- HTML:展示HTML内容,适用于富文本或网页布局。
- JSON:以JSON格式展示数据,便于查看结构化数据。
- KeyValues:以键值对形式展示数据。
- Label:展示文本标签,适用于简单的文本输出。
- Markdown:支持Markdown格式的文本展示。
- Plot:展示图表,如matplotlib生成的图表。
- Text:用于显示文本,适合较长的输出。
1、json列子
import gradio as gr
import json
# 示例 JSON 数据
json_data = {
"name": "Gradio",
"type": "Library",
"languages": ["Python", "JavaScript"],
"description": "Gradio is an open-source library that allows developers to build interactive applications with machine learning and data science projects."
}
# 将 JSON 数据转换为字符串格式
json_str = json.dumps(json_data, indent=4)
# 定义一个函数,它接受没有输入,并返回 JSON 字符串
def show_json():
return json_str
# 使用 Gradio 创建界面,JSON 组件展示数据
gr.Interface(fn=show_json,inputs=None, outputs='json').launch()没有输入,点击generate显示了json数据

2、html
import gradio as gr
def show_html():
return "<h1>Hello, Gradio!</h1><p>This is an HTML output.</p>"
gr.Interface(
fn=show_html,
inputs=None,
outputs="html"
).launch() 
3、plot
import gradio as gr
def process_list(my_list):
# 对列表进行处理的示例函数
return f"接收到列表,长度为: {my_list}"
# 创建一个包含列表输入的界面
gr.Interface(
process_list,
gr.List(label="输入列表"), # 定义输入为列表
"text",
title="列表输入示例"
).launch()
import gradio as gr
import plotly.graph_objects as go
# 创建一个简单的Plotly图表
def create_plot(x_data, y_data):
fig = go.Figure(data=go.Bar(x=x_data[0], y=y_data[0]))
return fig
# 创建Gradio界面
interface = gr.Interface(
fn=create_plot,
inputs=[
gr.List(label="X Axis Data"),
gr.List(label="Y Axis Data"),
],
outputs='plot',
)
# 运行Gradio界面
interface.launch()

4、markdown
import gradio as gr
# with open("example.md", "r") as f:
# md_content = f.read()
def show_markdown(markdown_text):
return markdown_text
interface = gr.Interface(
fn=show_markdown,
inputs=gr.Textbox(lines=10), # value = md_content
outputs=gr.Markdown()
)
interface.launch()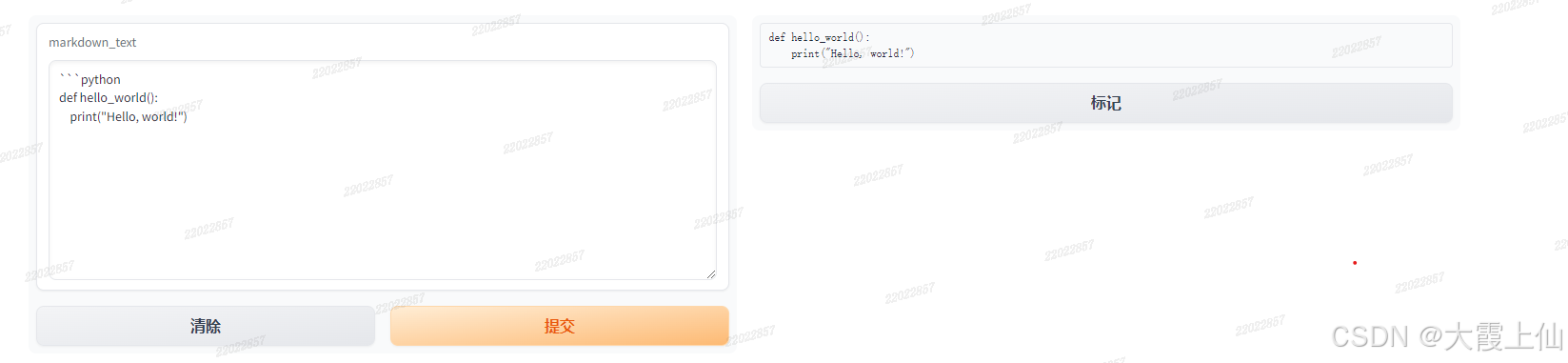















![[AWS]EKS启动HPA,HPA指标<unknown>,报错:error: Metrics API not available](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5f8e75374fa241baa05488791d50214b.png)