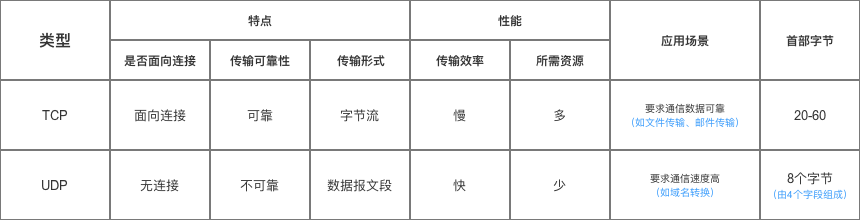
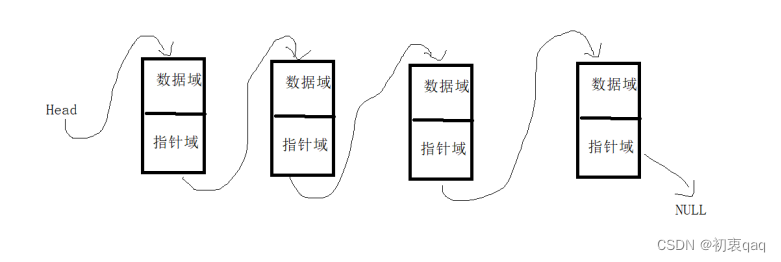
今天来介绍一下c语言如何手写一个单向链表,我们都知道链表是用来提高空间的利用效率的数据结构,其中包括了一个数据域和指针域,数据域用来存储数据,指针域用来指向下一个节点。数据结构如下
我们都知道数据结构最主要的是他的增删改查的功能,这边主要介绍五个操作链表的函数
SLIST *SList_Create();//创建链表
int SList_Print(SLIST *pHead);//遍历链表
int SList_NodeInsert(SLIST *pHead, int x, int y);//插入值 在x之前插入y 没查找到在尾部插入
int SList_NodeDel(SLIST *pHead, int y);//删除某个结点
int SLIST_Destory(SLIST *pHead);//清除链表1.首先是创建链表函数:这边主要功能是接收用户的输入然后直到用户输入-1结束链表的创建。下面是思路:需要三个辅助指针变量,即头节点pHead,新节点pM,当前节点pCur
(1)创建头节点
(2)循环接受用户输入创建新节点
(3)当前节点的指针域指向新节点,当前节点指向新节点
2. 遍历链表函数:这边只需要一个辅助指针变量(不需要也可以)
(1)循环遍历链表打印结果,遍历操作使用pCur=pCur->next,pCur->next就是下一个节点
3.插入值函数:需要三个辅助指针变量,即新节点指针变量pM用于创建新节点,pPre指向搜索到的节点的前一个节点,pCur指向搜索到的节点
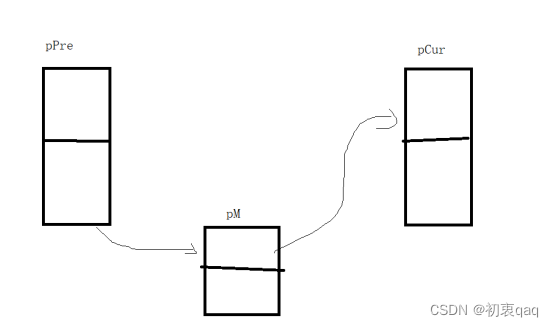
如图所示,插入一个新的节点就是用前一个节点指向新的节点,然后新节点的指针域指向当前节点即可实现。
这边需要注意的是,需要先将新节点指向当前节点,再将前节点指向当前节点。由于只有前节点的指针域指向了后节点,如果先让前结点指向新节点的话就会导致后节点无法找到。
4.删除节点函数:
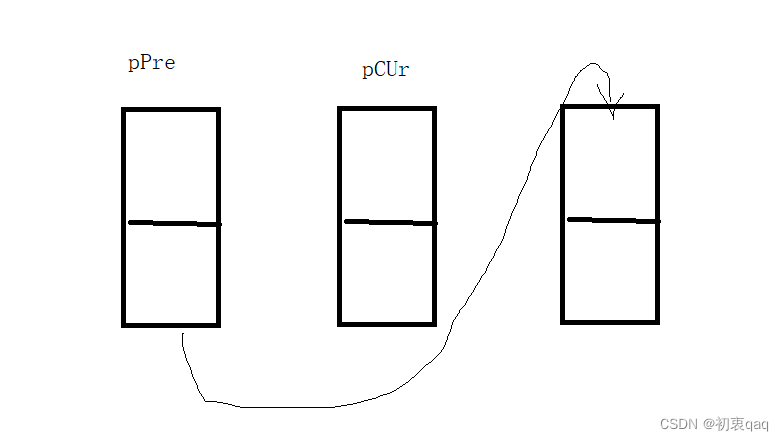
如图所示,将前一个节点指向当前节点的下一个节点即可,即pPre->next=pCur->next;
5.清除链表函数:遍历释放空间即可
下面是源码分享
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
}SLIST;
SLIST *SList_Create();//创建链表
int SList_Print(SLIST *pHead);//遍历链表
int SList_NodeInsert(SLIST *pHead, int x, int y);//插入值 在x之前插入y 没查找到在尾部插入
int SList_NodeDel(SLIST *pHead, int y);//删除某个结点
int SLIST_Destory(SLIST *pHead);//清除链表
//创建链表
//思路
//三个辅助指针变量
//1.创建节点 pM
//2.头节点 pHead
//3.当前结点 pCur
SLIST *SList_Create()
{
SLIST *pHead = NULL, *pM = NULL, *pCur = NULL;
int num;
//创建头节点
pHead = (SLIST *)malloc(sizeof(SLIST));
if (pHead == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
printf("\nplease enter you number:");
scanf("%d", &num);
pCur = pHead;
while (num != -1)
{
//创建新结点
pM = (SLIST *)malloc(sizeof(SLIST));
if (pM == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pM->data = num;
pM->next = NULL;
pCur->next = pM;
pCur = pCur->next;
printf("\nplease enter you number:");
scanf("%d", &num);
}
return pHead;
}
//遍历链表
int SList_Print(SLIST *pHead)
{
SLIST *pCur = NULL;
if (pHead == NULL ||pHead->next==NULL)
{
printf("list is null\n");
return -1;
}
pCur = pHead->next;
printf("\nbegin\n");
while (pCur)
{
printf("%d ", pCur->data);
pCur = pCur->next;
}
printf("\nend\n");
return 0;
}
//插入值 在x之前插入y
//创建新结点 pM
//利用两个辅助指针变量一前一后,找到要的值后
//先将新结点指向后结点再将头前结点指向新结点
int SList_NodeInsert(SLIST *pHead, int x, int y)
{
SLIST *pM = NULL, *pPre = NULL, *pCur = NULL;
pM = (SLIST *)malloc(sizeof(SLIST));
if (pM == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
pM->data = y;
pM->next = NULL;
pPre = pHead;
pCur = pHead->next;
while (pCur)
{
if (pCur->data == x)
{
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
pM->next = pCur;
pPre->next = pM;
return 0;
}
//移除某个结点
//两个辅助指针变量
int SList_NodeDel(SLIST *pHead, int y)
{
SLIST *pPre = NULL, *pCur = NULL;
pPre = pHead;
pCur = pHead->next;
while (pCur)
{
if (pCur->data == y)
{
break;
}
pPre = pCur;
pCur = pCur->next;
}
if (pCur == NULL)
{
printf("don't find %d\n", y);
return -1;
}
pPre->next = pCur->next;
free(pCur);
return 0;
}
int SLIST_Destory(SLIST *pHead)
{
SLIST *temp = NULL;
if (pHead == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//pHead = pHead->next;
temp = pHead->next;
while (temp)
{
free(pHead);
pHead->next = NULL;
pHead = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
SLIST *headlist = NULL;
headlist = SList_Create();
ret = SList_Print(headlist);
ret = SList_NodeInsert(headlist, 20, 19);
ret = SList_Print(headlist);
ret = SList_NodeDel(headlist,19);
ret = SList_Print(headlist);
ret = SLIST_Destory(headlist);
ret = SList_Print(headlist);
system("pause");
return 0;
}