使用Spring Event机制可以保证高扩展性:
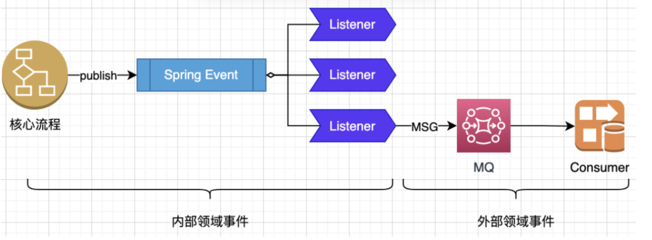
使用Spring Event来发布应用内部领域事件,对于事件监听器可通过注解或类的方式来扩展,Spring
Event内部使用观察者模式,但api使用层面可以完全解耦事件发布和事件监听:
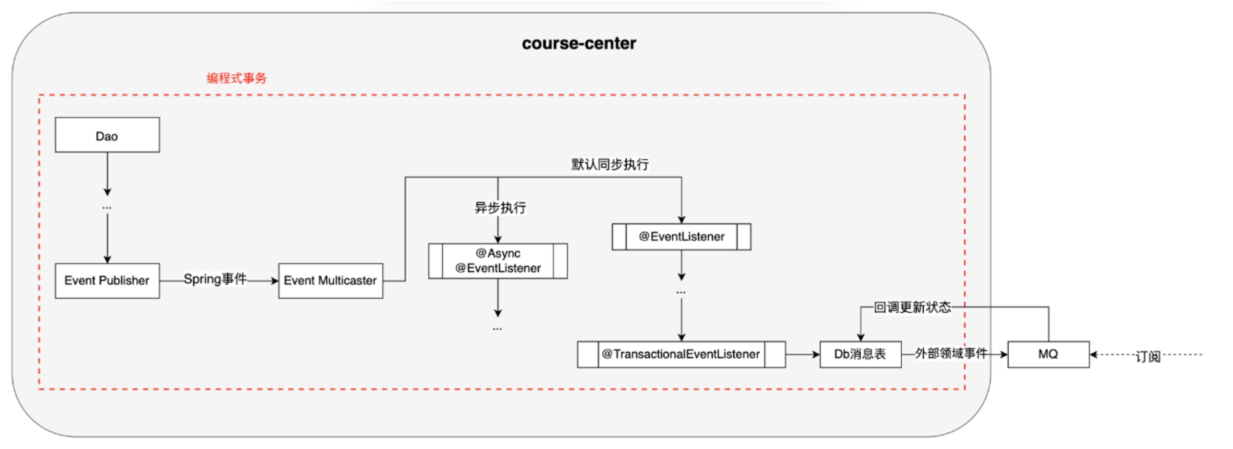
常用方式:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ClazzHourEventListener {
// 默认同步调用该方法,@Order注解编排顺序
@EventListener
@Order
public void listener1(ClazzHourDepletedMemEvent event) {
// ...
}
// @Async注解实现异步调用
@Async
@EventListener
public void listener2(ClazzHourDepletedMemEvent event) {
// ...
}
// 事务监听,默认在事务提交后同步执行该方法
@TransactionalEventListener
public void listener3(ClazzHourDepletedMemEvent event) {
// ...
}
}
注解实现事件监听需要考虑一下三个方面的内容:
- 异步:如何实现异步
- 事务:调用者的事务和监听器事务关系,包括异步情况下
- 异常处理:异常需要捕获吗?对事务有什么影响
测试如下:
@Service
public class BizService {
@Autowired
StudentMapper mapper;
@Autowired
ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
@Transactional
public void bizAction(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(120L);
student.setName("test1");
mapper.insert(student);
System.out.println("bizAction +"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 发布时间
publisher.publishEvent(new TestEvent());
}
}
@Component
public class TestTxListener {
@Autowired
StudentMapper studentMapper;
// 该步抛异常会导致后续listener无法运行
// 该步事务和BizService中是一个,抛异常会同时回滚
// @Order(2)
@EventListener
public void listener1(TestEvent event){
System.out.println("TestTxListener 1 +"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(121L);
student.setName("同步调用测试tx");
studentMapper.insert(student);
// throw new RuntimeException();
}
// 异步 情况下 该步事务和BizService中不是一个,这里抛异常不影响其他listenr执行,也不影响BizService事务
// 如果order优先级高的同步listener抛异常,这里也会执行不到
// @Order(1)
@Async("testTPE")
@EventListener
public void listener2(TestEvent event){
System.out.println("TestTxListener 2 +"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(122L);
student.setName("异步调用测试tx");
studentMapper.insert(student);
// throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
@Component
public class TestTxListener {
@Autowired
StudentMapper studentMapper;
// 默认同步调用,这里面跑出异常不影响其他TransactionalEventListener执行
// TransactionalEventListener 使用 TransactionSynchronization实现
// 这里的事务需要指定REQUIRES_NEW,或者使用编程式事务。否则无法提交,详见TransactionSynchronization
// The transaction will have been committed already, but the
// transactional resources might still be active and accessible.
// As a consequence, any data access code triggered at this point
// will still "participate" in the original transaction, allowing
// to perform some cleanup (with no commit following anymore!),
// unless it explicitly declares that it needs to run in a
// separate transaction. Hence: Use PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW for
// any transactional operation that is called from here.
// 但是,如果使用@Async,就没有这个问题,因为事务是绑定线程的,多线程propogation无作用
@Transactional(propogation=REQUIRES_NEW)
@Order(1)
@TransactionalEventListener
public void listener1(TestEvent event){
// 同步调用
System.out.println("TestTxListener 1 +"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(161L);
student.setName("同步调用测试tx");
studentMapper.insert(student);
// 不影响其他listener执行
throw new RuntimeException();
}
@Order(2)
// @Async 可异步
@TransactionalEventListener
public void listener2(TestEvent event){
System.out.println("TestTxListener 2 +"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(162L);
student.setName("异步调用测试tx");
studentMapper.insert(student);
}
}
由此可见 EventListener
执行过程中遇到异常终止,则后续的同步&异步EventListener都不会执行(之前的会执行,使用@Order控制顺序),而TransactionalEventListener相互之间不受影响。所以使用EventListener要做好异常处理。此外TransactionalEventListener方法内使用事务(默认afterCommit)需要注明@Transactional(
propogation=REQUIRES_NEW)或使用编程式事务,但是如果@Async异步时,就不需要指定,因为事务是绑定线程的。
ps:
org.springframework.modulith.events.ApplicationModuleListener
@Async
@Transactional(propagation=REQUIRES_NEW)
@TransactionalEventListener
@Documented
@Target({METHOD,ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface ApplicationModuleListener{
@AliasFor(annotation=org.springframework.context.event.EventListener.class,attribute="id")
String id();
@AliasFor(annotation=org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional.class,attribute="readOnly")
boolean readOnlyTransaction();
}