第一种,纯css
在给容器设置宽度后,使用css来省略文本超长部分,但是这样就看不到全部的内容
<template>
<div class="content">
<div class="text">{{ text }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const text = ref('这是一个内容特别长的div你知道吗不知道算了')
</script>
<style scoped>
.content {
width: 800px;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.text {
width: 200px;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>

第二种 ,使用el-tooltip
普通使用
限制内容的长度,通过长度来控制是否需要使用el-tooltip
但是这样有弊端,如果内容是全英文呢?或者中英结合呢?有特殊符号呢?
没关系,我们一步一步来
<template>
<div class="content">
<el-tooltip v-if="text.length > 13" :content="text">
<div class="text">{{ text }}</div>
</el-tooltip>
<div v-else class="text">{{ text }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const text = ref('这是一个内容特别长的div你知道吗不知道算了')
</script>
<style scoped>
.content {
width: 800px;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.text {
width: 200px;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>

普通使用-进阶版
不用文本的length来判断,而是通过文本所在容器的scrollWidth与clientWidth来判断
效果同上
<template>
<div class="content">
<el-tooltip v-if="isOverflow" :content="text">
<div class="text">{{ text }}</div>
</el-tooltip>
<div v-else class="text">{{ text }}</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted, nextTick } from 'vue';
const text = ref('这是一个内容特别长的div你知道吗不知道算了')
const isOverflow = ref(false);
onMounted(() => {
nextTick(() => {
const element = document.querySelector(`.content .text`);
isOverflow.value = element.scrollWidth > element.clientWidth;
})
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.content {
width: 800px;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.text {
width: 200px;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>

特殊使用
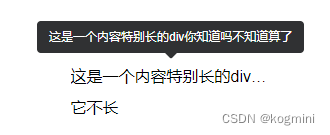
这里指的是在循环遍历的数据中,如何像普通使用-进阶版一样,把省略的内容呈现出来
<template>
<div class="content">
<div v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index" class="text-box">
<el-tooltip v-if="isOverflowing[index]" :content="item" placement="top">
<div class="text-content">{{ item }}</div>
</el-tooltip>
<div v-else class="text-content">{{ item }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted, nextTick } from 'vue';
const items = ['这是一个内容特别长的div你知道吗不知道算了', '它不长'];
const isOverflowing = ref([]);
const checkOverflow = () => {
isOverflowing.value = items.map((_, index) => {
const element = document.querySelector(`.text-box:nth-child(${index + 1}) .text-content`);
return element.scrollWidth > element.clientWidth;
});
};
onMounted(() => {
nextTick(() => {
checkOverflow();
});
});
</script>
<style scoped>
.content {
width: 800px;
margin: 100px auto;
}
.text-content {
width: 200px;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
cursor: pointer;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
特殊使用-进阶版
上面代码是一层遍历,如果是双层遍历就不能只通过document.querySelector来获取目标容器,需要结合ref与data-index动态属性
<template>
<div class="content">
<div v-for="(item, index) in userList" :key="index" class="user-item">
<div class="dept-box">
<div class="dept-name">
<div class="blue-circle"></div>
<el-tooltip v-if="isOverflowing[index]" effect="dark" :content="item.departmentName" placement="top">
<div class="name">{{ item.departmentName }}</div>
</el-tooltip>
<div v-else class="name">{{ item.departmentName }}</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="user-box">
<div v-for="(userItem, userIndex) in item.user" :key="userIndex" ref="textRefs" class="user"
:data-index="`${index}-${userIndex}`">
<div class="green-circle"></div>
<el-tooltip v-if="item.isOverflowing && item.isOverflowing[userIndex]" effect="dark"
:content="userItem.userName" placement="top">
<div class="username">{{ userItem.userName }}</div>
</el-tooltip>
<div v-else class="username">{{ userItem.userName }}</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted, nextTick } from 'vue';
const userList = ref([
{
departmentName: '部门1',
user: [{ userName: '超长用户名测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试' }, { userName: '正常用户名' }],
isOverflowing: []
},
{
departmentName: '这是一个名称特别长的部门你知道吗不知道算了害',
user: [{ userName: '正常用户名' }, { userName: '超长用户名测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试测试' }],
isOverflowing: []
}
]);
const isOverflowing = ref([]);
const textRefs = ref([]);
const checkOverflow = () => {
nextTick(() => {
//处理部门名超长
isOverflowing.value = userList.value.map((_, index) => {
const element = document.querySelector(`.user-item:nth-child(${index + 1}) .dept-box .dept-name .name`);
return element.scrollWidth > element.clientWidth;
});
//处理人员名超长
userList.value.forEach((item, index) => {
item.isOverflowing = item.user.map((_, userIndex) => {
const userElement = textRefs.value.find(ref => ref && ref.dataset && ref.dataset.index === `${index}-${userIndex}`);
if (userElement) {
const usernameElement = userElement.querySelector('.username');
if (usernameElement) {
return usernameElement.scrollWidth > usernameElement.clientWidth;
}
}
return false;
});
});
});
};
onMounted(() => {
checkOverflow();
});
</script>
<style scoped lang="less">
.content {
width: 800px;
margin: 100px auto;
.user-item {
.dept-box {
height: 46px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 8px;
cursor: pointer;
.dept-name {
font-weight: bold;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
background: #ffffff;
color: #395CD0;
.blue-circle {
width: 6px;
height: 6px;
border-radius: 6px;
margin-right: 16px;
background: #395CD0;
margin-left: 17px;
}
.name {
width: 137px;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
}
}
.user-box {
.user {
height: 22px;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
margin-top: 16px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #333333;
cursor: pointer;
.green-circle {
width: 6px;
height: 6px;
border-radius: 6px;
background: #7AC953;
margin-right: 12px;
margin-left: 44px;
}
.username {
width: 7.5vw;
font-size: 14px;
color: #333333;
overflow-x: hidden;
white-space: nowrap;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
}
}
}
}
</style>



总结
以上所有情况皆博主所遇,记录下来方便以后查找
如果有更好的解决方法,欢迎指导