K-近邻(K-NN, K-Nearest Neighbors)
原理
K-近邻(K-NN)是一种非参数分类和回归算法。K-NN 的主要思想是根据距离度量(如欧氏距离)找到训练数据集中与待预测样本最近的 K 个样本,并根据这 K 个样本的标签来进行预测。对于分类任务,K-NN 通过投票的方式选择出现最多的类别作为预测结果;对于回归任务,K-NN 通过计算 K 个最近邻样本的平均值来进行预测。
公式
K-NN 的主要步骤包括:
- 计算待预测样本与训练集中每个样本之间的距离。常用的距离度量包括欧氏距离、曼哈顿距离等。
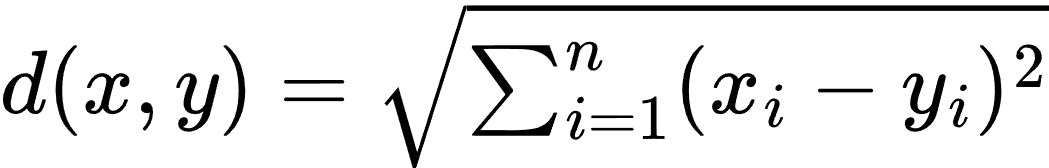
- 找到距离最近的 K 个样本。
- 对于分类任务,通过投票决定预测结果:
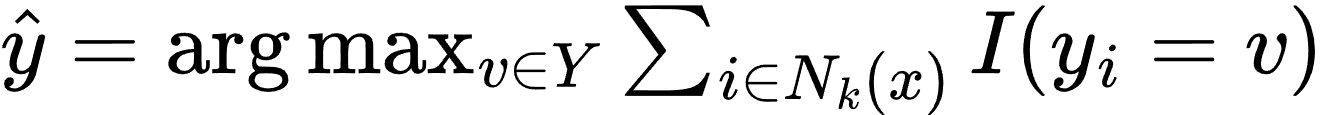
其中,Nk 表示样本 x 的 K 个最近邻样本集合,I 是指示函数。
- 对于回归任务,通过计算平均值决定预测结果:
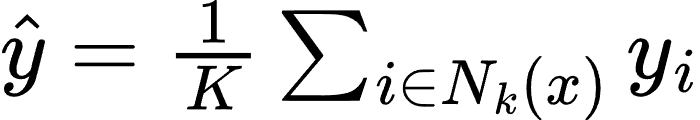
生活场景应用的案例
手写数字识别:K-NN 可以用于手写数字识别任务。假设我们有一个手写数字的图片数据集,每张图片都被标注了对应的数字。我们可以使用 K-NN 模型来识别新图片中的数字。
案例描述
假设我们有一个手写数字图片的数据集,包括以下特征:
- 图片像素值(每张图片由一个固定大小的像素矩阵表示)
我们希望通过这些像素值来预测图片中的数字。我们可以使用 K-NN 模型进行训练和预测。训练完成后,我们可以使用模型来识别新图片中的数字,并评估模型的性能。
代码解析
下面是一个使用 Python 实现上述手写数字识别案例的示例,使用了 scikit-learn 库。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
# 载入手写数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.data
y = digits.target
# 拆分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建K-NN模型并训练
k = 5
model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 评估模型
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(cm)
print("Classification Report:")
print(report)
# 可视化部分测试结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, y_pred):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8)
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {prediction}')
plt.show()在这个示例中:
- 我们使用了
sklearn.datasets中的手写数字数据集。这个数据集包含了 8x8 像素的图片,每张图片代表一个手写数字。 - 将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集。
- 使用训练集训练 K-NN 分类模型。
- 通过测试集进行预测并评估模型的性能。
- 输出准确率(accuracy)、混淆矩阵(confusion matrix)和分类报告(classification report)。
- 可视化部分测试结果,展示模型的预测效果。

这个案例展示了如何使用 K-NN 模型来识别手写数字,基于图片的像素值特征。模型训练完成后,可以用于预测新图片中的数字,并帮助解决实际的手写数字识别问题。
神经网络(Neural Network)
原理
神经网络是一种模仿生物神经元结构的计算模型,由多个节点(神经元)和连接(权重)组成。神经网络主要由输入层、隐藏层和输出层构成,每一层包含若干神经元。通过层与层之间的连接和激活函数(如ReLU、Sigmoid等),神经网络能够拟合复杂的非线性关系,实现分类、回归等任务。
训练神经网络的过程通常使用反向传播算法,通过计算损失函数的梯度来调整网络的权重,以最小化预测误差。
公式
- 神经元的线性组合:

其中,xi 是输入,wi 是权重,b 是偏置,z 是神经元的加权和。
- 激活函数: 常用的激活函数包括:
- Sigmoid 函数:
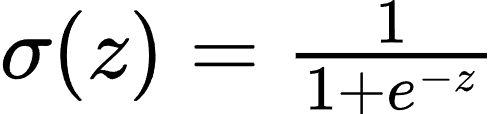
- ReLU 函数:
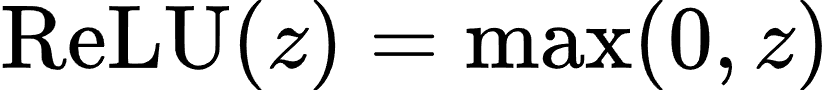
- 反向传播:
反向传播算法通过计算损失函数的梯度来更新权重:
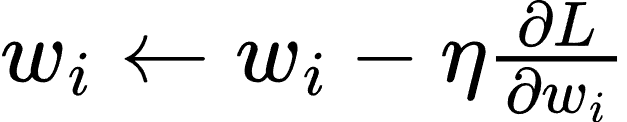
其中,η 是学习率,L 是损失函数。
生活场景应用的案例
图像分类:神经网络广泛应用于图像分类任务。假设我们有一个包含手写数字图片的数据集,每张图片都被标注了对应的数字。我们可以使用神经网络模型来识别新图片中的数字。
案例描述
假设我们有一个手写数字图片的数据集,包括以下特征:
- 图片像素值(每张图片由一个固定大小的像素矩阵表示)
我们希望通过这些像素值来预测图片中的数字。我们可以使用神经网络模型进行训练和预测。训练完成后,我们可以使用模型来识别新图片中的数字,并评估模型的性能。
代码解析
下面是一个使用 Python 实现上述手写数字识别案例的示例,使用了 tensorflow 和 keras 库。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
# 载入手写数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images
y = digits.target
# 预处理数据
X = X / 16.0 # 将像素值归一化到 [0, 1]
y = to_categorical(y, num_classes=10) # 将标签转换为one-hot编码
# 调整数据维度以适应TensorFlow模型
X = X.reshape(-1, 8, 8, 1) # 使用-1使reshape自动计算样本数量
# 拆分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建神经网络模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(8, 8, 1)), # 展平输入图像
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含128个神经元
Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含64个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层,包含10个神经元,对应10个类别
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
# 评估模型
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print("Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred_classes))
# 可视化部分测试结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, y_pred_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8) # 确保图像形状正确
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {prediction}')
plt.show()
在这个示例中:
- 我们使用了
sklearn.datasets中的手写数字数据集。这个数据集包含了 8x8 像素的图片,每张图片代表一个手写数字。 - 将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集,并对数据进行预处理,将像素值归一化并将标签转换为 one-hot 编码。
- 创建了一个包含两个隐藏层的神经网络模型。
- 使用训练集训练神经网络模型。
- 通过测试集进行预测并评估模型的性能。
- 输出准确率(accuracy)和分类报告(classification report)。
- 可视化部分测试结果,展示模型的预测效果。

这个案例展示了如何使用神经网络模型来识别手写数字,基于图片的像素值特征。模型训练完成后,可以用于预测新图片中的数字,并帮助解决实际的手写数字识别问题。
具体应用
- 对预测结果进行可视化展示:
-
- 在预测结果后,展示原始图片及其预测结果。
- 保存和加载训练好的模型:
-
- 保存训练好的模型。
- 加载已保存的模型进行预测。
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, load_model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from PIL import Image # 用于加载自定义图片
# 载入手写数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images
y = digits.target
# 预处理数据
X = X / 16.0 # 将像素值归一化到 [0, 1]
y = to_categorical(y, num_classes=10) # 将标签转换为one-hot编码
# 调整数据维度以适应TensorFlow模型
X = X.reshape(-1, 8, 8, 1) # 使用-1使reshape自动计算样本数量
# 拆分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建神经网络模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(8, 8, 1)), # 展平输入图像
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含128个神经元
Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含64个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层,包含10个神经元,对应10个类别
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
# 保存训练好的模型
model.save('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 加载训练好的模型
# model = load_model('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 评估模型
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print("Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred_classes))
# 可视化部分测试结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, y_pred_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8) # 确保图像形状正确
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {prediction}')
plt.show()
# 加载并预处理单张图片
def load_and_preprocess_image(filepath):
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L') # 转换为灰度图像
img = img.resize((8, 8)) # 调整图像大小为8x8
img = np.array(img) / 16.0 # 归一化像素值
img = img.reshape(1, 8, 8, 1) # 调整图像维度
return img
# 加载并预处理文件夹中的所有图片
def load_images_from_folder(folder):
images = []
filepaths = []
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
if filename.endswith(('png', 'jpg', 'jpeg')):
filepath = os.path.join(folder, filename)
img = load_and_preprocess_image(filepath)
images.append(img)
filepaths.append(filepath)
return np.vstack(images), filepaths
# 使用模型预测文件夹中的多张图片
def predict_custom_images_from_folder(folder):
imgs, filepaths = load_images_from_folder(folder)
preds = model.predict(imgs)
pred_classes = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)
return pred_classes, filepaths
# 示例:预测文件夹中的多张自定义图片并展示结果
custom_image_folder = 'path/to/your/folder' # 替换为自定义图片文件夹路径
predicted_classes, filepaths = predict_custom_images_from_folder(custom_image_folder)
# 打印预测结果并可视化
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(filepaths), figsize=(15, 3))
for ax, filepath, pred_class in zip(axes, filepaths, predicted_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L')
img = img.resize((8, 8))
img = np.array(img
ax.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {pred_class}')
print(f'The predicted class for {filepath} is: {pred_class}')
plt.show()a. 添加更多的训练数据来提高模型的准确性。
b. 使用混淆矩阵来详细分析模型的分类结果。
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, load_model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from PIL import Image
# 载入手写数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images
y = digits.target
# 预处理数据
X = X / 16.0 # 将像素值归一化到 [0, 1]
y = to_categorical(y, num_classes=10) # 将标签转换为one-hot编码
# 调整数据维度以适应TensorFlow模型
X = X.reshape(-1, 8, 8, 1) # 使用-1使reshape自动计算样本数量
# 拆分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 再拆分训练集以创建验证集
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 数据扩充
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=10,
zoom_range=0.1,
width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1
)
datagen.fit(X_train)
# 创建神经网络模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(8, 8, 1)), # 展平输入图像
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含128个神经元
Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含64个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层,包含10个神经元,对应10个类别
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
model.fit(datagen.flow(X_train, y_train, batch_size=32), epochs=20, validation_data=(X_val, y_val))
# 保存训练好的模型
model.save('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 加载训练好的模型
# model = load_model('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 评估模型
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print("Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred_classes))
# 生成混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred_classes)
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm, display_labels=np.arange(10))
disp.plot(cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.show()
# 可视化部分测试结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, y_pred_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8) # 确保图像形状正确
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {prediction}')
plt.show()
# 加载并预处理单张图片
def load_and_preprocess_image(filepath):
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L') # 转换为灰度图像
img = img.resize((8, 8)) # 调整图像大小为8x8
img = np.array(img) / 16.0 # 归一化像素值
img = img.reshape(1, 8, 8, 1) # 调整图像维度
return img
# 加载并预处理文件夹中的所有图片
def load_images_from_folder(folder):
images = []
filepaths = []
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
if filename.endswith(('png', 'jpg', 'jpeg')):
filepath = os.path.join(folder, filename)
img = load_and_preprocess_image(filepath)
images.append(img)
filepaths.append(filepath)
return np.vstack(images), filepaths
# 使用模型预测文件夹中的多张图片
def predict_custom_images_from_folder(folder):
imgs, filepaths = load_images_from_folder(folder)
preds = model.predict(imgs)
pred_classes = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)
return pred_classes, filepaths
# 示例:预测文件夹中的多张自定义图片并展示结果
custom_image_folder = 'path/to/your/folder' # 替换为自定义图片文件夹路径
predicted_classes, filepaths = predict_custom_images_from_folder(custom_image_folder)
# 打印预测结果并可视化
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(filepaths), figsize=(15, 3))
for ax, filepath, pred_class in zip(axes, filepaths, predicted_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L')
img = img.resize((8, 8))
img = np.array(img)
ax.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {pred_class}')
print(f'The predicted class for {filepath} is: {pred_class}')
plt.show()a. 使用更多的手写数字样本进行训练,以提高模型对手写数字的识别能力。
b. 尝试使用不同的模型架构,如卷积神经网络(CNN),以提高模型的识别准确率。
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, load_model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from PIL import Image
# 载入手写数字数据集
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images
y = digits.target
# 预处理数据
X = X / 16.0 # 将像素值归一化到 [0, 1]
y = to_categorical(y, num_classes=10) # 将标签转换为one-hot编码
# 调整数据维度以适应TensorFlow模型
X = X.reshape(-1, 8, 8, 1) # 使用-1使reshape自动计算样本数量
# 拆分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 再拆分训练集以创建验证集
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 数据扩充
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=5,
zoom_range=0.05,
width_shift_range=0.05,
height_shift_range=0.05
)
datagen.fit(X_train)
# 创建神经网络模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(8, 8, 1)), # 展平输入图像
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含128个神经元
Dense(64, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层,包含64个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层,包含10个神经元,对应10个类别
])
# 编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
history = model.fit(datagen.flow(X_train, y_train, batch_size=32), epochs=20, validation_data=(X_val, y_val))
# 保存训练好的模型
model.save('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 加载训练好的模型
# model = load_model('digit_recognition_model.h5')
# 评估模型
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_classes = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
y_true = np.argmax(y_test, axis=1)
print(f"Accuracy: {accuracy}")
print("Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(y_true, y_pred_classes))
# 生成混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred_classes)
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm, display_labels=np.arange(10))
disp.plot(cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.show()
# 可视化部分测试结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 5, figsize=(10, 3))
for ax, image, prediction in zip(axes, X_test, y_pred_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
image = image.reshape(8, 8) # 确保图像形状正确
ax.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {prediction}')
plt.show()
# 加载并预处理单张图片
def load_and_preprocess_image(filepath):
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L') # 转换为灰度图像
img = img.resize((8, 8)) # 调整图像大小为8x8
img = np.array(img) / 255.0 # 归一化像素值到 [0, 1]
img = img.reshape(1, 8, 8, 1) # 调整图像维度
return img
# 加载并预处理文件夹中的所有图片
def load_images_from_folder(folder):
images = []
filepaths = []
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
if filename.endswith(('png', 'jpg', 'jpeg')):
filepath = os.path.join(folder, filename)
img = load_and_preprocess_image(filepath)
images.append(img)
filepaths.append(filepath)
return np.vstack(images), filepaths
# 使用模型预测文件夹中的多张图片
def predict_custom_images_from_folder(folder):
imgs, filepaths = load_images_from_folder(folder)
preds = model.predict(imgs)
pred_classes = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)
return pred_classes, filepaths
# 示例:预测文件夹中的多张自定义图片并展示结果
custom_image_folder = 'path/to/your/folder' # 替换为自定义图片文件夹路径
predicted_classes, filepaths = predict_custom_images_from_folder(custom_image_folder)
# 打印预测结果并可视化
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(filepaths), figsize=(15, 3))
for ax, filepath, pred_class in zip(axes, filepaths, predicted_classes):
ax.set_axis_off()
img = Image.open(filepath).convert('L')
img = img.resize((8, 8))
img = np.array(img)
ax.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f'Pred: {pred_class}')
print(f'The predicted class for {filepath} is: {pred_class}')
plt.show()