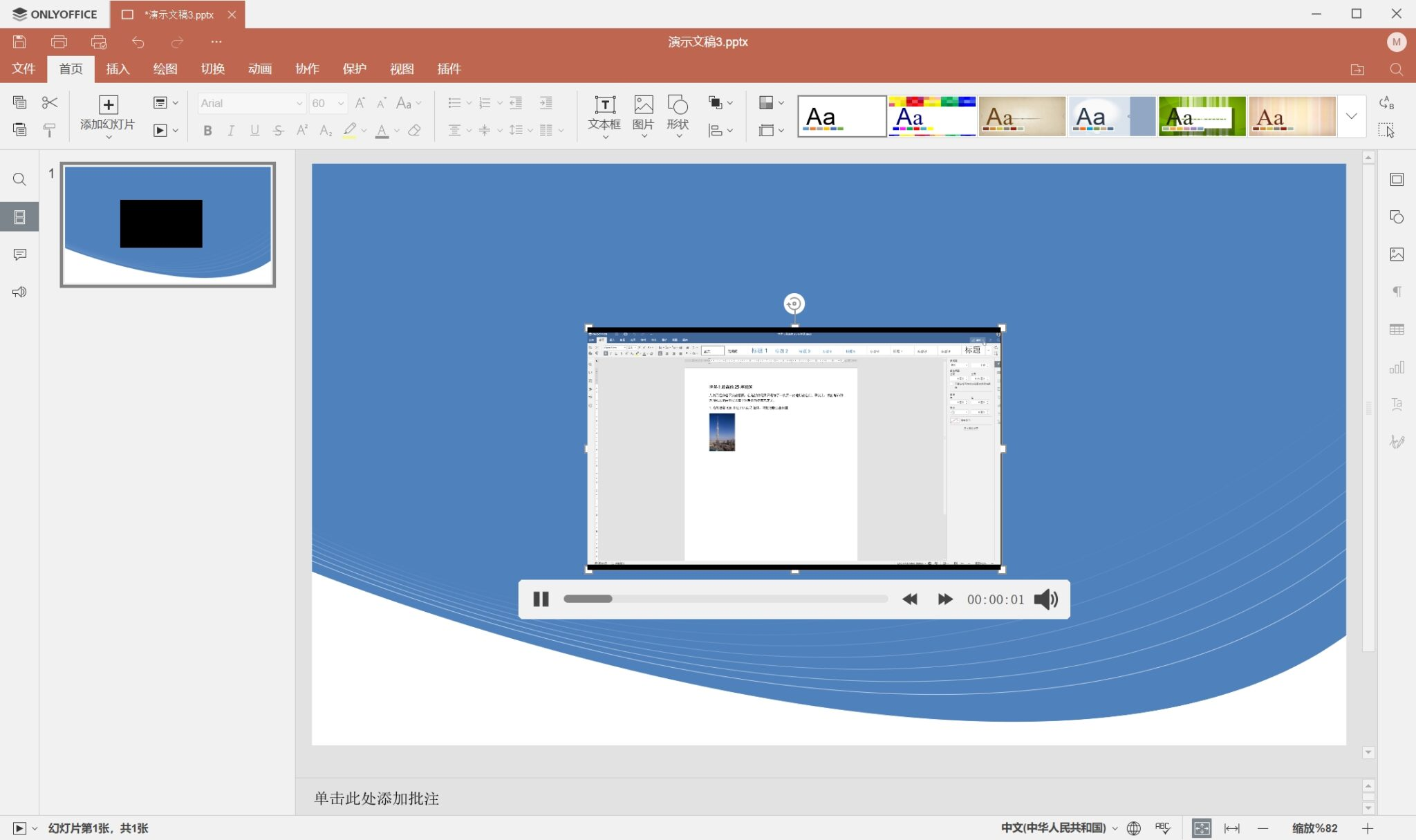
type: 'NODE';
name: string;
[x: string]: any;
};
[x: string]: any;
};
export type Data = Node | Edge;
复制代码
* 测试数据如下
const data: Data[] = [
{
id: ‘1’,
data: {
type: ‘NODE’,
name: ‘节点1’
}
},
{
id: ‘2’,
data: {
type: ‘NODE’,
name: ‘节点2’
}
},
{
id: ‘3’,
data: {
type: ‘NODE’,
name: ‘节点3’
}
},
{
id: ‘4’,
source: {
cell: ‘1’
},
target: {
cell: ‘2’
},
data: {
type: ‘EDGE’
}
},
{
id: ‘5’,
source: {
cell: ‘1’
},
target: {
cell: ‘3’
},
data: {
type: ‘EDGE’
}
}
];
复制代码
* 根据数据结构和测试数据`data:Data[]`,分为以下几个步骤:
1. 获得边的集合和节点的集合。
2. 根据边的集合和节点的集合,获得每个节点的有向邻居节点的集合。即以每个节点的为起点,通过边连接的下一个节点的集合。例如测试数据`节点1`,通过边`id4`和边`id5`,可以连接`节点2`和`节点3`,所以`节点1`的邻居节点是`节点2`和`节点3`,而`节点2`和`节点3`无有向邻居节点。
3. 最后根据有向邻居节点的集合,判断是否有环。
### 具体实现
* 获得边的集合和节点的集合
const edges: Map<string, Edge> = new Map(), nodes: Map<string, Node> = new Map();
const idMapTargetNodes: Map<string, Node[]> = new Map();
const initGraph = () => {
for (const item of data) {
const { id } = item;
if (item.data.type === ‘EDGE’) {
edges.set(id, item as Edge);
} else {
nodes.set(id, item as Node);
}
}
};
复制代码
* 获取有向邻居节点的集合,这里的集合,可以优化成`id`。我为了方便处理,存储了节点
const idMapTargetNodes: Map<string, Node[]> = new Map();
const initTargetNodes = () => {
for (const [id, edge] of edges) {
const { source, target } = edge;
const sourceId = source.cell, targetId = target.cell;
if (nodes.has(sourceId) && nodes.has(targetId)) { //防止有空的边,即边的起点和终点不在节点的集合里
const targetNodes = idMapTargetNodes.get(sourceId);
if (Array.isArray(targetNodes)) {
targetNodes.push(nodes.get(targetId) as Node);
} else {
idMapTargetNodes.set(sourceId, [nodes.get(targetId) as Node]);
}
}
}
};
复制代码
* 最后判断是否有环,有两种方式:递归和循环。都是深度优先遍历。`execute`是遍历所有节点,`hasCycle`是把图的某个节点做为起点,判断是否有环。如果以所有节点为起点,都没有环,说明这个图没有环。
1. 递归。`hasCycle`判断当前节点是否有环;`checked`是做优化,防止某些节点多次检查,回溯阶段,把当前节点加入`checked`;`visited`记录当前执行的`hasCycle`里是否访问过,如果访问过,就是有环。需要注意的是,每次执行`hasCycle`时,`visited`用的是一个变量,所以在回溯阶段需要把当前节点从`visited`里删除。
const checked: Set = new Set();
const hasCycle = (node: Node, visited: Set) => {
if (checked.has(node.id)) return false;
if (visited.has(node)) return true;
visited.add(node);
const { id } = node;
const targetNodes = idMapTargetNodes.get(id);
if (Array.isArray(targetNodes)) {
for (const item of targetNodes) {
if (hasCycle(item, visited)) return true;
}
}
checked.add(node.id);
visited.delete(node);
return false;
};
const execute = () => {
const visited: Set = new Set();
for (const [id, node] of nodes) {
if (hasCycle(node, visited)) return true;
checked.add(id);
}
return false;
};
复制代码
1. 循环。`checked`和递归时,作用一样,这里不做说明。`visited`是用来判断当前的节点是否遍历过,如果遍历过,就是有环。用循环实现深度优先遍历时,需要用`栈`来存储当前链路上的节点,即当前节点已经后代节点。并且从`栈`里面获取最后一个节点,作为当前遍历的节点。如果当前节点有向邻居节点不为空,就把有向邻居节点的最后一个节点拿出来压栈;如果有向邻居节点为空,就把当前的节点出栈。在压栈时,如果当前节点在`visited`里,就说明有环,如果没有就要把这个节点加入到`visited`。在出栈时,把当前节点从`visited`里删除掉,因为如果不删掉,当一个节点的多个邻居节点最终指向同一个节点时,会判断为有环。
const checked: Set = new Set();
const hasCycle = (node: Node) => {
const { id } = node;
if (checked.has(id)) return false;
const stack = [id];
const visited: Set = new Set();
visited.add(id);
while (stack.length > 0) {
const lastId = stack[stack.length - 1];
const targetNodes = idMapTargetNodes.get(lastId) || [];
if (targetNodes.length > 0) {
最后
前端CSS面试题文档,JavaScript面试题文档,Vue面试题文档,大厂面试题文档

.length > 0) {
最后
前端CSS面试题文档,JavaScript面试题文档,Vue面试题文档,大厂面试题文档
[外链图片转存中…(img-ze1QDx8k-1719237898712)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-pp9ZHRr7-1719237898713)]