shell脚本
一.shell基础
1.shell概念
2.shell脚本

3.shell脚本编写注意事项

二.编写shell脚本
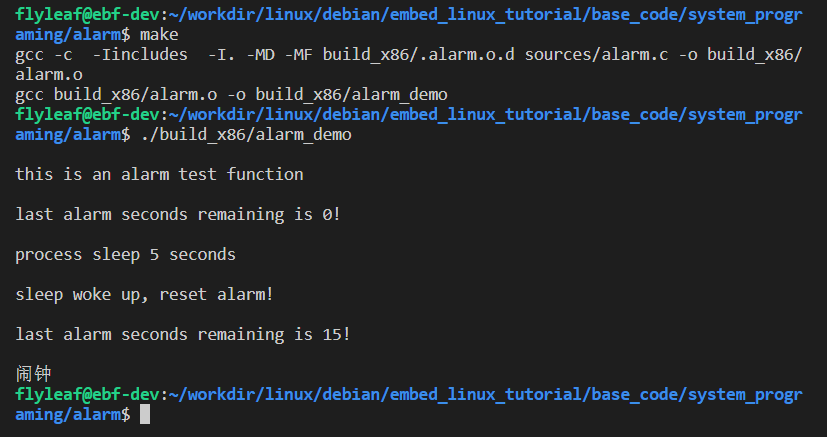
1.编写一个helloworld脚本,运行脚本
[root@shell ~]# vim helloworld.sh #!/bin/bash //声明 echo "hello world!" ls -lh /etc/ 运行脚本(四种方式): [root@shell ~]# bash helloworld.sh [root@shell ~]# sh helloworld.sh [root@shell ~]# source helloworld.sh [root@shell ~]# chmod +x helloworld.sh [root@shell ~]# ./helloworld.sh
2.编写一个nginx安装脚本
[root@shell ~]# mkdir /root/shell [root@shell ~]# vim /root/shell/install_nginx.sh #!/bin/bash yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make pcre-devel oprnssl-devel wget cd /usr/local/scr/ wget 'https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.26.1.tar.gz' tar xf nginx-1.26.1.tar.gz cd nginx-1.26.1 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx make -j 4 make install [root@shell shell]# cd /root/shell [root@shell shell]# sh install_nginx.sh
三.变量
1.自定义变量
[root@shell shell]# set a=3 [root@shell shell]# echo a a [root@shell shell]# unset a [root@shell shell]# echo a a [root@shell shell]# echo $a
2.环境变量
由系统维护,用于设置工作环境
脚本或者应用需要参数的时候使用
$PWD
$SHELL
$USER
[root@shell shell]# vim test1.sh #!/bin/bash echo $1 echo $2 echo $3 echo $4 echo $5 [root@shell shell]# bash test1.sh 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
[root@shell shell]# bash test1.sh t j j f b t j j f b
3.位置变量
[root@shell ~]# vim creat.sh #!/bin/bash useradd $1 echo $2|passwd --stdin $1 [root@shell ~]# sh creat.sh
4.预定义变量

[root@shell ~]# vim ss.sh #!/bin/bash #将所有的脚本参数输出 for x in "$*" do echo $x done [root@shell ~]# sh ss.sh a b c a b c [root@shell ~]# sh ss.sh g q i g d g q i g d 将*改为@运行 [root@shell ~]# sh ss.sh g q i g d g q i g d
四.判断语法
shell的返回值:运行一条命令,都会有一个返回值,0表示执行正常,非0表示执行异常。
[root@shell ~]# test 3 -gt 2 [root@shell ~]# echo $? 0
1.条件判断---if语句
[root@shell ~]# vim if.sh #!/bin/bash echo "1:" read a echo "2:" read b if [ $a -eq $b ]; then echo "相等" else echo "不相等" fi [root@shell ~]# sh if.sh 1: 3 2: 5 不相等
2.创建检测脚本,检测网络是否流畅
[root@shell ~]# vim web.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "输入网址:" web //read:命令行输入web的值 ping -c 3 $web &> /dev/null //连接某个网站三次 if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then //如果ping命令执行成功 echo "网络畅通" else echo "网络异常" fi root@shell ~]# sh web.sh 输入网址:www.baidu.com 网络畅通
五.字符串判断格式:

1.字符串的比较
[root@shell ~]# aaa="abc" [root@shell ~]# echo $aaa abc [root@shell ~]# test $aaa == "abc" [root@shell ~]# echo $? 0 [root@shell ~]# test $aaa == "dggn" [root@shell ~]# echo $? 1 [root@shell ~]# unset aaa [root@shell ~]# echo $aaa
2.案例
(1)创建简单的字符串判断脚本
[root@shell ~]# vim zfc.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "请输入账号" user echo $user if [ $user == "admin" ]; then echo "欢迎登录:$user" else echo "账号或密码错误" fi [root@shell ~]# sh zfc.sh 请输入账号admin admin 欢迎登录:admin [root@shell ~]# sh zfc.sh 请输入账号egu egu 账号或密码错误
(2)创建rpm查询软件是否安装
[root@shell ~]# vim rpm.sh #!/bin/bash rpm -qa|grep nginx #echo $? yum -y install epel.release if [ $? -eq 1 ];then yum -y install nginx else yum -y remove nginx yum -y install nginx fi [root@shell ~]# sh rpm.sh
六.文件,目录,权限的判断
1.格式:
2.常用操作符:

[root@shell ~]# touch abc [root@shell ~]# ls -lh abc -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 7月 26 11:26 abc [root@shell ~]# [ -e "abc" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 0 [root@shell ~]# [ -e "ewf" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 1 [root@shell ~]# [ -e "aaaaaa" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 1 [root@shell ~]# [ -w "aaaaaa" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 1 [root@shell ~]# [ -x "abc" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 1 [root@shell ~]# chmod +x abc [root@shell ~]# [ -x "abc" ] [root@shell ~]# echo $? 0 [root@shell ~]# ls -l abc -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 0 7月 26 11:26 abc
3.案例
nginx安装脚本优化,判断是否已经安装nginx
七.与或判断
判断多个条件
多个条件其中一个成立,或
多个条件都要成立,与
或运算判断:||
与运算判断:&&
1.或运算
[root@shell ~]# vim huo.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "请输入名称" name if [ $name == "haha" ]||[ $name == "xixi" ];then echo "成立" else echo "不成立" fi [root@shell ~]# sh huo.sh 请输入名称haha 成立
2.与运算
[root@shell ~]# vim yu.sh #!/bin/bish read -p "请输入年龄" age read -p "请输入性别" gender if [ $age -ge 30 ] && [ $gender == "女" ];then echo "涨工资" else echo"不加" fi [root@shell ~]# sh yu.sh 请输入年龄34 请输入性别女 涨工资
3.多层判断
[root@shell ~]# vim dc.sh #!/bin/bash echo "1新增文件 2删除文件 3修改文件 4查找文件" read -p "请选择序号" m if [ $m == 1 ];then touch aaaaa.txt elif [ $m == 2 ]; then rm -fr aaaaa.txt else echo "其他功能正在开发" fi [root@shell ~]# sh dc.sh

八.shell读取用户输入
1.read
格式:read -选项
[root@shell ~]# read -p "请输入" -s s 请输入[root@shell ~]# echo $s aadswdqdweqhjhbnhbuuiwefggywgywygfe [root@shell ~]# read -p "请输入" s 请输入dtdyuj [root@shell ~]# echo $s dtdyuj [root@shell ~]# read -p "三个变量" a b c 三个变量12 13 14 [root@shell ~]# echo $a 12 [root@shell ~]# echo $b 13 [root@shell ~]# echo $c 14 [rot@shell ~]# vim pas.sh #!/bin/bash read -p "username:" username read -p "password:" -s password useradd $useranme echo $password|passwd --stdin $username if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "账户$username注册成功" fi
九.循环语法
1.for循环
[root@shell ~]# vim int.sh #!/bin/bash for x in $* do echo $x done [root@shell ~]# sh int.sh 我 是 秦始皇 我 是 秦始皇 [root@shell ~]# vim int.sh #!/bin/bash for city in 青岛 北京 天津 do echo "$city是个好地方" done [root@shell ~]# sh city.sh 青岛是个好地方 北京是个好地方 天津是个好地方
在命令结果中循环
在命令结果中循环:
[root@shell ~]# vim 1.sh
#!/bin/bash
for u in $(awk -F':' '{print $1}' /etc/passwd)
do
echo "$u"
done
[root@shell ~]# sh 1.sh
检查某个网段的存活主机
[root@shell ~]# vim ping.sh
#!/bin/bash
for IP in $(echo 12.168.2.{1..150})
do
ping -c 2 -i 0.1 $IP &> /dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then
echo "$IPisup "
fi
done
[root@shell ~]# bash ping.sh
2.while循环
3.循环的break和continue
break ---直接退出
continue---退出当前循环,进入下次循环
九九乘法表
[root@shell ~]# vim jj.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..9};do
for j in {1..9};do
echo -n "$j*$i=$(($i*$j)) "
if [ $j == $i ];then
echo -e '\n'
break
fi
done
done
[root@shell ~]# bash jj.sh
1*1=1
1*2=2 2*2=4
1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9
1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16
1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 4*5=20 5*5=25
1*6=6 2*6=12 3*6=18 4*6=24 5*6=30 6*6=36
1*7=7 2*7=14 3*7=21 4*7=28 5*7=35 6*7=42 7*7=49
1*8=8 2*8=16 3*8=24 4*8=32 5*8=40 6*8=48 7*8=56 8*8=64
1*9=9 2*9=18 3*9=27 4*9=36 5*9=45 6*9=54 7*9=63 8*9=72 9*9=81
十.sed
sed是文本处理工具,用来读取文件内容
格式:sed '过滤+动作' 文件路径
sed选项:


[root@shell ~]# rm -rf * [root@shell ~]# cp /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 ./ [root@shell ~]# sed -n '2p' ifcfg-ens33 //打印第二行 PROXY_METHOD=none [root@shell ~]# sed -n '1,3p' ifcfg-ens33 //打印1到3行 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no [root@shell ~]# sed -n '1p;3p' ifcfg-ens33 //打印1,3行 TYPE=Ethernet BROWSER_ONLY=no
配置一个自动设置静态ip以及关闭selinux服务,关闭NetWorkManager,修改主机名脚本,ip和主机名使用read输入,这个操作只能在root下执行
[root@shell ~]# vim zd.sh
#!/bin/bash
#备份
cp /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33.bak
read -p "请输入ip地址:" ip
sed -i '/dhcp/s/dhcp/none/g' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '$aIPADDR='"$ip"'' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '$aNETMASK=255.255.255.0' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '$aGATEWAY=192.168.2.1' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '$aDNS1=8.8.8.8' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '$aDNS2=114.114.114.114' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
sed -i '/UUID/cUUID='"$(uuidgen)"'' /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33
#修改主机名
read -p "请输入主机名称:" hn
hostnamectl set-hostname $hn
#停用selinux
setenforce 0
sed -i '/SELINUX/cSELINUX=disabled' set /etc/selinux/config
#停用防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
#停用NetworkManager
systemctl stop NetworkManager
systemctl disable NetworkManager
[root@shell ~]# bash zd.sh