 2;
flag *=-1 ; //下一项与上一项符号相反
term = flag / n; //求出下一项的值term
}
pi = pi * 4;
printf("pi = %10.8f\n",pi); //输出π的近似值
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
pi = 3.14159065
2019/4/27
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#pragma once
//1.对10个数组元素依次赋值为0,1,2,,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,要求按照逆序输出.
int main(){
int i, a[10];
for (i = 0; i <= 9;++i){ //对数组元素a[0]-a[9]赋值
a[i] = i;
}
for (i = 9; i >= 0;--i){ //输出a[9]-a[0]这10个数组元素
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
//2.将一个二维数组行和列的元素互换,存到另外一个二维数组中.
int main(){
int a[2][3] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{4, 5, 6 } };
int b[3][2], i, j;
printf("array a:\n");
for (i = 0; i < 2;++i){ //处理a数组中的每一行中各元素
for (j = 0; j < 3;++j){ //处理a数组中的每一列中各元素
printf("%5d",a[i][j]); //输出a数组的一个元素
b[j][i] = a[i][j]; //将a数组中元素赋给b数组中相应的元素
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("array b:\n");
for (i = 0; i < 3; ++i){
for (j = 0; j < 2; ++j){
printf("%5d", b[i][j]); //输出b数组的一个元素
}
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Array A :
1 2 3
4 5 6
Array B :
1 4
2 5
3 6
//3.有一个3*4的矩阵,要求编程序求出其中值最大的那个元素的值,以及其所在
//的行号和列号.(打擂台算法)
int main(){
int i, j, row = 0, col = 0, colum = 0, max;
int a[3][4] = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 },
{ 9, 8, 7, 6 },
{ -10, 10, -5, 2 } };
max = a[0][0]; //先默认a[0][0]最大
for (i = 0; i < 3;++i){
for (j = 0; j < 4;++j){
if (a[i][j]>max){ //如果元素大于max,就取代
max = a[i][j];
row = i; //记下元素的行号
col = j; //记下元素的列号
}
}
}
printf("max=%2d\nrow=%2d\ncolum=%2d\n", max, row, colum);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
max = 10
row = 2
colum = 0
//4.输入一行字符,统计其中有多少个单词,单词之间用空格分隔开.
int main(){
char string[1024];
int i, num = 0, word = 0;
char c;
gets(string); //输入一个字符串
//只要字符不是'\0'就继续执行循环
for (i = 0; (c = string[i]) != '\0';++i){
if (c == ' '){ //如果是空格字符,使word置为0
word = 0;
}
else if (word == 0){ //如果不是空格字符且word原值为0
word = 1; //使word加1
++num; //num累加1,表示增加一个单词
}
}
printf("There are %d words in this line.\n", num);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
someone like you!
There are 3 words in this line.
//5.有三个字符串,要求找出其中"最大者".
int main(){
char str[3][20]; //定义二维数组
char string[20]; //定义一维数组,作为交换字符串时的临时字符数组
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3;++i){
//读入三个字符串,分别给str[0]str[1],str[2]
gets(str[i]);
}
//若str[0]>str[1],把str[0]的字符串赋值给string
if (strcmp(str[0],str[1])>0){
strcpy(string,str[0]);
}
//若str[0]<str[1],把str[1]的字符串赋值给string
else{
strcpy(string, str[1]);
}
//若str[2]<string,把str[2]的字符串赋值给string
if (strcmp(str[2], string) > 0){
strcpy(string, str[2]);
}
printf("\nthe largest string is:\n%s\n",string); //输出string
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
China
America
Brazil
the largest string is :
China
2019/4/30
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#pragma once
//1.将若干字符串按字母顺序(由小到大)输出.
//解题思路:
//(1)定义一个指针数组name, 用各字符串对它进行初始化, 即把各字符串中第1个
//字符的地址赋给指针数组的各元素;
//(2)用选择法排序, 但不是移动字符串, 而是改变指针数组的各元素的指向.
void sort(char* name[],int n){ //定义sort函数
char* temp;
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < n - 1;i++){ //使用选择法排序
k = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n;j++){
if (strcmp(name[k],name[j])>0){
k = j;
}
}
if (k != i){
temp = name[i];
name[i] = name[k];
name[k] = temp;
}
}
}
void print(char* name[],int n){ //定义print函数
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n;i++){
//按指针元素的顺序输出它们所指向的字符串
printf("%s\n",name[i]);
}
}
int main(){
void sort(char* name[], int n); //函数声明
void print(char* name[], int n);
char* name[] = { "Follow me", "BASIC", "Great Wall",
"FORTRAN", "Computer design" }; //定义指针数组
int n = 5;
sort(name, n); //调用sort函数,对字符串排序
print(name,n); //调用print函数,输出字符串
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//2.使用指着数据的指针变量.
int main(){
char* name[] = { "Follow me", "BASIC", "Great Wall",
"FORTRAN", "Computer design" };
char** p;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5;i++){
p = name + i;
printf("%s\n",*p);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Follow me
BASIC
Great Wall
FORTRAN
Computer design
//3.有一个指针数组,其元素分别指向一个整形数组的元素,用指向指针数据的
//指针变量,输出整形数组各元素的值.
int main(){
int a[5] = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
int* num[5] = { &a[0], &a[1], &a[2], &a[3], &a[4] };
int** p, i; //p是指向指针型数据的指针变量
p = num; //使p指向num[0]
for (i = 0; i < 5;i++){
printf("%d ",**p);
p++;
}
printf("\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1 3 5 7 9
//4.建立动态数组,输入5个学生的成绩,另外用一个函数检查其中有无低于60分的,
//输出不合格的成绩.
//解题思路:
//(1)使用malloc函数开辟一个动态自由区域, 用来存储5个学生的成绩, 得到这个
//动态域第1个字节的地址, 基类型为void型;
//(2)使用一个基类型为int的指针变量p来指向动态数组的各元素, 并且输出它们的值;
//(3)首先必须将malloc函数返回的void指针转换为整数指针,然后赋给p1.
void check(int* p){ //定义check函数
int i;
printf("They are fail:");
for (i = 0; i < 5;i++){
if (p[i]<60){
printf("%d ",p[i]); //输出不合格的成绩
}
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
void check(int*);
int* p1, i;
//开辟动态内存区,将地址转换成int*型,然后放在p1中
p1 = (int*)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++){
scanf("%d",p1+i); //输入5个学生的成绩
}
check(p1); //调用check函数
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
59 98 67 57 78
They are fail : 59 57