参考文章:cs231n assignment1——SVM
SVM
训练阶段,我们的目的是为了得到合适的 𝑊 和 𝑏 ,为实现这一目的,我们需要引进损失函数,然后再通过梯度下降来训练模型。


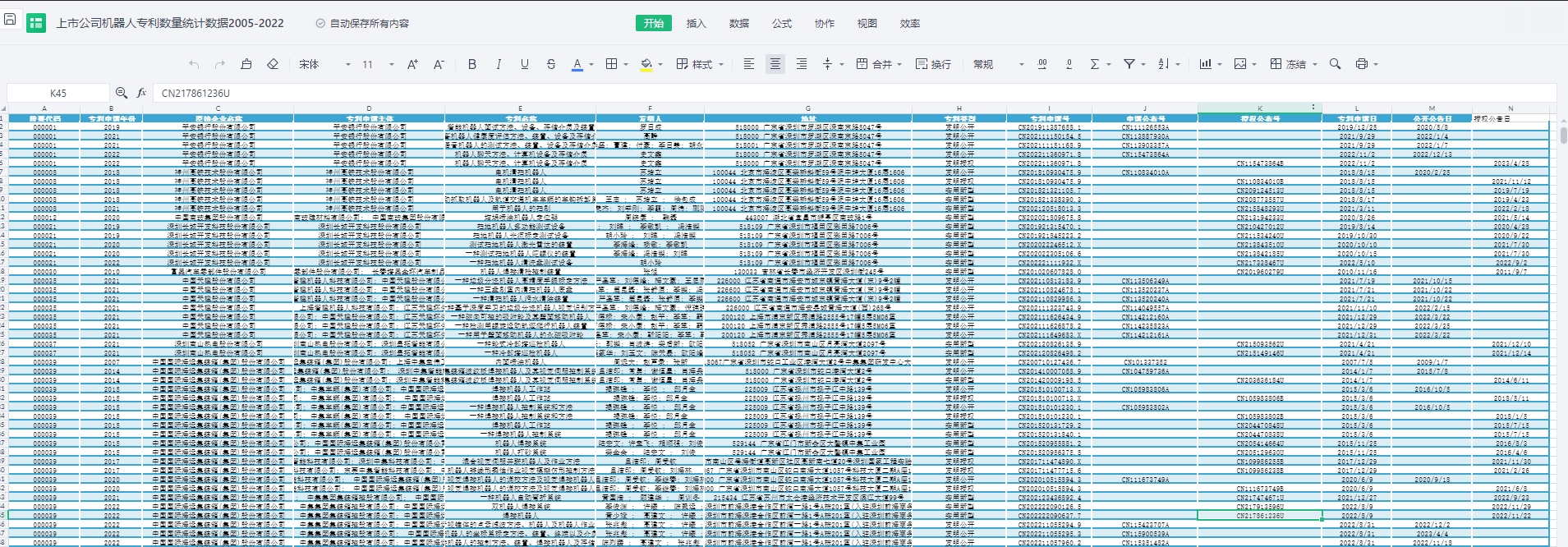
def svm_loss_naive(W, X, y, reg):
#梯度矩阵初始化
dW = np.zeros(W.shape) # initialize the gradient as zero
# compute the loss and the gradient
#计算损失和梯度
num_classes = W.shape[1]
num_train = X.shape[0]
loss = 0.0
for i in range(num_train):
#W*Xi
score = X[i].dot(W)
correct_score = score[y[i]]
for j in range(num_classes):
#预测正确
if j == y[i]:
continue
#W*Xi-Wyi*Xi+1
margin = score[j] - correct_score + 1 # 拉格朗日
if margin > 0:
loss += margin
#平均损失
loss /= num_train
#加上正则化λ||W||²
# Add regularization to the loss.
loss += reg * np.sum(W * W)
dW /= num_train
dW += reg * W
return loss, dW
向量形式计算损失函数

def svm_loss_vectorized(W, X, y, reg):
loss = 0.0
dW = np.zeros(W.shape)
num_train=X.shape[0]
classes_num=X.shape[1]
score = X.dot(W)
#矩阵大小变化,大小不同的矩阵不可以加减
correct_scores = score[range(num_train), list(y)].reshape(-1, 1) #[N, 1]
margin = np.maximum(0, score - correct_scores + 1)
margin[range(num_train), list(y)] = 0
#正则化
loss = np.sum(margin) / num_train
loss += 0.5 * reg * np.sum(W * W)
#大于0的置1,其余为0
margin[margin>0] = 1
margin[range(num_train),list(y)] = 0
margin[range(num_train),y] -= np.sum(margin,1)
dW=X.T.dot(margin)
dW=dW/num_train
dW=dW+reg*W
return loss, dW
SGD优化损失函数
使用批量随机梯度下降法来更新参数,每次随机选取batchsize个样本用于更新参数 𝑊 和 𝑏 。
for it in range(num_iters):
X_batch = None
y_batch = No
idxs = np.random.choice(num_train, batch_size, replace=True)
X_batch = X[idxs]
y_batch = y[idx
loss, grad = self.loss(X_batch, y_batch, reg)
loss_history.append(los
self.W -= learning_rate * gr
if verbose and it % 100 == 0:
print("iteration %d / %d: loss %f" % (it, num_iters, loss))
return loss_history
交叉验证调整超参数
为了获取最优的超参数,我们可以将整个训练集划分为训练集和验证集,然后选取在验证集上准确率最高的一组超参数。