1、使用AI的一个常用场景就是,接收人类的语言,识别人类的意图,最终进行相关的业务处理,这就是设计Tool Call / Function Call的初衷。
2、现在一般都说Tool Call,以前常叫Function Call,不要纠结。
一、安装环境
1.1 安装ollama
参考:【AI基础】大模型部署工具之ollama的安装部署-第一步:下载安装ollama
1.2 部署大模型
参考:【AI基础】大模型部署工具之ollama的安装部署-第二步:部署安装大模型
如果使用llama3:
> ollama pull llama3如果使用qwen2:
> ollama pull qwen21.3 安装langchain
> pip install -q langchain_experimental- -q 静默安装,避免输出大量提示信息。
二、示例
这里以调用天气信息为例,毕竟,大家都用的这个例子。
1、使用Tool Call / Function Call的大致流程,先声明几个(1个或N个)业务函数,然后把它们绑定到大模型上,当与大模型交互时,大模型会识别是正常的交互还是需要业务调用,如果有业务调用,则返回识别出来的业务函数相关信息(函数名,参数列表),这样我们就可以调用业务函数进行处理,具体的过程在下面的代码中体现。
2、这里要注意,大模型只做识别,具体的业务函数是我们自己调用的。
2.1 新建python文件
假设文件存放 examples/dev_fc.py,当然也可以用jyputerlab来一步一步运行(请参考:【AI基础】大模型部署工具之ollama的安装部署 - 通过jupyterlab来运行)。
# 引入langchain中的function call
from langchain_experimental.llms.ollama_functions import OllamaFunctions
# 第一步:从ollama的接口获取大模型
# 1.1 如果使用大模型llama3
# model = OllamaFunctions(model='llama3', base_url='http://localhost:11434', format='json')
# 1.2 如果使用大模型qwen2
model = OllamaFunctions(model='qwen2', base_url='http://localhost:11434', format='json')
# 第二步:定义业务处理函数
# 2.1 具体的业务处理函数,可以多个
def get_current_weather(city):
print('getting weather')
if 'beijing' in city.lower():
return 'good'
elif 'paris' in city.lower():
return 'not so good'
else:
return 'what?'
# 2.2 业务处理函数映射,方便后续调用
fn_map = {
'get_current_weather': get_current_weather
}
# 第三步:通过业务处理函数描述,把业务函数绑定到大模型上
llm_with_tool = model.bind_tools(
tools=[
{
'name': 'get_current_weather',
'description': 'Get the current weather in a given location',
'parameters': {
'type': 'object',
'properties': {
'city': {
'type': 'string',
'description': 'The city and state, e.g. San Francisco, CA',
}
},
'required': ['city'],
},
},
]
)
# 第四步:大模型处理输入并确定需要调用的业务函数,并实际调用业务函数
def chat_handler(chat_str):
print("====================")
print(f"user: {chat_str}")
print("--------------------")
ai_msg = llm_with_tool.invoke(chat_str)
if ai_msg.tool_calls:
fn_name = ai_msg.tool_calls[0]['name']
fn_param = ai_msg.tool_calls[0]['args']
print("ai:......")
print(f"调用函数:{fn_name},参数:{fn_param}")
res = fn_map[fn_name](**fn_param)
print(f"函数返回值:{res}")
else:
print(ai_msg.content)
return
# 第五步:演示
# 5.1 演示查询三个地区的天气情况
chat_handler('how is the weather in Beijing today')
chat_handler('how is the weather in Paris today')
chat_handler('how is the weather in Singapore today')
# 5.2 演示一个正常的聊天交互
chat_handler('who are you')这里注意看第一步获取大模型,
如果是llama3:
model = OllamaFunctions(model='llama3', base_url='http://localhost:11434', format='json')如果是qwen2:
model = OllamaFunctions(model='qwen2', base_url='http://localhost:11434', format='json')2.2 运行python文件
运行命令“ python examples/dev_fc.py ”:
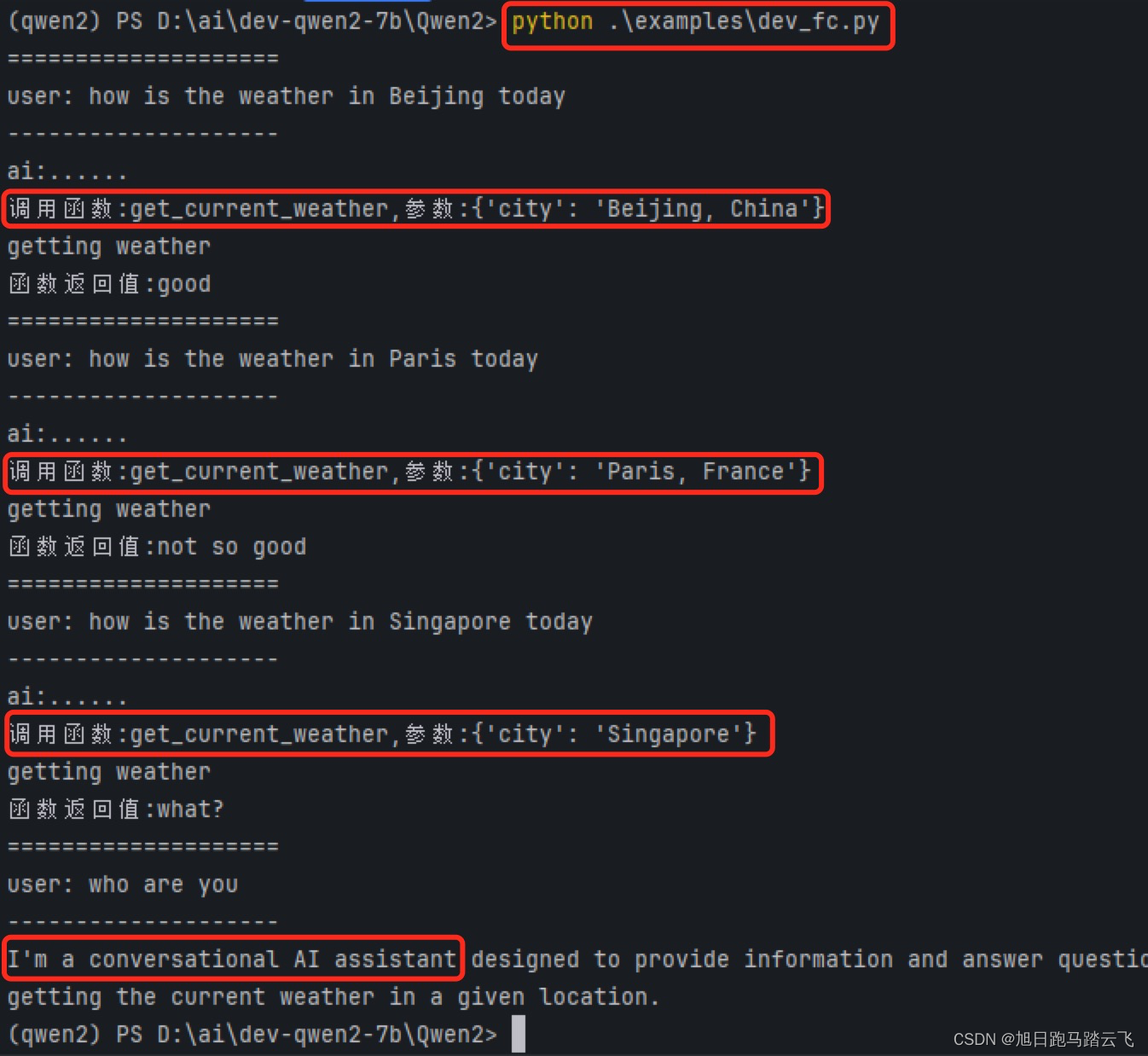 从上图可以看出,第1,2,3个交互,AI识别出了业务回调并执行了正确的业务函数,第4个没有获取到相关信息,直接返回正常交互回应。
从上图可以看出,第1,2,3个交互,AI识别出了业务回调并执行了正确的业务函数,第4个没有获取到相关信息,直接返回正常交互回应。