MySQL逻辑备份介绍
逻辑备份:
备份内容:数据库的结构定义语句+数据内容的插入语句,备份出来的文件是可以编辑的。
适用场景:数据量少的数据库,比较适合100G数据量以内的。
逻辑备份的特点:
- sql语句组成的文件,可以截取部分单独使用
- 备份文件比物理的小
- 可以细化到表/表的内容
- 速度慢
- 可以跨平台恢复/迁移
- 只能在线备份,在线恢复
逻辑备份工具:
- mysqldump(单线程)类似于Oracle的exp,mysqlpump(多线程,MySQL 5.7+)类似于Oracle的expdp,在线备份:mysql官方工具
- mydumper:开源的,基于mysqldump的一个优化,多线程,速度介于两者之间,主要用于mariadb、percona、官方的mysql
mysqldump 工具详解与备份恢复案例
mysqldump工具介绍
mysql 5.7之前主用,mysql 5.7之后也用的特别多,特别是互联网的业务,很多都是几个G,几十个G的数据量
create datebases;
create table;
insert into;
存储过程
触发器
函数
调度事件
工具使用演示:
#备份
mysqldump -uroot -proot --all-databases > db_fullbackup.sql
#恢复
#先不创建数据库直接恢复单个数据库会报错,提示数据库不存在
#全库恢复是不需要创建数据库的,恢复单独的数据库是需要先创建数据库(空库,数据还需要从备份文件恢复)
mysql> create database itpux default character set utf8; -- 相关信息可以去备份的文件里找
mysql -uroot -proot -o testdb < db_fullbackup.sql #-o 表示只有某个数据库
mysqldump 工具参数详解
mysqldump 帮助信息
[root@centos7 ~]# mysqldump --help
mysqldump Ver 10.13 Distrib 5.7.43, for linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Dumping structure and contents of MySQL databases and tables.
Usage: mysqldump [OPTIONS] database [tables]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --databases [OPTIONS] DB1 [DB2 DB3...]
OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --all-databases [OPTIONS]
Default options are read from the following files in the given order:
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf /usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf
The following groups are read: mysqldump client
The following options may be given as the first argument:
--print-defaults Print the program argument list and exit.
--no-defaults Don't read default options from any option file,
except for login file.
--defaults-file=# Only read default options from the given file #.
--defaults-extra-file=# Read this file after the global files are read.
--defaults-group-suffix=#
Also read groups with concat(group, suffix)
--login-path=# Read this path from the login file.
-A, --all-databases Dump all the databases. This will be same as --databases
with all databases selected.
-Y, --all-tablespaces
Dump all the tablespaces.
-y, --no-tablespaces
Do not dump any tablespace information.
--add-drop-database Add a DROP DATABASE before each create.
--add-drop-table Add a DROP TABLE before each create.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-add-drop-table to disable.)
--add-drop-trigger Add a DROP TRIGGER before each create.
--add-locks Add locks around INSERT statements.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-add-locks to disable.)
--allow-keywords Allow creation of column names that are keywords.
--apply-slave-statements
Adds 'STOP SLAVE' prior to 'CHANGE MASTER' and 'START
SLAVE' to bottom of dump.
--bind-address=name IP address to bind to.
--character-sets-dir=name
Directory for character set files.
-i, --comments Write additional information.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-comments to disable.)
--compatible=name Change the dump to be compatible with a given mode. By
default tables are dumped in a format optimized for
MySQL. Legal modes are: ansi, mysql323, mysql40,
postgresql, oracle, mssql, db2, maxdb, no_key_options,
no_table_options, no_field_options. One can use several
modes separated by commas. Note: Requires MySQL server
version 4.1.0 or higher. This option is ignored with
earlier server versions.
--compact Give less verbose output (useful for debugging). Disables
structure comments and header/footer constructs. Enables
options --skip-add-drop-table --skip-add-locks
--skip-comments --skip-disable-keys --skip-set-charset.
-c, --complete-insert
Use complete insert statements.
-C, --compress Use compression in server/client protocol.
-a, --create-options
Include all MySQL specific create options.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-create-options to disable.)
-B, --databases Dump several databases. Note the difference in usage; in
this case no tables are given. All name arguments are
regarded as database names. 'USE db_name;' will be
included in the output.
-#, --debug[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--debug-check This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--debug-info This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--default-character-set=name
Set the default character set.
--delete-master-logs
Delete logs on master after backup. This automatically
enables --master-data.
-K, --disable-keys '/*!40000 ALTER TABLE tb_name DISABLE KEYS */; and
'/*!40000 ALTER TABLE tb_name ENABLE KEYS */; will be put
in the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-disable-keys to disable.)
--dump-slave[=#] This causes the binary log position and filename of the
master to be appended to the dumped data output. Setting
the value to 1, will printit as a CHANGE MASTER command
in the dumped data output; if equal to 2, that command
will be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will
turn --lock-all-tables on, unless --single-transaction is
specified too (in which case a global read lock is only
taken a short time at the beginning of the dump - don't
forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all
cases any action on logs will happen at the exact moment
of the dump.Option automatically turns --lock-tables off.
-E, --events Dump events.
-e, --extended-insert
Use multiple-row INSERT syntax that include several
VALUES lists.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-extended-insert to disable.)
--fields-terminated-by=name
Fields in the output file are terminated by the given
string.
--fields-enclosed-by=name
Fields in the output file are enclosed by the given
character.
--fields-optionally-enclosed-by=name
Fields in the output file are optionally enclosed by the
given character.
--fields-escaped-by=name
Fields in the output file are escaped by the given
character.
-F, --flush-logs Flush logs file in server before starting dump. Note that
if you dump many databases at once (using the option
--databases= or --all-databases), the logs will be
flushed for each database dumped. The exception is when
using --lock-all-tables or --master-data: in this case
the logs will be flushed only once, corresponding to the
moment all tables are locked. So if you want your dump
and the log flush to happen at the same exact moment you
should use --lock-all-tables or --master-data with
--flush-logs.
--flush-privileges Emit a FLUSH PRIVILEGES statement after dumping the mysql
database. This option should be used any time the dump
contains the mysql database and any other database that
depends on the data in the mysql database for proper
restore.
-f, --force Continue even if we get an SQL error.
-?, --help Display this help message and exit.
--hex-blob Dump binary strings (BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB) in
hexadecimal format.
-h, --host=name Connect to host.
--ignore-error=name A comma-separated list of error numbers to be ignored if
encountered during dump.
--ignore-table=name Do not dump the specified table. To specify more than one
table to ignore, use the directive multiple times, once
for each table. Each table must be specified with both
database and table names, e.g.,
--ignore-table=database.table.
--include-master-host-port
Adds 'MASTER_HOST=<host>, MASTER_PORT=<port>' to 'CHANGE
MASTER TO..' in dump produced with --dump-slave.
--insert-ignore Insert rows with INSERT IGNORE.
--lines-terminated-by=name
Lines in the output file are terminated by the given
string.
-x, --lock-all-tables
Locks all tables across all databases. This is achieved
by taking a global read lock for the duration of the
whole dump. Automatically turns --single-transaction and
--lock-tables off.
-l, --lock-tables Lock all tables for read.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-lock-tables to disable.)
--log-error=name Append warnings and errors to given file.
--master-data[=#] This causes the binary log position and filename to be
appended to the output. If equal to 1, will print it as a
CHANGE MASTER command; if equal to 2, that command will
be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will turn
--lock-all-tables on, unless --single-transaction is
specified too (in which case a global read lock is only
taken a short time at the beginning of the dump; don't
forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all
cases, any action on logs will happen at the exact moment
of the dump. Option automatically turns --lock-tables
off.
--max-allowed-packet=#
The maximum packet length to send to or receive from
server.
--net-buffer-length=#
The buffer size for TCP/IP and socket communication.
--no-autocommit Wrap tables with autocommit/commit statements.
-n, --no-create-db Suppress the CREATE DATABASE ... IF EXISTS statement that
normally is output for each dumped database if
--all-databases or --databases is given.
-t, --no-create-info
Don't write table creation info.
-d, --no-data No row information.
-N, --no-set-names Same as --skip-set-charset.
--opt Same as --add-drop-table, --add-locks, --create-options,
--quick, --extended-insert, --lock-tables, --set-charset,
and --disable-keys. Enabled by default, disable with
--skip-opt.
--order-by-primary Sorts each table's rows by primary key, or first unique
key, if such a key exists. Useful when dumping a MyISAM
table to be loaded into an InnoDB table, but will make
the dump itself take considerably longer.
-p, --password[=name]
Password to use when connecting to server. If password is
not given it's solicited on the tty.
-P, --port=# Port number to use for connection.
--protocol=name The protocol to use for connection (tcp, socket, pipe,
memory).
-q, --quick Don't buffer query, dump directly to stdout.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-quick to disable.)
-Q, --quote-names Quote table and column names with backticks (`).
(Defaults to on; use --skip-quote-names to disable.)
--replace Use REPLACE INTO instead of INSERT INTO.
-r, --result-file=name
Direct output to a given file. This option should be used
in systems (e.g., DOS, Windows) that use carriage-return
linefeed pairs (\r\n) to separate text lines. This option
ensures that only a single newline is used.
-R, --routines Dump stored routines (functions and procedures).
--set-charset Add 'SET NAMES default_character_set' to the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-set-charset to disable.)
--set-gtid-purged[=name]
Add 'SET @@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' to the output. Possible
values for this option are ON, OFF and AUTO. If ON is
used and GTIDs are not enabled on the server, an error is
generated. If OFF is used, this option does nothing. If
AUTO is used and GTIDs are enabled on the server, 'SET
@@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' is added to the output. If GTIDs
are disabled, AUTO does nothing. If no value is supplied
then the default (AUTO) value will be considered.
--single-transaction
Creates a consistent snapshot by dumping all tables in a
single transaction. Works ONLY for tables stored in
storage engines which support multiversioning (currently
only InnoDB does); the dump is NOT guaranteed to be
consistent for other storage engines. While a
--single-transaction dump is in process, to ensure a
valid dump file (correct table contents and binary log
position), no other connection should use the following
statements: ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME TABLE,
TRUNCATE TABLE, as consistent snapshot is not isolated
from them. Option automatically turns off --lock-tables.
--dump-date Put a dump date to the end of the output.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-dump-date to disable.)
--skip-mysql-schema Skip adding DROP DATABASE for mysql schema.
--skip-opt Disable --opt. Disables --add-drop-table, --add-locks,
--create-options, --quick, --extended-insert,
--lock-tables, --set-charset, and --disable-keys.
-S, --socket=name The socket file to use for connection.
--secure-auth Refuse client connecting to server if it uses old
(pre-4.1.1) protocol. Deprecated. Always TRUE
--ssl-mode=name SSL connection mode.
--ssl Deprecated. Use --ssl-mode instead.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-ssl to disable.)
--ssl-verify-server-cert
Deprecated. Use --ssl-mode=VERIFY_IDENTITY instead.
--ssl-ca=name CA file in PEM format.
--ssl-capath=name CA directory.
--ssl-cert=name X509 cert in PEM format.
--ssl-cipher=name SSL cipher to use.
--ssl-key=name X509 key in PEM format.
--ssl-crl=name Certificate revocation list.
--ssl-crlpath=name Certificate revocation list path.
--tls-version=name TLS version to use, permitted values are: TLSv1, TLSv1.1,
TLSv1.2
--server-public-key-path=name
File path to the server public RSA key in PEM format.
--get-server-public-key
Get server public key
-T, --tab=name Create tab-separated textfile for each table to given
path. (Create .sql and .txt files.) NOTE: This only works
if mysqldump is run on the same machine as the mysqld
server.
--tables Overrides option --databases (-B).
--triggers Dump triggers for each dumped table.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-triggers to disable.)
--tz-utc SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' at top of dump to allow dumping of
TIMESTAMP data when a server has data in different time
zones or data is being moved between servers with
different time zones.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-tz-utc to disable.)
-u, --user=name User for login if not current user.
-v, --verbose Print info about the various stages.
-V, --version Output version information and exit.
-w, --where=name Dump only selected records. Quotes are mandatory.
-X, --xml Dump a database as well formed XML.
--plugin-dir=name Directory for client-side plugins.
--default-auth=name Default authentication client-side plugin to use.
--enable-cleartext-plugin
Enable/disable the clear text authentication plugin.
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
all-databases FALSE
all-tablespaces FALSE
no-tablespaces FALSE
add-drop-database FALSE
add-drop-table TRUE
add-drop-trigger FALSE
add-locks TRUE
allow-keywords FALSE
apply-slave-statements FALSE
bind-address (No default value)
character-sets-dir (No default value)
comments TRUE
compatible (No default value)
compact FALSE
complete-insert FALSE
compress FALSE
create-options TRUE
databases FALSE
default-character-set utf8
delete-master-logs FALSE
disable-keys TRUE
dump-slave 0
events FALSE
extended-insert TRUE
fields-terminated-by (No default value)
fields-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-optionally-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-escaped-by (No default value)
flush-logs FALSE
flush-privileges FALSE
force FALSE
hex-blob FALSE
host (No default value)
ignore-error (No default value)
include-master-host-port FALSE
insert-ignore FALSE
lines-terminated-by (No default value)
lock-all-tables FALSE
lock-tables TRUE
log-error (No default value)
master-data 0
max-allowed-packet 25165824
net-buffer-length 1046528
no-autocommit FALSE
no-create-db FALSE
no-create-info FALSE
no-data FALSE
order-by-primary FALSE
port 0
quick TRUE
quote-names TRUE
replace FALSE
routines FALSE
set-charset TRUE
single-transaction FALSE
dump-date TRUE
skip-mysql-schema FALSE
socket (No default value)
secure-auth TRUE
ssl TRUE
ssl-verify-server-cert FALSE
ssl-ca (No default value)
ssl-capath (No default value)
ssl-cert (No default value)
ssl-cipher (No default value)
ssl-key (No default value)
ssl-crl (No default value)
ssl-crlpath (No default value)
tls-version (No default value)
server-public-key-path (No default value)
get-server-public-key FALSE
tab (No default value)
triggers TRUE
tz-utc TRUE
user (No default value)
verbose FALSE
where (No default value)
plugin-dir (No default value)
default-auth (No default value)
enable-cleartext-plugin FALSE
[root@centos7 ~]#
mysqldump 默认选项
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
all-databases FALSE
all-tablespaces FALSE
no-tablespaces FALSE
add-drop-database FALSE
add-drop-table TRUE
add-drop-trigger FALSE
add-locks TRUE
allow-keywords FALSE
apply-slave-statements FALSE
bind-address (No default value)
character-sets-dir (No default value)
comments TRUE
compatible (No default value)
compact FALSE
complete-insert FALSE
compress FALSE
create-options TRUE
databases FALSE
default-character-set utf8
delete-master-logs FALSE
disable-keys TRUE
dump-slave 0
events FALSE
extended-insert TRUE
fields-terminated-by (No default value)
fields-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-optionally-enclosed-by (No default value)
fields-escaped-by (No default value)
flush-logs FALSE
flush-privileges FALSE
force FALSE
hex-blob FALSE
host (No default value)
ignore-error (No default value)
include-master-host-port FALSE
insert-ignore FALSE
lines-terminated-by (No default value)
lock-all-tables FALSE
lock-tables TRUE
log-error (No default value)
master-data 0
max-allowed-packet 25165824
net-buffer-length 1046528
no-autocommit FALSE
no-create-db FALSE
no-create-info FALSE
no-data FALSE
order-by-primary FALSE
port 0
quick TRUE
quote-names TRUE
replace FALSE
routines FALSE
set-charset TRUE
single-transaction FALSE
dump-date TRUE
skip-mysql-schema FALSE
socket (No default value)
secure-auth TRUE
ssl TRUE
ssl-verify-server-cert FALSE
ssl-ca (No default value)
ssl-capath (No default value)
ssl-cert (No default value)
ssl-cipher (No default value)
ssl-key (No default value)
ssl-crl (No default value)
ssl-crlpath (No default value)
tls-version (No default value)
server-public-key-path (No default value)
get-server-public-key FALSE
tab (No default value)
triggers TRUE
tz-utc TRUE
user (No default value)
verbose FALSE
where (No default value)
plugin-dir (No default value)
default-auth (No default value)
enable-cleartext-plugin FALSE
mysqldump 服务器相关的常用参数
#1. mysqldump 客户端读取:
my.cnf
[client]
[mysqldump]
#2. 相关参数
mysqldump -uroot -proot -h192.168.1.51 -P3306 .....
-u --user=
-p --password=
-h --host=
-P --port=
--protocol= tcp,socket,memory 指定协议
--max-allowed-packet= 指定最大分配的包
--net-buffer-legth 网络缓存的长度
mysqldump 备份内容的常用参数
可以备份:
可以备份所有数据库,几个数据库,一个数据库,一个表,几个表,一个表里面的内容,存储过程,函数
- -A,–all-databases 备份所有数据库
- -B,–databases database[tables] 备份一个或者几个数据库,可以分开写(用空格隔开)
- -y,-all-tablespaces 备份所有的表空间
- -n,–no-create-db 不导出数据库结构
- -t,–no-create-info 不导出表结构
- -d,–no-data 不导出数据,只导结构
- -R,–routines 导出存储过程和函数,默认是不导出的。
- –triggers 导出触发器,默认导出
- –skip-triggers 不导出触发器
- -E,–events 导出调度事件
- –ignore-table 不导出某个库的某个表,或者不导出几个表:testdb.test_t1
- -w,–where=‘’ 导出的时候加上条件
mysqldump 备份与事物和锁相关的选项
-
–single-transaction:
可以得到一致性的导出结果。只针对innodb,导出过程中不允许运行表的DDL 操作。
因为事务持有表的metadata lock 的共享锁,而DDL 会申请metadata lock 的互斥锁,所以会阻塞。
–single-transaction 还会关掉你默认的–lock-tables 选项( 即不加锁),因为mysqldump 默认会打开一个lock-tables,在导出过程中锁定所有的表。那么只能加–master-data 才能加锁。 -
–lock-tables
默认打开的。这个锁表是导一个锁一个,导完解锁。 -
–lock-all-tables
会把所有的表都给锁了,慢慢导,导完解锁。
上面这三个参数是互斥的(1,2,3),只能同时用一个。 -
–flush-logs
导出数据时刷新二进制日志,达到一致性导出。 -
–flush-privileges
导出权限 -
–master-data
有3 个值:
0:默认就是0,不写入binlog 日志记录
1:change master to … 记录binlog 文件及终点(当前备份到什么位置,在恢复或者做增量的时候就可以根据这个记录从特定的位置开始恢复,如果是从库会根据这个位置从master端去复制二进制日志)
2:#change master to … 记录binlog 文件及终点(加了这个参数,但是是注释的状态)mysqldump -uroot -p --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines testdb >testdb.sql
mysqldump 与复制相关的选项
- –master-data
有3 个值:
0:默认就是0,不写入binlog 日志记录
1:change master to … 记录binlog 文件及终点
2:#change master to … 记录binlog 文件及终点 - –dump-slave
在从库上面使用的,和–master-data 参数一样,是为了slave 建立下一级的slave - –apply-slave-statements
和–master-data=1 类似 - –include-master-host-port
结合–dump-slave=1/2,在导出中加入host、port - –delete-master-logs
在备份之后,删除master 的bin log 日志,默认打开–master-data=2,一般不用,因为日志一般不能随便删除。 - –set-gtid-purged
用于在gtid 的环境使用
mysqldump 与字符集相关的选项
- –set-charset
默认开启,–set-charset=1/0,是否开启字符集 - –default-character-set
指定是什么字符集,utf8,gbk,utf8mb4 - -N,–no-set-names
关闭–set-charset
mysqldump 控制是否生成DDL 语句的选项
–add-drop-database(add:drop database ddl),先删除数据库
–add-drop-table, 先删除表,默认打开的,禁用:–skip-add-drop-table
–add-drop-trigger 先删除触发器
–no-create-db,-n 不创建数据库(也就是说数据库必须存在才能往里面导数据)
–no-create-info,-t 不创建表(也就是说表必须存在才能往里面导数据)
mysqldump 其它语法
- -f,–force 强制性导出
- –log-error=/tmp/1.log
- –compatible=(oracle/mssql/postgresql)
mysqldump 常用备份命令使用案例
mysql> create database testdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit
Bye
[root@centos7 ~]#
[root@centos7 ~]# mysql -uroot -prootroot -S /mysql/data/3306/mysql.sock < testdb.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
[root@centos7 ~]#
mysql> use testdb
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_testdb |
+------------------+
| bm |
| dd |
| dq |
| gj |
| gw |
| jl |
| test11 |
| test12 |
| test_m1 |
| test_m5 |
| test_obj |
| test_sales |
| test_yg |
| yg |
+------------------+
14 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
命令案例
- 导出所有的数据库(库/表结构/数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --all-databases > fullbak01.sql
- 导出所有的数据库(库/表结构,但是不保存数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --all-databases --no-data > fullbak02.sql
- 只导出某一个表(结构+数据:testdb.yg)
mysqldump -uroot -proot testdb yg > testdb_yg_01.sql
- 只导出某一个表(结构,不包括数据:testdb.yg)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --no-data testdb yg > testdb_yg_02.sql
OR:
show create table testdb.yg\G
- 导出多个表(结构+数据:testdb.yg,testdb.bm)
mysqldump -uroot -proot testdb yg bm > testdb_yg_bm_01.sql
- 不创建表结构(只要数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --no-create-info testdb bm > testdb_bm.sql
OR
select * from testdb.bm into outfile '/tmp/testdb-bm.sql';
- 导出单个数据库(结构和数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --databases testdb > testdb07.sql
#如果不加 --datebases参数,在备份脚本中是不会出现创建数据库的语句
- 导出多个数据库(结构+数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --databases testdb testdb2 > testdb08.sql
- 导出单个数据库(只要结构,不要数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --no-data --databases testdb > testdb09.sql
- 导出多个数据库(只要结构,不要数据)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --no-data --databases testdb testdb2 > testdb10.sql
- 导出单个数据库(只要数据,不要结构)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --no-create-db --no-create-info --databases testdb > testdb11.sql
- 导出单个库(排除某个表)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --databases testdb --ignore-table=testdb.test_m5 > testdb12.sql
- 导出某个表的某一些数据(按条件)
mysqldump -uroot -proot testdb yg --where="employee_id < 105" > testdb13.sql
- 导出所有的数据库(库/表结构/数据/函数/存储过程)
mysqldump -uroot -proot -R -E --all-databases > fullbak14.sql
- 导出所有数据库(数据一致+导出权限+刷新日志)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases >fullbak15.sql
16.备份系统库
mysqldump -uroot -proot --skip-lock-tables --databases information_schema sys performance_schema > all-info-db.sql
mysqldump 深入解析与实现原理
必须打开数据库的general log,在my.cnf 加入下列参数,重启mysql 生效:
general_log = on
general_log_file=/mysql/log/3306/testdb-general.err
mysql> show variables like '%general_log%';
+------------------+------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+------------------------------------+
| general_log | ON |
| general_log_file | /mysql/log/3306/testdb-general.err |
+------------------+------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
分析mysqldump 全备的过程
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --routines --all-databases >fullbak16.sql
看日志
more /mysql/log/3306/testdb-general.err
43 2023-11-05T18:15:38.560334+08:00 2 Connect root@localhost on using Socket
44 2023-11-05T18:15:38.560806+08:00 2 Query show variables like '%bin%'
45 2023-11-05T18:16:58.126307+08:00 3 Connect root@localhost on using Socket
46 2023-11-05T18:16:58.126380+08:00 3 Connect Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
47 2023-11-05T18:17:07.614228+08:00 4 Connect root@localhost on using Socket
48 2023-11-05T18:17:07.614580+08:00 4 Query /*!40100 SET @@SQL_MODE='' */
49 2023-11-05T18:17:07.614755+08:00 4 Query /*!40103 SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' */
50 2023-11-05T18:17:07.615056+08:00 4 Query SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'gtid_mode'
51 2023-11-05T18:17:07.615806+08:00 4 Query FLUSH /*!40101 LOCAL */ TABLES
52 2023-11-05T18:17:07.616684+08:00 4 Query FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCK
53 2023-11-05T18:17:07.616913+08:00 4 Refresh
54 /mysql/app/mysql/bin/mysqld, Version: 5.7.43-log (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
55 Tcp port: 3306 Unix socket: /mysql/data/3306/mysql.sock
56 Time Id Command Argument
57 2023-11-05T18:17:07.622607+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL REPEATABLE READ
58 2023-11-05T18:17:07.622746+08:00 4 Query START TRANSACTION /*!40100 WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT */
59 2023-11-05T18:17:07.622941+08:00 4 Query SHOW MASTER STATUS
60 2023-11-05T18:17:07.623186+08:00 4 Query UNLOCK TABLES
63 2023-11-05T18:17:07.625654+08:00 4 Query SHOW DATABASES
64 2023-11-05T18:17:07.626218+08:00 4 Query SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'ndbinfo\_version'
65 2023-11-05T18:17:07.626834+08:00 4 Init DB mysql
66 2023-11-05T18:17:07.627065+08:00 4 Query SHOW CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `mysql`
67 2023-11-05T18:17:07.627303+08:00 4 Query SAVEPOINT sp
68 2023-11-05T18:17:07.627531+08:00 4 Query show tables
69 2023-11-05T18:17:07.627963+08:00 4 Query show table status like 'columns\_priv'
70 2023-11-05T18:17:07.628638+08:00 4 Query SET SQL_QUOTE_SHOW_CREATE=1
71 2023-11-05T18:17:07.628775+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION character_set_results = 'binary'
72 2023-11-05T18:17:07.628977+08:00 4 Query show create table `columns_priv`
73 2023-11-05T18:17:07.629271+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION character_set_results = 'utf8'
74 2023-11-05T18:17:07.629506+08:00 4 Query show fields from `columns_priv`
75 2023-11-05T18:17:07.630154+08:00 4 Query show fields from `columns_priv`
76 2023-11-05T18:17:07.630755+08:00 4 Query SELECT /*!40001 SQL_NO_CACHE */ * FROM `columns_priv`
493 2023-11-05T18:17:07.793839+08:00 4 Init DB sakila #处理sakila数据库
494 2023-11-05T18:17:07.794048+08:00 4 Query SHOW CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `sakila`
495 2023-11-05T18:17:07.794460+08:00 4 Query SAVEPOINT sp
496 2023-11-05T18:17:07.794618+08:00 4 Query show tables
497 2023-11-05T18:17:07.795207+08:00 4 Query show table status like 'actor'
498 2023-11-05T18:17:07.801202+08:00 4 Query SET SQL_QUOTE_SHOW_CREATE=1
499 2023-11-05T18:17:07.801396+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION character_set_results = 'binary'
500 2023-11-05T18:17:07.801591+08:00 4 Query show create table `actor`
501 2023-11-05T18:17:07.801855+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION character_set_results = 'utf8'
502 2023-11-05T18:17:07.802063+08:00 4 Query show fields from `actor`
503 2023-11-05T18:17:07.802522+08:00 4 Query show fields from `actor`
504 2023-11-05T18:17:07.803017+08:00 4 Query SELECT /*!40001 SQL_NO_CACHE */ * FROM `actor`
505 2023-11-05T18:17:07.803955+08:00 4 Query SET SESSION character_set_results = 'binary'
506 2023-11-05T18:17:07.804155+08:00 4 Query use `sakila`
关键步骤
首先连接数据库后,做的整个流程如下:
#第1步: FLUSH /*!40101 LOCAL */ tables
关闭打开的表,并且刷新查询缓存(表如果打开的话,有缓存在文件系统里面,并没有把真正的数据写到文件里面去,备份出来的数据可能是脏数据或者不一致的数据)
closes all open tables,forces all table in use to be closed,and flushes the query cache.
myisam:将脏数据刷到文件,同时关闭文件描述符,关闭文件。
innodb:并不会真正的关闭文件描述符,同时也不会写脏数据,所以这个功能在innodb 中用处不大。
#第2步: FLUSH tables with read lock
简称FTWRL:执行FLUSH tables 操作,会加一个全局读锁,主要还是获取一致性备份。
主要是避免比较长的事务没有关闭,会导致FLUSH tables with read lock 操作一直得不到锁,就会阻塞其它客户端的操作。
FTWRL:一般需要持有两把全局的MDL 锁(metadata lock),而且还需要关闭所有的表对象。(杀伤力比较大,非必要不要执行,如果是主库业务可能没办法访问,如果是备库有可能把SQL线程卡死,主备延迟)
FTWRL 主要包括3 个步骤:
A. 上全局读锁
B. 清理表缓存
C. 上全局commit 锁
#第3步: SET session transaction isolation level repeatable read
设置当前的事务隔离级别为RR,避免不可重复读和幻读
#第4步: START transaction /*!40100 WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT */
获取当前数据库的一个快照,由--single-transaction 决定。只适合支持事务的表,就是innodb 引擎。
主要是在开启事务的时候,对所有的表做一次select 操作,得到一个快照,备份时就可以一致。
start transaction:别人插入数据,本会话也能看见,出现备份不一致。
start transaction with consistent snapshot :当前会话,对之前的数据可见,对后面的新数据不可见。(在备份的时候用了该选项,在这个会话里面对之前的所有数据可见,后面的数据看不到,因为我们导出的时候可能会导很长时间,假设备份需要5小时,这5小时只能有新数据进来,后面的数据我不需要或者不想看到,做这步就是保证数据一致,比如从某个时间点开始备份,这个时间点之后加的数据都不备份,比如你是10点整开始备份的,10点之前的所有数据备走了,10点之后的数据一个都不备)
#第5步: SHOW master status
这个由--master-data 参数决定,记录了开始备份时,binlog 的状态信息,包括binlog file和log position(也就是说备份的时候从这个地方之前的全部备走,从这个地方之后的一个都不备份,如果要增量的话,就需要从这个位置之后开始增量)
#第6步: UNLOCK tables
释放锁。
#第7步: SHOW databases
查看要备份哪些数据库。
#第8步: 开始备份所有的数据库
A. 所的有备份,都不包括information_schema、sys、performance_schema。(因为这三个数据对用户来说是没有实际的数据,它们的数据都是从整个系统里面抽出来的,说白了就是统计信息,每次初始化还原的时候都会自动去建,把数据导进去的时候这三个数据库都会收集其他数据库的信息,所以说不需要)
如果要真备份这3 个数据库:
mysqldump -uroot -proot --skip-lock-tables --databases information_schema sys performance_schema > all-info-db.sql
B. 备份数据
select /*!40001 SQL_NO_CACHE */ * from `bm` (查询表的数据,查询的结果不会做缓存,查到了就往文件里写,不用内存)
C. 备份结构
show create database if not exists `testdb`,
show create table `bm`
D. 备份触发器
show triggers like 'bm'
E. 备份函数和存储过程
show function status where Db = 'testdb'
show procedure status where Db = 'testdb'
F. 保存点
savepoint sp
rollback to savepoint sp
release savepoint sp
设置savepoint点,然后备份完了后再回滚到savepoint;这样做的好处,不会阻塞在备份期间对已经备份完的表的DDL 操作。主要是提高DDL 的并发性。(如果都备份完了,还没有释放的话,做ddl就会夯死,也就是说如果不做回滚到保存点的话,做ddl会一直夯下去)
案例说明:第4步事务的效果
场景1
会话17
mysql(17) [(none)]> use testdb
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
#设置会话的隔离级别:可重复读
mysql(17) [testdb]> set session tx_isolation='REPEATABLE-READ';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]>
会话21
#设置会话的隔离级别:可重复读
mysql(21) [testdb]> set session tx_isolation='REPEATABLE-READ';
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]>
会话17:创建表,插入数据,并提交
create table test_t01(name varchar(10));
insert into test_t01 values('A1');
commit;
start transaction with consistent snapshot;
mysql(17) [testdb]> create table test_t01(name varchar(10));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]> insert into test_t01 values('A1');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
#运行事务(加一致性快照选项)
mysql(17) [testdb]> start transaction with consistent snapshot;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]>
#如上此时会话17看到的数据是只有刚刚插入的一条记录
会话21:插入一条数据,并提交
insert into test_t01 values('B1');
commit;
mysql(21) [testdb]> insert into test_t01 values('B1');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]>
mysql(21) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
| B1 |
+------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#如上会话21能看到会话17插入的数据和自己插入的数据
会话17再查询
mysql(17) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
此时会话17能查到的还是自己插入的数据,会话21插入的数据会话17看不到。
其他会话不管加了多少数据,会话17都是只能看到自己插入的那一条数据(做快照之前的数据)
场景2:
会话17:启动一个普通事务
mysql(17) [testdb]> start transaction;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]>
会话21:插入数据并提交
mysql(21) [testdb]> insert into test_t01 values('B2');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
| B1 |
| B2 |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#如上会话21能看到自己最新插入的数据和之前的数据
会话17
mysql(17) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
| B1 |
| B2 |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#如上会话17此时能看到会话21提交的数据。
案例说明:第8步保存点的效果
会话17
mysql(17) [testdb]> start transaction with consistent snapshot;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]> savepoint sp;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]> select * from test_t01;
+------+
| name |
+------+
| A1 |
| B1 |
| B2 |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]>
会话21:
mysql(21) [testdb]> truncate table test_t01; #hang住了
会话17
mysql(17) [testdb]> rollback to savepoint sp;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql(17) [testdb]>
会话21
mysql(21) [testdb]> truncate table test_t01; #解锁
Query OK, 0 rows affected (42.96 sec)
mysql(21) [testdb]>
重要:不能在业务高峰期做备份,建议不再用myisam 引擎,全部用innodb。
mysqldump 的大致实现过程:
- 连接
- 初始化信息
- 刷新表(锁表)
- 记录偏移量
- 开启事务(一致性快照)
- 记录偏移量
- 解锁表
- 查看要备份的表
- 开始备份所有的数据
分析mysqldump 事务和锁
-
–lock-tables
mysqldump -uroot -proot --lock-tables --database testdb > testdb.sql后台看general.log
总结:会在整个导出过程中加lock read local 所有的表。针对innodb 别人只能读;针对myisam 别人可以读和插入,但阻塞update。
-
–lock-all-tables
mysqldump -uroot -proot --lock-all-tables --database testdb > testdb.sql后台看general.log
总结:请求一个全局的读锁,会阻塞所有表的写入操作(insert,update,delete),保证数据的一致性,备份完了后会话断开,自动解锁。
-
–single-transaction
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --database testdb > testdb.sql后台看general.log
总结:单独使用,不会有任何锁,但是会对备份的表持有metedata lock 的共享锁。
-
–master-data
mysqldump -uroot -proot --master-data --database testdb > testdb.sql后台看general.log
-
–single-transaction 和–master-data
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data –database testdb > testdb.sql后台看general.log
总结:结合使用时,也就是在开始的时候会短暂的请求一个全局的读锁,会阻止所有表的写入操作
mysqldump 生产环境最佳的备份命令
全备(myisam):
mysqldump -uroot -proot --lock-all-tables --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases > db_fullbackup.sql
全备(innodb):
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases > db_fullbackup.sql
部分数据库(innodb):
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --routines --databases testdb testdb2 > dbbackup_testdb_testdb2.sql
备份mysql数据库的权限:
mysqldump -uroot -proot --flush-privileges --databases mysql > dbbackup_mysql.sql
如果想备份performance_schema,information_schema,sys数据库:
mysqldump -uroot -proot --skip-lock-tables --databases performance_schema information_schema sys > dbbackup_per_inf_sys.sql
有必须的时候需要加上–default-character-set=utf8/utf8mb4
关于增量(binlog):
将binlog 日志保存起来,保存之前刷新日志。
flush logs;
OR:
mysqladmin -uroot -prootroot flush logs
备份增量之前执行命令,刷日志,前面的日志全备走,恢复的时候,就是备份+增量日志,就可以恢复到最新或者任意时间点
mysqldump 生产环境自动化备份案例
1)全备:每天晚上2:00 执行全备脚本。
2)增量:每天13 点备份binlog 日志
前提:
-
一定要打开binlog日志功能
cat >> /mysql/data/3306/my.cnf << EOF [mysqld] log_bin=/mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog log_bin_index=/mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.index binlog_format='row' binlog_rows_query_log_events=on EOF #创建目录并授权: mkdir -p /mysql/log/3306/binlog chown -R mysql:mysql /mysql/log/3306/binlog chmod -R 755 /mysql/log/3306/binlog -
准备目录空间(不能和数据库放在同一个磁盘或存储,安全+性能)
mkdir -p /mysql/backup/backup-db mkdir -p /mysql/backup/backup-binlog mkdir -p /mysql/backup/scripts chown -R mysql:mysql /mysql/backup/ chmod -R 775 /mysql/backup/ -
准备备份脚本
backup-mysqldump-full.sh backup-mysql-binlog.sh #上传至/mysql/backup/scripts,并改后缀和权限 -
手工调试脚本(验证脚本是否有效)
-
配置crontab任务:
crontab -e 00 02 * * * /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysqldump-full.sh /dev/null 2>&1 00 13 * * * /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysql-binlog.sh /dev/null 2>&1
mysqldump 全备+增量的恢复案例1-所有库
第1步: 首先做全备
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases >db_fullbackup.sql
第2步: 做增量数据
use testdb;
-- drop table test_t;
create table test_t (name varchar(20));
insert into test_t
values('test01'),('test02'),('test03'),('test04'),('test05');
commit;
select * from test_t;
第3步: 备份binlog(备份增量)
sh /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysql-binlog.sh
#查看备份的日志
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# cat bak-bin.log
--------------------------------------------------------------------
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 22:38:12 Bakup Start...
testdb-binlog.000007 copying
testdb-binlog.000008 copying
testdb-binlog.000009 copying
testdb-binlog.000010 copying
testdb-binlog.000011 skip!
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 22:38:13 Bakup Complete! Next LogFile is: /mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.000011
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
执行清理
purge binary logs to ‘xxxx’;(把原来目录的二进制日志文件清掉,主从的话没有同步完,千万不要清,to ‘xxxx’ 根据全备的记录去清,因为做恢复的时候,目录里面是尽量不要有二进制文件存在,否则会出现混乱,清理的时候需要多注意。)
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000007 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000008 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000009 | 92244311 |
| testdb-binlog.000010 | 787 |
| testdb-binlog.000011 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
mysql> purge binary logs to 'testdb-binlog.000011';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000011 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
第4步: 模拟数据删除
cd /mysql/data/3306/
service mysql stop
rm -rf data-bak
mv data data-bak
第5步: 数据库安装及初始化
如果是本机,只需要初始化数据库
如果是异机,需要安装数据库并初始化,并使用原有的参数文件,最好是备份的时候一起拷走。
/mysql/app/mysql/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/mysql/data/3306/my.cnf --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/mysql/app/mysql --datadir=/mysql/data/3306/data
查看报错日志获取root初始化密码:
[root@centos7 3306]# tail -1 /mysql/log/3306/testdb-error.err
2023-11-05T22:39:51.894149+08:00 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: !1kZv2c*<l5P
[root@centos7 3306]#
启动mysql并重置密码
service mysql start
#使用临时密码连接
mysql -uroot -p --connect-expired-password
#修改密码
mysql> alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'root';
第6步: 恢复数据库
mysql -uroot -proot < db_fullbackup.sql
第7步: 检查数据,确认恢复成功,但是并没有增量的数据。
[root@centos7 ~]# mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb
mysql> select * from test_t;
ERROR 1146 (42S02): Table 'testdb.test_t' doesn't exist
mysql>
第8步: 恢复增量数据
#查看全备的信息
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -i 'change master to master_log_file' db_fullbackup.sql
-- CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='testdb-binlog.000010', MASTER_LOG_POS=154;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#查看二进制日志
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000011 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000012 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000013 | 92244260 |
+----------------------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
从全备的脚本中得出二进制日志文件到了000010,154位置(154位置为起始位置,也就是最新刷到该文件,全备后所有的变更都是从000010日志文件开始记录),如上可以看到000013这个日志记录的信息很多,猜想一下这个我们刚刚恢复数据库导入全部文件时候产生的二进制日志!!!12和13是做了切换所以日志量很少,基本没有信息(起始位置是154)
#备份的二进制日志
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# cat bak-bin.log
--------------------------------------------------------------------
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 22:38:12 Bakup Start...
testdb-binlog.000007 copying
testdb-binlog.000008 copying
testdb-binlog.000009 copying
testdb-binlog.000010 copying
testdb-binlog.000011 skip!
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 22:38:13 Bakup Complete! Next LogFile is: /mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.000011
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
查看备份的二进制日志文件和备份二进制日志文件的log,如上可以看到下一个文件是11也就是在11之前做的增量(10号存放的是增量数据)
找增量二进制不好找的话,最好的办法就是在第3步备份完成二进制日志之后,做一个日志清理,清理掉之前的日志信息,这样查询到最新的日志就是我们需要的增量的记录:
mysqlbinlog testdb-binlog.000010 > 10.sql
mysql -uroot -prootroot <10.sql
#检查数据
mysql> select * from test_t;
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| test01 |
| test02 |
| test03 |
| test04 |
| test05 |
+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
如上增量数据恢复回来了。
mysqldump 全备的恢复案例2-单个库
第1步: 做全备
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases >db_fullbackup.sql
第2步: 模拟数据库删除
mysql> drop database testdb;
Query OK, 16 rows affected (0.12 sec)
mysql>
第3步: 创建要恢复的数据库
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot -o testdb < db_fullbackup.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
ERROR 1049 (42000): Unknown database 'testdb'
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#如上不创建数据库直接恢复,会报错,提示识别不到数据库
#从全备脚本中找创建数据库相关的参数(字符集格式等这类的信息)
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -io '^create database.*testdb.*' db_fullbackup.sql
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#创建测试数据库
mysql> CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql>
第4步: 恢复数据库
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot -o testdb < db_fullbackup.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
第5步: 检查数据,确认恢复成功。
mysql> use testdb
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+------------------+
| Tables_in_testdb |
+------------------+
| bm |
| dd |
| dq |
| gj |
| gw |
| jl |
| test11 |
| test12 |
| test_m1 |
| test_m5 |
| test_obj |
| test_sales |
| test_t |
| test_t01 |
| test_yg |
| yg |
+------------------+
16 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
如上恢复成功。
mysqldump 全备的恢复案例3-单个表
第1步: 做全备
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases > db_fullbackup.sql
第2步: 模拟删除表
mysql> drop table testdb.test_t;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
第3步: 先从备份中找到创建表的DDL,先创建表,再导入数据
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb.test_t < db_fullbackup.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
ERROR 1049 (42000): Unknown database 'testdb.test_t'
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
如上恢复的时候直接使用数据库名 表名的方式,会报错提示找不到数据库,有个-o的参数可以针对数据库做恢复,恢复表和恢复库的方法完全不一样
#获取创建表的DDL
cat db_fullbackup.sql |sed -e '/./{H;$!d;}' -e 'x;/CREATE TABLE `test_t`/!d;q' |sed -e '/./{H;$!d;}' -e 'x;/CREATE TABLE `test_t`/!d;q';
[root@centos7 backup-db]# cat db_fullbackup.sql |sed -e '/./{H;$!d;}' -e 'x;/CREATE TABLE `test_t`/!d;q' |sed -e '/./{H;$!d;}' -e 'x;/CREATE TABLE `test_t`/!d;q';
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `test_t`;
/*!40101 SET @saved_cs_client = @@character_set_client */;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `test_t` (
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = @saved_cs_client */;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#获取 插入数据的命令
[root@centos7 backup-db]# egrep -io '^insert into `test_t`.*;$' db_fullbackup.sql
INSERT INTO `test_t` VALUES ('test01'),('test02'),('test03'),('test04'),('test05');
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
[root@centos7 backup-db]# egrep -io '^insert into `test_t`.*;$' db_fullbackup.sql > test_t.sql
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
改test_t.sql
加入commit;
第4步: 检查数据,确认恢复成功
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb < test_t.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
mysql> select * from testdb.test_t;
+--------+
| name |
+--------+
| test01 |
| test02 |
| test03 |
| test04 |
| test05 |
+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysqldump 全备+增量恢复案例-时间点
第1步: 准备数据
use testdb;
create table test_t02(
id int(10) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(16),
sex enum('m','w'),
age int(3)
);
insert into test_t02(name,sex,age) values
('test01','w',21),
('test02','w',22),
('test03','m',23),
('test04','m',24),
('test05','w',26);
commit;
select * from test_t02;
第2步: 做全备
mysqldump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases > db_fullbackup.sql
#查看日志刷到哪一个了
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -i 'change master to master_log_file' db_fullbackup.sql
-- CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='testdb-binlog.000016', MASTER_LOG_POS=154;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
第3步: 备份binlog日志
#查看备份binlog日志
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 23:42:52 Bakup Start...
testdb-binlog.000011 copying
testdb-binlog.000012 copying
testdb-binlog.000013 copying
testdb-binlog.000014 copying
testdb-binlog.000015 copying
testdb-binlog.000016 copying
testdb-binlog.000017 skip!
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 23:42:52 Bakup Complete! Next LogFile is: /mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.000017
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
#执行清理
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000011 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000012 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000013 | 92244999 |
| testdb-binlog.000014 | 85806048 |
| testdb-binlog.000015 | 1995 |
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> purge binary logs to 'testdb-binlog.000016';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
第4步: 确认时间点1
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2023-11-05 23:48:31 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#查看当前日志状态:
mysql> show master status;
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 154 | | | |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
第5步: 模拟业务对数据进行修改
update testdb.test_t02 set name='test0004' where name='test04';
commit;
update testdb.test_t02 set name='test0005' where name='test05';
commit;
select * from testdb.test_t02;
mysql> select * from test_t02;
+----+----------+------+------+
| id | name | sex | age |
+----+----------+------+------+
| 1 | test01 | w | 21 |
| 2 | test02 | w | 22 |
| 3 | test03 | m | 23 |
| 4 | test0004 | m | 24 |
| 5 | test0005 | w | 26 |
+----+----------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
第6步: 查看时间点2
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2023-11-05 23:52:42 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show master status;
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 930 | | | |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
delete from testdb.test_t02 where name='test02';
commit;
select * from testdb.test_t02;
mysql> select * from testdb.test_t02;
+----+----------+------+------+
| id | name | sex | age |
+----+----------+------+------+
| 1 | test01 | w | 21 |
| 3 | test03 | m | 23 |
| 4 | test0004 | m | 24 |
| 5 | test0005 | w | 26 |
+----+----------+------+------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
第7步: 查看时间点3
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2023-11-05 23:55:56 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> show master status;
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | Executed_Gtid_Set |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 1283 | | | |
+----------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
第8步: 再次备份binlog
sh /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysql-binlog.sh
#备份日志
--------------------------------------------------------------------
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 23:56:52 Bakup Start...
testdb-binlog.000016 exist!
testdb-binlog.000017 copying
testdb-binlog.000018 skip!
binlog-backup---2023-11-05 23:56:52 Bakup Complete! Next LogFile is: /mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.000018
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
第9步: 恢复数据1:整库恢复
#删除数据库(生产环境就可以拷贝库文件到另外一台机器上,先全库恢复,然后根据日志追到最新的数据)
drop database testdb;
#恢复整库的时候需要先创建数据库,否则会有以下的报错
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot -o testdb <db_fullbackup.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
ERROR 1049 (42000): Unknown database 'testdb'
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#从全备中整理创建数据库的ddl
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -io 'create database.*testdb.*' db_fullbackup.sql
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
mysql> CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
#恢复testdb数据库
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysql -uroot -prootroot -o testdb < db_fullbackup.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#检查数据
mysql> select * from testdb.test_t02;
+----+--------+------+------+
| id | name | sex | age |
+----+--------+------+------+
| 1 | test01 | w | 21 |
| 2 | test02 | w | 22 |
| 3 | test03 | m | 23 |
| 4 | test04 | m | 24 |
| 5 | test05 | w | 26 |
+----+--------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
如上表数据恢复了,但是数据还是原始数据。
第10步: 恢复数据2:binlog增量,要求恢复时间点到 2023-11-05 23:52:42
#查看日志刷到哪一个了(查看全备脚本):
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -i 'change master to master_log_file' db_fullbackup.sql
-- CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_LOG_FILE='testdb-binlog.000016', MASTER_LOG_POS=154;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
#查看现在二进制日志的情况:
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 1334 |
| testdb-binlog.000018 | 85807462 |
+----------------------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
如上最新的是18,因为备份之后清理过二进制日志,所以数据应该是16或者17里面,去这两个日志里面找对应的时间点,找到时间点以后,就可以确认恢复到哪个文件的什么位置
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v testdb-binlog.000016 |grep '23:52'
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v testdb-binlog.000017 |grep '23:52'
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 607 CRC32 0x9798d9b4 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=1 sequence_number=2 rbr_only=yes
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 681 CRC32 0x2f49013a Query thread_id=4 exec_time=0 error_code=0
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 767 CRC32 0xd5847d6a Rows_query
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 827 CRC32 0x926adbc4 Table_map: `testdb`.`test_t02` mapped to number 455
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 899 CRC32 0x27482067 Update_rows: table id 455 flags: STMT_END_F
#231105 23:52:00 server id 3306 end_log_pos 930 CRC32 0x66be74b4 Xid = 5076
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v testdb-binlog.000017 |grep '23:53'
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 995 CRC32 0x342aed02 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=2 sequence_number=3 rbr_only=yes
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 1069 CRC32 0xe8402d75 Query thread_id=4 exec_time=0 error_code=0
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 1140 CRC32 0x7fb42667 Rows_query
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 1200 CRC32 0x98e1b976 Table_map: `testdb`.`test_t02` mapped to number 455
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 1252 CRC32 0x8d6c9ba2 Delete_rows: table id 455 flags: STMT_END_F
#231105 23:53:52 server id 3306 end_log_pos 1283 CRC32 0xf2ed6560 Xid = 5081
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
如上17号文件里面能对上对应的时间点
注意:虽然日志16没有我们需要的数据,但是16也是需要恢复的,因为16也有一些其他的日志在里面,16全恢复,17恢复一部分
#恢复16日志
mysqlbinlog testdb-binlog.000016 > 16.sql
mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb < 16.sql
#恢复17日志
mysqlbinlog --stop-datetime="2023-11-05 23:52:42" --database=testdb testdb-binlog.000017|mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb
第11步: 验证数据:
mysql> select * from testdb.test_t02;
+----+----------+------+------+
| id | name | sex | age |
+----+----------+------+------+
| 1 | test01 | w | 21 |
| 2 | test02 | w | 22 |
| 3 | test03 | m | 23 |
| 4 | test0004 | m | 24 |
| 5 | test0005 | w | 26 |
+----+----------+------+------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
如上数据恢复了update的数据(我们先update 4,5 后delete2)
如果是在异机恢复,那么你需要再把这个表单独导出来,再导入到原库中
mysqldump -uroot -prootroot testdb test_t02 > testdb_test_t02.sql
#查看导出的脚本:
[root@centos7 backup-db]# cat testdb_test_t02.sql
-- MySQL dump 10.13 Distrib 5.7.43, for linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64)
--
-- Host: localhost Database: testdb
-- ------------------------------------------------------
-- Server version 5.7.43-log
/*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@@CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@@CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION=@@COLLATION_CONNECTION */;
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
/*!40103 SET @OLD_TIME_ZONE=@@TIME_ZONE */;
/*!40103 SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_SQL_MODE=@@SQL_MODE, SQL_MODE='NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO' */;
/*!40111 SET @OLD_SQL_NOTES=@@SQL_NOTES, SQL_NOTES=0 */;
--
-- Table structure for table `test_t02`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `test_t02`;
/*!40101 SET @saved_cs_client = @@character_set_client */;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `test_t02` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` enum('m','w') DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(3) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*!40101 SET character_set_client = @saved_cs_client */;
--
-- Dumping data for table `test_t02`
--
LOCK TABLES `test_t02` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `test_t02` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `test_t02` VALUES (1,'test01','w',21),(2,'test02','w',22),(3,'test03','m',23),(4,'test0004','m',24),(5,'test0005','w',26);
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `test_t02` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
/*!40103 SET TIME_ZONE=@OLD_TIME_ZONE */;
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=@OLD_SQL_MODE */;
/*!40014 SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS */;
/*!40014 SET UNIQUE_CHECKS=@OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS */;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT */;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS */;
/*!40101 SET COLLATION_CONNECTION=@OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION */;
/*!40111 SET SQL_NOTES=@OLD_SQL_NOTES */;
-- Dump completed on 2023-11-06 0:22:41
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
模拟生产删表:
mysql> drop table testdb.test_t02;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
恢复表
mysql -uroot -prootroot testdb < testdb_test_t02.sql
如上数据回来了。
通过mysqldump 迁移数据库的方案
迁移:一般是第一台机将数据恢复到第二台机。
mysql 跨机器数据库迁移方案(命令方法)
迁移所有的数据库
第1步: 先备份原来的所有数据库
第2步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库。
第3步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第4步: 原库刷二进制日志,停库。
第5步: 将原库的binlog 二进制日志拷到目标库,增量恢复。
第6步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
迁移单个数据库
第1步: 先备份原库的单个数据库
第2步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库。
第3步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第4步: 原库刷二进制日志,停库。
第5步: 将原库的binlog 二进制日志拷到目标库,增量恢复单个数据库。
第6步: 原库对应的权限一定要在目标库恢复
#权限备份函数
mysql_exp_grants()
{
mysql -B -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} $@ -e "SELECT CONCAT( 'SHOW CREATE USER ''', user, '''@''', host, ''';' ) AS query FROM mysql.user" | \
mysql -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} -f $@ | \
sed 's#$#;#g;s/^\(CREATE USER for .*\)/-- \1 /;/--/{x;p;x;}'
mysql -B -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} $@ -e "SELECT CONCAT( 'SHOW GRANTS FOR ''', user, '''@''', host, ''';' ) AS query FROM mysql.user" | \
mysql -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} -f $@ | \
sed 's/\(GRANT .*\)/\1;/;s/^\(Grants for .*\)/-- \1 /;/--/{x;p;x;}'
}
mysql_exp_grants > ./mysql_exp_grants_out_$Date.sql
第7步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
迁移单个表
第1步: 先备份原库的单个表。
第2步: 再锁定原表只能读,不能写。
第3步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库,创建对应的数据库。
第4步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第5步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
mysql 跨机器数据库迁移方案(图形方法)
navicat 工具:针对小业务,大业务很有可能夯死
sqlyog
mysql 云环境迁移方案
就和上面方法一样,本地导出,FTP 上传到云环境,恢复。
mysql 版本升级迁移
-
自带的工具升级
-
导入导出
mysqldump 字符集问题与字符集转换案例
使用mysqldump 导出的中文出现乱码问题
涉及到字符集的地方有3 个:
-
mysql 自身的设置
#客户端(一般都是根据服务端的来定) [client] port=3306 socket = /mysql/data/3306/mysql.sock #mysql工具的字符集 [mysql] default-character-set=utf8 #服务器的字符集 [mysqld] character-set-server=utf8 #查看服务器的字符集:(一定要和客户端的一样) mysql> show variables like '%character%'; +--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ | character_set_client | utf8 | | character_set_connection | utf8 | | character_set_database | utf8 | | character_set_filesystem | binary | | character_set_results | utf8 | | character_set_server | utf8 | | character_set_system | utf8 | | character_sets_dir | /mysql/app/mysql-5.7.43-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64/share/charsets/ | +--------------------------+----------------------------------------------------------------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec) OR: mysql> \s ...... Server characterset: utf8 Db characterset: utf8 Client characterset: utf8 Conn. characterset: utf8 ...... -
Linux服务器的字符集设置
[root@centos7 ~]# echo $LANG en_US.UTF-8 [root@centos7 ~]# -
使用工具的字符集设置(导入导出时设置)
#导出的时候可以加 --default-character-set=utf8选项 mysqldump -uroot -proot --default-character-set=utf8 --single-transaction --master-data=2 --flush-logs --flush-privileges --routines --all-databases >db_fullbackup.sql #查看导出的脚本的字符集: [root@centos7 backup-db]# head db_fullbackup.sql -- MySQL dump 10.13 Distrib 5.7.43, for linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64) -- -- Host: localhost Database: -- ------------------------------------------------------ -- Server version 5.7.43-log /*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@@CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT */; /*!40101 SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@@CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS */; /*!40101 SET @OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION=@@COLLATION_CONNECTION */; /*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */; #这里标明了是utf8 [root@centos7 backup-db]# grep 'DEFAULT CHARACTER SET' db_fullbackup.sql|head -1 CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `mysql` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */; [root@centos7 backup-db]# #检查导出的文件的字符集: [root@centos7 backup-db]# file db_fullbackup.sql db_fullbackup.sql: UTF-8 Unicode text, with very long lines [root@centos7 backup-db]# #设置当前环境变量的字符集 set names utf8; -
ssh客户端工具(xshell、CRT、MobaXterm)字符集
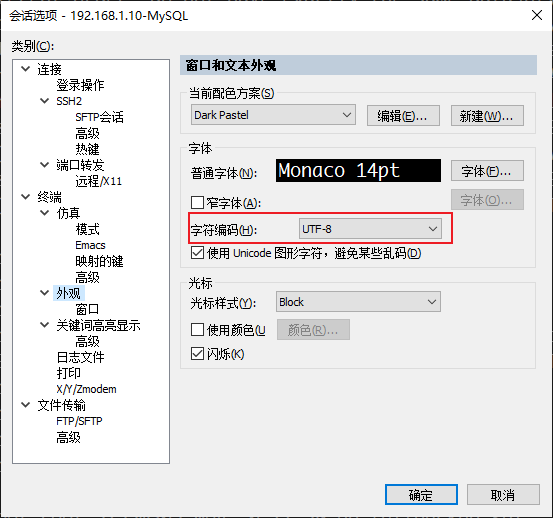
mysql 如何转换字符编码
#-t 到什么字符集,-f原字符集是什么,-c后面跟需要转换的文件
iconv -t utf-8 -f gbk -c db_fullbackup.sql > db_fullbackup_utf8.sql
通过mysqldump 来修改mysql 导出的字符集(字符集转换案例)
第1步: 创建测试数据
create database testdb1 charset gbk;
use testdb1;
create table test_t(
id int,
name varchar(20)
) engine=innodb,charset=gbk;
insert into test_t values(1,'情到');
insert into test_t values(2,'深处');
insert into test_t values(3,'人孤独');
commit;
mysql> show create table test_t\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: test_t
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `test_t` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=gbk
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
如上可以看出创建表的字符集为gbk
接下来,将testdb1由gbk 转换为utf8 字符集的数据库。
第2步: 先导出数据库及表的结构(UTF8),由GBK替换为utf8
mysqldump -uroot -proot --routines --default-character-set=utf8 --no-data testdb1 > testdb1_nodata.sql
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep gbk testdb1_nodata.sql
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=gbk;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
第3步: 修改itpuxdb_nodata.sql 中的定义
sed -i 's/gbk/utf8/g' testdb1_nodata.sql
第4步: 再导数据(按原库GBK导出)
一定要按照原库的GBK导出,这样导出的数据才不会乱,如果在导出的时候就转换的话,数据会乱。
GBK中一个汉字占两个字节,UTF8中一个汉字占三个字节
建议修改char/varchar 的长度为原来的1.5 倍,为了安全,导出时加–extended-insert参数。(加了extended-insert,就可以不考虑加长字符类型了,系统会自动处理)
mysqldump -uroot -proot --routines --default-character-set=gbk --extended-insert --no-create-info testdb1 > testdb1_data.sql
第5步: 修改testdb1_data.sql中的定义
/*!40101 SET NAMES gbk */;
......
LOCK TABLES `test_t` WRITE;
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `test_t` DISABLE KEYS */;
INSERT INTO `test_t` VALUES (1,'æ<83><85>å<88>°'),(2,'æ·±å¤<84>'),(3,'人å¤ç<8b>\¬');
/*!40000 ALTER TABLE `test_t` ENABLE KEYS */;
UNLOCK TABLES;
如上表数据也显示乱码
#由/*!40101 SET NAMES gbk */;修改为/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
sed -i 's/gbk/utf8/g' testdb1_data.sql
第6步: 创建新的数据库
create database testdb2 charset=utf8;
第7步: 导入对象结构
mysql -uroot -proot testdb2 < testdb1_nodata.sql
第8步: 导入数据方法2种:
1、 用navicat 工具(一定要在GBK编码下导入)
2、命令
mysql -uroot -proot testdb2 < testdb1_data.sql
如上可以看出直接导进入的数据是有问题的!!!
使用iconv工具转化一下导出的数据文件(导出的时候是按照GBK导出的,准备导入了转成UTF8)
iconv -t utf-8 -f gbk -c testdb1_data.sql > testdb1_data_new.sql
mysql -uroot -proot testdb2 < testdb1_data_new.sql
select * from test_t;
desc test_t;
show create table test_t\G
mysqlpump 工具详解与备份恢复案例
mysqlpump 工具介绍
mysql 5.7.8开始官方提供的一个逻辑备份工具:mysqlpump(建议mysql 5.7.11以后开始用,mysql 5.7.11之前事务和并行不兼容),用法和mysqldump类似区别在于mysqlpump是多线程速度快,而mysqldump是单线程。
mysqldump:类似于Oracle exp
mysqlpump:类似于Oracle expdp
help文档:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysqlpump.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/mysqlpump.html
mysqlpump 工具参数说明与使用总结
帮助信息
[root@centos7 ~]# mysqlpump --help
mysqlpump Ver 1.0.0 Distrib 5.7.43, for linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64)
Copyright (c) 2014, 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
MySQL utility for dumping data from databases to external file.
Usage: mysqlpump [OPTIONS] [--all-databases]
OR mysqlpump [OPTIONS] --databases DB1 [DB2 DB3...]
OR mysqlpump [OPTIONS] database [tables]
Default options are read from the following files in the given order:
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf /usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf
The following groups are read: client mysql_dump mysqlpump
The following options may be given as the first argument:
--print-defaults Print the program argument list and exit.
--no-defaults Don't read default options from any option file,
except for login file.
--defaults-file=# Only read default options from the given file #.
--defaults-extra-file=# Read this file after the global files are read.
--defaults-group-suffix=#
Also read groups with concat(group, suffix)
--login-path=# Read this path from the login file.
-?, --help Display this help message and exit.
--add-drop-database Add a DROP DATABASE before each CREATE DATABASE.
--add-drop-table Add a DROP TABLE before each CREATE TABLE.
--add-drop-user Add a DROP USER before each CREATE USER.
--add-locks Wrap data inserts on table with write lock on that table
in output. This doesn't work with parallelism.
-A, --all-databases Dump all databases. This is default behaviour if no
positional options are specified. Specifying this option
is mutually exclusive with --databases.
--bind-address=name IP address to bind to.
--character-sets-dir=name
Directory for character set files.
--complete-insert Use complete insert statements, include column names.
-C, --compress Use compression in server/client protocol.
--compress-output=name
Compresses all output files with LZ4 or ZLIB compression
algorithm.
-B, --databases Dump selected databases, specified in positional options.
Specifying this option is mutually exclusive with
--all-databases.
-#, --debug[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--debug-check[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--debug-info[=#] This is a non-debug version. Catch this and exit.
--default-character-set=name
Set the default character set.
--default-parallelism=#
Specifies number of threads to process each parallel
queue for values N > 0. if N is 0 then no queue will be
used. Default value is 2. If N > 1 then objects in dump
file can have lines intersected. Usage of values greater
than 1 is mutually exclusive with --single-transaction.
--default-auth=name Default authentication client-side plugin to use.
--defer-table-indexes
Defer addition of indexes of table to be added after all
rows are dumped.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-defer-table-indexes to disable.)
--events Dump event scheduler events.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-events to disable.)
--exclude-databases=name
Specifies comma-separated list of databases to exclude.
--exclude-events=name
Specifies comma-separated list of events to exclude.
--exclude-routines=name
Specifies comma-separated list of stored procedures or
functions to exclude.
--exclude-tables=name
Specifies comma-separated list of tables to exclude.
--exclude-triggers=name
Specifies comma-separated list of triggers to exclude.
--exclude-users=name
Specifies comma-separated list of users to exclude.
--extended-insert=# Allow usage of multiple-row INSERT syntax that include
several VALUES lists. Specifies number of rows to include
in single INSERT statement. Must be greater than 0
--get-server-public-key
Get public key from server
--hex-blob Dump binary strings (in fields of type BINARY, VARBINARY,
BLOB, ...) in hexadecimal format.
-h, --host=name Connect to host.
--include-databases=name
Specifies comma-separated list of databases and all of
its objects to include. If there are no exclusions then
only included objects will be dumped. Otherwise all
objects that are not on exclusion lists or are on
inclusion list will be dumped.
--include-events=name
Specifies comma-separated list of events to include. If
there is no exclusions then only included objects will be
dumped. Otherwise all objects that are not on exclusion
lists or are on inclusion list will be dumped.
--include-routines=name
Specifies comma-separated list of stored procedures or
functions to include. If there is no exclusions then only
included objects will be dumped. Otherwise all objects
that are not on exclusion lists or are on inclusion list
will be dumped.
--include-tables=name
Specifies comma-separated list of tables to include. If
there is no exclusions then only included objects will be
dumped. Otherwise all objects that are not on exclusion
lists or are on inclusion list will be dumped.
--include-triggers=name
Specifies comma-separated list of triggers to include. If
there is no exclusions then only included objects will be
dumped. Otherwise all objects that are not on exclusion
lists or are on inclusion list will be dumped.
--include-users=name
Specifies comma-separated list of users to include. If
there is no exclusions then only included objects will be
dumped. Otherwise all objects that are not on exclusion
lists or are on inclusion list will be dumped.
--insert-ignore Use INSERT IGNORE INTO for dumped rows instead of INSERT
INTO.
--log-error-file=name
Append warnings and errors to specified file.
--max-allowed-packet=#
The maximum packet length to send to or receive from
server.
--net-buffer-length=#
The buffer size for TCP/IP and socket communication.
--no-create-db Suppress CREATE DATABASE statements.
-t, --no-create-info
Suppress CREATE TABLE statements.
--parallel-schemas=name
[N:]<list of: schema_name separated with ','>. Process
tables in specified schemas using separate queue handled
by --default-parallelism threads or N threads, if N is
specified. Can be used multiple times to specify more
parallel processes.
-p, --password[=name]
Password to use when connecting to server. If password is
not given, it's solicited on the tty.
--plugin-dir=name Directory for client-side plugins.
-P, --port=# Port number to use for connection.
--protocol=name The protocol to use for connection (tcp, socket, pipe,
memory).
--replace Use REPLACE INTO for dumped rows instead of INSERT INTO.
--result-file=name Direct all output generated for all objects to a given
file.
--routines Dump stored procedures and functions.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-routines to disable.)
--secure-auth Refuse client connecting to server if it uses old
(pre-4.1.1) protocol. Deprecated. Always TRUE
--server-public-key-path=name
Path to file containing server public key
--set-charset Add 'SET NAMES default_character_set' to the output to
keep charsets consistent.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-set-charset to disable.)
--set-gtid-purged=name
Add 'SET @@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' to the output. Possible
values for this option are ON, OFF and AUTO. If ON is
used and GTIDs are not enabled on the server, an error is
generated. If OFF is used, this option does nothing. If
AUTO is used and GTIDs are enabled on the server, 'SET
@@GLOBAL.GTID_PURGED' is added to the output. If GTIDs
are disabled, AUTO does nothing. If no value is supplied
then the default (AUTO) value will be considered.
--single-transaction
Creates a consistent snapshot by dumping all tables in a
single transaction. Works ONLY for tables stored in
storage engines which support multiversioning (currently
only InnoDB does); the dump is NOT guaranteed to be
consistent for other storage engines. While a
--single-transaction dump is in process, to ensure a
valid dump file (correct table contents and binary log
position), no other connection should use the following
statements: ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE, RENAME TABLE,
TRUNCATE TABLE, as consistent snapshot is not isolated
from them. This option is mutually exclusive with
--add-locks option.
--skip-definer Skip DEFINER and SQL SECURITY clauses for Views and
Stored Routines.
-d, --skip-dump-rows
Skip dumping rows of all tables to output.
-S, --socket=name The socket file to use for connection.
--ssl Deprecated. Use ssl-mode instead.
--ssl-ca=name CA file in PEM format.
--ssl-capath=name CA directory.
--ssl-cert=name X509 cert in PEM format.
--ssl-cipher=name SSL cipher to use.
--ssl-crl=name Certificate revocation list.
--ssl-crlpath=name Certificate revocation list path.
--ssl-key=name X509 key in PEM format.
--ssl-mode=name SSL connection mode.
--ssl-verify-server-cert
Deprecated. Use ssl-mode=VERIFY_IDENTITY instead.
--tls-version=name TLS version to use.
--triggers Dump triggers.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-triggers to disable.)
--tz-utc SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00' at top of dump to allow dumping of
TIMESTAMP data when a server has data in different time
zones or data is being moved between servers with
different time zones.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-tz-utc to disable.)
-u, --user=name User for login if not current user.
--users Dump users with their privileges in GRANT format.
Disabled by default.
-V, --version Output version information and exit.
--watch-progress Shows periodically dump process progress information on
error output. Progress information include both completed
and total number of tables, rows and other objects
collected.
(Defaults to on; use --skip-watch-progress to disable.)
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
add-drop-database FALSE
add-drop-table FALSE
add-drop-user FALSE
add-locks FALSE
all-databases FALSE
bind-address (No default value)
character-sets-dir (No default value)
complete-insert FALSE
compress FALSE
compress-output (No default value)
databases FALSE
default-character-set UTF8MB4
default-parallelism 2
default-auth (No default value)
defer-table-indexes TRUE
events TRUE
exclude-databases (No default value)
exclude-events (No default value)
exclude-routines (No default value)
exclude-tables (No default value)
exclude-triggers (No default value)
exclude-users (No default value)
extended-insert 250
get-server-public-key FALSE
hex-blob FALSE
host (No default value)
include-databases (No default value)
include-events (No default value)
include-routines (No default value)
include-tables (No default value)
include-triggers (No default value)
include-users (No default value)
insert-ignore FALSE
log-error-file (No default value)
max-allowed-packet 25165824
net-buffer-length 1047552
no-create-db FALSE
no-create-info FALSE
parallel-schemas (No default value)
password (No default value)
plugin-dir (No default value)
port 0
protocol (No default value)
replace FALSE
result-file (No default value)
routines TRUE
secure-auth FALSE
server-public-key-path (No default value)
set-charset TRUE
set-gtid-purged AUTO
single-transaction FALSE
skip-definer FALSE
skip-dump-rows FALSE
socket (No default value)
ssl FALSE
ssl-ca (No default value)
ssl-capath (No default value)
ssl-cert (No default value)
ssl-cipher (No default value)
ssl-crl (No default value)
ssl-crlpath (No default value)
ssl-key (No default value)
ssl-mode (No default value)
ssl-verify-server-cert FALSE
tls-version (No default value)
triggers TRUE
tz-utc TRUE
user (No default value)
users FALSE
watch-progress TRUE
[root@centos7 ~]#
默认选项
Variables (--variable-name=value)
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
--------------------------------- ----------------------------------------
add-drop-database FALSE
add-drop-table FALSE
add-drop-user FALSE
add-locks FALSE
all-databases FALSE
bind-address (No default value)
character-sets-dir (No default value)
complete-insert FALSE
compress FALSE
compress-output (No default value)
databases FALSE
default-character-set UTF8MB4
default-parallelism 2
default-auth (No default value)
defer-table-indexes TRUE
events TRUE
exclude-databases (No default value)
exclude-events (No default value)
exclude-routines (No default value)
exclude-tables (No default value)
exclude-triggers (No default value)
exclude-users (No default value)
extended-insert 250
get-server-public-key FALSE
hex-blob FALSE
host (No default value)
include-databases (No default value)
include-events (No default value)
include-routines (No default value)
include-tables (No default value)
include-triggers (No default value)
include-users (No default value)
insert-ignore FALSE
log-error-file (No default value)
max-allowed-packet 25165824
net-buffer-length 1047552
no-create-db FALSE
no-create-info FALSE
parallel-schemas (No default value)
password (No default value)
plugin-dir (No default value)
port 0
protocol (No default value)
replace FALSE
result-file (No default value)
routines TRUE
secure-auth FALSE
server-public-key-path (No default value)
set-charset TRUE
set-gtid-purged AUTO
single-transaction FALSE
skip-definer FALSE
skip-dump-rows FALSE
socket (No default value)
ssl FALSE
ssl-ca (No default value)
ssl-capath (No default value)
ssl-cert (No default value)
ssl-cipher (No default value)
ssl-crl (No default value)
ssl-crlpath (No default value)
ssl-key (No default value)
ssl-mode (No default value)
ssl-verify-server-cert FALSE
tls-version (No default value)
triggers TRUE
tz-utc TRUE
user (No default value)
users FALSE
watch-progress TRUE
[root@centos7 ~]#
重点选项
参数用法和mysqldump类似,主要讲一些多出来的重要参数:
#1、--add-drop-user
在create user 语句之前增加drop user,这个参数要和--user 一起使用,否则不生效。
#2、--compress-output
默认不压缩输出,目前可以使用压缩的算法有lz4 和zlib.
#3、--default-parallelism
指定并行线程数据,默认是2 个,如果设置0 就不并行备份,如果是单表则并行无效。
每个线程在导入的时候,先写数据,最后再创二级索引(主键索引在创建表的时候建立、。
#4、--defer-table-indexes
延迟创建索引,直到所有的数据都加载完了之后再创建索引,默认开启。
关闭--skip-defer-table-indexes,就和mysqldump 类似了,先创建表和索引,再导数据,就慢了。
#5、--parallel-schemas
指定并行备份的库
--parallel-schemas=6:db1,3:db3 db1指定6个线程,db2指定3个线程
#6、排除对象
--exclude-databases
--exclude-events
--exclude-routines
--exclude-tables
--exclude-triggers
--exclude-users
#7、指定包含的对象
--include-databases
--include-events
--include-routines
--include-tables
--include-triggers
--include-users
#8、--skip-dump-rows
只备表结构,不备份数据。而mysqldump 支持--no-data,
#9、--users
备份数据库用户,如只备份用户,而不备份数据库:mysqlpump --exclude-databases=% --users
#10、--watch-progress
显示完成进度。
#11、-A,-all-database
mysqldump 时会备份权限表相关信息
mysqlpump 不会备份,如果要备份权限信息需要加--users,
mysqlpump 常用备份命令使用案例
1. 导出所有的库(不压缩)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --users > alldb01.sql
2. 导出所有的库(压缩LZ4)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --compress-output=LZ4 --all-databases --users > alldb02.sql.LZ4
3. 导出所有的库(压缩ZLIB—压缩效果最好)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --compress-output=ZLIB --all-databases --users > alldb03.sql.zlib
[root@centos7 backup-db]# ll -h
total 86M
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 51M Nov 7 20:35 alldb01.sql
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 22M Nov 7 20:40 alldb02.sql.LZ4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 14M Nov 7 20:40 alldb03.sql.zlib
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
4. 导出单个数据库(数据+结构)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb > testdb.sql
[root@centos7 backup-db]# head -20 testdb.sql
-- Dump created by MySQL pump utility, version: 5.7.43, linux-glibc2.12 (x86_64)
-- Dump start time: Tue Nov 7 20:42:27 2023
-- Server version: 5.7.43
SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0;
SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0;
SET @OLD_SQL_MODE=@@SQL_MODE;
SET SQL_MODE="NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO";
SET @@SESSION.SQL_LOG_BIN= 0;
SET @OLD_TIME_ZONE=@@TIME_ZONE;
SET TIME_ZONE='+00:00';
SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@@CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT;
SET @OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@@CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS;
SET @OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION=@@COLLATION_CONNECTION;
SET NAMES utf8mb4;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `testdb`.`bm` (
`DEPARTMENT_ID` decimal(12,0) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key column of departments table.',
`DEPARTMENT_NAME` varchar(90) NOT NULL COMMENT 'A not null column that shows name of a department. Administration,\nMarketing, Purchasing, Human Resources, Shipping, IT, Executive, Public\nRelations, Sales, Finance, and Accounting. ',
`MANAGER_ID` decimal(18,0) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'Manager_id of a department. Foreign key to employee_id column of employees table. The manager_id column of the employee table references this column.',
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -i '^commit' testdb.sql
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
这些需要注意导出的脚步中没有commit命令,恢复的时候需要注意!
5. 导出多个数据库(并行线程分开)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --parallel-schemas=2:testdb --parallel-schemas=2:testdb2 -B testdb testdb1 > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
or:
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --parallel-schemas=2:testdb,3:testdb1 -B testdb testdb1 > testdb2.sql 2>1.log
6. 导出多个数据库(并行线程不分开)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb testdb1 > testdb3.sql 2> 1.log
7. 导出单个数据库(结构+数据+过程+函数+触发器+事件)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --routines –triggers --events --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb > testdb.sql
存储过程和函数在mysqldump中默认是不备份的,加参数才备份,在mysqlpump中默认是备份的,不加参数都备份
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysqlpump --help|grep TRUE
(pre-4.1.1) protocol. Deprecated. Always TRUE
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
defer-table-indexes TRUE
events TRUE #默认备份事件
routines TRUE #默认备份存储过程和函数
set-charset TRUE
triggers TRUE #默认备份触发器
tz-utc TRUE
watch-progress TRUE
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
如上函数存储过程、触发器、事件在mysqlpump中都是默认导的,而mysqldump默认只导触发器。
[root@centos7 backup-db]# mysqldump --help|grep TRUE
(pre-4.1.1) protocol. Deprecated. Always TRUE
and boolean options {FALSE|TRUE} Value (after reading options)
add-drop-table TRUE
add-locks TRUE
comments TRUE
create-options TRUE
disable-keys TRUE
extended-insert TRUE
lock-tables TRUE
quick TRUE
quote-names TRUE
set-charset TRUE
dump-date TRUE
secure-auth TRUE
ssl TRUE
triggers TRUE #默认备份触发器
tz-utc TRUE
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
8. 只导出所有数据库的结构
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --add-drop-table --skip-dump-rows > alldb08.sql 2> 1.log
#注意 --add-drop-table选项
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -iC1 table alldb08.sql|head -3
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `mysql` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `mysql`.`engine_cost`;
CREATE TABLE `mysql`.`engine_cost` (
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --skip-dump-rows > alldb08.sql 2> 1.log
#不加--add-drop-table选项,则在创建表前不执行drop命令
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -iC1 table alldb08.sql|head -3
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `mysql` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `mysql`.`engine_cost` (
`engine_name` varchar(64) NOT NULL,
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
9. 只导出一个数据库的结构
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb --skip-dump-rows > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep -iA2 database testdb.sql
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `testdb`.`bm` (
`DEPARTMENT_ID` decimal(12,0) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key column of departments table.',
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
10. 只导出数据
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb --no-create-info > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
#导出的结构如下,先创建数据库,再插入表,然后创建索引,没有创建表结构的语句
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
INSERT INTO `testdb`.`bm` VALUES (10
......
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`dd` ADD KEY `LOC_CITY_IX` (`CITY`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`dd` ADD KEY `LOC_COUNTRY_IX` (`COUNTRY_ID`) USING BTREE;
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
#导出的结构如下,先创建数据库,创建表,再插入表,然后创建索引
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `testdb`.`bm` (
`DEPARTMENT_ID` decimal(12,0) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key column of departments table.',
......
PRIMARY KEY (`DEPARTMENT_ID`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='Departments table that shows details of departments where employees\nwork. Contains 27 rows; references with locations, employees, and job_history tables.'
;
CREATE TABLE `testdb`.`dd` (
`LOCATION_ID` decimal(12,0) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key of locations table',
......
PRIMARY KEY (`LOCATION_ID`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT='Locations table that contains specific address of a specific office,\nwarehouse, and/or production site of a company. Does not store addresses /\nlocations of customers. Contains 23 rows; references with the\ndepartments and countries tables. '
;
INSERT INTO `testdb`.`bm` VALUES (xxxxxxxxx;
USE `testdb`;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_LOCATION_IX` (`LOCATION_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_MGR_FK` (`MANAGER_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_LOC_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`LOCATION_ID`) REFERENCES `dd` (`LOCATION_ID`);
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_MGR_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`MANAGER_ID`) REFERENCES `yg` (`EMPLOYEE_ID`);
11. 只导出某一张表(结构+数据)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --include-databases=testdb --include-tables=bm > testdb_bm.sql 2>1.log
#导出结构如下:
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE TABLE `testdb`.`bm` (
`DEPARTMENT_ID` decimal(12,0) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Primary key column of departments table.',
......
PRIMARY KEY (`DEPARTMENT_ID`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC COMMENT=xxx
INSERT INTO `testdb`.`bm` VALUES (xxx;
USE `testdb`;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_LOCATION_IX` (`LOCATION_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_MGR_FK` (`MANAGER_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_LOC_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`LOCATION_ID`) REFERENCES `dd` (`LOCATION_ID`);
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_MGR_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`MANAGER_ID`) REFERENCES `yg` (`EMPLOYEE_ID`);
12. 只导某一张表的数据(不要表结构)
mysqlpump -uroot -prootroot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --no-create-info --include-databases=testdb --include-tables=bm > testdb_bm.sql 2> 1.log
#导出结构如下
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
INSERT INTO `testdb`.`bm` VALUES (xxx);
USE `testdb`;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_LOCATION_IX` (`LOCATION_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD KEY `DEPT_MGR_FK` (`MANAGER_ID`) USING BTREE;
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_LOC_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`LOCATION_ID`) REFERENCES `dd` (`LOCATION_ID`);
ALTER TABLE `testdb`.`bm` ADD CONSTRAINT `DEPT_MGR_FK` FOREIGN KEY (`MANAGER_ID`) REFERENCES `yg` (`EMPLOYEE_ID`);
13. 导出某一个数据库(排除某一张表)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --include-databases=testdb --exclude-tables=bm > testdb.sql 2>1.log
14. 导出某一个数据库(排除多张表)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --include-databases=testdb --exclude-tables=bm,dd > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
15. 导出所有的数据库(排除其中一个数据库)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --exclude-databases=testdb --users > alldb15.sql
[root@centos7 backup-db]# grep '^CREATE DATABASE' alldb15.sql
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `mysql` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `sakila` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb1` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET gbk */;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/ `testdb2` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
[root@centos7 backup-db]#
16. 恢复其中几个数据库
使用mysqlpump不建议全库恢复,尽量以单库单表的方式去恢复
#导出testdb、testdb1数据库
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 -B testdb testdb1 > testdb.sql 2> 1.log
#恢复
drop database testdb;
drop database testdb1;
mysql -uroot -proot < testdb.sql
17. 恢复一张表
#导出单表(结构+数据)
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-parallelism=2 --include-databases=testdb --include-tables=bm > testdb_bm.sql 2>1.log
#恢复
use testdb;
drop table bm;
mysql -uroot -proot testdb < testdb_bm.sql
重点:不要使用mysqlpump去全库恢复,建议单库/多库/表这样去恢复,只需要各个数据库+所有的用户和权限信息就可以了。
备份的时候,需要什么库,就备份什么库。(如果全备的话,后面恢复的时候还要考虑从备份文件里面找对应的数据库的数据,因为使用mysqlpump想要从全库的文件里面去恢复单个库的话有点困难,需要特殊处理)
mysqlpump 生产环境自动化备份案例
线上数据库备份场景:
1)全备:每天晚上2:00 执行全备脚本。
2)增量:每天13 点备份binlog 日志
前提:
-
一定要打开binlog日志功能
-
准备目录空间(不能和数据库放在同一个磁盘或存储,安全+性能)
mkdir -p /mysql/backup/backup-db mkdir -p /mysql/backup/backup-binlog mkdir -p /mysql/backup/scripts chown -R mysql:mysql /mysql/backup/ chmod -R 775 /mysql/backup/ -
准备备份脚本
backup-mysqlpump-full.sh backup-mysql-binlog.sh # 脚本重点 mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --exclude-databases=performance_schema,information_schema,sys,mysql > alldb01.sql 排除了performance_schema,information_schema,sys,mysql这四个库,performance_schema,information_schema,sys这三个数据库用不着,mysql数据库只用里面的权限,我们一般恢复的时候是新建一个数据库,新建完了再全库恢复,恢复的时候只需要恢复业务的表空间(也就是对应的业务数据库),不用去恢复系统数据库(performance_schema,information_schema,sys,mysql) -
手工调试脚本
-
配置crontab任务
crontab -e 00 02 * * * /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysqlpump-full.sh /dev/null 2>&1 00 13 * * * /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysql-binlog.sh /dev/null 2>&1
mysqlpump 全库+增量恢复案例
第1步: 首先做全备
mysqlpump -uroot -proot --single-transaction --default-character-set=utf8 --default-parallelism=2 --all-databases --exclude-databases=performance_schema,information_schema,sys,mysql >alldb01.sql
#查看master状态
mysql> show master status\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
File: testdb-binlog.000019
Position: 4036
Binlog_Do_DB:
Binlog_Ignore_DB:
Executed_Gtid_Set:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
#binary log
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 1334 |
| testdb-binlog.000018 | 85811341 |
| testdb-binlog.000019 | 4036 |
+----------------------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#刷日志
mysql> flush logs;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 1334 |
| testdb-binlog.000018 | 85811341 |
| testdb-binlog.000019 | 4087 |
| testdb-binlog.000020 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
第2步: 做增量数据
use testdb;
create table test_t03(
id int(10) primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(16),
sex enum('m','w'),
age int(3)
);
insert into test_t03(name,sex,age) values
('test01','w',21),
('test02','w',22),
('test03','m',23),
('test04','m',24),
('test05','w',26);
commit;
select * from test_t03;
第3步: 备份binlog(备份增量)
sh /mysql/backup/scripts/backup-mysql-binlog.sh
#备份日志
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]# cat bak-bin.log
--------------------------------------------------------------------
binlog-backup---2023-11-07 22:40:55 Bakup Start...
testdb-binlog.000016 copying
testdb-binlog.000017 copying
testdb-binlog.000018 copying
testdb-binlog.000019 copying
testdb-binlog.000020 copying
testdb-binlog.000021 skip!
binlog-backup---2023-11-07 22:40:55 Bakup Complete! Next LogFile is: /mysql/log/3306/binlog/testdb-binlog.000021
[root@centos7 backup-binlog]#
#查看当前的日志
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000016 | 205 |
| testdb-binlog.000017 | 1334 |
| testdb-binlog.000018 | 85811341 |
| testdb-binlog.000019 | 4087 |
| testdb-binlog.000020 | 968 |
| testdb-binlog.000021 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#执行清理日志
mysql> purge binary logs to 'testdb-binlog.000021';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000021 | 154 |
+----------------------+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
把原来目录的二进制日志文件清掉,主从的话没有同步完,千万不要清,to ‘xxxx’ 根据全备的记录去清,因为做恢复的时候,目录里面是尽量不要有二进制文件存在,否则会出现混乱,清理的时候需要多注意。
第4步: 模拟数据删除
cd /mysql/data/3306/
service mysql stop
rm -rf data-bak
mv data data-bak
第5步: 数据库安装及初始化
如果是本机,只需要初始化数据库
如果是异机,需要安装数据库并初始化,并使用原有的参数文件,最好是备份的时候一起拷走。
[root@centos7 3306]# /mysql/app/mysql/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/mysql/data/3306/my.cnf --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/mysql/app/mysql --datadir=/mysql/data/3306/data
[root@centos7 3306]# ll data
total 1054780
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 56 Nov 7 22:47 auto.cnf
-rw------- 1 mysql mysql 1676 Nov 7 22:47 ca-key.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 mysql mysql 1112 Nov 7 22:47 ca.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 mysql mysql 1112 Nov 7 22:47 client-cert.pem
-rw------- 1 mysql mysql 1680 Nov 7 22:47 client-key.pem
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 718 Nov 7 22:47 ib_buffer_pool
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 209715200 Nov 7 22:47 ibdata1
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 209715200 Nov 7 22:47 ibdata2
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 209715200 Nov 7 22:47 ibdata3
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 209715200 Nov 7 22:47 ib_logfile0
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 209715200 Nov 7 22:47 ib_logfile1
drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 4096 Nov 7 22:47 mysql
drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 4096 Nov 7 22:47 performance_schema
-rw------- 1 mysql mysql 1680 Nov 7 22:47 private_key.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 mysql mysql 452 Nov 7 22:47 public_key.pem
-rw-r--r-- 1 mysql mysql 1112 Nov 7 22:47 server-cert.pem
-rw------- 1 mysql mysql 1676 Nov 7 22:47 server-key.pem
drwxr-x--- 2 mysql mysql 12288 Nov 7 22:47 sys
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 10485760 Nov 7 22:47 undo001
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 10485760 Nov 7 22:47 undo002
-rw-r----- 1 mysql mysql 10485760 Nov 7 22:47 undo003
[root@centos7 3306]#
#查看报错日志后去root初始化密码
[root@centos7 3306]# tail -1 /mysql/log/3306/testdb-error.err
2023-11-07T22:47:47.948372+08:00 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: tLN)pzRUk8b+
[root@centos7 3306]#
#启动mysql
[root@centos7 3306]# service mysql start
Starting MySQL... SUCCESS!
[root@centos7 3306]#
#修改密码
mysql -uroot -p --connect-expired-password
mysql> alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified by 'root';
第6步: 恢复数据库
mysql -uroot -proot < alldb01.sql
第7步: 导入权限
如上查看备份的权限脚本,只有创建用户和授权的命令没有刷权限的命令,所以还需要修改一下脚本,加上刷权限命令。
第8步: 检查数据,确认恢复成功,但是并没有增量的数据。
第9步: 恢复增量数据
mysql> show binary logs;
+----------------------+-----------+
| Log_name | File_size |
+----------------------+-----------+
| testdb-binlog.000021 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000022 | 177 |
| testdb-binlog.000023 | 398 |
+----------------------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
如上此时最开始的是21号日志,而我们恢复完数据库的时候刷到20号日志的154位置,所以20号日志存放的是我们的增量数据
mysqlbinlog testdb-binlog.000020 > 20.sql
mysql -uroot -proot testdb < 20.sql
如上这4个数据库不需要恢复,这些(performance_schema,information_schema,sys)都是自动采集的,mysql只需要恢复权限即可。
我们的备份脚本排除这些数据库的原因,尤其是mysql数据库,因为mysqlpump这个工具如果把mysql数据库备份出来的话,恢复的时候导进去的话,mysql数据库就会出问题,除非你把mysql数据库删掉。
通过mysqlpump迁移数据库方案
迁移:一般是第一台机将数据恢复到第二台机。
mysql 跨机器数据库迁移方案(命令方法)
迁移所有的数据库
第1步: 先备份原来的所有数据库
第2步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库。
第3步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第4步: 原库刷二进制日志,停库。
第5步: 将原库的binlog 二进制日志拷到目标库,增量恢复。
第6步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
迁移单个数据库
第1步: 先备份原库的单个数据库
第2步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库。
第3步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第4步: 原库刷二进制日志,停库。
第5步: 将原库的binlog 二进制日志拷到目标库,增量恢复单个数据库。
第6步: 原库对应的权限一定要在目标库恢复
#权限备份函数
mysql_exp_grants()
{
mysql -B -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} $@ -e "SELECT CONCAT( 'SHOW CREATE USER ''', user, '''@''', host, ''';' ) AS query FROM mysql.user" | \
mysql -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} -f $@ | \
sed 's#$#;#g;s/^\(CREATE USER for .*\)/-- \1 /;/--/{x;p;x;}'
mysql -B -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} $@ -e "SELECT CONCAT( 'SHOW GRANTS FOR ''', user, '''@''', host, ''';' ) AS query FROM mysql.user" | \
mysql -u${mysql_user} -p${mysql_pass} -N -P${mysql_port} -f $@ | \
sed 's/\(GRANT .*\)/\1;/;s/^\(Grants for .*\)/-- \1 /;/--/{x;p;x;}'
}
mysql_exp_grants > ./mysql_exp_grants_out_$Date.sql
第7步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
迁移单个表
第1步: 先备份原库的单个表。
第2步: 再锁定原表只能读,不能写。
第3步: 目标库安装mysql,初始化数据库,再启动数据库,创建对应的数据库。
第4步: 将备份的文件拷到目标库上,做恢复。
第5步: 数据验证,目标库对外访问。
mysql 跨机器数据库迁移方案(图形方法)
navicat 工具:针对小业务,大业务很有可能夯死
sqlyog
mysql 云环境迁移方案
就和上面方法一样,本地导出,FTP 上传到云环境,恢复。
mysql 版本升级迁移
-
自带的工具升级
-
导入导出
关于字符集的问题
mysqldump可以处理字符集,对应的mysqlpump也可以处理字符集。
处理字符集与mysqldump类似