目录
一.接口说明
1.1 erase
1.2 replace(最好别用)
1.3 find
1.4 substr
1.5 rfind
1.6 find_first_of
1.7 find_last_of
二.string类的模拟实现
2.1 构造
2.2 无参构造
2.3 析构
2.4.【】运算符
2.5 迭代器
2.6 打印
2.7 reserve扩容
2.8 push_back尾插
2.9 append追加
2.10 insert插入
2.11 erase删除
2.12 swap交换
2.13 find寻找
2.14 运算符+=
2.15 substr
2.16 流插入<<
2.17 流提取>>
三.现代写法
拷贝构造
赋值拷贝
四.小拓展
五.全部代码
一.接口说明
1.1 erase
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1("hello world"); s1.erase(0, 4); cout << s1 << endl;//o world 从下标为0开始,删除4个字符 s1.erase(); cout << s1 << endl;// return 0; }
1.2 replace(最好别用)
int main() { string s1("hello world"); string s2; s1.replace(0, 1, "aaaa"); cout << s1 << endl;//aaaaello world return 0; }替换指定位置内容,并挪动后面数据。
1.3 find
int main() { string s1("hello world a b"); // 所有的空格替换为100% size_t pos = s1.find(' ', 0);//从下标为0位置开始找 while (pos != string::npos) { s1.replace(pos, 1, "100%"); // 效率很低,能不用就不要用了 pos = s1.find(' ', pos + 4); } cout << s1 << endl;//hello100%world100%a100%b return 0; }作用就是从头开始找到该字符并返回其下标位置。
之所以不用replace是因为有更好的替代~
int main() { string s1("hello world a b"); string s2; for (auto ch : s1) { if (ch == ' ') { s2 += "100%"; } else { s2 += ch; } } s1.swap(s2); cout << s1 << endl;//hello100%world100%a100%b return 0; }注意:
swap(s1,s2)与s1.swap(s2)可不一样,前者是通过有个中间变量进行交换,而后者是让双方指针进行交换,后者更为高效~
1.4 substr
int main() { string s1("hello"); string s2; s2 = s1.substr(1, 2); cout << s2 << endl;//el cout << s1.substr(1) << endl;//ello return 0; }在 str 中从 pos 位置开始,截取 n 个字符,然后将其返回
1.5 rfind
从末尾开始找字符并返回下标
int main() { //获取后缀名 string s1("Test.cpp"); string s2("Test.tar.zar"); size_t pos1 = s1.find('.'); size_t pos2 = s2.rfind('.'); if(pos1 != string::npos) { string s3 = s1.substr(pos1); cout << s3 << endl;//.cpp string s4 = s2.substr(pos2); cout << s4 << endl;//.zar } return 0; }
1.6 find_first_of
int main() { string s1("hello world"); size_t pos1 = s1.find_first_of("abcde"); cout << pos1 << endl;//1 pos1 = s1.find_first_of("ow"); cout << pos1 << endl;//4 return 0; }返回在选定字符串中任意一个字符第一次出现的下标。(从头开始遍历)
1.7 find_last_of
int main() { string s1("hello world"); size_t pos1 = s1.find_last_of("abcde"); cout << pos1 << endl;//10 pos1 = s1.find_last_of("h"); cout << pos1 << endl;//0 return 0; }返回在选定字符串中任意一个字符第一次出现的下标。(从尾开始遍历)
注意:find_first_not_of与find_last_not_of,就是返回指选定字符串之外的字符下标
int main() { string s1("hello world"); size_t pos1 = s1.find_first_not_of("abcde"); cout << pos1 << endl;//0 pos1 = s1.find_last_not_of("h"); cout << pos1 << endl;//10 return 0; }
二.string类的模拟实现
2.1 构造
首先实现构造函数的时候在初始化列表不能直接这么写,涉及到了权限放大~
也不能在私有成员那写:const char* _str,这样_str以后只能指向一处,无法修改指向,也意味着无法增删改。
namespace lj { class string { public: //构造 string(const char* str) { _size = strlen(str); _capacity = _size; _str = new char[_capacity + 1];//加1是因为在_capacity那被认为‘\0’是有效字符 strcpy(_str, str); } private: size_t _size; size_t _capacity; char* _str; }; void test_string1() { string s1("aabbcc");//构造成功 } }建议直接放弃在列表初始化,还得考虑声明顺序啥的挺麻烦~
2.2 无参构造
//无参构造 string() { _str = nullptr; _size = 0; _capacity = 0; } //返回c格式字符串 const char* c_str() { return _str; }
可惜这种无参写法不行,因为c_str是以指针的形式返回的(字符串形式),而cout接触到指针会认为是要打印字符串,直接解引用指针,一个空指针被解引用是错误的。
开辟个1字节的空间,里面放个字符(但不是有效字符)
不过与其写无参不如直接写缺省参数
//为什么字符串就能匹配上啊?,因为这样指针就能指向它,本身是地址。
2.3 析构
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}2.4.【】运算符
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _str[pos];
}//为什么里面还能有【】,因为这个是给内置类型使用的,自定义类型要自己自定义
2.5 迭代器
typedef char* iterator; iterator begin() { return _str; } iterator end() { return _str + _size; }
其实迭代器实现也挺简单的~
for+auto的遍历底层逻辑其实还是迭代器。
2.6 打印
首先调用size()函数的时候出现了权限放大的问题,调用运算符【】也是如此。所以在这里我们就要引入const成员函数进行修改~对需要改变自身的额外再写一个针对const权限函数,对不需要改变自身的加入const。
void print_str(const string& s) { for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { //s[i]++; cout << s[i] << endl; } string::const_iterator it = s.begin(); while (it != s.end()) { // *it = 'x'; cout << *it << " "; ++it; } cout << endl; }
2.7 reserve扩容
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];//还有一个开给\0
strcpy(tmp, _str);//拷贝所指向的内容
delete[] _str;//销毁旧空间
_str = tmp;//指向新空间
_capacity = n;
}
}2.8 push_back尾插
void push_back(char ch) { if (_size == _capacity) { size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2; reserve(newcapacity); } _str[_size] = ch; _size++; _str[_size] = '\0'; }
由于\0不算有效字符,所以最后计算完后_size都会与其下标相等,而这时候可以刚好插入字符。最后需要注意人工补上\0。
2.9 append追加
void append(const char* str) { size_t len = strlen(str);//计算所追加的长度 if (_size + len > _capacity) { reserve(_size + len); } strcpy(_str+_size, str); _size += len; }
//strcpy(_str+_size, str);为什么不是_size就行了呢?因为_size是一个数据不是一个指针,而_str是指针+数可以达到偏移的效果
2.10 insert插入
void insert(size_t pos, char ch) { assert(pos <=_size); if (_size == _capacity) { size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2; reserve(newCapacity); } size_t end = _size; while (pos < end) { _str[end] = _str[end - 1]; end--; } _str[pos] = ch; _size++; _str[_size] = '\0'; }需要注意的细节有点多:如果是这种写法
while (end >= (int)pos) { _str[end + 1] = _str[end]; --end; }最后end会减为负数,而其类型又是无符号整型,会一直陷入死循环。就算把end改为整型,在循环条件里又会和pos触发类型提升(小的向大的转,有符号向无符号转),最后还得强制转化pos类型才可以解决问题。所以直接换个写法一劳永逸~
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str) { assert(pos <= _size); size_t len = strlen(str); if (_size+len > _capacity) { reserve(_size+len); } size_t end = _size; while (pos < end) { _str[end+len-1] = _str[end - 1]; end--; } strncpy(_str + pos, str,len); _size+=len; _str[_size] = '\0'; }
2.11 erase删除
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos) { assert(pos <= _size); if (len == npos || pos + len > _size) { _str[pos] = '\0'; _size = pos; } else { strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);//很精妙 _size -= len; } }
2.12 swap交换
void swap(string& s) { std::swap(_str, s._str); std::swap(_size, s._size); std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity); }
如果没有中间的swap(string),那么swap(s1,s2)就会走与swap(a,b)一样的结果,产生中间变量。如果有中间的swap(string),那当我们swap(s1,s2)时进入其中就会让我们去调用string类里面的swap,只需要交换指针即可,不产生中间变量。
2.13 find寻找
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0) { for (size_t i = pos; i <= _size; i++) { if (_str[i] == ch) { return i; } } return npos; }
size_t find(const char*str, size_t pos = 0) { const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str); if (ptr == nullptr) { return npos; } else { return ptr - _str;//利用指针-指针 } }
2.14 运算符+=
string& operator+=(char ch) { push_back(ch); return *this; } string& operator+=(const char* str) { append(str); return *this; }
简单复用即可
2.15 substr
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) { assert(pos < _size); size_t end = pos+len; if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size) { end = _size; } string sub1; sub1.reserve(end - pos);//重新创个空间 for (size_t i = pos; i < end; i++)//拷贝内容 { sub1 += _str[i]; } return sub1; }
最终会报错~
问题一:因为是临时对象,这意味着出作用会就会调用析构函数(清理资源),而临时对象又指向临时资源,被清理后那就变成野指针了。
解决方法:写出拷贝构造(深拷贝)
string(const string& s) { //深拷贝 _str = new char[s._capacity + 1]; strcpy(_str, s._str); _size = s._size; _capacity = s._capacity; }问题二:在赋值拷贝中(s2=s1)会出现以下情况,要么s2的空间过大,与s1大小差距过大造成资源浪费。要么s2的空间太小,不足够容纳s1,只有二者刚刚好才合适。
// s2 = s1 string& operator=(const string& s) { if (this != &s)//不自己调用自己 { char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1]; strcpy(tmp, s._str); delete[] _str; _str = tmp; _size = s._size; _capacity = s._capacity; } return *this; }既然这样就重新构造一个与s1相仿的空间,再拷贝原内容进去,删掉s2所指的原来空间,令s2指向新空间,再浅拷贝,使得赋值拷贝合理化。
成功实现效果~
2.16 流插入<<
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s) { for (auto ch : s) { out << ch; } return out; }
2.17 流提取>>
void clear() { _size = 0; _str[0] = '\0'; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s) { s.clear(); char ch = in.get(); while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n') { s += ch; ch = in.get(); } return in; }
细节一:clear函数
如果没有_str[0] = '\0';由于cout<<s1是以_size为准的,在遍历的时候就停止流插入了。而cout<<s1.c_str()中由于其返回的是整段的字符串不看_size,是直接解引用的。那么在没有'\0'的情况下还是会输出,没有达成清理的效果。
另外如果没有clear函数清理原内容,那么cin最后做到的只是拼接。
细节二.get函数
如果ch以这样的方式提取那么最终会无法识别到‘ ’与‘\n’而死循环。因为in拿不到‘ ’与‘\n’,他们通常是作为分割符合使用的,所以会无视。只有get函数才能够识别并提取它们。
三.现代写法
备注:功能和传统写法一组,只是让代码行数更少
拷贝构造
//传统写法 string s2(s1) string(const string& s) { //深拷贝 _str = new char[s._capacity + 1]; strcpy(_str, s._str); _size = s._size; _capacity = s._capacity; } //现代写法 string s2(s1) string(const string& s) { string tmp(s._str);//调用构造,构造出与s1一样的空间与内容 swap(tmp);//s2与tmp交换指针 }
细节:s2必须得指向空(全缺省),如果指向其他地方那么tmp可能会出现随机值,报错。
赋值拷贝
//传统写法 s1 = s3 string& operator=(const string& s) { if (this != &s)//不自己调用自己 { char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1]; strcpy(tmp, s._str); delete[] _str; _str = tmp; _size = s._size; _capacity = s._capacity; } return *this; } //现代写法 s1 = s3 string& operator=(string s) { swap(s); return *this; }
四.小拓展
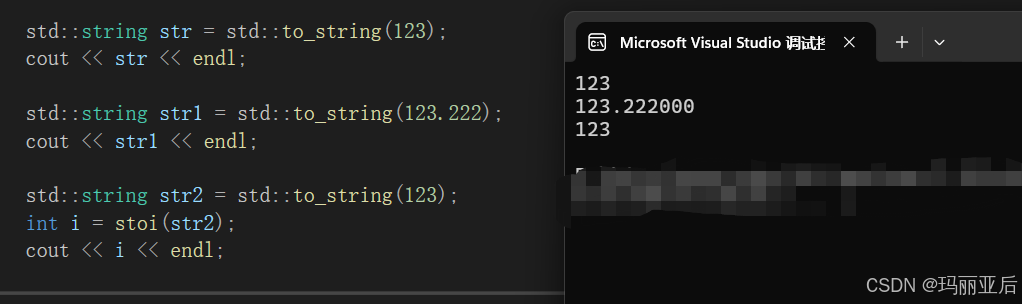
to_string可以识别各种类型然后转化为string。
stoi可以识别string类型然后转化为需要的类型。
五.全部代码
//string.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "string.h"
namespace lj
{
//构造
string::string(const char* str)//不能给'\0'类型不匹配,而字符串会默认带\0
{
_size = strlen(str);
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];//加1是因为在_capacity那被认为‘\0’是有效字符
strcpy(_str, str);
}
//现代写法 string s2(s1)
string::string(const string& s)
{
string tmp(s._str);//调用构造
swap(tmp);
}
//现代写法 s1 = s3
string& string::operator=(string s)
{
swap(s);
return *this;
}
string::~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}
char& string::operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _str[pos];
}
const char& string:: operator[](size_t pos)const
{
return _str[pos];
}
void string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];//还有一个开给\0
strcpy(tmp, _str);//拷贝所指向的内容
delete[] _str;//销毁旧空间
_str = tmp;//指向新空间
_capacity = n;
}
}
void string::push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);//计算所追加的长度
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
size_t newCapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(newCapacity);
}
size_t end = _size;
while (pos < end)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
end--;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size;
while (pos < end)
{
_str[end + len - 1] = _str[end - 1];
end--;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void string::erase(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len > _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);//很精妙
_size -= len;
}
}
void string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
size_t string::find(char ch, size_t pos)
{
for (size_t i = pos; i <= _size; i++)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t string::find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
const char* ptr = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (ptr == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return ptr - _str;//利用指针-指针
}
}
string& string::operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& string::operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
string string::substr(size_t pos, size_t len)
{
assert(pos < _size);
size_t end = pos + len;
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
end = _size;
}
string sub1;
sub1.reserve(end - pos);//重新创个空间
for (size_t i = pos; i < end; i++)//拷贝内容
{
sub1 += _str[i];
}
return sub1;
}
void string::clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[0] = '\0';
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{
for (auto ch : s)
{
out << ch;
}
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s)
{
s.clear();
char ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
};
//string.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace lj
{
class string
{
public:
//无参构造
/* string()
:_str(new char[1])
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
_capacity = 0;
}*/
//返回c格式字符串
const char* c_str()const
{
return _str;
}
//构造
string(const char* str = "");//不能给'\0'类型不匹配,而字符串会默认带\0
//现代写法 string s2(s1)
string(const string& s);
//现代写法 s1 = s3
string& operator=(string s);
~string();
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _str + _size;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos);
const char& operator[](size_t pos)const;
void reserve(size_t n);
void push_back(char ch);
void append(const char* str);
void insert(size_t pos, char ch);
void insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
void erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
void swap(string& s);
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0);
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
string& operator+=(char ch);
string& operator+=(const char* str);
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
void clear();
private:
size_t _size = 0;
size_t _capacity = 0;
char* _str = nullptr;
const static size_t npos = -1;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s);
istream& operator>>(istream& in, string& s);
}
//test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// //string s1("hello world");
// //s1.erase(0, 4);
// //cout << s1 << endl;//o world 从下标为0开始,删除4个字符
// //s1.erase();
// //cout << s1 << endl;//
//
// //string s1("hello world");
// //string s2;
// //s1.replace(0, 1, "aaaa");
// //cout << s1 << endl;//aaaaello world
// string s1("hello world a b");
// // 所有的空格替换为100%
// size_t pos = s1.find(' ', 0);
// while (pos != string::npos)
// {
// s1.replace(pos, 1, "100%");
// // 效率很低,能不用就不要用了
//
// pos = s1.find(' ', pos + 4);
// }
// cout << s1 << endl;//hello100%world100%a100%b
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string s1("hello world a b");
// string s2;
// for (auto ch : s1)
// {
// if (ch == ' ')
// {
// s2 += "100%";
// }
// else
// {
// s2 += ch;
// }
// }
// s1.swap(s2);
// cout << s1 << endl;//hello100%world100%a100%b
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string s1("hello");
// string s2;
// s2 = s1.substr(1, 2);
// cout << s2 << endl;//el
// cout << s1.substr(1) << endl;//ello
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// //获取后缀名
// string s1("Test.cpp");
// string s2("Test.tar.zar");
//
// size_t pos1 = s1.find('.');
// size_t pos2 = s2.rfind('.');
//
// if(pos1 != string::npos)
// {
// string s3 = s1.substr(pos1);
// cout << s3 << endl;//.cpp
//
// string s4 = s2.substr(pos2);
// cout << s4 << endl;//.zar
//
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
//int main()
//{
// string s1("hello world");
//
// size_t pos1 = s1.find_first_not_of("abcde");
// cout << pos1 << endl;//0
//
// pos1 = s1.find_last_not_of("h");
// cout << pos1 << endl;//10
//
//
// return 0;
//}
#include"string.h"
void print_str(const string& s)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
//s[i]++;
cout << s[i] << endl;
}
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
// *it = 'x';
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string1()
{
//string s1("aabbcc");//构造成功
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
//{
// s1[i]++;
//}
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s2;
cout << s2.c_str << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc");
//string::iterator it = s1.begin();
//while (it != s1.end())
//{
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
//}
//cout << endl;//a a b b c c
//string s1("aabbcc");
//for (auto ch : s1)
//{
// cout << ch << " ";
//}
//cout << endl;//a a b b c c
//string s3("hello");
//print_str(s3);//bb cc dd
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s1.push_back('a');
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s2;
//s2.push_back('a');
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
/*string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
s1.append("aaa");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;*/
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s1.insert(0, 'w');
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s1.insert(0, "ddd");
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s2("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s2.insert(12, "ddd");
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s1.erase(1, 2);
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//string s2("abc");
//s2.swap(s1);
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
/*string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
cout << s1.find('\0') << endl;
cout << s1.find('a',1) << endl;*/
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//cout << s1.find("cc",0) << endl;
//cout << s1.find('a', 1) << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s1 += 'a';
//cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
//string s2("aabbcc ddeeff");
//s2 += "bbb";
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//string s1("aabbcc ddeeff");
//string s2;
//s2 = s1.substr(3, 4);
//cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
//string str;
//string& s = str;
//string s1("abcd");
cout << s1 << endl;
//string s2("acacac");
//cout << s2 << endl;
//string s1("abcabc");
//cin >> s1;
//cout << s1 << endl;
/*string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;*/
//string s1("abc");
//cout << s1 << endl;
//string s2(s1);
//cout << s2 << endl;
//string s1("aaaaaa");
//string s3("xxxxxx");
//s1 = s3;
//cout << s1 << endl;
//cout << s3 << endl;
std::string str = std::to_string(123);
cout << str << endl;
std::string str1 = std::to_string(123.222);
cout << str1 << endl;
std::string str2 = std::to_string(123);
int i = stoi(str2);
cout << i << endl;
}
int main()
{
test_string1();
return 0;
}